UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
______________________________
FORM 10-K
______________________________
(Mark One) | | | | | |
| ☒ | ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
| For the fiscal year ended December 31, 2023 |
OR
| | | | | |
| ☐ | TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
| For the transition period from to . |
Commission file number 001-04321
______________________________
Roblox Corporation
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
______________________________
| | | | | |
| Delaware | 20-0991664 |
| (State or other jurisdiction of incorporation or organization) | (I.R.S. Employer Identification No.) |
| 970 Park Place, San Mateo, CA | 94403 |
| (Address of Principal Executive Offices) | (Zip Code) |
(888) 858-2569
Registrant’s telephone number, including area code
______________________________
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
| | | | | | | | |
| Title of each class | Trading Symbol(s) | Name of each exchange on which registered |
| Class A common stock, par value of $0.0001 per share | RBLX | New York Stock Exchange |
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act:
Indicate by check mark if the Registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Yes ☒ No ☐
Indicate by check mark if the Registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Act. Yes ☐ No ☒
Indicate by check mark whether the Registrant: (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports); and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes ☒ No ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the Registrant has submitted electronically every Interactive Data File required to be submitted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the Registrant was required to submit and post such files). Yes ☒ No ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the Registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, a smaller reporting company, or an emerging growth company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer”, “smaller reporting company”, and “emerging growth company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act. (Check one):
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Large accelerated filer | ☒ | Accelerated filer | ☐ |
| Non-accelerated filer | ☐ | Smaller reporting company | ☐ |
| | Emerging growth company | ☐ |
If an emerging growth company, indicate by check mark if the Registrant has elected not to use the extended transition period for complying with any new or revised financial accounting standards provided pursuant to Section 13(a) of the Exchange Act. ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the Registrant has filed a report on and attestation to its management’s assessment of the effectiveness of its internal control over financial reporting under Section 404(b) of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act (15 U.S.C. 7262(b)) by the registered public accounting firm that has prepared or issued its audit report. ☒
If securities are registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act, indicate by check mark whether the financial statements of the registrant included in the filing reflect the correction of an error to previously issued financial statements. ☐
Indicate by check mark whether any of those error corrections are restatements that required a recovery analysis of incentive-based compensation received by any of the registrant’s executive officers during the relevant recovery period pursuant to §240.10D-1(b). ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the Registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Act). Yes ☐ No ☒
The aggregate market value of voting Class A common stock held by non-affiliates of the Registrant on June 30, 2023, the last business day of the Registrant’s most recently completed second fiscal quarter (based on a closing price of $40.30 per share on June 30, 2023 as reported on the New York Stock Exchange) was approximately $16.3 billion. Solely for purposes of this disclosure, shares of Class A common stock held by executive officers, directors, and holders of more than 10% of our common stock of the Registrant as of such date have been excluded in that such persons may be deemed to be affiliates. This determination of affiliate status is not necessarily a conclusive determination for other purposes.
As of February 1, 2024, the Registrant had 581,551,952 shares of Class A common stock and 50,086,273 of Class B common stock, each with a par value of $0.0001 per share, outstanding.
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE
Portions of the Registrants’ definitive proxy statement relating to its 2024 annual meeting of shareholders (the “2024 Proxy Statement”) are incorporated by reference into Part III of this Annual Report on Form 10-K where indicated. The 2024 Proxy Statement will be filed with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission within 120 days after the end of the fiscal year to which this report relates.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
SPECIAL NOTE REGARDING FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS
This Annual Report on Form 10-K contains forward-looking statements within the meaning of the federal securities laws, which statements involve substantial risks and uncertainties. Forward-looking statements generally relate to future events or our future financial or operating performance. In some cases, you can identify forward-looking statements because they contain words such as “expect,” “anticipate,” “should,” “believe,” “hope,” “target,” “project,” “plan,” “goals,” “estimate,” “potential,” “predict,” “may,” “will,” “might,” “could,” “would,” “intend,” “shall,” “contemplate,” “opportunity,” or “continue” or the negative of these words or other similar terms or expressions that concern our expectations, strategy, plans, or intentions. Forward-looking statements contained in this Annual Report on Form 10-K include, but are not limited to, statements about:
•our expectations regarding future financial performance, including but not limited to our expectations regarding revenue, cost of revenue, changes in estimated paying user life, operating expenses, operating losses, operating leverage and our key metrics, and our ability to achieve and maintain future profitability;
•our ability to successfully execute our business and growth strategy, including our potential to scale and grow our advertising business, our international users, developers, and creators, and our ability to create new revenue opportunities;
•the sufficiency of our cash and cash equivalents to meet our liquidity needs;
•economic, seasonal, and industry trends;
•the functionality and economics of our platform on operating systems and through distribution channels and software application stores;
•the demand for our platform in general;
•our ability to retain and increase our number of users, developers, and creators;
•the impact of inflation and global economic conditions on our operations;
•challenges associated with our future of work and return to office plans;
•our ability to develop enhancements to our platform, and bring them to market in a timely manner;
•our beliefs about and objectives for future operations;
•our ability to attract and retain employees and key personnel and maintain our corporate culture;
•future acquisitions or investments, including infrastructure investments to increase capacity;
•the ability for developers to build, launch, scale, and monetize experiences for users;
•our expectations regarding our ability to generate revenue from our users;
•our ability to convert users into developers and creators;
•our expectations regarding new target demographics;
•our ability to continue to provide a safe and civil online environment, particularly for children;
•our ability to develop and protect our brand;
•our ability to maintain the security and availability of our platform;
•our ability to detect and minimize unauthorized use of our platform
•the impact of disruption in supply chains on our ability to expand or increase the capacity of the platform or replace defective equipment;
•our business model and expectations and management of future growth, including for headcount growth rate, expansion in international markets and expenditures associated with such growth;
•our ability to compete with existing and new competitors;
•our expectations regarding outstanding litigation and legal and regulatory matters;
•our expectations regarding the effects of existing and developing laws and regulations, including with respect to privacy, data protection, online safety, and the regulation of Robux as a security, both in the U.S. and internationally, including how such laws and regulations may interfere with user, developer and creator access to our platform and experiences;
•our expectations surrounding Robux as an attractive virtual currency;
•our goal to increase developer and creator earnings as much as possible;
•the impact of geopolitical events, including the war in Ukraine, Hamas’ attack against Israel and the ensuing war, and their impacts on economies globally;
•our expectations regarding new accounting standards;
•our ability to achieve and maintain effective control over financial reporting;
•the impact of foreign currency exchange rates and rising interest rates on results of operations;
•our estimates related to stock-based compensation expenses;
•generating sufficient cash to service our debt and other obligations that apply to our indebtedness; and
•the increased expenses associated with being a public company.
We caution you that the foregoing list may not contain all of the forward-looking statements made in this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
You should not rely upon forward-looking statements as predictions of future events. We have based the forward-looking statements contained in this Annual Report on Form 10-K primarily on our current expectations and projections about future events and trends that we believe may affect our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects. The outcome of the events described in these forward-looking statements is subject to risks, uncertainties and other factors, including those described in the section titled “Risk Factors” and elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K. Moreover, we operate in a very competitive and rapidly changing environment. New risks and uncertainties emerge from time to time and it is not possible for us to predict all risks and uncertainties that could have an impact on the forward-looking statements contained in this Annual Report on Form 10-K. We cannot assure you that the results, events and circumstances reflected in the forward-looking statements will be achieved or occur, and actual results, events or circumstances could differ materially from those described in the forward-looking statements.
Neither we nor any other person assumes responsibility for the accuracy and completeness of any of these forward-looking statements. Moreover, the forward-looking statements made in this Annual Report on Form 10-K relate only to events as of the date on which the statements are made. We undertake no obligation to update any forward-looking statements made in this Annual Report on Form 10-K to reflect events or circumstances after the date of this Annual Report on Form 10-K or to reflect new information or the occurrence of unanticipated events, except as required by law. We may not actually achieve the plans, intentions or expectations disclosed in our forward-looking statements and you should not place undue reliance on our forward-looking statements. Our forward-looking statements do not reflect the potential impact of any future acquisitions, mergers, dispositions, joint ventures or investments we may make.
SPECIAL NOTE REGARDING OPERATING METRICS
We manage our business by tracking several operating metrics, including average daily active users (“DAUs”), hours engaged, bookings, average bookings per DAU (“ABPDAU”), average new and returning monthly unique payers, monthly repurchase rate, and average bookings per monthly unique payer. As a management team, we believe each of these operating metrics provides useful information to investors and others. For information concerning these metrics as measured by us, see “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations.”
While these metrics are based on what we believe to be reasonable estimates of our user base for the applicable period of measurement, there are inherent challenges in measuring how our platform is used. These metrics are determined by using internal data gathered on an analytics platform that we developed and operate and have not been validated by an independent third party. This platform tracks user account and session activity. If we fail to maintain an effective analytics platform, our metrics calculations may be inaccurate. These metrics are also determined by certain demographic data provided to us by the user, such as age or gender. If our users provide us with incorrect or incomplete information, then our estimates may be inaccurate.
We believe that these metrics are reasonable estimates of our user base for the applicable period of measurement, and that the methodologies we employ and update from time-to-time to create these metrics are reasonable bases to identify trends in user behavior. Because we update the methodologies we employ to create metrics, our current period metrics may not be comparable to those in prior periods. For example, in the first quarter of 2023, we revised the methodology we use to calculate average monthly unique payers for payers who purchased prepaid cards through one of our specified distributors (the impact to average new and returning monthly unique payers and average bookings per monthly unique payer in periods prior to the first quarter of 2023 was not significant). Finally, the accuracy of our metrics may be affected by certain factors relating to user activity and systems and our ability to identify and detect attempts to replicate legitimate user activity, often referred to as botting. See the section titled “Risk Factors—Our user metrics and other estimates are subject to inherent challenges in measurement, and real or perceived inaccuracies in those metrics may significantly harm and negatively affect our reputation and our business.”
DAUs
We define a DAU as a user who has logged in and visited Roblox through our website or application on a unique registered account on a given calendar day. If a registered, logged in user visits Roblox more than once within a 24-hour period that spans two calendar days, that user is counted as a DAU only for the first calendar day. We believe this method better reflects global engagement on the platform compared to a method based purely on a calendar-day cutoff. DAUs for a specified period is the average of the DAUs for each day during that period. As an example, DAUs for the month of September would be an average of DAUs during that 30 day period.
Other companies, including companies in our industry, may calculate DAUs differently.
We track DAUs as an indicator of the size of the audience engaged on our platform. DAUs are also broken out by geographic region to help us understand the global engagement on our platform.
The geographic location data collected is based on the IP address associated with the account when an account is initially registered on Roblox. The IP address may not always accurately reflect a user’s actual location at the time they engaged with our platform. Historically, we have grouped Xbox users into Rest of World DAUs for the purposes of our reporting (we note that since the fourth quarter of 2020, Xbox users have represented less than 2% of our total quarterly DAUs and quarterly hours engaged). Beginning in the fourth quarter of 2023, Xbox users are reported in their respective geographies.
The platform data collected is based on the platform associated with the account when an account is initially registered on Roblox. The demographic data collected is self-reported to us and may not always accurately represent the actual attributes of the user.
Because DAUs measure account activity and an individual user may actively use our platform within a particular day on multiple accounts for which that individual registered, our DAUs are not a measure of unique individuals accessing Roblox. Additionally, if undetected, fraud and unauthorized access to our platform may contribute, from time to time, to an overstatement of DAUs. In many cases, fraudulent accounts are created by bots to inflate user activity for a particular developer’s content on our platform, thus making the developer’s experience or other content appear more popular than it really is. We strive to detect and minimize fraud and unauthorized access to our platform. See the sections titled “Risk Factors—Our user metrics and other estimates are subject to inherent challenges in measurement, and real or perceived inaccuracies in those metrics may significantly harm and negatively affect our reputation and our business,” and “Risk Factors—Some developers, creators, and users on our Platform may make unauthorized, fraudulent, or illegal use of Robux and other digital goods or experiences on our Platform, including through unauthorized third-party websites or “cheating” programs.”
Hours Engaged
We define hours engaged as the time spent by our users on the platform, which includes time spent in experiences (which refer to the titles that have been created by developers) and within platform features such as chat and avatar personalization. We calculate total hours engaged as the aggregate of user session lengths in a given period. We determine this length of time using internal company systems that track user activity on our platform, and aggregate discrete activities into a user session. We track hours engaged as an indicator of the user engagement on our platform. Hours engaged are also broken out by geographic region to help us understand the global engagement on our platform. See the sections titled “Risk Factors—Our user metrics and other estimates are subject to inherent challenges in measurement, and real or perceived inaccuracies in those metrics may significantly harm and negatively affect our reputation and our business.”
We continuously strive to detect and minimize unauthorized use of our platform, including, but not limited to, botting. As we continue to improve our ability to detect and deter unauthorized use of our Platform, we may see an impact to our overall hours engaged as our efforts to reduce botting become more successful.
Bookings
Bookings represent the sales activity in a given period without giving effect to certain non-cash adjustments, as detailed below. Substantially all of our bookings are generated from sales of virtual currency, which can ultimately be converted to virtual items on the platform. Sales of virtual currency reflected as bookings include one-time purchases or monthly subscriptions purchased via payment processors or through prepaid cards. Bookings are initially recorded in deferred revenue and recognized as revenues over the estimated period of time the virtual items purchased with the virtual currency are available on the platform (estimated to be the average lifetime of a paying user) or as the virtual items purchased with the virtual currency are consumed. Bookings also include an insignificant amount from advertising and licensing arrangements.
We believe bookings provide a timelier indication of trends in our operating results that are not necessarily reflected in our revenue as a result of the fact that we recognize the majority of revenue over the estimated average lifetime of a paying user, which was 28 months as of December 31, 2023. The change in deferred revenue constitutes the vast majority of the reconciling difference from revenue to bookings. By removing these non-cash adjustments, we are able to measure and monitor our business performance based on the timing of actual transactions with our users and the cash that is generated from these transactions. Over the long-term, the factors impacting our revenue and bookings trends are the same. However, in the short-term, there are factors that may cause revenue and bookings trends to differ.
We use this non-GAAP financial information to evaluate our ongoing operations and for internal planning and forecasting purposes. We believe that this non-GAAP financial information may be helpful to investors because it provides consistency and comparability with past financial performance. However, non-GAAP financial measures have limitations in their usefulness to investors because they have no standardized meaning prescribed by GAAP and are not prepared under any comprehensive set of accounting rules or principles. In addition, other companies, including companies in our industry, may calculate similarly titled non-GAAP financial measures differently or may use other measures to evaluate their performance, all of which could reduce the usefulness of our non-GAAP financial information as a tool for comparison. As a result, our non-GAAP financial information is presented for supplemental informational purposes only and should not be considered in isolation from, or as a substitute for financial information presented in accordance with GAAP.
Bookings are also broken out by geographic region based on the billing country of our payers, to help us understand the global engagement and monetization on our platform. The billing address may not always accurately reflect a payer’s actual location at the time of their purchase.
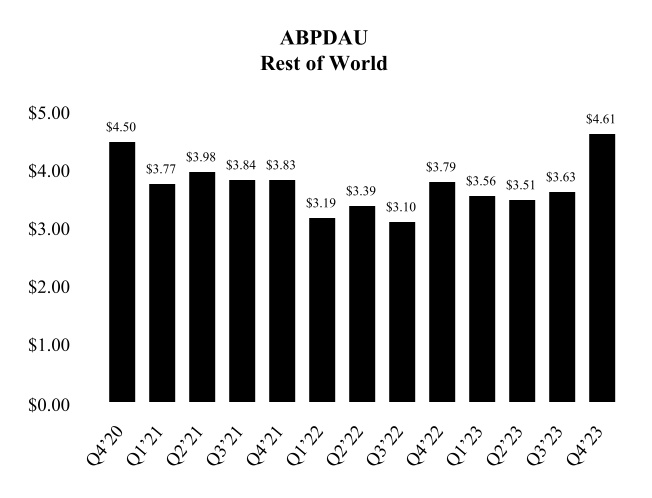
ABPDAU
We define ABPDAU as bookings in a given period divided by the DAUs for such period. We primarily use ABPDAU as a way to understand how we are monetizing across all of our users through the sale of virtual currency and subscriptions. ABPDAU is also broken out by geographic region to help us understand the global engagement on our platform.
Average New and Returning Monthly Unique Payers and Monthly Repurchase Rate
We define new monthly unique payers as user accounts that made their first purchase on the platform, or via redemption of prepaid cards, during a given month. Average new monthly unique payers for a specified period is the average of the new monthly unique payers for each month during that period. Because we do not always have the data necessary to link an individual who has paid under multiple user accounts, an individual may be counted as multiple new monthly unique payers.
We define returning monthly unique payers as user accounts that have made a purchase on the platform, or via redemption of prepaid cards, in the current month and in any prior month. Average returning monthly unique payers for a specified period is the average of the returning monthly unique payers for each month during that period. Because we do not always have the data necessary to link an individual who has paid under multiple user accounts, an individual may be counted as multiple returning monthly unique payers.
We define monthly repurchase rate as the returning monthly unique payers in the current month, divided by the sum of the prior month’s new monthly unique payers and returning monthly unique payers. Average monthly repurchase rate for a specified period is the average of the monthly repurchase rates for each month during that period.
Average Bookings per Monthly Unique Payer
We define average bookings per monthly unique payer as bookings in the specified period divided by the average monthly unique payers for the same specified period.
Part I
Item 1. BUSINESS
Overview
Roblox operates a free to use immersive platform for connection and communication (the “Roblox Platform” or “Platform”), where every day, millions of people come to create, play, work, learn, and connect with each other in experiences built by our global community of creators. Our vision is to reimagine the way people come together – in a world that is safe, civil, and optimistic. To achieve this vision, we are building an innovative company that, together with the Roblox community, has the ability to strengthen our social fabric and support economic growth for people around the world.
Our Platform consists of the Roblox Client, the Roblox Studio, and the Roblox Cloud. Roblox Client is the application that allows users to seamlessly explore 3D immersive experiences. Roblox Studio is the free toolset that allows developers and creators to build, publish, and operate 3D immersive experiences and other content accessed with the Roblox Client. Roblox Cloud includes the services and infrastructure that power our Platform.
Our mission is to connect a billion users with optimism and civility. We are constantly improving the ways in which our Platform supports shared experiences, ranging from how these experiences are built by an engaged community of developers and creators to how they are enjoyed and safely accessed by users across the globe.
Growth at Roblox has been driven primarily by a significant investment in technology and two mutually reinforcing network effects: content and social.
First, user-generated content, built by our community of developers and creators, powers our Platform. As developers and creators build increasingly high-quality content, more users are attracted to our Platform. With more users on our Platform, greater engagement and monetization opportunities exist, which in turn, makes Roblox more attractive to developers and creators, incentivizing them to design increasingly engaging content and encouraging new developers and creators to start building on our Platform.
Second, our Platform is social. When users join, they typically interact with friends, which inspires them to invite more friends, who in turn, invite their friends, driving organic growth. The more friends that each of our users have interacting on the Platform, the more valuable and engaging the Platform becomes. This drives more users to our Platform through word of mouth from their existing friends on the Platform.
Our User and Creator Community
Roblox is powered by content from our community of developers and creators who build immersive and engaging experiences found only on Roblox, as well as the vast majority of the items for customizing avatars. This content attracts our users to immerse themselves in the millions of experiences found on the Platform. Many of our users may also eventually become developers and creators, and nearly all developers and creators started as users.
Our Users
In the year ended December 31, 2023, 68.4 million average DAUs across over 190 countries enjoyed experiences on Roblox across mobile, desktop, and console platforms, of which on average, 852,000 were daily unique paying users. Our users are diversified across multiple dimensions, including age, geography, platform, and gender. Each day, users express themselves through their avatars, explore different worlds, and engage with others in the Roblox community. In the year ended December 31, 2023, there were over 3,000 experiences that generated at least 1 million hours of engagement and over 500 experiences that generated 10 million hours of engagement or more. During the year ended December 31, 2023, users spent 60.0 billion hours engaged on our Platform, or an average of 2.4 hours per DAU each day. Over the same period, our users explored an average of over 19 different experiences on the Roblox Platform per month.
Breakdown of Our Users(1)
Global DAU = 68.4 million(1)
(1)Represents the average during the year ended December 31, 2023. Refer to “Special Note Regarding Operating Metrics” for details on operating metrics used. Percentages presented are calculated from the underlying numbers in thousands and may not add to their respective totals due to rounding.
Our Developers and Creators
We offer developers and creators the ability to build engaging, immersive experiences and marketplace items that they can easily share with the Roblox community. We refer to users who create experiences and marketplace items as creators, while developers represent a subset of the creator community that create experiences on the Platform or build and sell custom tools to help other developers create experiences. In this way, our developers and creators enable us to offer a wide variety of experiences and avatar items and cost-effectively crowd-source our experiences, marketplace content, and developer tool ecosystem. In the year ended December 31, 2023, we had millions of active developers across more than 180 countries who had either created or updated an experience on the Roblox Platform. Our developer and creator community includes individuals with a wide spectrum of professional capabilities and team sizes, ranging from young students and independent hobbyists, all the way to full-time studios.
We measure the health and success of our developer and creator community based on their earnings and the user engagement in their experiences. As our Platform has scaled, our monetizing developers and creators have enjoyed meaningful earnings expansion over time, reflecting the increasing popularity and opportunities for monetization of our Platform and driving a growing incentive for our developers and creators to continue to build high-quality content.
Developers and creators are able to earn Robux through the following methods:
1.Monetizing a developed experience: Developers qualified for our Developer Exchange Program can earn Robux through:
a.In-experience purchases, which consist of microtransactions generated from the sale of in-experience virtual items, subscription-based offerings (including access to private servers), access to certain experiences, and/or passes granting special in-experience privileges.
b.Engagement-Based Payouts, which allows developers to earn Robux based on the share of time that Roblox Premium subscribers engage in their experience.
c.Immersive advertisements (“ads”), which are high-quality, in-experience native ad units that can programmatically serve ads through which developers can earn Robux from impressions and/or teleports generated.
2.Creating and selling or reselling avatar items: Creators can create and sell accessories, clothes, bodies, and heads for avatars in the Marketplace or in their own or other developers’ experiences.
3.Creating and selling Roblox Studio plugins: Through the Creator Store (formerly the Creator Marketplace), developers and creators can sell Roblox Studio plugins, which are extensions that add additional features or functionality to Roblox Studio and helps improve creator workflows.
There were over 5.0 million developers and creators who earned Robux on the Roblox Platform in the month ended December 31, 2023. As of December 31, 2023, over 16,500 developers and creators qualified for and were registered in our Developer Exchange Program, of which over 5,000 were newly qualified and registered during 2023. In order to be qualified for our Developer Exchange Program and eligible to exchange earned Robux for real-world currency, developers and creators must meet certain conditions, such as having earned the minimum amount of Robux required to qualify for the program, a verified developer account, and an account in good standing. On January 31, 2022, we reduced the minimum amount of earned Robux required to qualify for the program from 100,000 Robux to 50,000 Robux and subsequently on January 31, 2023, we further reduced the minimum requirement from 50,000 Robux to 30,000 Robux. We believe these reductions in the minimum amounts required incentivize our developer and creator community, and promote the long term growth and health of such community. For the year ended December 31, 2023, over 12,000 developers and creators actually exchanged their earned Robux for real-world currency through our Developer Exchange Program. For the same period, there were over 3,500 developers and creators that earned the equivalent of $10,000 or more in Robux and over 750 developers and creators that earned the equivalent of $100,000 or more in Robux.
Rewards and Experiences Breakdown
We invest in our developers and creators by providing a comprehensive set of free tools and services through Roblox Studio, the Roblox Open Cloud, and a range of other creator resources that enable them to easily build, publish, analyze, grow, and monetize experiences. We empower developers and creators to get started with minimal upfront costs as we cover hosting, storage, customer support, localization, regulatory requirements, payment processing, and platform fees. We provide appropriate support for all developers and creators to ensure engagement and growth in our developer and creator community. This includes managing and moderating our online developer and creator forums and operating special programs for aspiring and top developers and creators such as our annual Roblox Developers Conference. With Roblox Open Cloud, developers and creators can leverage a suite of backend APIs to seamlessly build and scale their experiences.
The investment in our developer and creator community has resulted in an ever-changing offering of diverse content for our users to explore and engage in. The chart below shows the percentage of in-experience engagement within the top 1,000 experiences by month from January 1, 2023 to December 31, 2023.
Our Products and Technology
The Roblox Platform is the underlying technology and infrastructure that supports shared experiences and is composed of three elements:
•Roblox Client—The free application that allows users to explore 3D immersive experiences.
•Roblox Studio—The free toolset that allows developers and creators to build, publish, and operate 3D immersive experiences and other content accessed with the Roblox Client.
•Roblox Cloud—The services and infrastructure that power the Roblox Client and Roblox Studio.
Since our founding, we have invested heavily in building the Roblox Platform, and as of December 31, 2023, 75% of our employees were dedicated to maintaining, improving, and expanding it. Our technology supports the following key characteristics of the Roblox Platform: Identity, Social Communication, Immersive, Low Friction, Variety of Content, Anywhere, Economy, and Safety.
Identity
The Roblox avatar system allows users to create and personalize their unique 3D identities. Our avatar technology supports a wide variety of character styles, ranging from classic avatars with blocky body shapes, to ones with more human proportions, from anime characters, to fantasy avatars, and more. Recently, Roblox introduced avatar animation, which mirrors a user’s movements and facial expressions on the avatar in real time, allowing more interactive and authentic communication.
The Roblox Client features the Avatar Editor, which enables users to manipulate the size and body shape of their avatars as well as equip their avatar with clothing, gear, animations, simulated gestures, or emotes, and other accessories from the Marketplace. Our avatar system allows users to attach practically any accessory to any avatar maximizing the combinatorial variety of avatar configurations supported by the Platform. Users manipulate their avatar through a consistent set of controls for emotes, basic movement, and tap-to-move functionality which adapts to dynamically changing virtual environments. The Roblox Client normalizes camera and avatar control inputs from different device form factors, including mobile, tablet, desktop, and game console, to simplify the process of building multiuser, multiplatform, and avatar-based experiences.
Within most experiences, avatars appear exactly how they were configured in the Avatar Editor, creating a sense of persistent identity. However, developers, when designing experiences, have the freedom to dynamically reconfigure all or part of the participating avatars to meet the specific needs of the developer’s experience.
Social Communication
The Roblox Client allows users to easily connect with real life friends (through features such as contact importer) and meet new friends (by matching users with similar characteristics, such as country location, for example). The social graph created by these connections is stored in the Roblox Cloud and requires mutual opt-in to avoid unwanted communications.
The social graph is central to human communication and connection. When a user chooses to join an experience, the Roblox Cloud is designed to automatically place that user into the same virtual environment as others connected through the social graph. In addition, most developers allow users to purchase private servers that allow groups of friends to share an exclusive, invite-only instance of a 3D immersive experience.
We’re building an immersive platform for communication and connection that has safety and civility at its foundation. The Roblox Platform supports text-based chat among users sharing the same 3D immersive experience and between users connected through the social graph. For safety, every text message passes through filters that block content which violates applicable Roblox Community Standards (e.g. personally identifiable information, profanity, or offensive language). Using advanced pattern matching and machine learning, our chat filters are constantly evolving and process billions of messages per day.
Recently, we expanded our communication features through chat with voice in certain geographies, allowing users aged 13 and over to communicate using their voice in Roblox experiences. This proximity-based feature simulates realistic communication through lip sync and is based on how close users are in an experience to other users who are speaking in that experience. In addition, the recently introduced avatar animation allows all users to use their camera to animate their avatar with their movement, allowing them to communicate and express themselves in more natural, real-time, and immersive ways.
Further, users can now connect through Roblox Connect, a way to communicate with another user within a 3D immersive experience. Either through the standalone Roblox Connect experience or within certain experiences that have embedded the capability behind Roblox Connect, people can call friends and have conversations as avatars together in a shared immersive space using voice and facial expressions.
Immersive
The Roblox Platform allows developers to build deeply immersive 3D environments where users can share synchronous experiences with others, independent of where they may be physically. The Roblox Client provides users with intuitive camera and input controls that are tuned for each device’s form factor. By abstracting these controls from developers, the process of building cross platform 3D immersive experiences is greatly simplified.
Developers use Roblox Studio to easily build 3D immersive experiences that are then rendered and simulated on the Roblox Platform. The Roblox Client leverages efficient low-level hardware-specific device APIs, such as Vulkan for Android devices and Metal for Apple devices, to efficiently render those experiences. Each experience combines thousands of meshes, textures, 3D models, and animations. Using Roblox Studio, developers can also insert immersive ad units into their environments, which are native and 3D structures, and include images and immersive portals.
Each 3D immersive experience is simulated in the Roblox Cloud with a custom physics engine built for rigid body and constraint-based physics. Using a combination of novel mathematical formulations and aggressive optimization, the engine can simulate a large number of complex mechanisms at high levels of fidelity. To achieve an optimal balance between latency, scale, and consistency, computations for the simulation are distributed across Roblox Clients and the Roblox Cloud.
Assets that make up the 3D immersive experience are stored in a persistent tree hierarchy that is the foundation for collaborative editing and interactive multiuser experiences. The hierarchy can be modified through APIs which serve as a powerful abstraction layer making it easy to create experiences that are consistent across all Roblox Clients, regardless of device type. During simulation, this data is dynamically replicated within the Roblox Cloud and selectively transmitted to Roblox Clients. The Roblox Client then constructs and renders its own view of the 3D immersive experience.
Low Friction
The Roblox Platform gives users the ability to interact with experiences almost instantly, on most popular client devices, and from anywhere in the world over existing broadband and cellular networks. As of December 31, 2023, the Roblox Client operates on iOS, Android, PC, Mac, Xbox, PlayStation, and virtual reality (“VR”) hardware such as Meta Quest, and supports VR experiences on PC. With the Roblox Platform, developers can build an experience once and then expect that experience to operate consistently on all supported devices.
The Roblox Client is designed for the rapid movement of users between experiences. Almost immediately upon launching a new experience, the Roblox Client will begin simulating and rendering the virtual world using a partial representation of the environment at a low level of detail. As more and higher fidelity assets are received by the Roblox Client, the fidelity of the experience automatically improves.
Assets are delivered to the Roblox Client through geographically distributed content delivery networks. The Roblox Cloud determines the format, level of detail, and priority of each asset sent in order to optimize for the capabilities and bandwidth available to the client device. For large experiences, the Roblox Client can dynamically purge unnecessary assets from device memory, ensuring that a single large experience can be experienced simultaneously on different devices regardless of device memory capacity.
The Roblox Cloud is central to enabling low-latency, responsive interactivity within 3D environments having millions of concurrent users. When a user joins a 3D immersive experience, the Roblox Cloud assigns that user to a particular game instance based on, among other considerations, the user’s social graph, geographic location, spoken language, and age group. When the number of users in a given experience increases, the Roblox Cloud automatically spawns additional server instances necessary to support additional users. The Platform optimally packs these instances onto physical servers and allocates compute resources based on the resource requirements of each instance. Developers can choose to allow up to 200 users within an instance, but may choose fewer to optimize their experience.
Developers have access to high-speed data stores in the Roblox Cloud where information about users and each simulated environment can be persisted. This, along with other services hosted in the Roblox Cloud, make it possible for a developer to build, launch, scale and monetize a 3D immersive experience without any additional tools or services.
The majority of services operated by the Roblox Cloud are hosted in Roblox managed data centers. For some of our high-speed databases, scalable object storage, and message queuing services we leverage Amazon Web Services. All servers tasked with simulating the virtual environment and optimizing assets for Roblox Clients are owned by Roblox and operate from data centers and regional edge data centers widely distributed across 19 cities in North America, Asia-Pacific, and Europe. As of December 31, 2023, the Roblox Cloud uses over 140,000 servers. The Roblox Cloud is designed to be fault tolerant and prepared for disaster recovery and we continue to expand into multiple data centers within and across geographic regions to improve reliability and fault tolerance.
Data centers in the Roblox Cloud are linked through a high-performance dedicated backbone network bypassing the public internet for server-to-server calls and we operate under an open peering policy where we have direct interconnection with Internet providers globally. Operating our own network maximizes performance and increases the immersiveness experienced by our users.
Variety of Content
Developers and creators build nearly all of the content for the Roblox Platform, including a variety of experiences from gaming, to education, to entertainment, and beyond. Their efforts contribute to an expanding content library that included over 13 million active experiences and millions of available Marketplace items during the year ended December 31, 2023.
Developers build, publish, and operate 3D immersive experiences with Roblox Studio, a free suite of tools accessible to all skill levels. Teams can work together using built-in access control management and collaborative editing. Once content is built, it can be replicated and shared across multiple experiences, giving developers the ability to scale their efforts and make rapid updates.
In addition to constructing 3D objects and environments, developers can script complex behaviors into their experience with Roblox Luau. Based on Lua, an interpreted light-weight programming language popular in the gaming industry, Roblox Luau adds an optional static type system and a highly optimized interpreter that maximizes performance on Roblox Clients and in the Roblox Cloud. Using scripts, developers can modify the environment, control object behavior, and create new ways for users to interact with the virtual environment. Within Roblox Studio, developers have access to a powerful script editor which supports autocomplete, debugging, and the ability to emulate the Roblox Client running on supported devices.
Roblox Studio also leverages artificial intelligence (“AI”) to help reduce friction for creators and developers, making it easier to build content on the Platform. These AI tools help developers and creators with varying levels of experience. For example, AI tools help beginner developers and creators with no coding experience by answering common questions, while AI tools such as Code Assist or Materials Generator help developers and creators with minimal coding experience learn how to write and improve code and create more complex materials.
Creators can share their work with other creators through the Creator Store. The Creator Store drives collaboration within our developer community, accelerates creation of new experiences, and provides additional ways for creators to monetize their work. As of December 31, 2023, the Creator Store contained millions of models, meshes, textures, scripts, audio clips, developer tools, and packaged combinations of these items.
We provide developers with reference material, tutorials, community forums, and analytics to build their creations. Creator Hub includes reference material, API documentation, and tutorials for developers. Developer Forum is a private forum for qualified developers which provides insight on new features, community initiatives, recruitment opportunities, bug reporting, and direct engagement with our employees. Edu Hub provides content for educators, students, and parents who are using Roblox as a tool to learn coding, 3D design, and digital civility. All developers on the Roblox Platform have access to dashboards that show daily visits to their experience, as well as earned Robux generated from their experience and Marketplace items.
Within the Roblox Client, users find experiences through personalized content recommendations and search. Recommendations are based on past user behavior, the social graph, and demographic information collected at signup. An emphasis is always placed on experiences where someone you are connected with is present. The search engine automatically learns user intent, accounting for misspellings, slang, and multilingual queries.
Anywhere
The Roblox Platform serves a global audience. In the year ended December 31, 2023, developers from over 180 countries and users spanning over 190 countries accessed our Platform.
Localization and compliance systems embedded within the Roblox Client and Roblox Cloud help to lower cultural barriers and enable our developers to meet regional requirements with little to no additional effort.
Developers can build experiences in their native language and then, using machine translation and advanced pattern recognition, the Roblox Cloud automatically translates those experiences into 16 languages including simplified Chinese, traditional Chinese, English, French, German, Indonesian, Italian, Japanese, Korean, Polish, Portuguese, Russian, Spanish, Thai, Turkish, and Vietnamese. Developers also have the ability to customize all or part of their translations if needed.
To meet an evolving global regulatory environment, the Roblox Client can adjust a user’s experience and available content based on their age, device type, current location and where the client application was obtained. This allows Roblox to dynamically apply relevant content filters, anti-addiction rules, payment limits, and parental consent requirements.
Economy
Roblox has a vibrant economy built on a currency called Robux, which can be purchased through the Roblox Client and Roblox website or through prepaid cards purchased via online and physical retailers. Roblox works with multiple payment and prepaid card processors including Apple, BlackHawk, Google, Incomm, and Stripe, amongst others. Roblox relies on payment processor partners to store account information.
Users can also acquire Robux through a monthly subscription to Roblox Premium. With a subscription, users receive discounted Robux along with access to exclusive or discounted items in the Marketplace. Developers may also choose to offer additional benefits to active Roblox Premium subscribers in the form of discounted virtual merchandise or access to exclusive in-experience features.
Developers and creators earn Robux by selling virtual content or access to virtual content (including through subscriptions), as well as through the incorporation of immersive ads into their experiences, which are ad units that developers can insert into their experience for Roblox to programmatically serve ad content from advertisers. There are two immersive and native ad formats: image ads, which are static, non-clickable images within the 3D space of an experience and immersive portals, which are static, non-clickable images where the ad unit includes a door that teleports a user to the advertiser’s experience and back again. Developers can also earn Robux through Engagement-Based Payouts based on the share of time that Roblox Premium users engage in their experiences. Engagement-Based Payouts incentivize developers to invest in the engagement of their experiences. The payout system is designed to protect against fraud and computes a developer’s earnings potential on a daily basis.
Roblox allows developers and creators to convert earned Robux into the real-world currency of their choice through our Developer Exchange Program. All Developer Exchange Program requests are reviewed on a risk-based approach to mitigate fraud and money laundering. Developers and creators participating in the program are required to create an account with our third party vendor which collects tax information, ensures regulatory compliance, and executes the payouts. Additionally, developers and creators aged 13 and up can convert earned Robux into ad credits to purchase ads on the Platform.
Safety
Multiple systems are integrated into the Roblox Platform to promote civility and ensure the safety of our users. These systems are designed to enforce our policies, protect users’ personal information, and abide by local laws. We leverage text-filtering, content moderation systems, and automated systems to proactively identify behaviors that may violate our policies.
Content submitted by developers and creators, including images, models, audio, and video, goes through a multi-step review process before appearing on the Platform. Images are evaluated for Child Sexual Abuse Material using PhotoDNA with flagged images automatically reported to the National Center for Missing and Exploited Children. Audio files are scanned for IP infringement. Finally, all assets are subject to review by humans or AI trained on our Community Standards. During the year ended December 31, 2023, including automated reviews, we evaluated over 300 million assets. Assets refer to images, audio files, and video files that developers upload to the Roblox Platform to include in their experiences and in the Marketplace.
When experiences are published or updated on the Roblox Platform, they are evaluated by a suite of AI driven tools that identify problematic language, potential bypasses to our safety systems, and content that falls outside our policies. A human review team is continuously operating to evaluate flagged experiences. The Roblox Platform includes a suite of anti-intruder technology leveraging machine learning, throttles, and circuit breakers designed to block automated bot attacks and mitigate the impact of humans who attempt to spam users and disrupt the service. We also leverage targeted penetration testing, a bug bounty program, code reviews, secure by design principles, security testing, and vulnerability scanning to promote the security of the Platform.
Roblox operates a customer service portal that provides self-help information along with ways to contact Roblox via email or from within the Roblox Client. In the year ended December 31, 2023, Roblox responded to millions of customer inquiries and had a human respond to actionable safety issues on average within 22 minutes of their submission.
Safety and Digital Civility
We aspire to build a safe and civil online society. We have no tolerance on our Platform for content or behavior that violates our Community Standards. Safety and civility systems are built into our Platform and apply to every experience. In many instances, our systems extend beyond minimum regulatory requirements.
Our Platform is designed to comply with the Children’s Online Privacy Protection Act (“COPPA”) and the General Data Protection Regulation (“GDPR”) regulations. We work closely with regulators, authorities, and safety groups in many countries. We endeavor to promptly report any suspected child exploitation or abuse materials to the relevant authorities.
We partner with leading global organizations focused on child and internet safety, including the WeProtect Global Alliance, Digital Wellness Lab, Family Online Safety Institute, UK Safer Internet Centre, the Internet Watch Foundation, and kidSAFE, among others. We are also a member of various organizations, such as the Association for United Kingdom Interactive Entertainment and the Technology Coalition, with a goal of cross-industry collaboration, knowledge and technology exchange in areas of user safety, and child safety. As a member of the Technology Coalition, we are committed to providing transparency and promoting child safety online. We continue to work diligently with other digital platforms to report bad actors and inappropriate content so that they can also take appropriate actions on their platforms.
Our Trust & Safety Systems
We use AI and a dedicated team of human moderators to review content, including images, sound, and video, uploaded into our Platform. Our scanning algorithms also review and monitor communications that flow through Roblox to block and protect users from inappropriate behavior, such as questions about personal information and instructions on how to connect on less protective third-party chat applications. The algorithms in our chat filters are age-sensitive: they monitor both what users can say and see based on their ages.
Throughout our site and in-experience, we provide our users with the ability to report activity that they find objectionable. Users can also block or mute other users with whom they do not want to interact. We also provide parents with customizable parental controls to limit or disable online chat or to restrict access to a curated list of age appropriate experiences.
We have a dedicated team and thousands of trust & safety agents whose role is to protect our users by focusing on detecting inappropriate content and behavior 24/7 through a combination of AI and human moderation. We take swift action to address any content or developer or creator that violates our terms of use once detected. We have a Safety Advisory Board, made up of global industry experts that advise on the best practices to protect our community.
We continue to invest in technology and people to combat bad actors who attempt to undermine our efforts to connect millions of people. Our priority remains the safety and digital civility of our community.
The Roblox Economy
We support our developer and creator community by providing the tools to build, publish, operate, drive discovery, and monetize content. Our economy enables developers and creators to generate income through Roblox. There were over 5.0 million developers and creators who earned Robux on the Roblox Platform in the month ended December 31, 2023. As of December 31, 2023, over 16,500 developers qualified for and were registered in our Developer Exchange Program and therefore met certain conditions, such as having earned the minimum amount of Robux required to qualify, having a verified developer account, and having an account in good standing, and were therefore eligible to exchange their earned Robux for real-world currency. Of such developers and creators, for the year ended December 31, 2023, over 12,000 developers and creators actually exchanged their earned Robux for real-world currency through our Developer Exchange Program. For the same period, there were over 3,500 developers and creators that earned the equivalent of $10,000 or more in Robux and over 750 developers and creators that earned the equivalent of $100,000 or more in Robux.
Business Model
When users sign up for Roblox, they can create an avatar and explore the vast majority of our experiences for free, although the business model for any given experience is ultimately up to its developer. Most free experiences allow users to spend Robux by purchasing experience-specific enhancements. Users can also use Robux to obtain items such as clothing, accessories, and emotes from our Marketplace or within an experience. Roblox retains a portion of every Robux transaction and distributes the rest to developers and creators. Robux can only be purchased from us at a price set by us, and can only be spent within our Platform. Robux have no monetary or intrinsic value outside of our Platform and can only be converted to real-world currency through our Developer Exchange Program. We are aware that some users seek to use unauthorized third-party websites to exchange Robux for real-world currency which is not permitted under our terms of use. We regularly monitor and screen usage of our Platform with the aim of identifying and preventing these activities, as well as regularly send cease-and desist letters to operators of third-party websites offering fraudulent Robux or digital goods offers.
Consistent with our free to use business model, a small portion of our users have historically been payers. For example, in the year ended December 31, 2023, of our 68.4 million DAUs, only 852,000 represented our average daily unique paying users. Similarly, in the year ended December 31, 2023, our average daily bookings per DAU was $0.14, whereas our average daily bookings per daily unique paying user was $11.32. We believe that maintaining and growing our overall number of users, including the number of users who may not purchase and spend Robux, is important to the success of our business. As a result, we believe that the number of users who choose to purchase and spend Robux will continue to constitute a small portion of our overall users.
Roblox also allows developers, creators, and brands to reach their audiences by purchasing ads. Further, Roblox offers sponsored experiences and sponsored avatar items, whereby developers and creators can pay to purchase ads to increase discoverability of their creations, which appear where experiences and items are discovered, including through search.
How Users Purchase Robux
Users can generally purchase Robux in two ways: as one-time purchases or via Roblox Premium, a subscription service that is billed monthly or annually and includes discounted Robux, access to exclusive in-experience benefits, exclusive and discounted marketplace items and the ability to buy, sell, and trade certain Avatar items. Roblox accepts payments through app stores, credit cards, and prepaid cards. The average price for a Robux for the year ended December 31, 2023 was $0.01.
How Developers and Creators Earn Robux
Robux are considered “earned” if a developer or creator receives them as payments for a bona fide third-party transaction through the Roblox Platform. We offer developers and creators five mechanisms to earn Robux:
•sale of access to their experiences and enhancements in their experiences, which may be one-time or recurring;
•Engagement-Based Payouts, which reward developers for the amount of time that Roblox Premium subscribers spend in their experiences;
•generating impressions for ad units within their experiences and teleporting users to other experiences through ad portals;
•sale of content and tools between developers; and
•sale of Avatar items to users (through the Marketplace or directly within experiences).
Generally, as users purchase and subsequently spend Robux on Roblox, creators of the virtual item receive 30% of the Robux, the seller or distributor of the virtual item receives 40% of the Robux, and the Platform receives 30% of the Robux. Oftentimes, the creator of the virtual item is also the seller of that item. Creators that sell their own creations within their experiences receive 70% of the Robux spent, as they are acting both as the creator and the seller. Creators that make their virtual items available through the Marketplace receive 30% of the Robux spent, as Roblox is both the seller and the Platform for these transactions. Creators also receive 70% of the Robux spent for sales of plugins and other assets that appear in the Creator Store. As it relates to generating impressions for ads units and portals, developers earn Robux based on the number of impressions and teleports that occur within their experience.
Earned Robux are deposited into the virtual accounts of the developers and creators, who can convert Robux into real-world currency at an exchange rate which is determined by Roblox in its sole discretion of 1 Robux to $0.0035 as of December 31, 2023, if they qualify for and are registered in our Developer Exchange Program. In order to be qualified for our Developer Exchange Program and eligible to exchange earned Robux for real-world currency, developers and creators must meet certain conditions, such as having earned the minimum amount of Robux required to qualify for the program, a verified developer account, and an account in good standing. On January 31, 2022, we reduced the minimum amount of earned Robux required to qualify for the program from 100,000 Robux to 50,000 Robux and subsequently on January 31, 2023, we further reduced the minimum requirement from 50,000 Robux to 30,000 Robux. We believe these reductions in the minimum amounts required incentivize our developer and creator community, and promote the long term growth and health of such community. As of December 31, 2023 and 2022, over 16,500 and 11,000 developers and creators were qualified and registered in our Developer Exchange Program, respectively. For the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022, developers and creators earned $740.8 million and $623.9 million, respectively.
Our developers and creators do not always exchange their Robux into real-world currency. Some choose to reinvest their Robux into developer tools from the Creator Store, purchase ad credits to promote their experiences on the Platform, or spend the Robux as any other user would.
Our Growth Strategies
We are continually innovating the Roblox Platform, including making significant investments in high fidelity avatars, more realistic experiences, AI tools, and other social features, as well as more diverse opportunities for monetization. We believe that these innovations have the potential to transform how people express themselves, socialize, communicate, play, learn, work, and transact together around the world. We are focused on the following key growth strategies:
•Roblox Everywhere: We want to give users the ability to interact with experiences almost instantly across the most popular client devices. As of December 31, 2023, the Roblox Client operates on iOS, Android, PC, Mac, Xbox, PlayStation, and VR hardware, such as Meta Quest, and supports VR experiences on PC. We believe the investments we are making will facilitate a high quality, intuitive experience for users across all devices, and enable developers and creators to publish once and instantly on all supported devices across a global audience.
•Platform for Everyone: As we expand the diversity of content, experiences, and communications that people can have on Roblox, we believe there is significant potential to increase our penetration and engagement across all demographics. We ultimately aim to be a brand that serves everyone. We also look to continue expanding new verticals such as brand partnerships, education, and communication.
•International Expansion: We believe there is significant potential for us to grow the global reach of our Platform. We believe some of that will occur by the same organic, word of mouth user, creator, and developer growth that we have seen in markets like the U.S., Canada, and the United Kingdom. In addition, we are investing in technology that will also enhance our growth around the world. For example, we believe that features such as automated translation and built-in regional compliance will enable us to scale usage in global markets, allowing developers to publish in multiple languages and allowing users to communicate with each other even when they speak different languages.
•Vibrant Economy: We believe there is significant potential to increase monetization on our Platform and we are constantly investing in new ways to empower our creator community. First, we are actively working with our developer and creator community to help them improve their monetization. Second, we believe Roblox Premium, our subscription service, will increase our conversion of our free users to paying users and the retention of our paying users. Third, we expect to continue working with leading brands to build unique commerce opportunities and help them reach their audiences at scale within Roblox experiences through immersive ads. Our immersive ads system is designed to be native to the experience in which it is placed and will provide unique commerce opportunities for brands on the Platform. Immersive ads also provide developers and creators with another monetization method on the Platform.
Brand and Marketing
Our go-to-market approach is driven by the strength and continued enhancement of our brand, organic adoption across our user, creator and developer communities, and an influencer-based marketing strategy, with a goal to demonstrate the Platform’s wide-ranging appeal across demographics, geographies, and interests.
Users build a direct relationship with the Roblox brand by establishing an identity and creating their social graph. Users are able to navigate across an integrated universe of experiences on our Platform and engage on the Platform with other users in their social graph. We believe this approach helps to create a flywheel that brings new users to the Platform, and promotes loyalty and engagement.
We have millions of experiences to choose from on Roblox, and developers continue to build new experiences on the Platform and publish them daily. As experiences on the Platform grow in popularity, this success accrues to the Roblox brand and serves to draw in new audiences. Our approach is to amplify these experiences on both earned and owned channels which builds awareness and affinity for Roblox. This approach includes educating our creators, users, and brands on the Platform’s capabilities and innovations, all of which elevates each stakeholder’s experience.
We operate a highly efficient marketing model. Our approach is highly organic, with our user, creator and developer adoption driven by mutually reinforcing content and social network effects. We also leverage our influencer community to increase brand awareness and our reach across all age demographics.
We believe safety and civility is an integral and differentiating part of our brand. We have invested heavily in creating a safe and civil platform, which has allowed us to both grow and retain our user base.
Competition
We compete for both users, developers, and creators. We compete to attract and retain our users’ attention on the basis of our content and user experiences. We compete for users and their engagement hours with global technology leaders such as Amazon, Apple, Meta Platforms, Google, Microsoft, and Tencent, global entertainment companies such as Comcast, Disney, and ViacomCBS, global gaming companies such as Activision Blizzard (now owned by Microsoft), Electronic Arts, Take-Two, Epic Games, Krafton, and Valve, online content platforms including Netflix, Spotify, and YouTube, as well as social platforms such as Facebook, TikTok, Instagram, Pinterest, X (formerly known as Twitter), Reddit, Discord, and Snap. We are able to compete for these users based on our variety of content, personalized user experience, and various engaging and social features.
We rely on developers and creators to create the content that leads to and maintains user engagement (including maintaining the quality of experiences). We compete to attract and retain developers and creators by providing them with the free tools to easily build, publish, operate, and monetize content. We compete for developers and creators and engineering talent with gaming platforms such as Epic Games, Unity, Meta Platforms, and Valve Corporation, who provide developers and creators the ability to create or distribute interactive content. We are able to compete for these developers and creators because of our comprehensive offering to build, publish, and operate experiences on our Platform, our free and easy-to-use technology, our broad user reach, our economic rewards system, our brand, our reputation for innovation, our developer and creator-centric culture, and our mission.
Seasonality
We have historically experienced seasonality in monetization on our Platform and tend to generate higher levels of bookings in the fourth quarter of the year primarily due to the end-of-year holiday season. We also typically see higher levels of engagement in the months of June, July, and August, which are summer periods in the northern hemisphere, and lower levels of engagement in the post-summer months of September, October, and November. While bookings are typically strongest in the fourth quarter, this trend may not be reflected in the revenue recognized in the same period due to the timing of our revenue recognition (see section “Revenue Recognition” within Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Information, Note 1, “Overview and Summary of Significant Accounting Policies”, for further discussion on the Company’s revenue recognition policy). These seasonal impacts may be more or less pronounced in the future or different altogether.
Security, Privacy, Data Protection and Regulatory Matters
We are subject to a number of U.S. federal and state and foreign laws and regulations that involve matters central to our business. These laws and regulations may involve privacy, data protection, security, rights of publicity, content regulation, intellectual property, gambling, loot boxes, ratings, competition, protection of minors, including verified parental consent, consumer protection, communication, credit card processing, taxation, anti-bribery, anti-money laundering and corruption, economic or other trade prohibitions or sanctions or securities law compliance or other subjects. Many of these laws and regulations are still evolving and being tested in courts and could be interpreted and applied in a manner that is inconsistent from country to country or state to state and inconsistent with our current policies and practices and in ways that could harm our business. In addition, the application and interpretation of these laws and regulations often are uncertain, particularly in the new and rapidly evolving industry in which we operate. The costs of complying with these laws and regulations are high and likely to increase in the future, particularly as the degree of regulation increases, our business grows and our geographic scope expands. Further, the impact of these laws and regulations may disproportionately affect our business in comparison to our peers in the technology sector that have greater resources. Any failure on our part to comply with these laws and regulations may subject us to significant liabilities or penalties, or otherwise adversely affect our business, financial condition or operating results. It is imperative that we secure the creative assets, performance and user data that are critical to our business. We devote considerable resources to our security program with the intent to continually improve our services and how we securely store and separate user assets. Our intent is to make it easy for our developers and creators to securely build and distribute their content on our Platform.
We rely on a variety of statutory and common-law frameworks and defenses relevant to the content available on our service, including the Digital Millennium Copyright Act (“DMCA”), the Communications Decency Act, and the fair-use doctrine in the U.S., and the Electronic Commerce Directive in the European Union (“EU”). However, each of these statutes is subject to uncertain or evolving judicial interpretation and regulatory and legislative amendments. In addition, pending or recently adopted legislation in the EU may impose additional obligations or liability on us associated with content uploaded by users to our Platform. If the rules, doctrines or currently available defenses change, if international jurisdictions refuse to apply protections similar to those that are currently available in the U.S. or the EU, or if a court were to disagree with our application of those rules to our service, we could be required to expend significant resources to try to comply with the new rules or incur liability, and our business, revenue and financial results could be harmed.
We are also subject to U.S. federal and state and foreign laws and regulations regarding privacy and data protection, including with respect to the collection, storage, sharing, use, processing, transfer, disclosure, and protection of personal data. For example, the California Consumer Privacy Act (“CCPA”), went into effect on January 1, 2020. The CCPA requires covered companies to, among other things, provide new disclosures to California consumers, and afford such consumers new abilities to opt-out of the sale of personal information. Additionally, the California Privacy Rights Act (“CPRA”) became effective on January 1, 2023. The CPRA significantly modifies the CCPA, potentially resulting in further uncertainty and requiring us to incur additional costs and expenses in an effort to comply. Similar legislation has been proposed or adopted in other states. Aspects of the CCPA and these other state laws and regulations, as well as their enforcement, remain unclear, and we may be required to modify our practices in an effort to comply with them. California has also enacted the California Age-Appropriate Design Code Act (“ADCA”), which will take effect on July 1, 2024. The ADCA implements into law certain principles taken from the U.K.’s Age Appropriate Design Code (“AADC”), which went into effect in September 2021, and imposes substantial new obligations upon companies that offer online services, products, or features “likely to be accessed” by children, defined under the ADCA as anyone under 18 years of age. A U.S. District Court judge in the Northern District of California granted a request for preliminary injunction finding that the plaintiff is likely to succeed on its claim that the AADC violates the First Amendment. The California Attorney General has since filed an appeal. In addition, foreign data protection, privacy, consumer protection, communication, content regulation, and other laws and regulations may be more restrictive and burdensome. For example, GDPR imposes stringent operational requirements for entities processing personal information and significant penalties for non-compliance. Under GDPR, fines up to 20 million Euros or up to 4% of the annual global revenues of the infringer, whichever is greater, can be imposed for violations. In addition, the EU’s Digital Services Act, which became fully applicable on February 17, 2024 imposes new content moderation obligations, notice and transparency obligations, advertising restrictions and other requirements on digital platforms to protect consumers and their rights online. The evolving regulatory landscape internationally results in uncertainty and could require us to incur additional costs and expenses to comply.
Children’s privacy has also been a focus of recent enforcement activity and subjects our business to potential liability that could adversely affect our business, financial condition or operating results. The Federal Trade Commission and state attorneys general in the U.S. have in recent years increased enforcement of COPPA, which requires companies to obtain parental consent before collecting personal information from children under the age of 13. In addition, the FTC released proposed updates to COPPA and are requesting comments prior to publishing a final version of the updated COPPA rule. In addition, GDPR prohibits certain processing of personal information of children under the age of 13-16 (depending on the country) without parental consent. The CCPA requires companies to obtain the consent of children in California under the age of 16 (or parental consent for children under the age of 13) before selling their personal information. Actual or perceived noncompliance with the AADC may result in audits or other proceedings by the United Kingdom’s Information Commissioner Office, the body set up to uphold information rights in the United Kingdom, and other regulators in the EEA or Switzerland, as noncompliance with the AADC may indicate noncompliance with applicable data protection law. Although we take reasonable efforts to comply with these laws and regulations, we may in the future face claims under COPPA, the GDPR, the CCPA, the ADCA, and the AADC, or other laws or actual or asserted obligations relating to children’s privacy. There are also a number of legislative proposals pending before the U.S. Congress, various state legislative bodies and foreign governments concerning content regulation and data protection that could affect us if enacted in the future.
We take a variety of technical and organizational security measures and other measures designed to protect our data, including data pertaining to our users, employees and business partners. Despite measures we put in place, we may be unable to anticipate or prevent unauthorized access to such data.
Non-compliance with any applicable laws and regulations could result in penalties or significant legal liability. Although we take reasonable efforts to comply with applicable laws and regulations, there can be no assurance that we will not be subject to regulatory action, including fines, in the event of an incident or as the result of a regulatory investigation. We or our third-party service providers could be adversely affected if legislation or regulations are expanded to require changes in our or our third-party service providers’ business practices or if governing jurisdictions interpret or implement their legislation or regulations in ways that negatively affect our or our third-party service providers’ business, results of operations, or financial condition.
Government authorities outside the U.S. may also seek to restrict access to or block our Platform, prohibit or block the hosting of certain content available through our Platform or impose other restrictions that may affect the accessibility or usability of our Platform in that country for a period of time or even indefinitely. In addition, some countries have enacted laws that allow websites to be blocked for hosting certain types of content or may require websites to remove certain restricted content. Our privacy policy and terms and conditions of use describe our practices concerning, the use, transmission, and disclosure of user information and are posted on our website.
For additional information, please see the sections titled “Risk Factors—Risks Related to Our Business—If the security of our Platform is compromised, it could compromise our and our developers’, creators’, and users’ private information, disrupt our internal operations, and harm public perception of our Platform, which could cause our business and reputation to suffer,” “Risk Factors—Risks Related to Our Business—Some developers, creators, and users on our Platform may make unauthorized, fraudulent, or illegal use of Robux and other digital goods or experiences on our Platform, including through unauthorized third-party websites or “cheating” programs,” and “Risk Factors—Risks Related to Government Regulations—Because we store, process, and use data, some of which contains personal information, we are subject to complex and evolving federal, state, and international laws and regulations regarding privacy, cybersecurity, data protection, and other matters. Many of these laws and regulations are subject to change and uncertain interpretation, and could result in investigations, claims, changes to our business practices, increased cost of operations, and declines in user growth, retention, or engagement, any of which could significantly harm our business.”
Intellectual Property
Our intellectual property is an important aspect of our business, and our success depends in part on our ability to enforce and defend our intellectual property rights. We rely on a combination of patents, copyrights, trademarks, trade secrets, know-how, license agreements, contractual provisions, non-disclosure agreements, and confidentiality procedures to establish and protect our intellectual property rights. In addition to the protection provided by our intellectual property rights, we maintain a policy requiring our employees, consultants, and other third parties to enter into confidentiality and proprietary rights agreements to control access to our intellectual property.
As of December 31, 2023, we owned more than 160 U.S. patents relating to aspects of our actual or contemplated operations and technologies. Our issued patents are scheduled to expire between 2025 and 2041. We also had more than 250 pending patent applications in the U.S. and abroad. There can be no assurance that each of our patent applications will result in the issuance of a patent. In addition, any resulting issued patents may have claims narrower than those in our patent applications. We seek to protect our proprietary inventions relevant to our business through patent protection; however, we are not dependent on any particular patent or application for the operation of our business.
We have registered “Roblox,” “Robux,” and our corporate logo as trademarks in the U.S. and other jurisdictions. In total, we are the owner of over 453 trademark filings and have over 39 trademark applications in the U.S. and foreign countries as of December 31, 2023. There can be no assurance that each of our trademark applications will result in the issuance of a trademark or that each resulting trademark registration will be able to be maintained. As of December 31, 2023, we were the registered holder of over 1,700 domestic and international domain names. We continually monitor the registration of our domain names, trademarks, and service marks in the U.S. and in certain locations outside the U.S.
Despite our efforts, we may not be able to obtain or maintain sufficient protection for or successfully enforce our intellectual property. Any current and future patents, trademarks and other intellectual property or other proprietary rights we own or license, or otherwise have a right to use, may be contested, circumvented or found unenforceable or invalid. Our existing and future patents, copyrights, trademarks, trade secrets, domain names and other intellectual property rights may not provide us with competitive advantages, distinguish our products from those of our competitors or prevent competitors from launching comparable products. We may also be dependent on third-party content, technology and intellectual property in connection with our business. Further, we may not be able to prevent third parties from infringing, diluting or otherwise misappropriating or violating our intellectual property rights, and we may face challenges to the validity or enforceability of our intellectual property rights. We cannot guarantee that our business does not and will not infringe or misappropriate the rights of third parties. We expect to continue to face allegations from third parties, including our competitors and “non-practicing entities,” that we have infringed or otherwise violated their intellectual property rights. While we do not anticipate that these allegations, if they were to result in litigation against us, would have a materially adverse impact on our business, financial condition or operating results, there can be no guarantee that such lawsuits would not have a materially adverse impact on us. Further, certain federal statutes in the U.S. may apply to us with respect to various activities of our users, including the DMCA, provide immunity from monetary damages for online service providers such as us from, among other things, infringing content uploaded to our Platform by our users provided we comply with certain statutory requirements. The immunity is part of a statutory safe harbor. To enjoy the benefits of the safe harbor and be immune from monetary damages for infringing content uploaded by our users, we have to register a designated agent with the U.S. Copyright Office and maintain that filing on a periodic basis with the U.S. Copyright Office. We must also expeditiously remove any infringing content upon acquiring actual knowledge of such infringement or, in the absence of actual knowledge, if we become aware of facts or circumstances from which infringing activity is apparent. We must also adopt, reasonably implement, and inform users of our Platform about a policy that provides for the termination in appropriate circumstances of users who are repeat infringers of the copyrights of third parties. If we fail to comply with the conditions for qualifying for safe harbor protection, we may be subject to monetary damages for infringing content on our Platform. The damages for copyright infringement can range from $750 to $30,000 per work infringed and, in the case of willful infringement, up to $150,000 per work infringed. Alternatively, copyright owners could seek to recover their actual damages and our profits. As we host millions of user uploaded works, we could be subject to significant damages claims if we are determined not to comply with the DMCA safe harbors. Intellectual property disputes are common in our sector, and, as we face increasing competition or grow our business, there is an ongoing risk that we may become involved in legal disputes involving intellectual property claims. In addition to the protection provided by our intellectual property rights, we maintain a policy requiring our employees, consultants, and other third parties to enter into confidentiality and proprietary rights agreements to control access to our intellectual property.
For additional information on risks relating to intellectual property, please see the sections titled “Risk Factors—Risks Related to Intellectual Property—Claims by others that we infringe their proprietary technology or other rights, the activities of our users, or the content of the experiences on our Platform could subject us to liability and harm our business,” “Risk Factors—Risks Related to Intellectual Property—Failure to protect or enforce our intellectual property rights or the costs involved in such enforcement would harm our business,” and “Risk Factors—Risks Related to Intellectual Property—We use open source software as part of, and in connection with certain experiences on, our Platform, which may pose particular intellectual property and security risks to and could have a negative impact on our business.”
Human Capital
As of December 31, 2023, we employed 2,457 full time employees. In addition, we had thousands of trust & safety agents across the globe. In order to continue to evolve the Roblox Platform, we must continue to invest in attracting and retaining key talent, especially those focused on product and engineering. We monitor our progress with human capital metrics such as turnover, time to fill open roles, ratio of internally developed talent to external hires, ratio of technical talent to overall employees, and employee engagement. Our brand, market position, reputation for innovation, and developer and creator-centric culture support our ability to recruit best-in-class engineering talent. As of December 31, 2023, we had over 1,800 employees in product and engineering functions, accounting for approximately 75% of our total full time employees, and over 100 of our full time employees were located outside of the U.S. In October 2023, we asked a number of our remote employees to begin working from our San Mateo headquarters by July 2024 in an effort to further promote engaging, collaborative, and productive team environments.
We have embraced four core values since we founded Roblox and focus on incorporating them into our daily actions:
•Respect the Community. We consider our impact on the world, strive to respect everyone’s best interests, and communicate authentically. We prioritize community before company, company before team, and team before individual.
•We are Responsible. We are responsible for both the intended and unintended consequences of our actions.
•Take the Long View. We set a long term vision, even when making short term decisions. Challenge the status quo, think big, and look for innovation in whatever we do.
•Get Stuff Done. We drive execution by taking initiative and relentlessly iterating towards the long term goal.
To help focus our core values and to promote and support diversity, inclusion and equity, we have established several affinity groups. Our affinity groups are inclusive, voluntary, and employee-led whose aim is to promote inclusion at the Company and allow networking, mentorships, and other opportunities for professional and personal development. They include groups for women, racial and ethnic minorities, and people who identify as LGBTQIA+.
Corporate Information
We were incorporated in 2004. Our principal executive offices are located at 970 Park Place, San Mateo, California 94403, and our telephone number is (888) 858-2569. Our website address is www.corp.roblox.com. Information contained on, or that can be accessed through, our website is not incorporated by reference into this Annual Report on Form 10-K. “Roblox,” “Robux,” our logo and our other registered or common law trademarks, service marks or trade names appearing in this Annual Report on Form 10-K are the property of Roblox Corporation. Other trademarks and trade names referred to in this Annual Report on Form 10-K are the property of their respective owners. Solely for convenience, trademarks and trade names referred to in this Annual Report on Form 10-K, including logos, artwork and other visual displays, may appear without a trademark symbol, but such references are not intended to indicate in any way that we will not assert, to the fullest extent under applicable law, our rights or the rights of the applicable licensor to these trademarks and trade names. We do not intend our use or display of other entities’ trade names, trademarks or service marks to imply a relationship with, or endorsement or sponsorship of us by, any other entity.
Available Information
We file electronically with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (“SEC”), our annual reports on Form 10-K, quarterly reports on Form 10-Q, current reports on Form 8-K, and amendments to those reports filed or furnished pursuant to Section 13(a) or 15(d) of the Exchange Act. We make available on our website at ir.roblox.com, free of charge, copies of these reports and other information as soon as reasonably practicable after we electronically file such material with, or furnish it to, the SEC.
Investors, the media and others should note that we intend to announce material information to the public through filings with the SEC, the investor relations page on our website, at www.ir.roblox.com, press releases, public conference calls and webcasts. We use these channels, as well as social media, our blog at https://blog.roblox.com/ and our Creator Hub page at https://create.roblox.com/docs, including our Developer Forum at https://devforum.roblox.com/, to communicate with our developers and creators, users, and the public about our company, our Platform and other issues, and the information disclosed by the foregoing channels could be deemed to be material information. As such, we encourage investors, the media and others to follow the channels listed above and to review the information disclosed through such channels. However, information contained on, or that can be accessed through, these channels does not constitute a part of this prospectus and is not incorporated by reference herein. Any updates to the list of disclosure channels through which we will announce information will be posted on the investor relations page on our website.
Item 1A. Risk Factors
RISK FACTORS
A description of the risks and uncertainties associated with our business is set forth below. You should carefully consider the risks described below, as well as the other information in this Annual Report on Form 10-K, including our consolidated financial statements and “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations.” The occurrence of any of the events or developments described below could materially and adversely affect our business, financial condition, results of operations, and growth prospects. In such an event, the market price of our Class A common stock could decline, and you may lose all or part of your investment. Additional risks and uncertainties not presently known to us or that we currently believe are not material may also impair our business, financial condition, results of operations, and growth prospects.
Risk Factors Summary
Below is a summary of the principal factors that make an investment in our Class A common stock speculative or risky:
•We have a history of net losses and we may not be able to achieve or maintain profitability in the future.
•Our business is affected by seasonal demands, and our financial condition and results of operations will fluctuate from quarter to quarter, which makes our financial results difficult to predict and may not fully reflect our underlying performance.
•We experienced rapid growth in prior periods and our prior growth may not be indicative of our future growth or the growth of our market.
•We depend on effectively operating with mobile operating systems, hardware, and networks that we do not control; changes to any of these or our Platform may significantly harm our user retention, growth, engagement, and monetization, or require us to change our data collection and privacy, cybersecurity, and data protection practices, business models, operations, practices, advertising activities or application content, which could restrict our ability to maintain our Platform through these systems, hardware, and networks and would adversely impact our business.
•Because we recognize revenue from bookings over the estimated average lifetime of a paying user or as the virtual items are consumed, changes in our business may not be immediately reflected in our operating results.
•If our business becomes constrained by changing legal and regulatory requirements, including with respect to privacy, cybersecurity and data protection, artificial intelligence (“AI”), consumer protection, communication, verified parental consent and user-generated content, or enforcement by government regulators, including fines, orders, or consent decrees in the US or other jurisdictions in which we operate, our operating results will suffer.
•The success of our business model is contingent upon our ability to provide a safe online environment for children to experience and if we are not able to continue to provide a safe environment, our business will suffer dramatically.
•If we are not able to provide sufficiently reliable services to our developers, creators, and users and maintain the performance of our Platform in the event of outages, constraints, disruptions or degradations in our services and our Platform, our business and reputation will suffer.
•If the security of our Platform is compromised, it could compromise our and our developers’, creators’, and users’ proprietary information, disrupt our internal operations and harm public perception of our Platform, which could cause our business and reputation to suffer.
•We must continue to attract and retain highly qualified personnel in very competitive markets to continue to execute on our business strategy and growth plans.
•We may identify material weaknesses or otherwise fail to maintain an effective system of internal controls, which may result in material misstatements of our consolidated financial statements or cause us to fail to meet our periodic reporting obligations.
•Our business and results of operations are affected by fluctuations in currency exchange rates.
•We may incur liability as a result of content published using our Platform or as a result of claims related to content generated by our developers, creators, and users, including copyright infringement, and legislation regulating content on our Platform may require us to change our Platform or business practices.
•The loss of one or more of the members of our senior management team or other key personnel (or the inability to attract senior management or other key personnel), in particular our Founder, President, CEO and Chair of our Board of Directors, David Baszucki, could significantly harm our business.
•The public trading price of our Class A common stock is volatile and may decline.
•The dual class stock structure of our common stock has the effect of concentrating voting control in our Founder, which may limit or preclude your ability to influence corporate matters, including the election of directors and the approval of any change of control transaction.
•Securities or industry analysts or other third parties may publish inaccurate or unfavorable research about us, our business or our market which may cause the market price and trading volume of our Class A common stock to decline.
Risks Related to Our Business
We have a history of net losses and we may not be able to achieve or maintain profitability in the future.
We have incurred net losses since our inception, and we expect to continue to incur net losses in the foreseeable future. We incurred net losses attributable to common stockholders of $1,151.9 million, $924.4 million and $491.7 million for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022, and 2021, respectively. As of December 31, 2023, we had an accumulated deficit of $3,060.3 million. We also expect our operating expenses to continue to increase, and if our growth does not increase to offset these anticipated increases in our operating expenses, our business, results of operations, and financial condition will be harmed, and we may not be able to achieve or maintain profitability. We expect our costs and investments to continue to increase in future periods as we intend to continue to make investments to grow our business, including an expected increase in infrastructure, stock-based compensation expenses, and acquisitions. These efforts may be more costly than we expect and may not result in increased revenue or growth of our business. In addition to the expected costs to grow our business, we have incurred and expect to continue to incur significant additional legal, accounting, and other expenses as a public company. Compliance with these rules and regulations continues to increase our legal and financial compliance costs and demand on our systems, and requires significant attention from our senior management that could divert their attention away from the day-to-day management of our business. If we fail to increase our revenue to sufficiently offset the increases in our operating expenses, we will not be able to achieve or maintain profitability in the future.
Our business is affected by seasonal demands, and our financial condition and results of operations will fluctuate from quarter to quarter, which makes our financial results difficult to predict and may not fully reflect our underlying performance.
Historically, our business has been highly seasonal, with the highest percentage of our bookings occurring in the fourth quarter when holidays permit our users to spend increased time on our Platform and lead to increased spend on pre-paid Robux gift cards, and we expect this trend to continue. We also typically see higher levels of engagement in the months of June, July, and August, which are summer periods in the northern hemisphere, and lower levels of engagement in the post-summer months of September, October, and November. For example, our bookings for the quarter ending December 31, 2023 represented approximately 32% of our bookings for fiscal 2023. We may also experience fluctuations due to factors that may be outside of our control that affect user, developer, or creator engagement with our Platform.
Accordingly, our quarterly results of operations have fluctuated in the past and will fluctuate in the future, both based on the seasonality of our business as well as external factors impacting the global economy, our industry and our company, including, but not limited to our ability to maintain and grow our user base, user engagement, developer base and developer engagement; the level of demand for our platform; the ability of our developers to monetize their experiences; increased competition; our pricing model; the maturation of our business; our ability to introduce new revenue streams such as advertising; legislative or regulatory changes; macroeconomic conditions, such as high inflation, recessionary or uncertain environments, and fluctuating foreign currency exchange rates; our ability to maintain operating margins, cash used in operating activities, and free cash flow; system failures or actual or perceived breaches or other incidents relating to privacy or cybersecurity; adverse litigation judgments, settlements, or other litigation and dispute-related costs; adverse media coverage or unfavorable publicity; the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting; changes in our effective tax rate; and changes in accounting standards, policies, guidance, interpretations, or principles. As a result, you should not rely on our past quarterly results of operations as indicators of future performance. You should take into account the risks and uncertainties frequently encountered by companies in rapidly evolving market segments.
We experienced rapid growth in prior periods, and our prior growth rates may not be indicative of our future growth or the growth of our market.
We experienced rapid growth in prior periods relative to our quarterly forecast and historic trends, which may not be indicative of our financial and operating results in future periods. Activity levels in prior periods are not sustainable, and our growth rates have moderated in most markets. The long-term impact to our business, operations, and financial results will depend on numerous evolving factors that we may not be able to accurately predict. For example, our bookings increased 171% from the year ended December 31, 2019 to the year ended December 31, 2020, while our bookings increased 23% from the year ended December 31, 2022 to the year ended December 31, 2023. Our revenue, bookings, and user base growth rates have slowed and may continue to slow, and we may not experience any growth in bookings or our user base during periods where we are comparing against historical periods. We believe our overall market acceptance, revenue growth, and increases in bookings depend on a number of factors, some of which are not within our control. There can be no assurance that users will not reduce their usage or engagement with our Platform or reduce their discretionary spending on Robux, which would adversely impact our revenue and financial condition. If we are unable to continue to maintain the attractiveness of our Platform to developers, creators, and users, they may no longer seek new experiences in our Platform, which would result in decreased market acceptance, fewer bookings, and lower revenue and could harm our operations.
We depend on effectively operating with third-party mobile operating systems, hardware, and networks that may make changes affecting our operating costs, as well as our ability to maintain our Platform which would hurt our ability to operate our business.
For the year ended December 31, 2023, 30% of our revenue was attributable to Robux sales through the Apple App Store and 17% of our revenue was attributable to Robux sales through the Google Play Store. Because of the significant use of our Platform on mobile devices, our application must remain interoperable with these and other popular mobile app stores and platforms, and related hardware. We are subject to the standard policies and terms of service of these operating systems, as well as policies and terms of service of the various software application stores that make our application and experiences available to our developers, creators, and users. These policies and terms of service govern the availability, promotion, distribution, content, and operation of applications and experiences on such operating systems and stores. Each provider of these operating systems and stores has broad discretion to change and interpret its terms of service and policies with respect to our Platform and those changes may be unfavorable to us and our developers’, creators’, and users’ use of our Platform. If an operating system provider or application store limits or discontinues access to, or changes the terms governing, its operating system or store for any reason, it could adversely affect our business, financial condition, or results of operations.
Additionally, an operating system provider or application store could also limit or discontinue our access to its operating system or store if it establishes more favorable relationships with one or more of our competitors, launches a competing product itself, or it otherwise determines that it is in its business interests to do so. If competitors control the operating systems and related hardware our application runs on, they could make interoperability of our Platform more difficult or display their competitive offerings more prominently than ours. There is no guarantee that new devices, platforms, systems and software application stores will continue to support our Platform or that we will be able to maintain the same level of service on these new systems. If it becomes more difficult for our users, developers or creators to access and engage with our Platform, our business and user retention, growth, and engagement could be significantly harmed.
Similarly, at any time, our operating system providers or application stores can change their policies on how we operate on their operating system or in their application stores by, for example, applying content moderation for applications and advertising or imposing technical or code requirements. These actions by operating system providers or application stores may affect our ability to collect, process, and use data as desired and could negatively impact our ability to leverage data about the experiences our developers create, which in turn could impact our resource planning and feature development planning for our Platform.
We rely on third-party distribution channels and third-party payment processors to facilitate Robux purchases by our Platform users. If we are unable to maintain a good relationship with such providers, if their terms and conditions change, or fail to process or ensure the safety of users’ payments, our business will suffer.
Purchases of Robux and other products (e.g., prepaid gift cards) on our Platform are facilitated through third-party online distribution channels and third-party payment processors. We utilize these distribution channels, such as Amazon, Apple, Blackhawk, ePay, Google, Incomm, PayPal, Vantiv, Stripe, and Xsolla, to receive cash proceeds from sales of our Robux through direct purchases on our Platform. For our experiences accessed through mobile platforms such as the Apple App Store and the Google Play Store, we are required to share a portion of the proceeds from in-game sales with the platform providers. For operations through the Apple App Store and Google Play Store, we are obligated to pay up to 30% of any money paid by users to purchase Robux to Apple and Google and this amount could increase. These costs are expected to remain a significant operating expense for the foreseeable future. If the amount these platform providers charge increases, it could have a material impact on our ability to pay developers and our results of operations. Each provider of an operating system or application store may also change its fee structure or add fees associated with access to and use of its operating system, which could have an adverse impact on our business. There have been litigation and governmental inquiries over application store fees, and Apple or Google could modify their platform in response to such litigation and inquiries in a manner that may harm us. Any scheduled or unscheduled interruption in the ability of our users to transact with these distribution channels could adversely affect our payment collection and, in turn, our revenue and bookings.
Additionally, we do not directly process purchases of Robux on our Platform, and, thus, any information on those purchases (e.g., debit and credit card numbers and expiration dates, personal information, and billing addresses) is disclosed to the third-party online platform and service providers facilitating Robux purchases by users (such as Vantiv, Stripe, and Xsolla). We do not have control over the security measures of those providers, and their security measures may not be adequate. We could be exposed to litigation and possible liability if our users’ transaction information involving Robux purchases is compromised, which could harm our reputation and our ability to attract users and may materially adversely affect our business.
We also rely on the stability of such distribution channels and their payment transmissions, and third-party payment processors, to ensure the continued payment services provided to our users. If any of these providers fail to process or ensure the security of users’ payments for any reason, our reputation may be damaged and we may lose our paying users, and users may be discouraged from purchasing Robux in the future, which, in turn, would materially and adversely affect our business, financial condition, and prospects.
In addition, from time to time, we encounter fraudulent use of payment methods, which could impact our results of operations and if not adequately controlled and managed could create negative consumer perceptions of our service. If we are unable to maintain our fraud and chargeback rate at acceptable levels, card networks may impose fines, our card approval rate may be impacted and we may be subject to additional card authentication requirements. The termination of our ability to process payments on any major payment method would significantly impair our ability to operate our business.
Our estimates or judgments relating to our critical accounting policies could cause our results of operations to fall below expectations, and changes in our business may not be immediately reflected in our operating results.
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with GAAP requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the amounts reported in our financial statements and accompanying notes. For example, the majority of the virtual items available on our Platform are durable virtual items, which, when acquired, are recognized ratably over the estimated period of time the virtual items are available to the user (estimated to be the average lifetime of a paying user). Every quarter, we complete an assessment of our estimated paying user life, which is used for revenue recognition of durable virtual items and calculated based on historical monthly retention data for each paying user cohort to project future participation on our Platform. We calculate the average historical monthly retention data by determining the weighted average of monthly paying users that have spent time on our Platform. In 2021, our estimated paying user life was 23 months. In the first quarter of 2022, we updated our estimated paying user life from 23 months to 25 months, which was subsequently updated to 28 months in the third quarter of 2022. Based on the carrying amount of deferred revenue and deferred cost of revenue as of December 31, 2021, these changes in estimates resulted in a decrease in revenue of $344.9 million and a decrease in cost of revenue of $79.3 million during the twelve months ended December 31, 2022. Much of the revenue we report in each quarter is the result of purchases of Robux during previous periods. Consequently, a decline in purchases of Robux in any one quarter will not be fully reflected in our revenue and operating results for that quarter. Any such decline, however, will negatively impact our revenue and operating results in future quarters. Accordingly, the effect of significant near-term downturns in purchases of Robux for a variety of reasons may not be fully reflected in our results of operations until future periods.
We are subject to state, federal, and international regulations and any changes in such regulations could harm or prevent our ability to operate our Platform in those jurisdictions.
Uncertainty over changes in laws and regulations could adversely affect our ability to operate across demographics and geographies or our developer’s ability to monetize their experiences in some geographies. The widespread availability of user generated content is a relatively newer development, and the regulatory framework is new and evolving. In addition, many states and foreign governments have enacted legislation designed to protect children and regulate violent content, and we expect additional legislation to be enacted, that focuses on online safety. If we are unable to comply with applicable regulations, some of the experiences on our Platform, or our entire Platform, may not be available in such jurisdictions, and our ability to execute on our business model and grow our business would be severely impacted.
We are also subject to content moderation obligations, notice and transparency obligations, advertising restrictions and other requirements on digital platforms to protect consumers and their rights online, and existing and new regulations and policies with respect to privacy, biometrics, data protection, cybersecurity, gambling, loot boxes, intellectual property, childhood protection, consumer protection, ratings, and taxes. Additionally, the Federal Trade Commission regulates and restricts deceptive or unfair commercial activities, including with relation to targeted advertising. We are subject to regulations with respect to advertising, in particular, advertising to minors, and advertising regulations could differ based on the jurisdiction of the user. We may not be able to implement an advertising model that is compliant with regulations in all jurisdictions in which we operate. These requirements may increase our moderation and compliance related costs and expenses, reduce the overall use or demand of our Platform, or result in significant injunctive and monetary remedies for violations.
Moreover, changes to these laws, regulations, standards, or obligations could require us to change our business model, take on more onerous obligations, including, but not limited to, applying for government-issued licenses to operate, establishing a local presence in certain jurisdictions, or developing localized product offerings, and impact the functionality of our Platform. The costs of compliance with, and other burdens imposed by, these laws, regulations, standards, and obligations, could be prohibitively expensive. Furthermore, any inability to adequately address these burdens, would harm our ability to operate our Platform, limit the attractiveness of our Platform, or reduce overall demand for our Platform, which would harm our business, financial condition, and results of operations.
The success of our business model is contingent upon maintaining a strong reputation and brand, including our ability to provide a safe online environment for children to experience.
Our Platform hosts a number of experiences intended for audiences of varying ages, a significant percentage of which are designed to be experienced by children. As a user-generated content platform, it is relatively easy for developers, creators, and users to upload content that can be viewed broadly. Although illicit activities are in violation of our terms and policies, and we attempt to block objectionable material, we are unable to prevent all such violations from occurring. We continue to make significant efforts to provide a safe and enjoyable experience for users of all ages. We invest significant technical and human resources to prevent inappropriate content on our Platform by reviewing all images, audio, video, and 3D models at the time of upload in order to block inappropriate content before users have a chance to encounter it on our Platform. Notwithstanding our efforts, from time to time, inappropriate content is successfully uploaded onto our Platform and can be viewed by others prior to being identified and removed by us. Moreover, measures intended to make our Platform more attractive to an older, age verified audience, such as less highly moderated or unmoderated chat and the introduction of experiences with mature content, and new methods of communication could fail to gain sufficient market acceptance by its intended audience and may create the perception that our Platform is not safe for young users. In addition, the introduction of experiences for users who are 17 years of age and older may create the perception that our Platform is not safe for young users and may cause some operating system providers, application stores, or regulatory agencies to require a higher age rating for our Platform, which could cause us to become less available to younger users and harm our business, financial condition, and results of operations. In addition, children may attempt to evade our age verification system, which could lead them to be exposed to inappropriate behavior by participating in experiences that are not age-appropriate or that feature spatial voice chat. While we have introduced experience guidelines that will allow users to flag certain explicit content in our games, and are updating our parental controls, users may still be exposed to content that may not be age-appropriate. Unintentional access to this content could cause harm to our audience and to our reputation of providing a safe environment for children to play online. If we are unable to limit, or are perceived as not being able to sufficiently limit, all or substantially all age-inappropriate content to only users who have been verified as being the appropriate age for such content, parents and children will lose their trust in the safety of our Platform, which would harm our overall acceptance by these audiences and would likely result in significantly reduced revenue, bookings, profitability, and ultimately, our ability to continue to successfully operate our Platform.
In addition to limiting content to the age-appropriate audience and blocking other inappropriate content, we have statutory obligations under U.S. federal law to block or remove child pornography and report offenses to the National Center for Missing and Exploited Children. While we have dedicated technology and trained human moderator staff that can detect and remove sexual content involving children, there have been instances where such content has been uploaded, and any future non-compliance by us or allegations of non-compliance by us with respect to U.S. federal laws on child pornography or the sexual exploitation of children could significantly harm our reputation, create criminal liability, and could be costly and time consuming to address or defend. We may also be subject to additional criminal liability related to child pornography or child sexual exploitation under other domestic and international laws and regulations.
We believe that maintaining, protecting, and enhancing our reputation and brand is critical to grow the number of developers, creators, and users on our Platform, especially given the safe and civil atmosphere that we strive to achieve for our users, many of whom are children. Maintaining, protecting, and enhancing our brand will depend largely on our ability to continue to provide reliable high-quality, engaging, and shared experiences on our Platform. If users, developers, or creators do not perceive our Platform to be reliable or of high quality, the value of our brand could diminish, thereby decreasing the attractiveness of our Platform. Further, we have faced and are currently defending allegations that our Platform has been used by criminal offenders to identify and communicate with children and to possibly entice them to interact off-Platform, outside of the restrictions of our chat, content blockers, and other on-Platform safety measures. While we devote considerable resources to prevent this from occurring, we are unable to prevent all such interactions from taking place. We have also received and may continue to receive a high degree of media coverage, including the use of our Platform for illicit or objectionable ends. For example, we have experienced negative media publicity related to the age of some of our developers, the content that developers produce for, or the conduct of users on our Platform that may be deemed illicit, explicit, profane, or otherwise objectionable. Additional unfavorable publicity has covered our privacy, cybersecurity, or data protection practices, terms of service, product changes, product quality, litigation or regulatory activity, our use of generative AI, the actions of our users, and the actions of our developers or creators whose products are integrated with our Platform. Our reputation and brand could also be negatively affected by the actions of developers and users that are hostile, inappropriate, or illegal, whether on or off our Platform. Actual or perceived incidents or misuses of user data or other privacy or security incidents, the substance or enforcement of our community standards, the quality, integrity, characterization and age-appropriateness of content shared on our Platform, or the actions of other companies that provide similar services to ours, has in the past, and could in the future, adversely affect our reputation. Any criminal incidents or allegations involving Roblox, whether or not we are directly responsible, could adversely affect our reputation as a safe place for children and hurt our business. Any negative publicity could create the perception that we do not provide a safe online environment and may have an adverse effect on the size, engagement, and loyalty of our developer, creator, and user community, which would adversely affect our business and financial results. Maintaining, protecting, and enhancing our reputation and brand may require us to make substantial investments, and these investments may not be successful.
If we fail to retain users or add new users, or if our users decrease their level of engagement with our Platform, revenue, bookings, and operating results will be harmed.
We view DAUs as a critical measure of our user engagement, and adding, maintaining, and engaging users has been and will continue to be necessary to our continued growth. Our DAU growth rate has fluctuated in the past and may slow in the future due to various factors including: the introduction of new experiences or virtual items on our Platform, performance issues with our Platform, higher market penetration rates, the availability of our Platform across markets and user demographics, which may be impacted by regulatory or legal requirements, including the use of verified parental consent, changing responses to outbreaks of COVID-19, and competition from a variety of entertainment sources for our users and their time. In addition, our strategy seeks to expand the age groups and geographic markets that make up our users. If and when we achieve maximum market penetration rates among any particular user cohort overall and in particular geographic markets, future growth in DAUs will need to come from other age or geographic cohorts, which may be difficult, costly or time consuming for us to achieve. Accessibility to the internet and bandwidth or connectivity limitations as well as regulatory requirements, may also affect our ability to further expand our user base in a variety of geographies. If our DAU growth rate slows or becomes stagnant, or we have a decline in DAUs, or we fail to effectively monetize users in certain geographic markets, our financial performance will increasingly depend on our ability to elevate user activity or increase the monetization of our users.
Our business plan assumes that the demand for interactive entertainment offerings will increase for the foreseeable future. However, if this market shrinks or grows more slowly than anticipated or if demand for our Platform does not grow as quickly as we anticipate, whether as a result of competition, product obsolescence, budgetary constraints of our developers, creators, and users, technological changes, unfavorable economic conditions, uncertain geopolitical or regulatory environments or other factors, we may not be able to increase our revenue and bookings sufficiently to ever achieve profitability and our stock price would decline.
Moreover, a large number of our users are under the age of 13. This demographic may be less brand loyal and more likely to follow trends, including viral trends, than other demographics. These and other factors may lead users to switch to another entertainment option rapidly, which can interfere with our ability to forecast usage or DAUs and would negatively affect our user retention, growth, and engagement. We also may not be able to penetrate other demographics in a meaningful manner to compensate for the loss of DAUs in this age group. Falling user retention, growth, or engagement rates could seriously harm our business.
We depend on our developers to create digital content that our users find compelling, and if we fail to properly incentivize our developers and creators to develop and monetize content, our business will suffer.
We spend substantial amounts of time and money to research, develop, and enhance versions of our Platform to incorporate additional features, improve functionality or other enhancements and prioritize user safety and security in order to meet the rapidly evolving demands of our developers, creators, and users. Maintaining adequate research and development resources, such as the appropriate personnel and development technology, to meet the demands of the market is essential. Developments and innovations on our Platform may rely on new or evolving technologies which are still in development and may never be fully developed. For instance, use of AI algorithms presents risks associated with developing technologies, which create technical challenges for us to successfully maintain our technology. In addition, the use of AI involves significant technical complexity and requires specialized expertise. This specialized expertise can be difficult and costly to obtain given the increasing industry focus on AI development and competition for talent.
Our Platform relies on our developers and creators to create experiences and virtual items on our Platform for our users, and we believe the interactions between and within the developer, creator, and user communities on our Platform create a thriving and organic ecosystem, and this network effect drives our growth. To facilitate and incentivize the creation of the experiences and virtual items by developers our Platform offers developers an opportunity to earn Robux, a virtual currency on our Platform. When virtual items are acquired on our Platform, the originating developer or creator earns a portion of the Robux paid for the item. Developers are able to exchange their accumulated earned Robux for real-world currency under certain conditions outlined in our Developer Exchange Program. While we have millions of developers and creators on our Platform, 48% of engagement hours were spent in the top 50 experiences in the month ending December 31, 2023 and only 526 experiences had engagement hours of 10 million or more. The loss of any of our top developers could have a material impact on our business, financial condition, and operations. If we fail to provide a sufficient return to developers, they may elect to develop user-generated content on other platforms, which would result in a loss of revenue.
Despite our efforts, users, developers, or creators may become dissatisfied with our billing or payment policies, our handling of personal data, or other aspects of our Platform. If we fail to adequately address these or other user, developer, or creator complaints, negative publicity about us or our Platform could diminish confidence in and the use of our Platform. If we do not provide the right technologies, education or financial incentives to our developers and creators, they may develop fewer experiences or virtual items or be unable to or choose not to monetize their experiences, and our users may elect to not participate in the experiences or acquire the virtual items, and, thus, our Platform, revenue, and bookings could be adversely affected. Additionally, if we fail to anticipate developers’ and creators’ needs, the quality of the content they create may not attract users to engage with experiences and result in a decline of users on our Platform. When we develop new or enhanced features for our Platform, we typically incur expenses and expend resources upfront to develop, market, promote, and sell new features, and we may not be able to realize some or all of the anticipated benefits of these investments.
If we are not successful in our efforts to further develop live experiences on our Platform, our business could suffer.
We have undergone efforts to further develop the live experiences available on our Platform, such as virtual concerts, classrooms, meetings, and conferences and to offer commercial partners with branding opportunities in conjunction with key events, such as a product launch. There is no guarantee that these efforts will be successful or that users will engage with these experiences. New features or enhancements and changes to the existing features of our Platform, such as these live experiences, could fail to attain sufficient market acceptance for many reasons, including failure to predict market demand accurately in terms of functionality and to supply features that meet this demand in a timely fashion; defects, errors, or failures; negative publicity about performance, safety, privacy, or effectiveness; delays in releasing new features or enhancements on our Platform; and introduction or anticipated introduction of competing products by competitors. The failure to obtain market acceptance for these live experiences would negatively affect our business, financial condition, results of operations, and brand.
If we experience outages, constraints, disruptions, or degradations in our services, Platform support and/or technological infrastructure, our ability to provide sufficiently reliable services to our customers and maintain the performance of our Platform could be negatively impacted, which could harm our relationships with our developers, creators, and users, and, consequently, our business.
Our users expect fast, reliable, and resilient systems to enhance their experience and support their activity on our Platform, which depends on the continuing operation and availability of our Platform from our global network of data centers controlled and operated by us and our external service providers, including third-party “cloud” computing services. We also provide services to our developer and creator community through our Platform, including DevForum and Creator Hub for tutorials, hosting, customer service, regulatory compliance, and translation, among many others. The experiences and technologies on our Platform are complex software products and maintaining the sophisticated internal and external technological infrastructure required to reliably deliver these experiences and technologies is expensive and complex. The reliable delivery and stability of our Platform has been, and could in the future be, adversely impacted by outages, disruptions, failures, or degradations in our network and related infrastructure or those of our partners or service providers.
We have experienced outages from time to time since our inception when the Platform is unavailable for all or some of our users, developers, and creators, including in May 2022 and October 2021. In addition, there may be times when access to our Platform for users, developers, and creators may be temporarily unavailable or limited. This could be due to proactive actions we take while we provide critical updates or as an unexpected outcome of routine maintenance, which most recently occurred in July 2023. Outages can be caused by a number of factors, including a move to a new technology, the demand on our Platform exceeding the capabilities of our technological infrastructure, delays or failures resulting from natural disasters, manmade disasters, or other catastrophic events, the migration of data among data centers and to third-party hosted environments, and issues relating to our reliance on third-party software, third-party application stores, and third parties that host our Platform in areas where we do not operate our own data centers. The unavailability of our Platform, particularly if outages should become more frequent or longer in duration, could cause our users to seek other entertainment options, including those provided by our competitors, which may adversely affect our financial results. If we or our partners or third party service providers experience outages and our Platform is unavailable or if our developers, creators, and users are unable to access our Platform within a reasonable amount of time or at all, as a result of any such events, our reputation and brand may be harmed, developer, creator and user engagement with our Platform may be reduced, and our revenue, bookings and profitability could be negatively impacted. We may also experience a negative impact to our financial results as a result of decreased usage on our Platform or decrease of payouts to developers and creators. We may not have full redundancy for all of our systems at all times and our disaster recovery planning may not be sufficient to address all aspects of any unanticipated consequence or incident or allow us to maintain business continuity at profitable levels or at all. Further, in the event of damage or service interruption, our business interruption insurance policies will not adequately compensate us for any losses that we may incur. These factors in turn could further reduce our revenues, subject us to liability, or otherwise harm our business, financial condition, or results of operations.
In addition to the events described above, our data and our technological infrastructure may also be subject to local and federal administrative actions or regulations, changes to legal or permitting requirements, and litigation that could stop, limit, or delay operations. Despite a reliability program focused on anticipating and solving issues that may impact the availability of our Platform and precautions taken at our data centers, such as disaster recovery and business continuity arrangements, the occurrence of spikes in usage volume, the occurrence of a natural disaster, a hacking event or act of terrorism, a decision to close the facilities without adequate notice, our inability to secure additional or replacement data center capacity as needed, or other unanticipated problems at our data centers could result in interruptions or delays on our Platform, impede our ability to scale our operations or have other adverse impacts upon our business and adversely impact our ability to serve our developers, creators, and users.
Customer support personnel and technologies are critical to resolve issues and to allow developers, creators, and users to realize the full benefits that our Platform provides and provide an excellent customer experience. High-quality support is important for the retention of our existing developers, creators, and users and to encourage the expansion of their use of our Platform. We must continue to invest in the infrastructure required to support our Platform. If we do not help our developers, creators, and users quickly resolve issues and provide effective ongoing support, our ability to maintain and expand our Platform to existing and new developers, creators, and users could suffer. In addition, if we do not make sufficient investments in servers, software or personnel in support of our infrastructure, to scale effectively and accommodate increased demands placed on our infrastructure, the reliability of our underlying infrastructure will be harmed and our ability to provide a quality experience for our developers, creators, and users will be significantly harmed. This would lead to a reduction in the number of developers, creators, and users on our Platform, a reduction in our revenues, bookings, and ability to compete, and our reputation with existing or potential developers, creators, or users could suffer.
The lack of comprehensive encryption for communications on our Platform may increase the impact of a security breach or incident.
Communications on our Platform are not comprehensively encrypted at this time. As such, any security breach or incident that involves unauthorized access, acquisition, disclosure, or use of communications on our Platform may be particularly impactful to our business. We may experience greater incident response forensics, data recovery, legal fees, and costs of notification related to any such potential incident, and we may face an increased risk of reputational harm, regulatory enforcement, and consumer litigation, which could further harm our business, financial condition, results of operations, and future business opportunities.
If the security of our Platform is compromised, it could compromise our and our developers’, creators’, and users’ private information, disrupt our internal operations, and harm public perception of our Platform, which could cause our business and reputation to suffer.
We collect and store personal data and certain other sensitive and proprietary information in the operation of our business, including developer, creator, user and employee information, and other confidential data. While we have implemented measures designed to prevent unauthorized access to or loss of our confidential data, malware, ransomware, viruses, hacking, social engineering, spam, and phishing attacks have occurred and may occur on our Platform and our systems and those of our third-party service providers again in the future. Because of the popularity of our Platform, we believe that we are an attractive target for these sorts of attacks and have seen the frequency of these types of attacks increase.
The techniques used by malicious actors to obtain unauthorized access to, to sabotage, systems or networks, or to utilize our systems maliciously are constantly evolving and generally are not recognized until launched against a target. Consequently, despite the measures we have taken, we may be unable to anticipate these techniques, detect or react in a timely manner, or implement preventive measures, which could result in delays in our detection or remediation of, or other responses to, security breaches and other security-related incidents. The use of open source software used in our Platform has exposed us to security vulnerabilities in the past and will likely continue to expose us to security vulnerabilities in the future. For example, in December 2021, a vulnerability in popular logging software, Log4j, was publicly announced, and while we have taken steps to ensure these and similar vulnerabilities have been patched in our systems, we cannot guarantee that all vulnerabilities have been patched in every system upon which we are dependent or that additional critical vulnerabilities of open source software which we rely upon will not be discovered. Our use of AI in our products and business practices may increase or create additional cybersecurity risks, including risks of security breaches and incidents.
Our Platform and service operate in conjunction with, and we are dependent upon, third-party products, services, and components. Our ability to monitor our third-party service providers’ cybersecurity is limited, and in any event, attackers may be able to circumvent our third-party service providers’ cybersecurity measures. There have been and may continue to be significant attacks on certain of our third-party providers, and we cannot guarantee that our or our third-party providers’ systems and networks have not been breached or that they do not contain exploitable defects or bugs that could result in a breach of or disruption to our systems and networks or the systems and networks of third parties that support us and our Platform and service. If there is a security vulnerability, error, or other bug in one of these third-party products, services, or components and if there is a security exploit targeting them or even simply the allegation of a vulnerability or security exploit targeting one of these third-party products, services or components, we could face increased costs, claims, liability, reduced revenue, and harm to our reputation or competitive position. We and our service providers may be unable to anticipate these techniques, react, remediate, or otherwise address any security vulnerability, breach, or other incident in a timely manner, or implement adequate preventative measures.
If any unauthorized access to our network, systems or data, including our sensitive and proprietary information, personal data from our users, developers, or creators, or other data, or any other loss or unavailability of, or unauthorized use, modification, disclosure, or other processing of personal data or any other security breach or incident, occurs or is believed to have occurred, whether as a result of third-party action, employee negligence, error or malfeasance, defects, social engineering techniques, ransomware attacks, or otherwise, our reputation, brand and competitive position could be damaged, our and our users’, developers’ and creators’ data and intellectual property could potentially be lost or compromised, and we could be required to spend capital and other resources to alleviate problems caused by such actual or perceived breaches or incidents and remediate our systems. In the past, we have experienced social engineering and phishing attacks, and if similar attacks occur and are successful, this could have a negative impact on our business or result in unfavorable publicity. Additionally, we contract with certain third parties to store and process certain data for us, including our distribution channels, and these third parties face similar risks of actual and potential security breaches and incidents, which could present similar risks to our business, reputation, financial condition, and results of operations.
We incur significant costs in an effort to detect and prevent security breaches and other security-related incidents, including those to secure our product development, test, evaluation, and deployment activities, and we expect our costs will increase as we make improvements to our systems and processes to prevent future breaches and incidents. The economic costs to us to reduce cyber or other security problems, such as spammers, errors, bugs, flaws, “cheating” programs, defects or corrupted data, could be significant and may be difficult to anticipate or measure. Even the perception of these issues may cause developers, creators, and users to use our Platform less or stop using it altogether, and the costs could divert our attention and resources, any of which could result in claims, demands, and legal liability to us, regulatory investigations and other proceedings, and otherwise harm our business, reputation, financial condition, or results of operations. There could also be regulatory fines imposed for certain data breaches that take place around the world. Further, certain laws and regulations relating to privacy, biometrics, cybersecurity, and data protection, such as the California Consumer Privacy Act (“CCPA”), allow for a private right of action, which may lead to consumer litigation for certain data breaches that relate to specified categories of personal information. From time to time, we do identify product vulnerabilities, including through our bug bounty program. Although we have policies and procedures in place designed to swiftly characterize the potential impact of such vulnerabilities and develop appropriate patching or upgrade recommendations and also maintain policies and procedures related to vulnerability scanning and management of our internal corporate systems and networks, such policies and procedures may not be followed or detect every issue, and from time to time, we have, and may in the future again, need to proactively disable access to our Platform in order to provide necessary patching or upgrades.
Although we maintain cyber and privacy insurance, subject to applicable deductibles and policy limits, such coverage may not extend to all types of incidents relating to privacy, data protection, or cybersecurity, and it may be insufficient to cover all costs and expenses associated with such incidents. Further, such insurance may not continue to be available to us in the future on economically reasonable terms, or at all, and insurers may deny us coverage as to any future claim. The successful assertion of one or more large claims against us that exceed available insurance coverage, or the occurrence of changes in our insurance policies, including premium increases or the imposition of large deductible or co-insurance requirements, could have a material adverse effect on our business, including our financial condition, operating results, and reputation.
The expansion of our Platform outside the United States exposes us to risks inherent in international operations.
We operate our Platform throughout the world and are subject to risks and challenges associated with international business. For the year ended December 31, 2023, approximately 78% of our DAUs and 36% of our revenue was derived from outside the U.S. and Canada region. We intend to continue to expand internationally, and this expansion is a critical element of our future business strategy. However, as we continue to expand internationally, including into developing countries where consumer discretionary spending is relatively weak, while our DAUs increase, the growth rate of our bookings could decelerate due to weaker spending by users from those regions, and our ABPDAU has been and may continue to be negatively impacted. While we have a number of developers, creators, and users outside of the U.S., we have limited offices located outside of the U.S. and Canada, and there is no guarantee that our international expansion efforts will be successful. The risks and challenges associated with expanding our international presence and operations include:
•greater difficulty in enforcing contracts and accounts receivable collection, and longer collection periods;
•higher costs of doing business internationally, including increased accounting, travel, infrastructure, legal and compliance costs;
•double taxation of our international earnings and potentially adverse tax consequences due to changes in the tax laws of the U.S. or the foreign jurisdictions in which we operate;
•compliance with multiple, ambiguous, or evolving governmental laws and regulations, including those relating to employment, tax, content regulation, privacy, data protection, anti-corruption, import/export, customs, anti-boycott, sanctions and embargoes, antitrust, data transfer, storage and security, content monitoring, preclusion, and removal, online entertainment offerings, advertising and consumers in general, and industry-specific laws and regulations, particularly as these rules apply to interactions with children;
•expenses related to monitoring and complying with differing labor regulations, especially in jurisdictions where labor laws may be more favorable to employees than in the U.S.;
•increased exposure to fluctuations in exchange rates between the U.S. dollar and foreign currencies in markets where we do business;
•challenges inherent to efficiently recruiting and retaining qualified employees in foreign countries and maintaining our company culture and employee programs across all of our offices;
•management communication and integration problems resulting from language or cultural differences and geographic dispersion;
•the uncertainty of protection for intellectual property in some countries;
•the uncertainty of our exposure to third-party claims of intellectual property infringement and the availability of statutory safe harbors in some countries;
•foreign exchange controls that might prevent us from repatriating cash earned outside the U.S.;
•risks associated with trade restrictions and foreign legal requirements, and greater risk of unexpected changes in regulatory requirements, tariffs and tax laws, trade laws, and export and other trade restrictions;
•risks relating to the implementation of exchange controls, including restrictions promulgated by the Office of Foreign Asset Control (“OFAC”), and other similar trade protection regulations and measures;
•exposure to regional or global public health issues, and to travel restrictions and other measures undertaken by governments in response to such issues;
•general economic and political conditions in these foreign markets, including political and economic instability in some countries and regions;
•localization of our services, including translation into foreign languages and associated expenses and the ability to monitor our Platform in new and evolving markets and in different languages to confirm that we maintain standards consistent with our brand and reputation;
•regulatory frameworks or business practices favoring local competitors;
•changes in the perception of our Platform by governments in the regions where we operate or plan to operate;
•uncertainty regarding the imposition of and changes in the U.S.’ and other governments’ trade regulations, trade wars, tariffs, other restrictions or other geopolitical events, and without limitation, including the evolving relations between the U.S. and China, evolving relations with Russia due to Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, and the escalation of regional tension as a result of Hamas’ attack against Israel and the ensuing war; and
•natural disasters, acts of war, and terrorism, and resulting changes to laws and regulations, including changes oriented to protecting local businesses.
These and other factors could harm our ability to generate revenue and bookings outside of the U.S. and, consequently, adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations. We may not be able to expand our business and attract users in international markets and doing so will require considerable management attention and resources. International expansion is subject to the particular challenges of supporting a business in an environment of multiple languages, cultures, customs, legal systems, alternative dispute systems, regulatory systems and commercial infrastructures. We may not be able to offer our Platform in certain countries, and expanding our international focus may subject us to risks that we have not faced before or increase risks that we currently face.
If we are unable to successfully grow our user base, compete effectively with other platforms, and further monetize our Platform, our business will suffer.
We have made, and are continuing to make, investments to enable our developers and creators to design and build compelling content and deliver it to our users on our Platform. Existing and prospective developers may not be successful in creating content that leads to and maintains user engagement (including maintaining the quality of experiences); they may fail to expand the types of experiences that they can build for users; or our competitors may entice our developers, users and potential users away from, or to spend less time with, our Platform, each of which could adversely affect users’ interest in our Platform and lead to a loss of revenue opportunities and harm our results of operations. The multitude of other entertainment options, online gaming, and other interactive experiences is high, making it difficult to retain users who are dissatisfied with our Platform and seek other entertainment options.
Additionally, we may not succeed in further monetizing our Platform and user base. As a result, our user growth, user engagement, financial performance and ability to grow revenue could be significantly harmed if we fail to increase or maintain DAUs; our user growth outpaces our ability to monetize our users, including if our user growth occurs in markets that are not profitable; we fail to provide the tools and education to our developers and creators to enable them to monetize their experiences and developers do not create engaging or new experiences for users; we fail to establish a successful advertising model; we fail to increase or maintain the amount of time spent on our Platform, the number of experiences that our users engage with, or the usage of our technology for our developers; we fail to increase the features of our Platform, allowing it to more broadly serve the entertainment, education, communication and business markets; we fail to increase penetration and engagement across all demographics or measures intended to make our Platform more attractive to older-age verified users create the perception that our Platform is not safe for young users; or the experiences on our Platform do not maintain or gain popularity.
If we are able to continue to grow, we will need to manage our growth effectively, which could require expanding our internal IT systems, technological operations infrastructure, financial infrastructure, and operating and administrative systems and controls. In addition, we have expended in the past and may in the future expend significant resources to launch new features and changes on our Platform that we are unable to monetize, which may significantly harm our business. Any future growth would add complexity to our organization and require effective coordination across our organization, and an inability to do so would adversely affect our business, financial conditions, and results of operations.
We introduced our users to offerings for Robux that are subscription-based. Only a small portion of our users regularly purchase Robux compared to all users who use our Platform in any period. While we intend for these efforts to generate increased recurring revenues from our existing user base, they may cause users to decrease their purchases of Robux and decrease these users’ overall spend on our Platform. Our ability to continue to attract and retain users of our paid subscription services will depend in part on our ability to consistently provide our subscribers with a quality experience. If our users do not perceive these offerings to be of value, or if we introduce new or adjust existing features or pricing in a manner that is not favorably received by them, we may not be able to attract and retain subscribers or be able to convince users to become subscribers of such additional service offerings, and we may not be able to increase the amount of recurring revenue from our user base. If users fail to purchase Robux at rates similar to or greater than they have historically and if we fail to attract new paying users, or if our paying users fail to continue interacting with the Platform and purchasing Robux as they increase in age, our revenue will suffer. Subscribers may cancel their subscription to our service for many reasons, including a perception that they do not use the service sufficiently, the need to reduce household expenses, competitive services that provide a better value or experience or as a result of changes in pricing. If our efforts to attract and retain subscribers are not successful, our business, operating results, and financial condition may be adversely impacted.
Introduction of new technology could harm our business and results of operations.
The market for an immersive platform for connection and communication is a new and evolving market characterized by rapid, complex, and disruptive changes in technology and user, developer, and creator demands that could make it difficult for us to effectively compete. The expectations and needs of our users, developers, and creators are constantly evolving. Our future success depends on a variety of factors, including our continued ability to innovate, introduce new products and services efficiently, enhance and integrate our products and services in a timely and cost-effective manner, extend our core technology into new applications, and anticipate technological developments. If we are unable to react quickly to new technology trends—for example the continued growth of generative AI solutions which disrupts the ways developers create experiences or may disrupt the way users consume virtual goods—it may harm our business and results of operation. Further, social and ethical issues relating to the use of new and evolving technologies such as AI in our offerings, may result in reputational harm and liability, and may cause us to incur additional research and development costs to resolve such issues. AI presents emerging ethical issues and if we enable or offer solutions that draw controversy due to their perceived or actual impact on society, we may experience brand or reputational harm, competitive harm, or legal liability. Failure to address AI ethics issues by us or others in our industry could undermine public confidence in AI.
In addition, our use of generative AI in aspects of our Platform may present risks and challenges that could increase as AI solutions become more prevalent. The Roblox Cloud may be relied upon in the future for increasingly complex decision-making as it integrates hardware, accelerated machine learning AI, including generative AI, for a broad range of compute tasks, including control of non-player characters, improved personalization, synthetic content generation, and automation of the player experience. It is possible that at some point the Roblox Cloud may make decisions unpredictably or autonomously, which can raise new or exacerbate existing ethical, technological, legal, and other challenges, and may negatively affect the performance of the Roblox Platform and the user, developer, and creator experience. However, AI algorithms may be flawed. Datasets may be insufficient or contain biased information. These deficiencies and other failures of AI systems could subject us to competitive harm, regulatory action, legal liability, and brand or reputational harm.
Our user metrics and other estimates are subject to inherent challenges in measurement, and real or perceived inaccuracies in those metrics may significantly harm and negatively affect our reputation and our business.
We regularly review metrics, including our DAUs, hours engaged, unique payers, user demographics, and ABPDAU to evaluate growth trends, measure our performance, and make strategic decisions. These metrics are calculated using internal data gathered on an analytics platform that we developed and operate and have not been validated by an independent third party. Our metrics and estimates may also differ from estimates published by third parties or from similarly titled metrics of our competitors due to differences in methodology or the assumptions on which we rely. If our estimates are inaccurate, then investors will have less confidence in our company and our prospects, which could cause the market price of our Class A common stock to decline, and our reputation and brand could be harmed.
While these metrics are based on what we believe to be reasonable estimates of our user base for the applicable period of measurement, there are inherent challenges in measuring how our Platform is used and as a result, the metrics may overstate the number of DAUs, monthly unique payers, average monthly repurchase rate, hours engaged, ABPDAU, and average bookings per monthly unique payer. The methodologies used to measure these metrics require significant judgment and are also susceptible to algorithm or other technical errors. In addition, we are continually seeking to improve our estimates of our user base and hours engaged, and such estimates may change due to improvements or changes in our methodology. We regularly review our processes for calculating these metrics, and from time to time we discover inaccuracies in our metrics or make adjustments to improve their accuracy, which can result in adjustments to our historical metrics. Our ability to recalculate our historical metrics may be impacted by data limitations or other factors that require us to apply different methodologies for such adjustments.
Additionally, there are users who have multiple accounts, fake user accounts, or fraudulent accounts created by bots to inflate user activity for a particular developer or creator on our Platform, thus making the developer’s or creator’s experience or other content appear more popular than it really is. We strive to detect and minimize fraud and unauthorized access to our Platform, and these practices are prohibited in our terms of service, and we implement measures to detect and suppress that behavior. If we are successful in our efforts to minimize fraud, the use of bots and unauthorized access to our Platform, our operating results may be negatively affected. Some of our demographic data may also be incomplete or inaccurate. For example, because users self-report their dates of birth, our age demographic data may differ from our users’ actual ages. If our users provide us with incorrect or incomplete information regarding their age or other attributes, then our estimates may prove inaccurate.
Errors or inaccuracies in our metrics or data could also result in incorrect business decisions and inefficiencies. For instance, if a significant understatement or overstatement of active users or hours engaged were to occur, we may expend resources to implement unnecessary business measures or fail to take required actions to attract a sufficient number of users to satisfy our growth strategies. If our investors or developers do not perceive our user, geographic, or other demographic metrics to be accurate representations of our user base, or if we discover material inaccuracies in our user, geographic, or other demographic metrics, our reputation may be seriously harmed. Our developers, creators, and brand and other partners may also be less willing to allocate their budgets or resources to our Platform, which could seriously harm our business.
We rely on suppliers for certain components of the equipment we use to operate our Platform and any disruption in the availability of these components could delay our ability to expand or increase the capacity of our Platform or replace defective equipment.
We rely on suppliers for several components of the equipment we use to operate our Platform. Our reliance on these suppliers exposes us to risks, including reduced control over production costs and constraints based on the current availability, terms, and pricing of these components. While the network equipment and servers we purchase generally are commodity equipment and we believe an alternative supply source for network equipment and servers on substantially similar terms could be identified quickly, our business could be adversely affected until those efforts are completed. In addition, the technology equipment industry has experienced component shortages and delivery delays, and we have and may in the future experience shortages or delays, including as a result of increased demand in the industry, natural disasters, export and import control restrictions, or our suppliers lacking sufficient rights to supply the components in all jurisdictions in which we have data centers and edge data centers that support our Platform. For example, supply chain constraints for servers and other networking equipment required for our operations has resulted and could in the future result in disruptions and delays for these components and the delivery and installation of such components at our data centers and edge data centers. If our supply of certain components is disrupted or delayed, there can be no assurance that additional supplies or components can serve as adequate replacements for the existing components or that supplies will be available on terms that are favorable to us, if at all. Any disruption or delay in the supply of our hardware components may delay the opening of new data centers, edge data centers, co-location facilities or the creation of fully redundant operations, limit capacity expansion, or replacement of defective or obsolete equipment at existing data centers and edge data centers or cause other constraints on our operations that could damage our ability to serve our developers, creators, and users.
Some developers, creators, and users on our Platform may make unauthorized, fraudulent, or illegal use of Robux and other digital goods or experiences on our Platform, including through unauthorized third-party websites or “cheating” programs.
Robux and digital goods on our Platform have no monetary value outside of our Platform, but users have made and may in the future make unauthorized, fraudulent, or illegal sales and/or purchases of Robux and other digital goods on or off of our Platform, including through unauthorized third-party websites in exchange for real-world currency. For example, some users have made fraudulent use of credit cards owned by others on our Platform to purchase Robux and offer the purchased Robux for sale at a discount on a third-party website. For the year ended December 31, 2023, total chargebacks to us from this fraud was approximately 3.11% of bookings.
While we regularly monitor and screen usage of our Platform with the aim of identifying and preventing these activities, and regularly monitor third-party websites for fraudulent Robux or digital goods offers as well as regularly send cease-and-desist letters to operators of these third-party websites, we are unable to control or stop all unauthorized, fraudulent, or illegal transactions in Robux or other digital goods that occurs on or off of our Platform. Although we are not responsible for such unauthorized, fraudulent, and/or illegal activities conducted by these third parties, our user experience may be adversely affected, and users and/or developers may choose to leave our Platform if these activities are pervasive. These activities may also result in negative publicity, disputes, or even legal claims, and measures we take in response may be expensive, time consuming, and disruptive to our operations.
In addition, unauthorized, fraudulent, and/or illegal purchases and/or sales of Robux or other digital goods on or off of our Platform, including through third-party websites, bots, fake accounts, or “cheating” or malicious programs that enable users to exploit vulnerabilities in the experiences on our Platform or our partners’ websites and platforms, could reduce our revenue and bookings by, among other things, decreasing revenue from authorized and legitimate transactions, increasing chargebacks from unauthorized credit card transactions, causing us to lose revenue and bookings from dissatisfied users who stop engaging with the experiences on our Platform, or could increase costs that we incur to develop technological measures to curtail unauthorized transactions and other malicious programs, or could reduce other operating metrics.
Under our community rules for our Platform, which developers, creators, and users are obligated to comply with, we reserve the right to temporarily or permanently ban individuals for breaching our Terms of Use by violating applicable law or Roblox policies which include engaging in illegal activity on the Platform. We have banned individuals as a result of unauthorized, fraudulent, or illegal use of Robux or other digital goods on our Platform. We have also employed technological measures to help detect unauthorized Robux transactions and continue to develop additional methods and processes through which we can identify unauthorized transactions and block such transactions. However, there can be no assurance that our efforts to prevent or minimize these unauthorized, fraudulent, or illegal transactions will be successful.
We have made and are continuing to make investments in privacy, data protection, user safety, cybersecurity, and content review efforts to combat misuse of our services and user data by third parties, including investigations of individuals we have determined to have attempted to access and, in some cases, have accessed, user data without authorization. Our internal teams also continually monitor and address any unauthorized attempts to access data stored on servers that we own or control or data available to our third-party customer service providers. As a result of these efforts, we have discovered and disclosed, and anticipate that we will continue to discover and disclose, additional incidents of misuse of or unauthorized access of user data or other undesirable activity by third parties. We have taken steps to protect the data that we have access to, but despite these efforts, our security measures, or those of our third-party service providers, could be insufficient or breached as a result of third-party action, malfeasance, employee errors, service provider errors, technological limitations, defects or vulnerabilities in our Platform or otherwise. Additionally, many of our employees and third-party service providers with access to user data currently are and may in the future be working remotely, which may increase our or our third-party service providers’ risk of security breaches or incidents. Moreover, the risk of state-supported and geopolitical-related cyber-attacks may increase with recent geopolitical events. We may not discover all such incidents or activity or be able to respond to or otherwise address them, promptly, in sufficient respects or at all. Such incidents and activities have in the past, and may in the future, involve the use of user data or our systems in a manner inconsistent with our terms, contracts or policies, the existence of false or undesirable user accounts, theft of in-game currency or virtual items in valid user accounts, and activities that threaten people’s safety on- or offline. We may also be unsuccessful in our efforts to enforce our policies or otherwise remediate any such incidents. Any of the foregoing developments, whether actual or perceived, may negatively affect user trust and engagement, harm our reputation and brands, require us to change our business practices in a manner adverse to our business, and adversely affect our business and financial results. Any such developments may also subject us to future litigation and regulatory inquiries, investigations, and proceedings, including from data protection authorities in countries where we offer services and/or have users, which could subject us to monetary penalties and damages, divert management’s time and attention, and lead to enhanced regulatory oversight.
We focus our business on our developers, creators, and users, and acting in their interests in the long-term may conflict with the short-term expectations of analysts and investors.
A significant part of our business strategy and culture is to focus on long-term growth and developer, creator, and user experience over short-term financial results. We expect our expenses to continue to increase in the future as we broaden our developer, creator, and user community, as developers, creators, and users increase the amount and types of experiences and virtual items they make available on our Platform and the content they consume, as we continue to seek ways to increase payments to our developers and as we develop and further enhance our Platform, expand our technical infrastructure and data centers, and hire additional employees to support our expanding operations. As a result, in the near- and medium-term, we may continue to operate at a loss, or our near- and medium-term profitability may be lower than it would be if our strategy were to maximize near- and medium-term profitability. We expect to continue making significant expenditures to grow our Platform and develop new features, integrations, capabilities, and enhancements to our Platform for the benefit of our developers, creators, and users. We will also be required to invest in our internal IT systems, technological operations infrastructure, financial infrastructure, and operating and administrative systems and controls. Such expenditures may not result in improved business results or profitability over the long-term. If we are ultimately unable to achieve or improve profitability at the level or during the time frame anticipated by securities or industry analysts, investors and our stockholders, the trading price of our Class A common stock may decline.
We may require additional capital to meet our financial obligations and support business growth, and this capital might not be available on acceptable terms or at all.
We intend to continue to make significant investments to support our business growth and may require additional funds to respond to business challenges, improve our Platform and operating infrastructure or acquire complementary businesses, personnel, and technologies. Accordingly, we may need to engage in additional equity or debt financings. If we raise additional funds through future issuances of equity or convertible debt securities, our existing stockholders could suffer significant dilution, and any new equity securities we issue could have rights, preferences, and privileges superior to those of our Class A common stock. Any debt financing that we secure in the future could involve offering security interests and undertaking restrictive covenants relating to our capital raising activities and other financial and operational matters, which may make it more difficult for us to obtain additional capital and to pursue business opportunities, including potential acquisitions. Recently, the trading prices of technology companies have been highly volatile, which may reduce our ability to access capital on favorable terms or at all. Also, to the extent outstanding additional shares subject to options and warrants to purchase our capital stock are authorized and exercised, there will be further dilution. The amount of dilution could be substantial depending on the size of the issuance or exercise. If we are unable to obtain adequate financing or financing on terms satisfactory to us when we require it, our ability to continue to support our business growth and to respond to business challenges could be significantly impaired, and our business, financial condition or results of operations may be harmed.
The popularity of our Lua scripting language is a key driver of content creation and engagement with our Platform, and if other programming languages or platforms become more popular with our developers, it may affect engagement with and content creation for our Platform.
Roblox experiences are programmed using Lua scripting language on the Roblox Platform. In order to enhance the attractiveness of our Platform to potential developers, we have made the Lua scripting language available without charge. The Lua scripting language permits developers on the Roblox Platform to develop customized add-on features for their own or others’ use, and we have trained our developers on how to write add-on programs using Lua scripting language. As part of this strategy, we have encouraged the development of an active community of Lua programmers similar to those which have emerged for other software platforms. The widespread use and popularity of our Lua scripting language is critical to creating engaging content on and demand for our Platform. If developers do not find the Lua scripting language or our Platform simple and attractive for developing content or determine that our Lua scripting language or other features of our Platform are undesirable or inferior to other scripting languages or platforms, or Lua scripting language becomes unavailable for use by the developers for any reason, they may shift their resources to developing content on other platforms and our business may be harmed.
We rely on Amazon Web Services for a portion of our cloud infrastructure in certain areas, and as a result any disruption of AWS would negatively affect our operations and significantly harm our business.
We rely on Amazon Web Services (“AWS”) as a third-party provider for a portion of our backend services, including for some of our high-speed databases, scalable object storage, and message queuing services, as well as virtual cloud infrastructure. For location-based support areas, we outsource certain aspects of the infrastructure relating to our cloud-native Platform. As a result, our operations depend, in part, on AWS’ ability to protect their services against damage or interruption from natural or manmade disasters. Our developers, creators, and users need to be able to access our Platform at any time, without interruption or degradation of performance. Although we have disaster recovery plans that utilize multiple AWS availability zones to support our cloud infrastructure, any incident affecting their infrastructure that may be caused by natural or manmade disasters and other similar events beyond our control, could adversely affect our cloud-native Platform. Any disruption of or interference with our use of AWS could impair our ability to deliver our Platform reliably to our developers, creators, and users.
Additionally, if AWS were to experience a hacking attack or another security incident, it could result in unauthorized access to, damage to, disablement or encryption of, use or misuse of, disclosure of, modification of, destruction of, or loss of our data or our developers’, creators’, and users’ data or disrupt our ability to provide our Platform or service. A prolonged AWS service disruption affecting our cloud-native Platform for any of the foregoing reasons would adversely impact our ability to serve our users, developers, and creators and could damage our reputation with current and potential users, developers, and creators, expose us to liability, result in substantial costs for remediation, cause us to lose users, developers, and creators, or otherwise harm our business, financial condition, or results of operations. and users. We may also incur significant costs for using alternative hosting cloud infrastructure services or taking other actions in preparation for, or in reaction to, events that damage or interfere with the AWS services we use.
We have entered into an enterprise agreement with AWS and a supplemental private pricing addendum that will remain in effect until June 2026. In the event that our AWS service agreements are terminated, or there is a lapse of service, elimination of AWS services or features that we utilize, we could experience interruptions in access to our Platform as well as significant delays and additional expense in arranging for or creating new facilities or re-architecting our Platform for deployment on a different cloud infrastructure service provider, which would adversely affect our business, financial condition, and results of operations.
We must continue to attract and retain users, developers, and creators, and highly qualified personnel in very competitive markets to continue to execute on our business strategy and growth plans, and the loss of key personnel or failure to attract and retain users, developers, and creators could significantly harm our business.
We compete for users, developers, and creators. We compete to attract and retain our users’ attention and their engagement hours with other global technology leaders such as Amazon, Apple, Meta Platforms, Google, Microsoft, and Tencent, global entertainment companies such as Comcast, Disney, ViacomCBS, and Warner Bros Discovery, global gaming companies such as Activision Blizzard (now owned by Microsoft), Electronic Arts, Take-Two, Epic Games, Krafton, NetEase, and Valve, online content platforms including Netflix, Spotify, and YouTube, as well as social platforms such as Facebook, TikTok, Instagram, WhatsApp, Pinterest, X (Twitter), Reddit, Discord and Snap.
We also rely on developers and creators to create the content that leads to and maintains user engagement (including maintaining the quality of experiences). We compete to attract and retain developers and engineering talent with gaming and metaverse platforms such as Epic Games, Unity, Meta Platforms, and Valve Corporation, which also give developers the ability to create or distribute interactive content. We do not have any agreements with our developers that require them to continue to use our Platform for any time period. Some of our developers have developed attractive businesses in developing content, including games, on our Platform. In the future, if we are unable to continue to provide value to these developers and they have alternative methods to publish and commercialize their offerings, they may not continue to provide content to our Platform. Should we fail to provide compelling advantages to continued use of our ecosystem to developers, they may elect to develop content on competing interactive entertainment platforms. If a significant number of our developers no longer provide content, we may experience an overall reduction in the quality of our experiences, which could adversely affect users’ interest in our Platform and lead to a loss of revenue opportunities and harm our results of operations.
We expect competition to continue to increase in the future. Many of our existing competitors have, and some of our potential competitors could have, substantial competitive advantages, such as larger sales and marketing budgets and resources; broader and more established relationships with users, developers, and creators; greater resources to make acquisitions and enter into strategic partnerships; lower labor and research and development costs; larger and more mature intellectual property portfolios; and substantially greater financial, technical, and other resources.
Additionally, we depend on the continued services and performance of our Founder, President, CEO and Chair of our Board of Directors, David Baszucki, members of our senior management team, and other key personnel. David Baszucki has been responsible for our strategic vision, and should he stop working for us for any reason, it is unlikely that we would be able to immediately find a suitable replacement. We do not maintain key man life insurance for David Baszucki, and do not believe any amount of key man insurance would allow us to recover from the harm to our business if David Baszucki were to leave the Company for any reason. Similarly, members of our senior management team and other key personnel are highly sought after and others may attempt to encourage these individuals to leave the Company. The loss of one or more of the members of the senior management team or other key personnel for any reason, or the inability to attract new or replacement members of our senior management team, other key personnel, or highly qualified employees could disrupt our operations, create uncertainty among investors, adversely impact employee retention and morale, and significantly harm our business.
Our business and results of operations are affected by fluctuations in currency exchange rates.
As we continue to expand our international operations, we become more exposed to the effects of fluctuations in currency exchange rates. We generally collect revenue from our international markets in the local currency. For the year ended December 31, 2023, approximately 78% our DAUs and 36% of our revenue was derived from outside the U.S. and Canada region. While we periodically adjust the price of Robux to account for the relative value of this local currency to the U.S. dollar, these adjustments are not immediate nor do they typically exactly track the underlying currency fluctuations. As a result, rapid appreciation of the U.S. dollar against these foreign currencies has harmed and may in the future harm our reported results and cause the revenue derived from our foreign users and overall revenue to decrease. In addition, even if we do adjust the cost of our Robux in foreign markets to fluctuations in the U.S. dollar, such fluctuations could change the costs of purchasing Robux to our users outside of the U.S., which may adversely affect our business, results of operations and financial condition, or improve our financial performance.
We also incur expenses for employee compensation and other operating expenses at our non-U.S. locations in the local currency. Additionally, global events as well as geopolitical developments, including conflict in Europe and inflation have caused, and may in the future cause, global economic uncertainty, and uncertainty about the interest rate environment, which could amplify the volatility of currency fluctuations. Fluctuations in the exchange rates between the U.S. dollar and other currencies could result in the dollar equivalent of our expenses being higher which may not be offset by additional revenue earned in the local currency. This could impact our reported results of operations. To date, we have not engaged in any hedging strategies and any such strategies, such as forward contracts, options, and foreign exchange swaps related to transaction exposures that we may implement in the future to mitigate this risk may not eliminate our exposure to foreign exchange fluctuations. Moreover, the use of hedging instruments may introduce additional risks if we are unable to structure effective hedges with such instruments.
We plan to continue to make acquisitions and investments in other companies, which could require significant management attention, disrupt our business, dilute our stockholders, and significantly harm our business.
As part of our business strategy, we have made and intend to make acquisitions to add specialized employees and complementary companies, features, and technologies. Our ability to acquire and successfully integrate larger or more complex companies, features, and technologies is unproven. In the future, we may not be able to find other suitable acquisition or investment candidates, and we may not be able to complete acquisitions or similar strategic transactions on favorable terms, if at all. The pursuit of potential acquisitions may divert the attention of management and cause us to incur significant expenses related to identifying, investigating, and pursuing suitable acquisitions, whether or not they are consummated. Our previous and future acquisitions may not achieve our goals, and any future acquisitions we complete could be viewed negatively by users, developers, creators, partners, or investors. In addition, if we fail to successfully close transactions or integrate new teams into our corporate culture, or fail to integrate the features and technologies associated with these acquisitions, our business could be significantly harmed. Any integration process may require significant time and resources, and we may not be able to manage the process successfully. We may not successfully evaluate or use the acquired products, technology, and personnel, or accurately forecast the financial impact of an acquisition, including accounting charges which could be recognized as a current period expense. We also may not achieve the anticipated benefits of synergies from the acquired business, may encounter challenges with incorporating the acquired features and technologies into our Platform while maintaining quality and security standards consistent with our brand, or may fail to identify security vulnerabilities in acquired technology prior to integration with our technology and Platform. We may also incur unanticipated liabilities that we assume as a result of acquiring companies, including claims related to the acquired company, its offerings or technologies or potential violations of applicable law or industry rules and regulations arising from prior or ongoing acts or omissions by the acquired business that were not discovered during diligence. We will pay cash, incur debt, or issue equity securities to pay for any acquisitions, any of which could significantly harm our business. In addition, it generally takes several months after the closing of an acquisition to finalize the purchase price allocation. Therefore, it is possible that our valuation of an acquisition may change and result in unanticipated write-offs or charges, impairment of our goodwill, or a material change to the fair value of the assets and liabilities associated with a particular acquisition, any of which could significantly harm our business. Selling equity to finance any such acquisition would also dilute our stockholders. Incurring debt would increase our fixed obligations and could also include covenants or other restrictions that would impede our ability to manage our operations.
Our acquisition strategy may not succeed if we are unable to remain attractive to target companies or expeditiously close transactions. If we develop a reputation for being a difficult acquirer or having an unfavorable work environment, or if target companies view our Class A common stock unfavorably, we may be unable to consummate key acquisition transactions essential to our corporate strategy and our business may be significantly harmed.
Our ability to use our net operating loss carryforwards and certain other tax attributes may be limited, each of which could significantly harm our business.
As of December 31, 2023, we had federal net operating loss carryforwards of $2,382.3 million, which do not expire, federal net operating loss carryforwards of $52.2 million, which begin to expire in 2035, state net operating loss carryforwards of $1,261.4 million, which begin to expire in 2024, and foreign net operating loss carryforwards of $66.8 million, which begin to expire in 2024. Utilization of our net operating loss carryforwards and other tax attributes may be subject to limitations on utilization or benefit due to the ownership change limitations provided by Sections 382 and 383 of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended (the “Code”), and other similar provisions. All of the $2,382.3 million of federal net operating losses are carried forward indefinitely but the deductibility of these losses is generally limited to 80% of current year taxable income. Our net operating loss carryforwards may also be subject to limitations under state law. If our net operating loss carryforwards and other tax attributes expire before utilization or are subject to limitations, our business and financial results could be harmed.
Our estimates or judgments relating to our critical accounting policies may be based on assumptions that change or prove to be incorrect, which could cause our results of operations to fall below expectations of securities analysts and investors.
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with GAAP requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the amounts reported in our financial statements and accompanying notes. We base our estimates on historical experience and on various other assumptions that we believe to be reasonable under the circumstances, as described in the section titled “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations.” The results of these estimates form the basis for making judgments about the recognition and measurement of certain assets and liabilities and revenue and expenses that is not readily apparent from other sources. In addition to revenue recognition and estimates of the average lifetime of a paying user, our accounting policies that involve judgment include those related to assumptions used for estimating the fair value of common stock to calculate stock-based compensation, capitalization of internal-use software costs, valuation of goodwill and intangible assets, certain accrued liabilities, and valuation allowances associated with income taxes. If our assumptions change or if actual circumstances differ from those in our assumptions, our results of operations could be adversely affected, which could cause our results of operations to fall below the expectations of securities analysts and investors, resulting in a decline in the market price of our Class A common stock.
Our results of operations may be harmed if we are required to collect sales, value added, or other similar taxes for the purchase of our virtual currency, or for the sale of content between our developers, creators, and users.
Although we, either directly or through our third-party distribution channels, collect and remit taxes from users in certain countries and regions on the sale of our virtual currency, there are some jurisdictions in which we operate where we do not currently collect taxes from users. The application of tax laws pertaining to the collection of sales, value added, and similar taxes to e-commerce businesses, such as ours, is a complex and evolving area. For example, many countries have recently enacted tax laws that require non-resident providers to register for and levy value added taxes on electronically provided services to such country’s residents. This would require us to calculate, collect, and remit value added taxes in some jurisdictions, even if we have no physical presence in such jurisdictions. Further, we may need to invest substantial amounts to modify our solutions or our business model to be able to collect and remit sales, value added or similar taxes under such tax laws in the future.
Further, many jurisdictions have also adopted or are considering adopting marketplace facilitator laws that shift the burden of tax collection to online marketplaces. If we are characterized as a marketplace facilitator for the sale of content between our developers, creators, and users, we may need to invest substantial amounts to modify our solutions or business model to be able to meet any reporting and collection obligations with respect to sales, value added, or similar taxes. A successful assertion by a jurisdiction that we should have been or should be collecting additional sales, value added, or other taxes for the sale of content between our developers, creators, and users, could, among other things, result in substantial tax payments, create significant administrative burdens for us, discourage potential users, developers or creators from subscribing to our Platform, or otherwise harm our business, results of operations, and financial condition.
We may not realize the benefits expected through our China joint venture.
In February 2019, we entered into a joint venture agreement with Songhua River Investment Limited, referred to as Songhua, an affiliate of Tencent Holdings Ltd. (“Tencent Holdings”), under which we created Roblox China Holding Corp (the “China JV”), of which we own a 51% ownership interest. Through a wholly-owned subsidiary based in Shenzhen, branded as “Luobu,” the China JV is engaged in the development, localization, and licensing to Chinese creators of a Chinese version of Roblox Studio. Luobu also develops and oversees relations with local Chinese developers and helps them build and publish experiences and content for our global Platform. In December 2020, Shenzhen Tencent Computer Systems Co. Ltd (“Tencent”), received a required publishing license from the Chinese government, which enabled Tencent to publish a localized version of the Roblox Client as a game in China under the name “Luobulesi.” The license could be withdrawn if Tencent fails to comply with applicable existing or future regulations. Such withdrawal could significantly impair or eliminate the ability to publish and operate Luobulesi in China. The Luobulesi app is not currently available to users in China while we and Tencent build the next version of Luobulesi.
Tensions between the U.S. and China have resulted in trade restrictions that could harm our ability to participate in Chinese markets and numerous additional such restrictions have been threatened by both countries. Sustained uncertainty about, or worsening of, current global economic conditions and further escalation of trade tensions between the U.S. and China could result in a global economic slowdown and long-term changes to global trade, including retaliatory trade restrictions that could restrict our ability to participate in the China JV. We may find it difficult or impossible to comply with these or other conflicting regulations in the U.S. and China, which could make it difficult or impossible to achieve our business objectives in China or realize a return on our investment in this market.
Relations may also be compromised if the U.S. pressures the Chinese government regarding its monetary, economic, or social policies. Changes in political conditions in China and changes in the state of China-U.S. relations are difficult to predict and could adversely affect the operations or financial condition of the China JV. In addition, because of our proposed involvement in the Chinese market, any deterioration in political or trade relations might result in our products being perceived as less attractive in the U.S. or elsewhere. The Committee on Foreign Investment in the U.S. (“CFIUS”) has continued to apply a more stringent review of certain foreign investment in U.S. companies, including investment by Chinese entities, and has made inquiries to us with respect to Tencent Holding’s equity investment in us and involvement in the China JV. We cannot predict what effect any further inquiry by CFIUS into our relationship with Tencent and Tencent Holdings or changes in China-U.S. relations overall may have on our ability to effectively support the China JV or on the operations or success of the China JV.
The Chinese economic, legal, and political landscape also differs from other countries in many respects, including the level of government involvement and regulation, control of foreign exchange, and uncertainty regarding the practical enforceability of intellectual property rights. The laws, regulations and legal requirements in China are also subject to frequent changes and the exact obligations under and enforcement of laws and regulations are often subject to unpublished internal government interpretations and policies which makes it challenging to ascertain compliance with such laws. We may incur increased operating expenses related to cybersecurity and data protection in China, including with respect to access to Chinese user data and confidential company information as well as any network interconnections and cross border system integrations.
In addition to market and regulatory factors, any future success of the China JV will require a collaborative effort with Tencent to build and operate Luobu and Luobulesi as together, they will form the exclusive basis for growing our penetration in the China market. In addition, upon the occurrence of certain events, such as a termination of certain of the contractual relationships applicable to Luobu, a change of control of us, or the acquisition of 20% of our outstanding securities by certain specified Chinese industry participants, we may be required to purchase Songhua’s interest in the China JV at a fair market value determined at the time of such purchase. Any future requirement to purchase the interest in China JV from Songhua may have a material adverse effect upon our liquidity, financial condition, and results of operations both as a result of the purchase of such interests and the fact that we would need to identify and partner with an alternative Chinese partner in order for operations to continue in the China market.
The stock-based compensation expense related to our RSUs and other outstanding equity awards has increased our expenses in recent periods and may continue to do so in future periods due to grants of RSUs to new and existing employees.
We have granted performance-based stock unit awards to our executives, which vest based on continued service as well as the Company’s stock performance over a three-year performance period or the Company’s cumulative Bookings and cumulative Covenant Adjusted EBITDA generated over a two-year performance period.
In February 2021, our leadership development and compensation committee granted the CEO Long-Term Performance Award, an RSU award under our 2017 Plan to David Baszucki covering 11,500,000 shares of our Class A common stock. We estimated the grant date fair value of the CEO Long-Term Performance Award using a model based on multiple stock price paths developed through the use of a Monte Carlo simulation that incorporates into the valuation the possibility that the achievement of certain price goals may not be satisfied. The weighted-average grant date fair value of the CEO Long-Term Performance Award was estimated to be $20.19 per share, and we estimate that we will recognize total stock-based compensation expense of approximately $232.2 million over the derived service period of each of the seven separate tranches of the CEO Long-Term Performance Award that are eligible to vest based on the achievement of certain stock price goals. If the achievement of these stock price goals are met sooner than the derived service period, we will adjust our stock-based compensation expense to reflect the cumulative expense associated with the vested award. We will recognize stock-based compensation expense if service is provided by Mr. Baszucki over the requisite service period, regardless of whether the stock price goals are achieved.
Risks Related to Government Regulations
We are subject to laws and regulations worldwide, many of which are unsettled and still developing, which could increase our costs or adversely affect our business.
We are subject to a variety of laws in the U.S. and abroad that affect our business. As a global Platform with users in over 180 countries, we are subject to a myriad of regulations and laws regarding consumer protection, including the use of prepaid cards, subscriptions, advertising, electronic marketing, protection of minors, including verified parental consent, privacy, biometrics, cybersecurity, data protection and data localization requirements, AI, online services, online gaming, anti-competition, freedom of speech, labor, real estate, taxation, escheatment, intellectual property ownership and infringement, tax, export and national security, tariffs, anti-corruption and telecommunications, all of which are continuously evolving and developing. The scope and interpretation of the laws that are or may be applicable to us, which in some cases can be enforced by private parties in addition to government entities, are often uncertain and may be conflicting, particularly laws outside the U.S., and compliance with laws, regulations and similar requirements may be burdensome and expensive. Laws and regulations may be inconsistent from jurisdiction to jurisdiction, which may increase the cost of compliance and doing business and expose us to possible litigation, penalties or fines. Any such costs, which may rise in the future as a result of changes in these laws and regulations or in their interpretation, could make our Platform less attractive to our users, developers, or creators or cause us to change or limit our ability to sell our Platform. We have policies and procedures designed to ensure compliance with applicable laws and regulations, but we cannot assure you that we will not experience violations of such laws and regulations or our policies and procedures.
In addition, there are ongoing academic, political, and regulatory discussions in the U.S., Canada, Europe, United Kingdom, Australia, and other jurisdictions regarding whether certain mechanisms that may be included in the experiences on our Platform, such as features commonly referred to as “loot boxes,” and certain genres of experiences, such as social casino, that may reward gambling, should be subject to a higher level or different type of regulation than other genres of experiences to protect consumers, in particular minors and persons susceptible to addiction, and, if so, what such regulation should include. In July 2022, Spanish gambling regulators introduced a bill aimed at prohibiting minors from accessing “loot boxes”, which if passed, may require us to limit the availability of certain features in Spain. Australia may in the future require higher age-rating for content containing “loot boxes”. If we are required to increase the age rating for certain content in Australia, we may become less attractive for the younger users. In addition, the introduction of experiences for users who are 17 and older may cause regulatory agencies to require a higher age rating for our Platform, which could cause us to become less attractive to younger users and harm our business, financial condition and results of operations. Other countries may adopt similar rules, which may have a negative impact on our revenue. In addition, it is possible that similar lawsuits could be filed against us in Brazil or possibly other jurisdictions. Also, new regulation by the U.S. federal government and its agencies, such as the FTC, state agencies or foreign jurisdictions, which may vary significantly, could require that certain content in the experiences on our Platform be modified or removed, increase the costs of operating or monitoring the experiences on our Platform, impact user engagement and thus the functionality and effectiveness of our Platform or otherwise harm our business performance. It is difficult to predict how existing or new laws may be applied. If we become liable, directly or indirectly, under these laws or regulations, we could be harmed, and we may be forced to implement new measures to reduce our exposure to this liability. This may require us to expend substantial resources or to modify our Platform, which would harm our business, financial condition and results of operations. In addition, the increased attention focused upon liability issues as a result of lawsuits and legislative proposals could harm our reputation or otherwise impact the growth of our business. Any costs incurred as a result of this potential liability could harm our business, financial condition, or results of operations.
Governmental agencies in any of the countries in which we, our users, developers, or creators are located from time to time seek to and could seek to block access to, impose restrictions on, or require a license for our Platform, our website, operating system platforms, application stores or the internet generally for a number of reasons, including cybersecurity, privacy, data protection, confidentiality, or regulatory concerns which may include, among other things, governmental restrictions on certain content in a particular country, requirements to establish a local presence in a particular jurisdiction, and a requirement that user information be stored on servers in a country within which we operate. Moreover, the adoption of any laws or regulations adversely affecting the growth, popularity or use of the internet, including laws impacting Internet neutrality, could decrease the demand for our Platform and increase our operating costs. The legislative and regulatory landscape regarding the regulation of the internet and, in particular, internet neutrality, in the U.S and internationally is subject to uncertainty. Governmental agencies could issue fines or penalties if there are instances where we are found not to have been in compliance with regulations in any of these areas. Users generally need to access the internet, including in geographically diverse areas, and also mobile platforms such as the Apple App Store and the Google Play Store, to engage with experiences on our Platform. If governmental or other entities block, limit or otherwise restrict developers, creators, and users from accessing our Platform, or users from engaging with experiences on our Platform, we may need to take on more onerous obligations, limit the functionality of our Platform, and/or establish certain local entities, each of which could adversely affect our results of operations or subject us to additional fines and penalties.
Because we store, process, and use data, some of which contains personal information, we are subject to complex and evolving federal, state, and international laws and regulations regarding privacy, cybersecurity, data protection, and other matters. Many of these laws and regulations are subject to change and uncertain interpretation, and could result in investigations, claims, changes to our business practices, increased cost of operations, and declines in user growth, retention, or engagement, any of which could significantly harm our business.
We are subject to a variety of laws and regulations in the U.S. and other countries that involve matters central to our business, including privacy, cybersecurity, and data protection. The regulatory frameworks for these matters worldwide are rapidly evolving and are likely to remain uncertain for the foreseeable future.
Certain privacy, biometrics, cybersecurity, and data protection laws and regulations have placed and will continue to place significant privacy, data protection, and cybersecurity obligations on organizations such as ours and may require us to continue to change our policies and procedures. For example, the European Union’s (“EU”) General Data Protection Regulation (“GDPR”) imposed more stringent data protection requirements regarding EU personal data, and its provisions include increasing the maximum level of fines that EU regulators may impose for the most serious breaches of noncompliance of €20 million or 4% of annual global revenues of the previous year, whichever is greater. Such fines would be in addition to (i) the rights of individuals to sue for damages in respect of any data privacy breach which causes them to suffer harm, (ii) the right of individual member states to impose additional sanctions over and above the administrative fines specified in the GDPR, and (iii) the ability of supervisory authorities to impose orders requiring companies to modify their practices. If we are found not to be compliant with GDPR or similar requirements, including obligations to comply with data protection requirements when transferring personal data from the European Economic Area (“EEA”), Switzerland, and the United Kingdom (“U.K.”) to the U.S., we may be subject to significant fines and the risk of civil litigation.
The United Kingdom maintains the Data Protection Act of 2018 and the UK GDPR, which collectively implement and complement the GDPR and provide for penalties for noncompliance of up to the greater of £17.5 million or four percent of worldwide revenues, uncertainty remains regarding the future of data protection in the United Kingdom. On June 28, 2021, the European Commission announced a decision of “adequacy” concluding that the United Kingdom ensures an equivalent level of data protection to the GDPR, which provides some relief regarding the legality of continued personal data flows from the EEA to the U.K. Such adequacy decision must, however, be renewed after four years and may be modified or revoked in the interim. We cannot fully predict how the Data Protection Act, the UK GDPR and other United Kingdom data protection laws or regulations may develop in the medium to longer term, nor the effects of divergent laws and guidance regarding how data transfers to and from the United Kingdom will be regulated.
In addition, various local, national, and foreign laws and regulations apply to our operations, including the Children’s Online Privacy Protection Act (“COPPA”), in the U.S., Article 8 of the GDPR and similar regulations in other jurisdictions. COPPA imposes strict requirements on operators of websites or online services directed to children under 13 years of age (or 16 years of age under other regulatory regimes). 42% of our DAUs were under the age of 13 during the year ended December 31, 2023. COPPA requires companies to obtain verifiable parental consent before collecting personal information from children under the age of 13. Both the U.S. federal government and the states can enforce COPPA and violations of COPPA can lead to significant fines. No assurances can be given that our compliance efforts will be sufficient to avoid allegations of COPPA violations, and any non-compliance or allegations of non-compliance could expose us to significant liability, penalties and loss of revenue, significantly harm our reputation, and could be costly and time consuming to address or defend. To the extent we rely on consent for processing personal data under the GDPR, consent or authorization from the holder of parental responsibility is required in certain cases for the processing of personal data of children under the age of 16, and member states may enact laws that lower that age to 13. Additionally, in certain jurisdictions the law may allow minors to disaffirm their contracts, including our Terms of Use. If minors on our Platform are able to avoid enforcement of our Terms of Use under applicable law, it could have a material adverse impact on our business, financial condition, results of operations, and cash flow.
We are also monitoring updated guidance from the United Kingdom’s Information Commissioner Office (“ICO”) on the Age Appropriate Design Code (“AADC”), which focuses on online safety and protection of children’s privacy online. The AADC became effective September 2, 2021, and noncompliance with the AADC may result in audits or other proceedings by the ICO, the regulatory body set up to uphold information rights in the United Kingdom, and other regulators in the EEA or Switzerland, as noncompliance with the AADC may indicate noncompliance with applicable data protection law. In addition, we are monitoring developments with the EU’s, Digital Services Act (“DSA”), which became fully applicable on February 17, 2024. The DSA imposes new content moderation obligations, notice and transparency obligations, advertising restrictions and other requirements on digital platforms to protect consumers and their rights online. Noncompliance with the DSA could result in fines of up to 6% of annual global revenues, which are in addition to the ability of civil society organizations and non-governmental organizations to lodge class action lawsuits. We may incur liabilities, expenses, costs, and other operational losses under the GDPR and laws and regulations of applicable EU Member States and the United Kingdom relating to privacy, cybersecurity and data protection in connection with any measures we take to comply with them.
Other jurisdictions have adopted laws and regulations addressing privacy, data protection, and cybersecurity, many of which share similarities with the GDPR. For example, Law no. 13.709/2018 of Brazil, the Lei Geral de Proteção de Dados Pessoais or LGPD, entered into effect on September 18, 2020, authorizing a private right of action for violations. Penalties may include fines of up to 2% of the organization’s revenue in Brazil in the previous year or 50M reais (approximately $9.5 million U.S. dollars). The LGPD applies to businesses (both inside and outside Brazil) that process the personal data of users who are located in Brazil. The LGPD provides users with the similar rights as the GDPR regarding their data. A Brazilian Data Protection Authority, Brazilian National Data Protection Authority (Autoridade Nacional de Proteção de Dados) has been established to provide rules and guidance on how to interpret and implement the LGPD’s requirements, including regarding notice of processing, data transfer requirements, and other compliance obligations, such as security measures, recordkeeping, training, and governance. Additionally, the Personal Information Protection Law, or PIPL of the People’s Republic of China (“PRC”), was adopted on August 20, 2021, and went into effect on November 1, 2021. The PIPL shares similarities with the GDPR, including extraterritorial application, data minimization, data localization, and purpose limitation requirements, and obligations to provide certain notices and rights to citizens of the PRC. The PIPL allows for fines of up to 50 million renminbi or 5% of a covered company’s revenue in the prior year. Our approach with respect to the LGPD and PIPL may be subject to further evaluation and change, our compliance measures may not be fully adequate and may require modification, we may expend significant time and cost in developing and maintaining a privacy governance program, data transfer or localization mechanisms, or other processes or measures to comply with the LGPD, the PIPL, and any implementing regulations or guidance under these regimes, and we may potentially face claims, litigation, investigations, or other proceedings or liability regarding the LGPD or PIPL and may incur liabilities, expenses, costs, and other operational losses under the LGPD and PIPL and any measures we take to comply with them.
In addition, the CCPA, which established a new privacy framework for covered businesses such as ours, went into effect in January 2020, requiring us to modify our data processing practices and policies and incur compliance related costs and expenses. The CCPA provides for civil penalties for violations, as well as a private right of action for data breaches, which may increase the likelihood and cost of data breach litigation. Additionally, the California Privacy Rights Act (“CPRA”), was approved in November 2020, and significantly modified the CCPA. The CPRA went into effect on January 1, 2023 and, among other things, gives California residents the ability to limit the use of their sensitive information, provides for penalties for CPRA violations concerning California residents under the age of 16, and establishes a new agency to implement and enforce the law. Further, the CCPA has prompted similar legislative developments in other states in the U.S., including laws enacted in Virginia, Colorado, Utah, Connecticut, Florida, Iowa, Indiana, Montana, Tennessee, Oregon, Delaware, Texas, and New Jersey. These developments create the potential for a patchwork of overlapping but different state laws. Other states, including California, Utah and Arkansas, have passed legislation imposing substantial new obligations upon companies that offer online services, products, or features “likely to be accessed” by children 17 years of age or under, or certain types of social media and digital services, respectively. The California legislation includes certain requirements and principles from the AADC including, among other things, data protection impact assessments and the implementation of privacy by design. The laws in Utah and Arkansas impose new restrictions and obligations in connection with users who are, or are deemed to be, under 18, including access restrictions and restrictions on abilities for minors to create accounts. Many states have also passed their own laws that require verifiable parental consent before allowing children to create an account or impact companies that process children’s personal data. Some countries also are considering or have passed legislation requiring local storage and processing of data, or similar requirements, which could increase the cost and complexity of operating our products and services and other aspects of our business. The potential effects of new and evolving legislation relating to privacy, cybersecurity, data protection, and related matters, such as age verification, are far-reaching, create the potential for a patchwork of overlapping but different laws, and may require us to modify practices and policies, incur substantial costs and expenses, or restrict our operations. Additionally, requirements for verified parental consent before allowing children to create an account may limit the use of our Platform or reduce or overall demand for our Platform, which could harm our business, financial condition, and results of operations.
We believe we take reasonable efforts to comply with all applicable laws, regulations, and other legal obligations and certain industry codes of conduct relating to privacy, cybersecurity, and data protection. However, it is possible that the obligations imposed on us by applicable laws and regulations, industry codes of conduct or other actual or asserted obligations relating to privacy, cybersecurity, data protection, or related matters, may be interpreted and applied in inconsistent manners and may conflict with other rules or our practices in certain jurisdictions. Additionally, due to the nature of our service, we are unable to maintain complete control over cybersecurity or the implementation of measures that reduce the risk of a security breach or incident. For example, our customers may accidentally disclose their passwords or store them on a mobile device that is “SIM swapped,” lost, or stolen, creating the perception that our systems are not secure against third-party access. Any failure or perceived failure by us to comply with our privacy policies, our obligations to users or other third parties relating to privacy, cybersecurity or data protection, or our other policies or obligations relating to privacy, cybersecurity, data protection, or related matters, or any actual or perceived compromise of security, including any such compromise that results in the unauthorized loss, unavailability, modification, release, transfer, or other processing of personal information or other user, developer or creator data, may result in governmental investigations and enforcement actions, litigation, claims or public statements against us by consumer advocacy groups or others and could cause our developers, creators, and users to lose trust in us, any or all of which could have an adverse effect on our business, financial condition, or results of operations.
Legal and regulatory restrictions on virtual currencies like Robux may adversely affect our Platform, experiences, and virtual items on our Platform, which may negatively impact our revenue, bookings, business, and reputation.
The regulations that apply to virtual currencies in the jurisdictions in which we operate are subject to change. It is possible that regulators in the U.S. or elsewhere may take regulatory actions in the future that restrict our ability to license Robux, allow users to acquire or use other digital goods available on our platform, or that prohibit developers or creators on our Platform from earning Robux. We also make prepaid gift cards available for sale internationally that may be used to redeem Robux, and regulators may impose restrictions or bans on the sale of such prepaid gift cards. Any such restrictions or prohibitions may adversely affect our Platform, business, revenue, and bookings. In the United States, the SEC, its staff, and similar state regulators have deemed certain virtual currencies to be securities subject to regulation under the federal and state securities laws. While we do not consider Robux to be a security, if Robux were subject to the federal or state securities laws of the U.S., we may be required to redesign our Platform considerably, in a manner that would be disruptive to operations and costly to implement, which may threaten the viability of the Platform. We may also be subject to enforcement or other regulatory actions by federal or state regulators, as well as private litigation, which could be costly to resolve.
The increased use of interactive entertainment offerings like ours by consumers, including younger consumers, may prompt calls for more stringent consumer protection laws and regulations throughout the world that may impose additional burdens on companies such as ours making virtual currencies like Robux available for sale. Any such changes would require us to devote legal and other resources to address such regulation. For example, some existing laws regarding the regulation of currency, money transmitters and other financial institutions, and unclaimed property have been interpreted to cover virtual currencies, like Robux.
Although we have structured Robux, as well as our sales of other digital goods and prepaid cards on our Platform, with applicable laws and regulations in mind, including applicable laws relating to money laundering and money transmission services, and believe we are in compliance with all applicable laws, it is possible that a relevant regulator may disagree, which could expose us to penalties. If a relevant regulator disagreed with our analysis of and compliance with applicable laws, we may be required to seek licenses, authorizations, or approvals from those regulators, which may be dependent on us meeting certain capital and other requirements and may subject us to additional regulation and oversight, all of which could significantly increase our operating costs.
Changes in current laws or regulations or the imposition of new laws and regulations in the U.S. or elsewhere that prohibit us from making Robux available on our Platform would require us to make significant changes to our Platform, which would materially impair our business, financial condition, and operating results.
We are subject to various governmental export control, trade sanctions, and import laws and regulations that require our compliance and may subject us to liability if we violate these controls.
In some cases, our software and experiences are subject to export control laws and regulations, including the Export Administration Regulations administered by the U.S. Department of Commerce and trade and economic sanctions, including those administered by OFAC, which we collectively refer to as Trade Control Laws and Regulations. Thus, we are subject to laws and regulations that could limit our ability to offer access or full access to our Platform and experiences to certain persons and in certain countries or territories. For example, certain U.S. laws and regulations administered and enforced by OFAC, may limit our ability to give certain users, developers, and creators access to aspects of our Platform and experiences. Trade Control Laws and Regulations are complex and dynamic, and monitoring and ensuring compliance can be challenging. In addition, we rely on our payment processors for compliance with certain of these Trade Control Laws and Regulations, including preventing paid activity by users, developers, and creators that attempt to access our Platform from various jurisdictions comprehensively sanctioned by OFAC, including Cuba, Iran, North Korea, Syria, and sanctioned regions of Ukraine. Users, developers, and creators from certain of these countries and territories have access to our Platform and experiences and there can be no guarantee we will be found to have been in full compliance with Trade Control Laws and Regulations during all relevant periods. Any failure by us or our payment processors to comply with the Trade Control Laws and Regulations may lead to violations of the Trade Control Laws and Regulations that could expose us to liability. Additionally, following Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, the United States and other countries imposed certain economic sanctions and severe export control restrictions against Russia and Belarus, could impose wider sanctions and additional export restrictions or take other actions that could impact our business should the conflict further escalate. Any failure to comply with applicable laws and regulations also could have negative consequences for us, including reputational harm, government investigations, and monetary penalties.
In addition, various foreign governments may also impose controls, export license requirements, and/or restrictions applicable to our Platform and experiences. Compliance with such applicable regulatory requirements may create delays in the introduction of our Platform in some international markets or prevent certain international users from accessing our Platform.
Changes in tax laws could have a material adverse effect on our business, cash flow, results of operations or financial conditions.
We are subject to tax laws, regulations, and policies of several taxing jurisdictions. Changes in tax laws, as well as other factors, could cause us to experience fluctuations in our tax liability and reporting obligations and effective tax rates and otherwise adversely affect our tax positions, cost of compliance, and/or our tax liabilities. Certain jurisdictions, such as Canada, the United Kingdom and France, have recently enacted or have proposed to enact a digital services tax on certain digital revenue streams. Other jurisdictions, such as Brazil, have proposed indirect tax reform which may impose value added tax on the sales of electronically supplied services. Such laws and other attempts to impose taxes on e-commerce activities would likely increase the cost to us of operating our business, discourage potential customers from subscribing to our Platform, or otherwise adversely affect our business, results of operations or financial conditions. In addition, the E.U.’s Directive 2011/16/EU on administrative cooperation in the field of taxation (referred to as “DAC7”), which implements new digital platform reporting rules, may require us to modify our data processing and reporting practices and policies, which may cause us to incur substantial costs and expenses to comply.
Finally, the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development has proposed the Pillar One framework as part of the OECD/G20 Base Erosion and Profit Shifting (BEPS) Project, which would revise existing profit allocation and nexus rules to require profit allocation based on location of sales versus physical presence for certain large multinational businesses, but if implemented, could result in the removal of unilateral digital services tax initiatives described above. Any developments or changes in federal, state, or international tax laws or tax rulings could adversely affect our compliance costs, effective tax rate, and our operating results.
We are subject to the Foreign Corrupt Practices Act and similar anti-corruption and anti-bribery laws, and anti-money laundering laws, and non-compliance with such laws can subject us to criminal or civil liability and harm our business, financial condition and results of operations.
We are subject to the Foreign Corrupt Practices Act, U.S. domestic bribery laws, the UK Bribery Act and other anti-corruption and anti-bribery laws, and anti-money laundering laws in the countries in which we conduct activities. Anti-corruption and anti-bribery laws have been enforced aggressively in recent years and are interpreted broadly to generally prohibit companies, their employees, agents, representatives, business partners, and third-party intermediaries from authorizing, offering or providing, directly or indirectly, improper payments or benefits to recipients in the public or private sector in order to influence official action, direct business to any person, gain any improper advantage, or obtain or retain business. These laws also require that we keep accurate books and records and maintain internal controls and compliance procedures designed to prevent any such actions.
With regard to our international business, we have engaged with business partners and third-party intermediaries to market our solutions and obtain necessary permits, licenses, and other regulatory approvals. We or our employees, agents, representatives, business partners or third-party intermediaries have had direct or indirect interactions with officials and employees of government agencies or state-owned or affiliated entities. We can be held liable for the corrupt or other illegal activities of our employees, agents, representatives, business partners or third-party intermediaries, even if we do not authorize such activities and notwithstanding having policies, training, and procedures to address compliance with these laws, we cannot assure you that no violations of our policies or these laws will occur.
Detecting, investigating, and resolving actual or alleged violations of anti-corruption and anti-bribery laws and anti-money laundering laws can require a significant diversion of time, resources, and attention from senior management, as well as significant defense costs and other professional fees. In addition, noncompliance with these laws could subject us to whistleblower complaints, investigations, sanctions, settlements, prosecution, enforcement actions, fines, damages, other civil or criminal penalties or injunctions against us, our officers, or our employees, disgorgement of profits, suspension or debarment from contracting with the U.S. government or other persons, reputational harm, adverse media coverage, and other collateral consequences. If any subpoenas or investigations are launched, or governmental or other sanctions are imposed, or if we do not prevail in any possible civil or criminal proceeding, our reputation, business, financial condition, prospects and results of operations and the price of our Class A common stock could be harmed. Responding to any investigation or action will likely result in a materially significant diversion of management’s attention and resources and significant defense costs and other professional fees.
We may incur liability as a result of content published using our Platform or as a result of claims related to content generated by our developers, creators, and users, including copyright infringement, and legislation regulating content on our Platform may require us to change our Platform or business practices.
Our success relies in part on the ability of developers and creators to drive engagement with content that is challenging, engaging, fun, interesting, and novel. Developers and creators are responsible for clearing the rights to all of the content they upload to our service, but some developers or creators may upload content that infringes the rights or violates the terms of use of third parties in violation of our Terms of Use. We rely upon legal protections in various jurisdictions to protect us from claims of monetary damages for content that is uploaded to and stored on our system at the direction of our users but those protections may change or disappear over time, increasing our exposure for claims of copyright or other intellectual property infringement. If we should lose or fail to qualify for statutory or other legal protections that immunize us from monetary damages for intellectual property infringement, the damages could be significant and have a material impact on our business. While we have implemented measures designed to limit our exposure to claims of intellectual property infringement, intellectual property owners may allege that we failed to take appropriate measures to prevent infringing activities on our systems, that we turned a blind eye to infringement, or that we facilitated, induced or contributed to infringement.
Even though we are not required to monitor uploaded content for copyright infringement in the U.S., we have chosen to do so through the services of a third-party audio monitoring service. We now monitor all uploaded sound recordings to exclude recordings owned or controlled by the major record labels and any other record labels who provide their music to the third-party audio monitoring service. These record labels register certain of their content with our service provider. When audio is uploaded to our Platform, we check the service provider’s system to exclude recordings owned or controlled by these record labels from being published on our Platform. If our monitoring proves ineffective or we cease to rely upon a third-party monitoring service to exclude certain content from our platform, our risk of liability may increase.
In the past, certain record companies and music publishers, either directly or through their authorized representatives, claimed that we are subject to liability for allegedly infringing content that was uploaded and may continue to exist on our Platform. We vigorously disputed such claims of infringement by such labels and publishers and reached settlements. However, we could be subject to additional claims in the future. An adverse judgment against us in any such lawsuit could require us to settle any claims for an undetermined amount which could have a material impact on our business, financial condition, or results of operations.
The EU enacted copyright laws such as the Copyright Directive that came into effect on June 6, 2019 that may require us to use best efforts in accordance with the high industry standards of professional diligence to exclude infringing content from our Platform that may be uploaded by our users. In addition, the monitoring and reporting obligations of the DSA may apply also with respect to copyright infringements that would fall outside the scope of the Copyright Directive.
In April 2021, the European Commission proposed the Artificial Intelligence Act (“AI Act”), on which the European Council and Parliament reached political agreement in December 2023. The AI Act proposes a framework of prohibitions as well as disclosure, transparency and other regulatory obligations based on various levels of risk for businesses introducing AI systems in the EU. If enacted and applicable to us, the AI Act could require us to alter or restrict our use of AI both in features or products available to our users and in our systems that interact with our users, depending on respective levels of risk-categorization under the AI Act. The AI Act also could require us to comply with monitoring and reporting requirements. As a result, we may need to devote substantial time and resources to evaluate our obligations under the AI Act and to develop and execute a plan to ensure compliance.
We may also be required to enter into license agreements with various licensors, including record labels, music publishers, performing rights organizations, and collective management organizations, to obtain licenses that authorize the storage and use of content uploaded by our users. We may not be able to develop technological solutions to comply with these license agreements on economically reasonable terms and there is no guarantee that we will be able to enter into agreements with all relevant rights holders on terms that we deem reasonable. Compliance may therefore negatively impact our financial prospects.
Further, new content related regulations, including the DSA, which became fully applicable on February 17, 2024, may increase our compliance cost.
Risks Related to Intellectual Property
Claims by others that we infringe their proprietary technology or other rights, the activities of our users, or the content of the experiences on our Platform could subject us to liability and harm our business.
We have been and may in the future become subject to intellectual property disputes, and may become subject to liability, costs, and awards of damages and/or injunctive relief as a result of these disputes. Our success depends, in part, on our ability to develop and commercialize our Platform without infringing, misappropriating, or otherwise violating the intellectual property rights of third parties. However, there is no assurance that our technologies or Platform will not be found to infringe, misappropriate, or otherwise violate the intellectual property rights of third parties. We also have agreements with third parties to manufacture and distribute merchandise based on user content on our Platform, and there is a possibility that such content could be found to be infringing. Lawsuits are time-consuming and expensive to resolve and they divert management’s time and attention. Further, because of the substantial amount of discovery required in connection with intellectual property litigation, we risk compromising our confidential information during this type of litigation. Companies in the internet, technology, and gaming industries own large numbers of patents, copyrights, trademarks, domain names, and trade secrets and frequently enter into litigation based on allegations of infringement, misappropriation, or other violations of intellectual property or other rights. As we face increasing competition and gain a higher profile, the possibility of intellectual property rights and other claims against us grows. Our technologies may not be able to withstand any third-party claims against their use. In addition, many companies have the capability to dedicate substantially greater resources to enforce their intellectual property rights and to defend claims that may be brought against them.
We have a number of issued patents. We have also filed a number of additional U.S. and foreign patent applications but these applications may not successfully result in issued patents. Any patent litigation against us may involve patent holding companies or other adverse patent owners that have no relevant product revenue, and therefore, our patents and patent applications may provide little or no deterrence as we would not be able to reach meaningful damages if we assert them against such entities or individuals. If a third party is able to obtain an injunction preventing us from accessing or exercising intellectual property rights, or if we cannot license or develop alternative technology for any infringing aspect of our business, we could be forced to limit or cease access to our Platform or cease business activities related to such intellectual property. In addition, we may need to settle litigation and disputes on terms that are unfavorable to us. We may be required to make substantial payments for legal fees, settlement fees, damages, royalties, license, or other fees in connection with a claimant securing a judgment against us. Although we carry general liability insurance, our insurance may not cover potential claims of this type or may not be adequate to cover all liability that may be imposed. We cannot predict the outcome of lawsuits and cannot ensure that the results of any such actions will not have an adverse effect on our business, financial condition, or results of operations. Any intellectual property claim asserted against us, or for which we are required to provide indemnification, may require us to cease selling or using or recall products that incorporate the intellectual property rights that we allegedly infringe, misappropriate, or violate; make substantial payments for legal fees, settlement payments, or other costs or damages; obtain a license, which may not be available on reasonable terms or at all, to sell or use the relevant technology; or redesign or rebrand the allegedly infringing products to avoid infringement, misappropriation, or violation, which could be costly, time-consuming, or impossible.
Furthermore, certain federal statutes in the U.S. may apply to us with respect to various activities of our users, including the Digital Millennium Copyright Act of 1998 (“DMCA”) and Section 230 of the Communications Decency Act (“CDA”). For example, we filter communications to eliminate speech we determine to be offensive based on our objective of creating a civil and safe place for all users. Bills have recently been proposed in Congress calling for a range of changes to Section 230 of the CDA which include a complete repudiation of the statute to modifications of it in such a way as to remove certain social media companies from its protection. The U.S. Supreme Court has also heard two cases in its most recent term that may result in substantial changes to the scope of protection provided to interactive computer services such as Roblox. If Section 230 of the CDA were so repealed, amended, or modified by judicial determination we could potentially be subject to liability if we continue to censor speech, even if that speech were offensive to our users, or we could experience a decrease in user activity and revenues if we are unable to maintain a safe environment for our users if certain blocking and screening activities are prohibited by law. In addition, certain states have either passed or are debating laws that would create potential liability for moderating or removing certain user content. While we believe these laws are of dubious validity under the U.S. Constitution and in light of Section 230 of the CDA, they nevertheless present some risk to our content-moderation efforts going forward.
While we rely on a variety of statutory and common-law frameworks and defenses, including those provided by the DMCA, the CDA, the fair-use doctrine in the U.S. and the E-Commerce Directive in the EU, differences between statutes, limitations on immunity, requirements to maintain immunity, and moderation efforts in the many jurisdictions in which we operate may affect our ability to rely on these frameworks and defenses, or create uncertainty regarding liability for information or content uploaded by developers, creators, or users or otherwise contributed by third parties to our Platform. As an example, Article 17 of the Directive on Copyright in the Digital Single Market was passed in the EU, which affords copyright owners some enforcement rights that may conflict with U.S. safe harbor protections afforded to us under the DMCA. Member states in the EU are in the process of determining how Article 17 will be implemented in their particular country. In addition, the EU’s DSA became fully applicable on February 17, 2024. The DSA imposes additional obligations as provided under the E-Commerce Directive and includes new content moderation obligations, notice and transparency obligations, advertising restrictions and other requirements on digital platforms to protect consumers and their rights online. In countries in Asia and Latin America, generally there are not similar statutes to the CDA or the DSA. The laws of countries in Asia and Latin America generally provide for direct liability if a platform is involved in creating such content or has actual knowledge of the content without taking action to take it down. Further, laws in some Asian countries also provide for primary or secondary liability, which can include criminal liability, if a platform failed to take sufficient steps to prevent such content from being uploaded. Although these and other similar legal provisions provide limited protections from liability for platforms like ours, if we are found not to be protected by the safe harbor provisions of the DMCA, CDA or other similar laws, or if we are deemed subject to laws in other countries that may not have the same protections or that may impose more onerous obligations on us, including Article 17, we may owe substantial damages and our brand, reputation, and financial results may be harmed.
Additionally, any content created by using generative AI tools may not be subject to copyright protection which may adversely affect our intellectual property rights in, or ability to commercialize or use, the content. In the United States, a number of civil lawsuits have been initiated related to the foregoing and other concerns, the outcome of any one of which may, amongst other things, require us to limit the ways in which we use AI in our business. While AI-related lawsuits to date have generally focused on the AI service providers themselves, our use of any output produced by generative AI tools may expose us to claims, increasing our risks of liability.
Even if the claims do not result in litigation or are resolved in our favor, these claims, and the time and resources necessary to resolve them, could divert the resources of our management and harm our business and operating results. Moreover, there could be public announcements of the results of hearings, motions or other interim proceedings or developments and if securities analysts or investors perceive these results to be negative, it could have a substantial adverse effect on the price of our Class A common stock. We expect that the occurrence of infringement claims is likely to grow as the market for our Platform grows. Accordingly, our exposure to damages resulting from infringement claims could increase, and this could further exhaust our financial and management resources.
Indemnity provisions in various agreements potentially expose us to substantial liability for intellectual property infringement and other losses.
Some of our agreements with third parties include indemnification provisions under which we agree to indemnify these third parties for losses suffered or incurred as a result of claims of intellectual property infringement, or other liabilities relating to or arising from our software, services, Platform, or other contractual obligations. Large indemnity payments could harm our business, results of operations, and financial condition. Although we normally contractually limit our liability with respect to such indemnity obligations, those limitations may not be fully enforceable in all situations, and we may still incur substantial liability under those agreements. Any dispute with a third-party with respect to such obligations could have adverse effects on our relationship with such party and harm our business and results of operations.
Failure to protect or enforce our intellectual property rights or the costs involved in such enforcement would harm our business.
Our success depends to a significant degree on our ability to obtain, maintain, protect, and enforce our intellectual property rights, including our proprietary software technology, know-how, and our brand. We rely on a combination of trademarks, trade secret laws, patents, copyrights, service marks, contractual restrictions, and other intellectual property laws and confidentiality procedures to establish and protect our proprietary rights. However, the steps we take to obtain, maintain, protect, and enforce our intellectual property rights may be inadequate. We will not be able to protect our intellectual property rights if we are unable to enforce our rights or if we do not detect unauthorized use of our intellectual property rights. If we fail to protect our intellectual property rights adequately, or fail to continuously innovate and advance our technology, our competitors could gain access to our proprietary technology and develop and commercialize substantially identical products, services, or technologies. In addition, defending our intellectual property rights might entail significant expense and may not ultimately be successful.
Further, any patents, trademarks, or other intellectual property rights that we have or may obtain may be challenged or circumvented by others or invalidated or held unenforceable through administrative processes, including re-examination, inter partes review, interference and derivation proceedings, and equivalent proceedings in foreign jurisdictions, such as opposition proceedings or litigation. In addition, despite our pending patent applications, there is no assurance that our patent applications will result in issued patents. Even if we continue to seek patent protection in the future, we may be unable to obtain or maintain patent protection for our technology. In addition, any patents issued from pending or future patent applications or licensed to us in the future may not provide us with competitive advantages, or it may be successfully challenged by third parties. Furthermore, legal standards relating to the validity, enforceability, and scope of protection of intellectual property rights are uncertain. Despite our precautions, it may be possible for unauthorized third parties to copy our Platform and use information that we regard as proprietary to create products that compete with ours. Patent, trademark, copyright, and trade secret protection may not be available to us in every country in which our products are available. The value of our intellectual property could diminish if others assert rights in or ownership of our trademarks and other intellectual property rights, or trademarks that are similar to our trademarks. We may be unable to successfully resolve these types of conflicts to our satisfaction. In some cases, litigation or other actions may be necessary to protect or enforce our trademarks and other intellectual property rights. In addition, the laws of some foreign countries may not be as protective of intellectual property rights as those in the U.S., and mechanisms for enforcement of intellectual property rights may be inadequate. As we expand our global activities, our exposure to unauthorized copying and use of our Platform and proprietary information will likely increase.
We rely, in part, on trade secrets, proprietary know-how, and other confidential information to maintain our competitive position. While we enter into confidentiality and invention assignment agreements with our employees and consultants and enter into confidentiality agreements with other third parties, including suppliers and other partners, we cannot guarantee that we have entered into such agreements with each party that has or may have had access to our proprietary information, know-how and trade secrets or that has or may have developed intellectual property in connection with their engagement with us. Moreover, there are no assurances that these agreements will be effective in controlling access to, distribution, use, misuse, misappropriation, reverse engineering, or disclosure of our proprietary information, know-how, and trade secrets. Further, these agreements may not prevent our competitors from independently developing technologies that are substantially equivalent or superior to our Platform. These agreements may be breached, and we may not be able to detect any such breach and may not have adequate remedies for any such breach even if we know about it.
We use open source software as part of, and in connection with certain experiences on, our Platform, which may pose particular intellectual property and security risks to and could have a negative impact on our business.
We have in the past and may in the future continue to use open source software in our codebase and our Platform. Some open source software licenses require users who make available open source software as part of their proprietary software to publicly disclose all or part of the source code to such proprietary software or make available any derivative works of such software free of charge, under open source licensing terms. The terms of various open source licenses have not been interpreted by courts, and there is a risk that such licenses could be construed in a manner that imposes unanticipated conditions or restrictions on our use of the open source software. Enforcement activity for open source licenses can also be unpredictable. Were it determined that our use was not in compliance with a particular license, we may be required to release our proprietary source code, defend claims, pay damages for breach of contract or copyright infringement, grant licenses to our patents, re-engineer our games or products, discontinue distribution in the event re-engineering cannot be accomplished on a timely basis, or take other remedial action that may divert resources away from our game development efforts, any of which could negatively impact our business. Open source compliance problems can also result in damage to reputation and challenges in recruitment or retention of engineering personnel. Although we have certain policies and procedures in place to monitor our use of open-source software that are designed to avoid subjecting our Platform to open source licensing conditions, those policies and procedures may not be effective to detect or address all such conditions.
Additionally, although we devote significant resources to ensuring the security of our use of open source software on our Platform, we cannot ensure that these security measures will be sufficient to prevent or mitigate the damage caused by a cybersecurity incident or network disruption, and our open source software may be vulnerable to hacking, insider threats, employee error or manipulation, theft, system malfunctions, or other adverse events.
Risks Related to Ownership of our Class A Common Stock
The public trading price of our Class A common stock is volatile and could decline regardless of our operating performance.
To date, the public trading price of our Class A common stock has been volatile, similar to other newly public companies that have historically experienced highly volatile trading prices. The public trading price of our Class A common stock may fluctuate in response to various factors, including those listed in this Annual Report on Form 10-K, some of which are beyond our control. These fluctuations could cause you to lose all or part of your investment in our Class A common stock since you might be unable to sell your shares at or above the price you paid. Factors that could cause fluctuations in the public trading price of our Class A common stock include the following:
•the number of shares of our Class A common stock made available for trading;
•sales or expectations with respect to sales of shares of our Class A common stock by holders of our Class A common stock;
•price and volume fluctuations in the overall stock market from time to time;
•volatility in the trading prices and trading volumes of technology stocks;
•changes in operating performance and stock market valuations of other technology companies generally, or those in our industry in particular;
•failure of securities analysts to maintain coverage of us, changes in financial estimates by securities analysts who follow us or our failure to meet these estimates or the expectations of investors;
•any plans we may have to provide or not provide disclosure about certain key metrics, financial guidance, or projections, which may increase the probability that our financial results are perceived as not in line with analysts’ expectations;
•if we do provide disclosure about certain key metrics, financial guidance, or projections, any changes with respect to timing or our failure to meet those projections;
•announcements by us or our competitors of new services or platform features;
•the public’s reaction to our press releases, other public announcements, and filings with the SEC;
•rumors and market speculation involving us or other companies in our industry;
•actual or anticipated changes in our results of operations or fluctuations in our results of operations;
•actual or anticipated developments in our business, our competitors’ businesses, or the competitive landscape generally;
•litigation involving us, our industry or both, or investigations by regulators into our operations or those of our competitors;
•actual or perceived privacy or security breaches or other incidents;
•developments or disputes concerning our intellectual property or other proprietary rights;
•announced or completed acquisitions of businesses, services, or technologies by us or our competitors;
•new laws or regulations, public expectations regarding new laws or regulations or new interpretations of existing laws or regulations applicable to our business;
•changes in accounting standards, policies, guidelines, interpretations, or principles;
•any significant change in our management or other key personnel;
•other events or factors, including those resulting from war, such as Russia’s invasion of Ukraine and Hamas’ attack against Israel, incidents of terrorism, pandemics, or wildfires, earthquakes or severe weather and power outages or responses to these events; and
•general economic conditions and slow or negative growth of our markets.
In addition, stock markets, and the market for technology companies in particular, have experienced price and volume fluctuations that have affected and continue to affect the market prices of equity securities of many companies. Stock prices of many companies, including technology companies, have fluctuated in a manner often unrelated to the operating performance of those companies. In the past, following periods of volatility in the overall market and the market price of a particular company’s securities, securities class action litigation has often been instituted against these companies. This litigation, if instituted against us, could result in substantial costs and a diversion of our management’s attention and resources. In addition, we may be subject to stockholder activism, which can lead to additional substantial costs, distract management, and impact the manner in which we operate our business in ways we cannot currently anticipate.
The dual class stock structure of our common stock has the effect of concentrating voting control in David Baszucki, our Founder, President, CEO, and Chair of our Board of Directors, which limits or precludes your ability to influence corporate matters, including the election of directors and the approval of any change of control transaction.
Our Class B common stock has 20 votes per share, and our Class A common stock has one vote per share. Our Founder, President, CEO, Chair of our Board of Directors, and largest stockholder, David Baszucki, and his affiliates, beneficially own 100% of our outstanding Class B common stock, together as a single class, representing a substantial percentage of the voting power of our capital stock, which voting power may increase over time as Mr. Baszucki exercises or vests in his equity awards. Mr. Baszucki and his affiliates could exert substantial influence over matters requiring approval by our stockholders. This concentration of ownership may limit or preclude your ability to influence corporate matters for the foreseeable future, including the election of directors, amendments of our organizational documents, and any merger, consolidation, sale of all or substantially all of our assets, or other major corporate transaction requiring stockholder approval. In addition, this may prevent or discourage unsolicited acquisition proposals or offers for our capital stock that you may believe are in your best interest as one of our stockholders. We believe we are eligible for, but do not intend to take advantage of, the “controlled company” exemption to the corporate governance rules for NYSE-listed companies. We cannot predict whether our dual class structure will result in a lower or more volatile trading price of our Class A common stock, in adverse publicity, or other adverse consequences. For example, certain index providers, such as S&P Dow Jones, exclude companies with multiple classes of common stock from being added to certain stock indices, including the S&P 500. As a result, the dual class structure of our common stock may trigger actions or publications by stockholder advisory firms or institutional investors critical of our corporate governance practices or capital structure, or prevent the inclusion of our Class A common stock in certain indices and, as a result, large institutional investors, mutual funds, exchange-traded funds, and other investment vehicles that attempt to passively track those indices may not invest in our Class A common stock. Any exclusion from certain indices could result in a less active trading market for our Class A common stock. As a result, the trading price of our Class A common stock could be adversely affected. Delaware law and provisions in our amended and restated certificate of incorporation and amended and restated bylaws could make a merger, tender offer, or proxy contest difficult, thereby depressing the market price of our Class A common stock.
If securities or industry analysts or other third parties do not publish research or publish inaccurate or unfavorable research about us, our business, or our market, or if they change their recommendation regarding our Class A common stock adversely, the market price and trading volume of our Class A common stock could decline.
The market price and trading volume for our Class A common stock will depend in part on the research and reports that securities or industry analysts and other third parties publish about us, our business, our market or our competitors. The analysts’ estimates are based upon their own opinions and are often different from our estimates or expectations or incorrect. If any of the analysts who cover us change their recommendation regarding our Class A common stock adversely, provide more favorable relative recommendations about our competitors or publish inaccurate or unfavorable research about our business, the price of our Class A common stock would likely decline. If few securities analysts commence coverage of us, or if one or more of these analysts cease coverage of us or fail to publish reports on us regularly, we could lose visibility in the financial markets and demand for our securities could decrease, which could cause the price and trading volume of our Class A common stock to decline. In addition, third parties regularly publish data about us and other mobile, gaming, and social platform companies with respect to DAUs, revenue, bookings, top experience, or game charts, hours engaged and other information concerning social game application usage. These metrics are proprietary to the provider, and in many cases do not accurately reflect the actual levels of bookings, revenue, or usage of our experiences across all platforms. There is a possibility that third parties could change their methodologies for calculating these metrics in the future. To the extent that securities analysts or investors base their views of our business or prospects on such third-party data, the price of our Class A common stock may be volatile and may not reflect the performance of our business.
Delaware law and provisions in our amended and restated certificate of incorporation and amended and restated bylaws could make a merger, tender offer, or proxy contest difficult, thereby depressing the market price of our Class A common stock.
Our status as a Delaware corporation and the anti-takeover provisions of the Delaware General Corporation Law may discourage, delay, or prevent a change in control by prohibiting us from engaging in a business combination with an interested stockholder for a period of three years after the date of the transaction in which the person became an interested stockholder, even if a change of control would be beneficial to our existing stockholders. In addition, our amended and restated certificate of incorporation and amended and restated bylaws will contain provisions that may make the acquisition of our company more difficult, including the following:
•any amendments to our amended and restated certificate of incorporation or our amended and restated bylaws will require the approval of at least 66 2/3% of our then-outstanding voting power;
•our Board of Directors is classified into three classes of directors with staggered three-year terms and stockholders will only be able to remove directors from office for cause;
•upon the conversion of our Class A common stock and Class B common stock into a single class of common stock, our stockholders will only be able to take action at a meeting of stockholders and will not be able to take action by written consent for any matter;
•our amended and restated certificate of incorporation does not provide for cumulative voting;
•vacancies on our Board of Directors will be able to be filled only by our Board of Directors and not by stockholders;
•a special meeting of our stockholders may only be called by the chairperson of our Board of Directors, our CEO, our President, or a majority of our Board of Directors;
•certain litigation against us can only be brought in Delaware;
•our amended and restated certificate of incorporation authorizes 100 million shares of undesignated preferred stock, the terms of which may be established and shares of which may be issued without further action by our stockholders; and
•advance notice procedures apply for stockholders to nominate candidates for election as directors or to bring matters before an annual meeting of stockholders.
These provisions, alone or together, could discourage, delay, or prevent a transaction involving a change in control of our company. These provisions could also discourage proxy contests and make it more difficult for stockholders to elect directors of their choosing and to cause us to take other corporate actions they desire, any of which, under certain circumstances, could limit the opportunity for our stockholders to receive a premium for their shares of our Class A common stock, and could also affect the price that some investors are willing to pay for our Class A common stock.
Our amended and restated bylaws provide that the Court of Chancery of the State of Delaware and the federal district courts of the United States will be the exclusive forums for substantially all disputes between us and our stockholders, which could limit our stockholders’ ability to obtain a favorable judicial forum for disputes with us or our directors, officers, or employees.
Our amended and restated bylaws provide that the Court of Chancery of the State of Delaware (or, if the Court of Chancery does not have jurisdiction, another State court in Delaware or the federal district court for the District of Delaware) is the exclusive forum for the following (except for any claim as to which such court determines that there is an indispensable party not subject to the jurisdiction of such court (and the indispensable party does not consent to the personal jurisdiction of such court within ten days following such determination), which is vested in the exclusive jurisdiction of a court or forum other than such court or for which such court does not have subject matter jurisdiction):
•any derivative action or proceeding brought on behalf of us;
•any action asserting a claim of breach of a fiduciary duty;
•any action asserting a claim against us arising under the Delaware General Corporation Law, our amended and restated certificate of incorporation or our amended and restated bylaws (as either may be amended from time to time); and
•any action asserting a claim against us that is governed by the internal affairs doctrine.
This provision would not apply to suits brought to enforce a duty or liability created by the Exchange Act, or any other claim for which the U.S. federal courts have exclusive jurisdiction.
Our amended and restated bylaws further provide that the federal district courts of the U.S. will be the exclusive forum for resolving any complaint asserting a cause of action arising under the Securities Act. These exclusive-forum provisions may limit a stockholder’s ability to bring a claim in a judicial forum that it finds favorable for disputes with us or our directors, officers, or other employees, which may discourage lawsuits against us and our directors, officers, and other employees. Any person or entity purchasing or otherwise acquiring any interest in any of our securities shall be deemed to have notice of and consented to these provisions. There is uncertainty as to whether a court would enforce such provisions, and the enforceability of similar choice of forum provisions in other companies’ charter documents has been challenged in legal proceedings. We also note that stockholders cannot waive compliance (or consent to noncompliance) with the federal securities laws and the rules and regulations thereunder. It is possible that a court could find these types of provisions to be inapplicable or unenforceable, and if a court were to find either exclusive-forum provision in our amended and restated bylaws to be inapplicable or unenforceable in an action, we may incur additional costs associated with resolving the dispute in other jurisdictions, which could significantly harm our business.
We do not expect to pay dividends in the foreseeable future.
We have never declared nor paid cash dividends on our capital stock. We currently intend to retain any future earnings to finance the operation and expansion of our business, and we do not anticipate declaring or paying any dividends to holders of our capital stock in the foreseeable future. Consequently, you may need to rely on sales of our Class A common stock after price appreciation, which may never occur, as the only way to realize any future gains on your investment.
Risks Related to our Indebtedness
We may not be able to generate sufficient cash to service our debt and other obligations, including our obligations under the 2030 Notes.
Our ability to make payments on our indebtedness, including the 2030 Notes, and our other obligations will depend on our financial and operating performance, which is subject to prevailing economic and competitive conditions and to certain financial, business, and other factors beyond our control. We cannot assure you that we will maintain a level of cash flows from operating activities sufficient to permit us to pay the principal, premium, if any, and interest on our indebtedness, including the 2030 Notes, and other obligations.
If we are unable to service our debt and other obligations from cash flows, we may need to refinance or restructure all or a portion of our debt obligations prior to maturity. Our ability to refinance or restructure our debt and other obligations will depend on various factors, including the condition of the capital markets and our financial condition at such time. Any refinancing or restructuring could be at higher interest rates, less favorable terms, or may require us to comply with more onerous covenants, which could further restrict our business operations. If our cash flows are insufficient to service our debt and other obligations, we may not be able to refinance or restructure any of these obligations on commercially reasonable terms or at all. Any refinancing or restructuring could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, or financial condition.
If our cash flows are insufficient to fund our debt and other obligations and we are unable to refinance or restructure these obligations, we could face substantial liquidity problems and may be forced to reduce or delay investments and capital expenditures, or to sell material assets or operations to meet our debt and other obligations. We cannot assure you that we would be able to implement any of these alternative measures on satisfactory terms (if at all) or that the proceeds from such alternatives would be adequate to meet any debt or other obligations then due. If it becomes necessary to implement any of these alternative measures, our business, results of operations, or financial condition could be materially and adversely affected.
Our indebtedness could have adverse consequences to us.
Our indebtedness could have adverse consequences to us, including the following:
•making it more difficult for us to satisfy our obligations with respect to the 2030 Notes and our other indebtedness;
•requiring us to dedicate a substantial portion of our cash flow from operations to debt service payments on our and our subsidiaries’ debt, which reduces the funds available for working capital, capital expenditures, acquisitions, and other general corporate purposes;
•requiring us to comply with restrictive covenants in the Indenture, which limit the manner in which we conduct our business;
•limiting our flexibility in planning for, or reacting to, changes in the industry in which we operate;
•placing us at a competitive disadvantage compared to any of our less leveraged competitors;
•increasing our vulnerability to both general and industry-specific adverse economic conditions; and
•limiting our ability to obtain additional debt or equity financing to fund future working capital, capital expenditures, acquisitions or other general corporate requirements and increasing our cost of borrowing.
General Risks
If we are unable to maintain effective disclosure and internal controls over financial reporting, our ability to produce timely and accurate financial statements or comply with applicable regulations may be impaired.
We are subject to the reporting requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (“the Exchange Act”), the Sarbanes-Oxley Act, and the rules and regulations of the listing standards of the NYSE. The Sarbanes-Oxley Act requires, among other things, that we maintain effective disclosure controls and procedures and internal control over financial reporting. Our disclosure controls and other procedures are designed to ensure that information required to be disclosed by us in the reports that we will file with the SEC is recorded, processed, summarized, and reported within the time periods specified in SEC rules and forms and that information required to be disclosed in reports under the Exchange Act is accumulated and communicated to our principal executive and financial officers.
Our current controls and any new controls that we develop may become inadequate because of changes in conditions in our business. In addition, changes in accounting principles or interpretations could also challenge our internal controls and require that we establish new business processes, systems, and controls to accommodate such changes. If these new systems, controls, or standards and the associated process changes do not operate as intended, it could adversely affect our financial reporting systems and processes, our ability to produce timely and accurate financial reports, or the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting. Moreover, our business may be harmed if we experience problems with any new systems and controls that result in delays in their implementation or increased costs to correct any post-implementation issues that may arise. We have identified in the past, and may identify in the future, deficiencies in our controls, which could harm our results of operations or cause us to fail to meet our reporting obligations and may result in a restatement of our financial statements for prior periods. If we are not able to comply with the requirements of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act in a timely manner, or if we are unable to maintain proper and effective internal controls over financial reporting, we may not be able to produce timely and accurate financial statements. If that were to happen, our investors could lose confidence in our reported financial information, the trading price of our Class A common stock could decline, and we could be subject to sanctions or investigations by the SEC or other regulatory authorities. Any failure to implement and maintain effective internal control over financial reporting also could adversely affect the results of periodic management evaluations and annual independent registered public accounting firm attestation reports.
Any legal proceedings or claims against us could be costly and time-consuming to defend and could harm our reputation regardless of the outcome.
We are and/or may in the future become subject to legal proceedings and claims that arise in the ordinary course of business, including intellectual property, privacy, biometrics, cybersecurity, data protection, product liability, consumer protection, employment, class action, whistleblower, contract, securities, tort, civil Racketeer Influenced and Corrupt Organizations Act (“RICO”), and other litigation claims, including claims related to our advertising practices and use of generative AI, and governmental and other regulatory investigations and proceedings. As a result of disclosure of information in filings required of a public company, our business and financial condition will become more visible, which may result in threatened or actual litigation, including by competitors. We have been and may continue to be subject to legal proceedings asserting claims arising from allegations that we disabled access to virtual items found to violate our Terms of Use, that we have facilitated gambling by minors, that we have misrepresented the safety of our Platform, that our Platform is addictive or otherwise unsafe, and suits related to our refund policies. In these and similar lawsuits brought on behalf of child users, the court may allow minors to disaffirm or avoid enforcement of our Terms of Use, depending on the circumstances. We have and may continue to be subject to legal proceedings asserting claims on behalf of shareholders related to allegations that discussions of our growth prospects have been misleading and unsustainable due to concerns related to safety and our implementation of parental controls on the Platform. Such matters can be time-consuming, divert management’s attention and resources, cause us to incur significant expenses or liability, or require us to change our business practices. The expense of litigation and the timing of this expense from period to period are difficult to estimate, subject to change, and could adversely affect our financial condition and results of operations. Because of the potential risks, expenses, and uncertainties of litigation, we may, from time to time, settle disputes, even where we have meritorious claims or defenses, by agreeing to settlement agreements. Any of the foregoing could adversely affect our business, financial condition, and results of operations.
Catastrophic events may disrupt our business.
Natural disasters or other catastrophic events may cause damage or disruption to our operations, international commerce, and the global economy, and thus could harm our business. We have our headquarters and a large employee presence in San Mateo, California, an area which in recent years has been increasingly susceptible to fires, severe weather events, and power outages, any of which could disrupt our operations, and which contains active earthquake zones. In the event of a major earthquake, hurricane, or catastrophic event such as fire, power loss, rolling blackouts or power loss, telecommunications failure, pandemic, geopolitical conflict such as the Russian invasion of Ukraine and Hamas’ attack against Israel and the ensuing war, cyber-attack, war, other physical security threats or terrorist attack, we may be unable to continue our operations and may endure system interruptions, reputational harm, delays in our Platform development, lengthy interruptions in our Platform, breaches of security, and loss of critical data, all of which would harm our business, results of operations, and financial condition. Acts of terrorism and similar events would also cause disruptions to the internet or the economy as a whole. Global climate change could also result in natural disasters occurring more frequently or with more intense effects, which could cause business interruptions. The long-term effects of the COVID-19 pandemic and recovery from it on society and developer, creator, and user engagement remain uncertain, and a subsequent health crisis or pandemic, as well as the actions taken by various governmental, business and individuals in response, will impact our business, operations and financial results in ways that we may not be able to accurately predict. In addition, the insurance we maintain would likely not be adequate to cover our losses resulting from disasters or other business interruptions. Our disaster recovery plan may not be sufficient to address all aspects of any unanticipated consequence or incident, we may not be able to maintain business continuity at profitable levels or at all, and our insurance may not be sufficient to compensate us for the losses that could occur.
Our operations are subject to the effects of a rising rate of inflation and volatile global economic conditions.
The United States, Europe, and other key global markets have recently experienced historically high levels of inflation. If the inflation rate continues to increase, it will likely affect all of our expenses, including, but not limited to, employee compensation expenses and energy expenses and it may reduce consumer discretionary spending, which could affect the buying power of our users, developers, and creators and lead to a reduced demand for our Platform.
Geopolitical developments, such as the war in Ukraine, Hamas’ attack against Israel and the ensuing war, and tensions with China, and the responses by central banking authorities to control inflation, can increase levels of political and economic unpredictability globally and increase the volatility of global financial markets. Adverse macroeconomic conditions, including lower consumer confidence, persistent unemployment, wage and income stagnation, slower growth or recession, changes to fiscal and monetary policy, inflation, higher interest rates, currency fluctuations, economic and trade sanctions, the availability and cost of credit, and the strength of the economies in which we and our users are located, have adversely affected and may continue to adversely affect our consolidated financial condition and results of operations.
Additionally, we maintain cash balances at third-party financial institutions in excess of the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (the “FDIC”) insurance limit. If the financial conditions affecting the banking industry and financial markets cause additional banks and financial institutions to enter receivership or become insolvent, our ability to access our existing cash, cash equivalents and investments, or to draw on our existing lines of credit, may be threatened and could have a material adverse effect on our business and financial condition.
Item 1B. Unresolved Staff Comments
None.
Item 1C. Cybersecurity
We have established policies and processes for assessing, identifying, and managing material risk from cybersecurity threats, and have integrated these processes into our overall enterprise risk management systems and processes. We routinely assess material risks from cybersecurity threats, including taking reasonable steps to detect any potential unauthorized occurrence on or behaviors conducted through our information systems that may result in adverse effects on the confidentiality, integrity, or availability of our information systems or any information residing therein.
Risk Management and Strategy
We conduct periodic risk assessments to identify significant cybersecurity threats that may affect information systems that are vulnerable to such cybersecurity threats and regularly review these risk assessments for changes in our business practices and the external cybersecurity landscape as well as the impacts of our security processes. These risk assessments include identification of reasonably foreseeable internal and external risks and evaluation of the likelihood and potential damage that could result from the realization of such risks.
Following our risk assessments, we evaluate when and how to design, implement, and maintain reasonable safeguards to minimize the identified risks and address any identified gaps in existing safeguards, and proceed with such design, implementation, and maintenance as deemed appropriate. We devote significant resources and designate high-level personnel, including our Chief Information Security Officer (“CISO”) who reports to our Chief Technology Officer, to manage the risk assessment and mitigation process. Our CISO has served in various roles in information technology and information security for over 15 years, including leading information security initiatives and incident response at two other large public companies and serving as the Chief Security Officer for the Arkansas Department of Human Services and working for the United States Department of Defense. He has an MS in Information Assurance from the University of Advanced Technology in Arizona and a BS in Computer Science from the University of Arkansas at Little Rock.
We also engage third-party service providers in connection with our risk assessment process and certain risk management processes. Our collaboration with these third-party service providers includes threat assessments and consultation on security enhancements.
We perform risk-tiered information security risk reviews for certain third-party service providers who have access to sensitive Company, user or employee information, reviewing areas such as data protection, endpoint management and protection, phishing, business continuity, and incident response management.
We also share and receive threat intelligence with federal, state, and local government agencies, peers and other organizations, information sharing and analysis centers, and cybersecurity associations.
Governance
Our Board of Directors has the ultimate responsibility for the oversight of our risk management framework, which is designed to identify, assess, and manage risks to which our Company is exposed, as well as to foster a corporate culture of integrity. Management is responsible for the day-to-day oversight and management of strategic, operational, legal and compliance, cybersecurity, and financial risks.
The Audit and Compliance Committee (the “ACC”) is central to the Board of Directors’ oversight of cybersecurity risks and has been delegated the primary responsibility for this domain. The ACC is composed of independent board members with diverse expertise including, risk management, technology, and finance, equipping them to oversee cybersecurity risks effectively. The ACC has also engaged a cybersecurity advisor to assist them in cybersecurity matters. In overseeing the Company’s cybersecurity risks and mitigation strategies, at least quarterly the CISO, members of management, and the ACC’s cybersecurity advisor, review and discuss with the ACC guidelines, practices and policies to identify, monitor, and address enterprise risks, including cybersecurity risks. The ACC then oversees and monitors management’s plans to address such risks.
Our CISO, and management committee on cybersecurity consisting of our Chief Technology Officer, General Counsel, Chief Financial Officer, and CISO, are primarily responsible for assessing and managing our material risks from cybersecurity threats and overseeing our cybersecurity policies and processes, including those described in “Risk Management and Strategy” above. The processes by which our CISO, and our management committee on cybersecurity, are informed about and monitor the prevention, detection, mitigation, and remediation of cybersecurity incidents includes both manual reviews and automated reviews of our systems and data, a bug bounty program, self-reporting, participation in information sharing forums on cybersecurity, proactive education of our service providers and product and application security reviews.
In the event of a cybersecurity incident, the CISO is equipped with a well-defined incident response plan to guide response actions. This incident response plan includes immediate actions to mitigate the impact of the incident, long-term strategies for remediation and prevention of future incidents, and provides for internal notification of the incident functional areas (e.g. legal) as well as senior leadership and the ACC of the Board of Directors, as appropriate.
Our CISO provides briefings to the ACC at least quarterly regarding, among other topics, recent notable cybersecurity incidents, even if immaterial, and the Company’s response, cybersecurity systems testing results, the cybersecurity landscape and emerging risks and threats, compliance with regulatory requirements and industry standards.
Notwithstanding the extensive approach we take to cybersecurity, including managing associated risks, we may not be successful in managing risks from cybersecurity threats, including identifying, preventing, or mitigating a cybersecurity incident that could have a material adverse effect on us. While we maintain cybersecurity insurance, the costs related to cybersecurity threats or disruptions may not be fully insured.
For additional information regarding whether any risks from cybersecurity threats, including as a result of any previous cybersecurity incidents, have materially affected or are reasonably likely to materially affect our company, including our business strategy, results of operations, or financial condition, please refer to Item 1A, “Risk Factors,” in this annual report on Form 10-K, including the risk factors entitled “Risks Related to Our Business: If the security of our Platform is compromised, it could compromise our and our developers’, creators’, and users’ private information, disrupt our internal operations, and harm public perception of our Platform, which could cause our business and reputation to suffer.”
Item 2. Properties
As of December 31, 2023, our corporate headquarters consisted of approximately 348,360 square feet of office space in San Mateo, California, with lease terms expiring between 2027 and 2031. In addition, we possess approximately 619,409 square feet of separate office space in San Mateo, California, with lease terms expiring between 2029 and 2035.
We lease additional office space internationally in Canada, the United Kingdom, and China. We also operate several data centers in the U.S. in Florida, Georgia, Illinois, New Jersey, Texas, Virginia, California, and Washington and around the world including in France, Germany, Hong Kong, Japan, Poland, Singapore, the Netherlands, India, Australia, and the United Kingdom pursuant to various lease agreements.
We believe our existing facilities including the planned expansion under newly signed leases are adequate to meet our current requirements and for our operations in the foreseeable future.
Item 3. Legal Proceedings
The information set forth under the heading “Legal Proceedings” in Note 9, Commitments and Contingencies, in Part II, Item 8 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K is incorporated herein by reference.
Item 4. Mine Safety Disclosures
None.
Part II
Item 5. Market for Registrant’s Common Equity, Related Stockholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities
Our Class A common stock, par value $0.0001 per share, is listed on the New York Stock Exchange (“NYSE”), under the symbol “RBLX” and began trading on March 10, 2021. Prior to that date, there was no public trading market for our Class A common stock.
Our Class B common stock is not listed nor traded on any stock exchange, but is convertible into shares of our Class A common stock on a one-for-one basis.
Holders of Record
As of February 1, 2024, there were 1,687 stockholders of record of our Class A common stock. The actual number of holders of our Class A common stock is greater than the number of record holders and includes stockholders who are beneficial owners, but whose shares are held in street name by brokers or other nominees. The number of holders of record presented here also does not include stockholders whose shares may be held in trust by other entities.
As of February 1, 2024, there were 3 holders of record of our Class B common stock. All shares of our Class B common stock are beneficially owned by David Baszucki.
Dividend Policy
We have never declared or paid any cash dividends on our capital stock. We currently intend to retain any future earnings and do not expect to pay any dividends in the foreseeable future. Any future determination to declare cash dividends will be made at the discretion of our Board of Directors, subject to applicable laws, and will depend on a number of factors, including our financial condition, results of operations, capital requirements, contractual restrictions, general business conditions and other factors that our Board of Directors may deem relevant.
Stock Performance Graph
The performance graph below shall not be deemed “soliciting material” or to be “filed” with the SEC, for purposes of Section 18 of the Exchange Act, or otherwise subject to the liabilities under that Section, and shall not be deemed to be incorporated by reference into any of our filings under the Securities Act.
The performance graph below shows the cumulative total return to our stockholders between March 10, 2021 (the date that our Class A common stock commenced trading on the NYSE) through December 31, 2023, in comparison to the S&P 500 Index and the S&P 500 Information Technology Index. The graph assumes (i) that $100 was invested in our Class A common stock at its closing price on March 10, 2021 and in each of the S&P 500 Index and the S&P 500 Information Technology Index at their respective closing prices on February 28, 2021, and (ii) reinvestment of gross dividends. The stock price performance shown in the graph represents past performance and should not be considered an indication of future stock price performance.
*$100 invested on March 10, 2023 in Roblox Class A common stock or February 28, 2021 in index, including reinvestment of dividends. Fiscal year ending December 31.
Unregistered Sales of Equity Securities
Other than any sales that were already disclosed under a Current Report on Form 8-K or Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q during the year ended December 31, 2023, there have been no other sales of unregistered securities by the Company.
Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities
None.
Item 6. [Reserved]
Item 7. Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations
The following discussion and analysis of our financial condition, results of operations, and cash flows should be read in conjunction with the consolidated financial statements, and the related notes appearing under “Consolidated Financial Statements and Supplementary Data” in Item 8 of this filing. This discussion and analysis and other parts of this Annual Report on Form 10-K contain forward-looking statements, such as those relating to our plans, objectives, expectations, intentions, and beliefs, that involve risks, uncertainties and assumptions. Our actual results could differ materially from these forward-looking statements as a result of many factors, including those discussed in the section titled “Risk Factors,” “Special Note Regarding Forward-Looking Statements”, and “Special Note Regarding Operating Metrics” included elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K. Our historical results are not necessarily indicative of the results that may be expected for any periods in the future. Unless the context otherwise requires, all references in this report to “Roblox,” the “Company”, “we,” “our,” “us,” or similar terms refer to Roblox Corporation and its subsidiaries.
This section of our Annual Report on Form 10-K discusses our financial condition as of and results of operations for the fiscal years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022, as well as year-to-year comparisons between fiscal years 2023 and 2022. A discussion of our financial condition as of and results of operations for the fiscal year ended 2021 and year-to-year comparisons between fiscal years 2022 and 2021 that is not included in this Annual Report on Form 10-K can be found in “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” in our Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2022.
Amounts reported in millions are rounded based on the amounts in thousands. As a result, the sum of the components reported in millions may not equal the total amount reported in millions due to rounding. In addition, percentages presented are calculated from the underlying numbers in thousands and may not add to their respective totals due to rounding.
Overview
People from around the world come to Roblox every day to connect with friends. Together they create, play, work, learn, and connect with each other in experiences built by our global community of creators. Our Platform is powered by user-generated content and draws inspiration from gaming, entertainment, social media, and even toys.
Our free to use immersive platform for connection and communication consists of the Roblox Client, the Roblox Studio, and the Roblox Cloud (collectively, the “Roblox Platform” or the “Platform”). Roblox Client is the free application that allows users to explore 3D immersive experiences. Roblox Studio is the free toolset that allows developers and creators to build, publish, and operate 3D immersive experiences and other content accessed with the Roblox Client. Roblox Cloud includes the services and infrastructure that power our Platform.
Our mission is to connect a billion users with optimism and civility. We are constantly improving the ways in which our Platform supports shared experiences, ranging from how these experiences are built by an engaged community of developers and creators to how they are enjoyed and safely accessed by users across the globe.
Consistent with our free to play business model, a small portion of our users have historically been payers. For example, in the year ended December 31, 2023, of our 68.4 million DAUs, only approximately 852,000 represented our average daily unique paying users. Similarly, in the year ended December 31, 2023, our average daily bookings per DAU was $0.14, whereas our average daily bookings per daily unique paying user was $11.32. We believe that maintaining and growing our overall number of users, including the number of users who may not purchase and spend Robux, is important to the success of our business. As a result, we believe that the number of users who choose to purchase and spend Robux will continue to constitute a small portion of our overall users.
Our primary areas of investment have been, and we expect will continue to be, our developer and creator community, and the people, technology, and infrastructure required to keep improving the Roblox Platform. These areas of focus are how we drive the business and are reflected in our operating cost structure, which primarily consists of four major areas: payment processing and other fees, compensation and benefits, developer earnings, and direct infrastructure.
Key Metrics
We believe our performance is dependent upon many factors, including the key metrics described below that we track and review to measure our performance, identify trends, formulate financial projections, and make strategic decisions.
Operating Metrics
We manage our business by tracking several operating metrics, including those outlined below. As a management team, we believe each of these operating metrics provides useful information to investors and others. For complete definitions and limitations of these metrics, refer to the section titled “Special Note Regarding Operating Metrics” of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Average Daily Active Users (“DAU”)
We define a DAU as a user who has logged in and visited Roblox through our website or application on a unique registered account on a given calendar day. If a registered, logged in user visits Roblox more than once within a 24-hour period that spans two calendar days, that user is counted as a DAU only for the first calendar day. We track DAUs as an indicator of the size of the audience engaged on our Platform. We believe that the growth in DAUs reflects the increasing value of our Platform.
Hours engaged
We define hours engaged as the time spent by our users on the Platform, which includes time spent in experiences and also within features such as chat and avatar personalization. We believe that the growth in hours engaged reflects the increasing value of our Platform.
Bookings
Bookings is a non-GAAP financial measure and represents the sales activity in a given period without giving effect to certain non-cash adjustments. Bookings is presented for supplemental informational purposes only and should not be considered in isolation from, or as a substitute for, financial information presented in accordance with GAAP. Refer to the section “Non-GAAP Financial Measures” below for further discussion on this measure, including its limitations.
Below we also include revenue calculated in accordance with GAAP, the most directly comparable financial measure to bookings.
Average Bookings per DAU (“ABPDAU”)
We define ABPDAU as bookings in a given period divided by the DAUs for the same period. We use ABPDAU as a way to understand our monetization across our users through the sale of virtual currency and subscriptions.
Refer to the section titled “Non-GAAP Financial Measures” for the definition of and discussion on bookings, including its limitations as a non-GAAP financial measure.
Average New and Returning Monthly Unique Payers and Monthly Repurchase Rate
We define new monthly unique payers as user accounts that made their first purchase on the platform, or via redemption of prepaid cards, during a given month. Average new monthly unique payers for a specified period is the average of the new monthly unique payers for each month during that period.
We define returning monthly unique payers as user accounts that have made a purchase on the platform, or via redemption of prepaid cards, in the current month and in any prior month. Average returning monthly unique payers for a specified period is the average of the returning monthly unique payers for each month during that period.
We define monthly repurchase rate as the returning monthly unique payers in the current month, divided by the sum of the prior month’s new monthly unique payers and returning monthly unique payers. Average monthly repurchase rate for a specified period is the average of the monthly repurchase rates for each month during that period.
We use these measures to understand our monetization across our payers through the sale of virtual currency and subscriptions.
Average Bookings per Monthly Unique Payer
We define average bookings per monthly unique payer as bookings in the specified period divided by the average monthly unique payers for the same specified period. We use this measure to understand our monetization across our payers through the sale of virtual currency and subscriptions. Refer to the section titled “Non-GAAP Financial Measures” for the definition of and discussion on bookings, including its limitations as a non-GAAP financial measure.
Non-GAAP Financial Measures
In addition to our results determined in accordance with GAAP, we believe the following non-GAAP financial measures are useful in evaluating our performance. We use this non-GAAP financial information to evaluate our ongoing operations, for internal planning and forecasting purposes, and to evaluate our operating performance. We believe that this non-GAAP financial information may be helpful to investors because it provides consistency and comparability with past financial performance. However, non-GAAP financial measures have limitations in their usefulness to investors because they have no standardized meaning prescribed by GAAP and are not prepared under any comprehensive set of accounting rules or principles. In addition, other companies, including companies in our industry, may calculate similarly titled non-GAAP financial measures differently or may use other measures to evaluate their performance, all of which could reduce the usefulness of our non-GAAP financial information as a tool for comparison. As a result, our non-GAAP financial information is presented for supplemental informational purposes only and should not be considered in isolation from, or as a substitute for financial information presented in accordance with GAAP.
Bookings
Bookings represent the sales activity in a given period without giving effect to certain non-cash adjustments, as detailed below. Substantially all of our bookings are generated from sales of virtual currency, which can ultimately be converted to virtual items on the Roblox Platform. Sales of virtual currency reflected as bookings include one-time purchases or monthly subscriptions purchased via payment processors or through prepaid cards. Bookings are initially recorded in deferred revenue and recognized as revenues over the estimated period of time the virtual items purchased with the virtual currency are available on the Roblox Platform (estimated to be the average lifetime of a paying user) or as the virtual items purchased with the virtual currency are consumed. Bookings also include an insignificant amount from advertising and licensing arrangements.
We believe bookings provide a timelier indication of trends in our operating results that are not necessarily reflected in our revenue as a result of the fact that we recognize the majority of revenue over the estimated average lifetime of a paying user. The change in deferred revenue constitutes the vast majority of the reconciling difference from revenue to bookings. By removing these non-cash adjustments, we are able to measure and monitor our business performance based on the timing of actual transactions with our users and the cash that is generated from these transactions. Over the long-term, the factors impacting our revenue and bookings trends are the same. However, in the short-term, there are factors that may cause revenue and bookings trends to differ.
The following table presents a reconciliation of revenue, the most directly comparable financial measure calculated in accordance with GAAP, to bookings, for each of the periods presented (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, |
| | 2023 | | 2022 | | |
| Reconciliation of revenue to bookings: | | | | | |
| Revenue | $ | 2,799,274 | | | $ | 2,225,052 | | | |
| Add (deduct): | | | | | |
| Change in deferred revenue | 742,308 | | | 662,378 | | | |
| Other | (20,802) | | | (15,172) | | | |
| Bookings | $ | 3,520,780 | | | $ | 2,872,258 | | | |
Free cash flow
We define free cash flow as net cash provided by operating activities less purchases of property, equipment, and intangible assets acquired through asset acquisitions. We believe that free cash flow is a useful indicator of our unit economics and liquidity that provides information to management and investors about the amount of cash generated from our core operations that, after the purchases of property, equipment, and intangible assets, can be used for strategic initiatives.
The following table presents a reconciliation of net cash provided by operating activities, the most directly comparable financial measure calculated in accordance with GAAP, to free cash flow, for each of the periods presented (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, |
| | 2023 | | 2022 | | |
| Reconciliation of net cash provided by operating activities to free cash flow: | | | | | |
| Net cash provided by operating activities | $ | 458,180 | | | $ | 369,296 | | | |
| Deduct: | | | | | |
| Acquisition of property and equipment | (320,667) | | | (426,163) | | | |
| Purchases of intangible assets | (13,500) | | | (1,500) | | | |
| Free cash flow | $ | 124,013 | | | $ | (58,367) | | | |
Acquisition of property and equipment primarily includes servers, infrastructure equipment, tenant improvements, and capitalized software licenses.
Change in Accounting Estimate
Quarterly, we complete an assessment of our estimated paying user life, which is used for revenue recognition of durable virtual items and calculated based on historical monthly retention data for each paying user cohort to project future participation on the Roblox Platform.
In the first quarter of 2022, we updated our estimated paying user life from 23 months to 25 months, which was subsequently updated again to 28 months in the third quarter of 2022. Based on the carrying amount of deferred revenue and deferred cost of revenue as of December 31, 2021, these changes in estimates resulted in a decrease in revenue of $344.9 million and a decrease in cost of revenue of $79.3 million during the year ended December 31, 2022.
The estimated paying user life was 28 months throughout the year ended December 31, 2023.
Refer to the heading “Critical Accounting Policies and Estimates — Revenue Recognition” below for a complete discussion on the Company’s revenue recognition policies.
Components of Results of Operations
Revenue
We generate substantially all of our revenue through the sale of virtual content or access to virtual content to users, enabling them to enhance their social experience on the Roblox Platform. We recognize revenue over the estimated period of time the virtual items are available to the user on the Roblox Platform (estimated average lifetime of a paying user) or at the time the virtual item is consumed. The estimated average lifetime of a paying user is calculated based on the monthly retention data for each paying user cohort. We then calculate the average retention period by determining the weighted-average period paying users have spent on the Platform and are projected to participate in the Roblox environment.
Other revenue streams include an insignificant amount of revenue from advertising and licensing arrangements. We plan to invest in and expand our advertising business for the foreseeable future.
All of our revenue is recorded net of taxes assessed by a government authority that are both imposed on and concurrent with specific revenue transactions between us and our users, and estimated chargebacks and refunds.
Costs and Expenses
We allocate shared costs, such as certain facilities (including rent and depreciation on equipment and leasehold improvements shared by all departments) and software costs, to all departments based on headcount. As such, allocated shared costs are reflected in each expense category, with the exception of cost of revenue and developer exchange fees expense.
Personnel costs generally include employee expenses (salaries, benefits, and stock-based compensation expense) and contractor expenses, and are reflected in each expense category, with the exception of cost of revenue and developer exchange fees. In the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022, personnel costs were $1,654.9 million and $1,180.5 million, respectively.
Cost of revenue
Cost of revenue primarily consists of third-party payment processing fees charged by the various distribution channels in connection with sales of our virtual currency. We initially defer payment processing fees and recognize them as expense over the same period as the respective revenue. Cost of revenue also includes costs associated with the printing of prepaid cards.
Cost of revenue as a percentage of revenue is affected by shifts in user purchasing preferences and trends. While in recent years, we saw a shift of our sales toward prepaid card distribution channels and credit card sales directly through our website, which are subject to lower processing fees compared to other distribution channels, such as the Apple App Store, Google Play Store, and consoles such as Xbox and PlayStation, we have seen this trend moderate over the last several quarters. We expect to see the overall distribution channel mix shift to higher processing fees continue in future periods with some seasonal variations.
We intend to use nearly all of any efficiencies earned in this area over time to increase earnings for our developers and creators.
Developer exchange fees
Developer exchange fees expense represent the amount earned by developers and creators on the Roblox Platform that are qualified and registered in the Developer Exchange Program. Developers and creators are able to exchange their earned Robux for real-world currency under certain conditions outlined in our Developer Exchange Program. Developers and creators can earn Robux primarily through the sale of access to their experiences and enhancements in their experiences, the incorporation of immersive ads, the sale of content and tools between developers through the Creator Store (formerly the Creator Marketplace), and the sale of items to users through the Marketplace. Developers can also earn Robux through our engagement-based reward program that rewards developers based on the number of hours spent in their experiences by Roblox Premium subscribers (the “Engagement-Based Payouts” program).
In order to be qualified for our Developer Exchange Program and eligible to exchange earned Robux for real-world currency, developers and creators must meet certain conditions, such as having earned the minimum amount of Robux required to qualify for the program, a verified developer account, and an account in good standing. On January 31, 2022, we reduced the minimum amount of earned Robux required to qualify for the program from 100,000 Robux to 50,000 Robux and subsequently on January 31, 2023, we further reduced the minimum requirement from 50,000 Robux to 30,000 Robux. We believe these reductions in the minimum amounts required incentivize our developer and creator community, and promote the long term growth and the health of such community. As of December 31, 2023, over 16,500 developers and creators qualified for and were registered in our Developer Exchange Program.
Over the next few years, a major goal is to increase our developer and creator earnings by creating new earnings methods and enhancing existing ones, as well as through efficiencies realized in other areas of our business, while maintaining reasonable margins.
Infrastructure and trust & safety
Infrastructure and trust & safety expenses consist primarily of expenses related to the operation of our data centers and technical infrastructure. These costs include third-party service providers costs, such as cloud computing or other hosting and data storage, facilities-related expenses for our co-located data centers and edge data centers that we lease and operate, and network and bandwidth costs, as well as depreciation and associated support and maintenance costs of our servers and infrastructure equipment. In the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022, depreciation and amortization expense related to infrastructure and trust & safety was $179.9 million and $108.0 million, respectively. Infrastructure and trust & safety expenses also include personnel costs and moderation and customer support related costs, as well as allocated overhead expenses, to support our infrastructure and trust & safety initiatives.
We plan to continue increasing the capacity, capability, and reliability of our infrastructure to support more sophisticated content, more users, and increased engagement. We expect to moderate our investment in infrastructure in fiscal year 2024, but generally expect to increase the dollar amount of our investment in infrastructure for the foreseeable future thereafter as we continue to build out our global infrastructure. We intend to achieve scalability by building and maintaining our own technical infrastructure, while generally generating operating leverage over the long-term.
Research and development
Research and development expenses consist primarily of personnel costs and allocated overhead expenses for our engineering, design, product management, data science, and other employees engaged in maintaining and enhancing the functionality of the Platform. Research and development expenses also include costs associated with our Game Fund program, which funds certain developers up front to develop new experience types for the Platform. We plan to increase research and development expenses for the foreseeable future primarily driven by increased headcount to develop new features, functionality, and innovation of our product. However, we plan to slow our headcount growth rate and expect to generate operating leverage beginning in fiscal year 2024 and generally through the end of fiscal year 2025.
General and administrative
General and administrative expenses consist primarily of personnel costs and allocated overhead for our finance and accounting, legal, human resources, talent acquisition, and other administrative teams. General and administrative expenses also include professional services fees such as outside legal, accounting, audit, and outsourcing services, and other corporate expenses, as well as certain accruals and settlements associated with legal proceedings. We expect to moderate our headcount growth in fiscal year 2024, but generally expect to increase general and administrative expenses for the foreseeable future thereafter to support the growth of the business.
Sales and marketing
Sales and marketing expenses consist primarily of personnel costs and allocated overhead for our marketing, business development, brand partnerships, and developer relations functions, as well as user acquisition expenses. Other expenses include those associated with market research, branding, public relations, and developer relations programs, including our annual Roblox Developer Conference. We plan to increase our sales and marketing expenses for the foreseeable future, primarily to support the growth of our business.
Interest income
Interest income consists primarily of interest earned and net accretion/(amortization) of our short-term investments, long-term investments, and cash equivalents.
Interest expense
Interest expense consists primarily of contractual interest and amortization of debt issuance costs on our 3.875% Senior Notes due 2030 (the “2030 Notes”).
Other income/(expense), net
Other income/(expense), net primarily includes foreign currency exchange gains/(losses) and realized gains/(losses) on our short-term and long-term investments, as well as certain insurance recoveries (if any).
Provision for/(benefit from) income taxes
Provision for/(benefit from) income taxes consists primarily of state, U.S. federal and foreign income taxes. We maintain a full valuation allowance on our federal, state, and foreign deferred tax assets as we have concluded that it is not likely that the deferred assets will be utilized.
Results of Operations
The following tables set forth our results of operations for the periods presented in dollars and as a percentage of our revenue for each period presented (in thousands, except percentages):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2023 | | 2022 |
| Revenue | $ | 2,799,274 | | | 100 | % | | $ | 2,225,052 | | | 100 | % |
| Cost and expenses: | | | | | | | |
Cost of revenue (1) | 649,115 | | | 23 | % | | 547,658 | | | 25 | % |
| Developer exchange fees | 740,752 | | | 27 | % | | 623,855 | | | 28 | % |
Infrastructure and trust & safety (2) | 878,361 | | | 31 | % | | 689,081 | | | 31 | % |
Research and development (2) | 1,253,598 | | | 45 | % | | 873,477 | | | 39 | % |
General and administrative (2) | 390,055 | | | 14 | % | | 297,317 | | | 13 | % |
Sales and marketing (2) | 146,460 | | | 5 | % | | 117,448 | | | 5 | % |
| Total cost and expenses | 4,058,341 | | | 145 | % | | 3,148,836 | | | 142 | % |
| Loss from operations | (1,259,067) | | | (45) | % | | (923,784) | | | (42) | % |
| Interest income | 141,818 | | | 5 | % | | 38,842 | | | 2 | % |
| Interest expense | (40,707) | | | (1) | % | | (39,903) | | | (2) | % |
| Other income/(expense), net | (527) | | | — | % | | (5,744) | | | — | % |
| Loss before income taxes | (1,158,483) | | | (41) | % | | (930,589) | | | (42) | % |
| Provision for/(benefit from) income taxes | 454 | | | — | % | | 3,552 | | | — | % |
| Consolidated net loss | (1,158,937) | | | (41) | % | | (934,141) | | | (42) | % |
Net loss attributable to noncontrolling interests (3) | (6,991) | | | — | % | | (9,775) | | | — | % |
| Net loss attributable to common stockholders | $ | (1,151,946) | | | (41) | % | | $ | (924,366) | | | (42) | % |
| Net loss per share attributable to common stockholders, basic and diluted | $ | (1.87) | | | | | $ | (1.55) | | | |
| Weighted-average shares used in computing net loss per share attributable to common stockholders—basic and diluted | 616,445 | | | | | 595,559 | | | |
______________________________
(1)Depreciation of servers and infrastructure equipment included in infrastructure and trust & safety.
(2)Includes stock-based compensation expense as follows (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2023 | | 2022 |
| Infrastructure and trust & safety | $ | 92,147 | | | $ | 56,197 | |
| Research and development | 607,593 | | | 398,899 | |
| General and administrative | 131,577 | | | 109,607 | |
| Sales and marketing | 36,650 | | | 24,795 | |
| Total stock-based compensation expense | $ | 867,967 | | | $ | 589,498 | |
(3)Our consolidated financial statements include our majority-owned subsidiary Roblox China Holding Corp. The ownership interest of a minority investor, Songhua River Investment Limited, is recorded as a noncontrolling interest.
Comparison of the Years Ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
Revenue
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, | | 2022 to 2023 |
| 2023 | | 2022 | | % Change |
| | | | | |
| (dollars in thousands) | | |
| Revenue | $ | 2,799,274 | | | $ | 2,225,052 | | | 26 | % |
Revenue in the year ended December 31, 2023 increased $574.2 million, or 26%, compared to the year ended December 31, 2022. The increase is primarily due to a higher amortization of prior period deferred revenue and an increase in bookings in the current period. The increase in bookings was primarily driven by a higher average number of daily unique paying users during 2023, which increased from approximately 725,000 in 2022 to approximately 852,000 in 2023. The average number of daily unique paying users represents the number of user accounts that made a purchase on the Platform, including via redemption of prepaid cards for Robux, on an average daily basis during the respective period. The overall increase in revenue was offset by a longer average estimated paying user life during 2023 as compared to 2022 (during which the estimated paying user life increased from 23 months as of December 31, 2021 to 28 months by the third quarter of 2022).
Refer to the heading “Change in Accounting Estimate” earlier in this section for more information on the change in paying user life estimates in fiscal year 2022.
Cost of revenue
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, | | 2022 to 2023 |
| 2023 | | 2022 | | % Change |
| | | | | |
| (dollars in thousands) | | |
| Cost of revenue | $ | 649,115 | | | $ | 547,658 | | | 19 | % |
Cost of revenue increased $101.5 million, or 19%, for the year ended December 31, 2023 compared to the year ended December 31, 2022. The increase is primarily due to a net increase of $99.9 million in expense for payment processing fees, primarily driven by a higher amortization of prior period deferred cost of revenue and an increase in current period payment processing fees from the related growth in bookings. The overall increase in expense for payment processing fees was offset by the aforementioned increases in our estimated paying user life – as payment processing fees are also amortized over the estimated paying user life – as well as a shift of our sales toward distribution channels with lower processing fees.
Refer to the heading “Change in Accounting Estimate” earlier in this section for more information on the change in paying user life estimates in fiscal year 2022.
Developer exchange fees
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, | | 2022 to 2023 |
| 2023 | | 2022 | | % Change |
| | | | | |
| (dollars in thousands) | | |
| Developer exchange fees | $ | 740,752 | | | $ | 623,855 | | | 19 | % |
Developer exchange fees increased $116.9 million, or 19%, for the year ended December 31, 2023 compared to the year ended December 31, 2022. The increase is primarily driven by an increase in amounts earned by developers and creators due to the growth in bookings over the same period. However, the growth in bookings exceeded the growth in developer exchange fees, primarily driven by changes in non-USD pricing, which impacts the amount of developer exchange fees incurred.
Infrastructure and trust & safety
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, | | 2022 to 2023 |
| 2023 | | 2022 | | % Change |
| | | | | |
| (dollars in thousands) | | |
| Infrastructure and trust & safety | $ | 878,361 | | | $ | 689,081 | | | 27 | % |
Infrastructure and trust & safety expenses increased $189.3 million, or 27%, for the year ended December 31, 2023 compared to the year ended December 31, 2022. The increase is primarily driven by an increase of $89.0 million related to data center, hosting, and other hardware and software costs (including depreciation and amortization expense). The increase was further driven by an increase of $66.5 million in personnel costs, which includes an increase of $36.0 million in stock-based compensation expense, primarily due to an increase in headcount to support our infrastructure growth. Finally, the increase was supplemented by an increase of $24.0 million in moderation and customer support related costs.
Research and development
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, | | 2022 to 2023 |
| 2023 | | 2022 | | % Change |
| | | | | |
| (dollars in thousands) | | |
| Research and development | $ | 1,253,598 | | | $ | 873,477 | | | 44 | % |
Research and development expenses increased $380.1 million, or 44%, for the year ended December 31, 2023 compared to the year ended December 31, 2022. The increase is primarily due to an increase of $333.3 million in personnel costs, which includes an increase of $208.7 million in stock-based compensation expense, primarily due to continued growth in headcount supporting our engineering, design, and product teams. The increase was further supplemented by an increase of $25.6 million in facilities-related costs, primarily driven by higher rent expense associated with our office leases.
General and administrative
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, | | 2022 to 2023 |
| 2023 | | 2022 | | % Change |
| | | | | |
| (dollars in thousands) | | |
| General and administrative | $ | 390,055 | | | $ | 297,317 | | | 31 | % |
General and administrative expenses increased $92.7 million, or 31%, for the year ended December 31, 2023 compared to the year ended December 31, 2022. The increase is primarily due to an increase of $56.7 million in personnel costs, which includes an increase of $22.0 million in stock-based compensation expense, primarily due to increased headcount. The increase was further driven by an increase of $10.4 million in professional services expenses and $9.5 million of withholding-related taxes. The increase was also supplemented by an impairment charge of $7.0 million related to the operating lease right-of-use asset and related leasehold improvements of a portion of our San Mateo headquarters for which a sub-lease agreement was executed during the first quarter of 2023. For more information regarding the sub-lease transaction, refer to Note 3, “Leases” to the notes to consolidated financial statements.
Sales and marketing
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, | | 2022 to 2023 |
| 2023 | | 2022 | | % Change |
| | | | | |
| (dollars in thousands) | | |
| Sales and marketing | $ | 146,460 | | | $ | 117,448 | | | 25 | % |
Sales and marketing expenses increased $29.0 million, or 25%, for the year ended December 31, 2023 compared to the year ended December 31, 2022. The increase is primarily due to $17.9 million in personnel costs, which includes an increase in stock-based compensation expense of $11.9 million, primarily due to continued growth in headcount to support our sales and marketing teams, as well as an increase of $7.2 million in advertising and promotional expenses.
Interest income, interest expense, other income/(expense), net, and provision for/(benefit from) income taxes
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, | | 2022 to 2023 |
| 2023 | | 2022 | | % Change |
| | | | | |
| (dollars in thousands) | | |
| Interest income | $ | 141,818 | | | $ | 38,842 | | | 265 | % |
| Interest expense | $ | (40,707) | | | $ | (39,903) | | | 2 | % |
| Other income/(expense), net | $ | (527) | | | $ | (5,744) | | | (91) | % |
| Provision for/(benefit from) income taxes | $ | 454 | | | $ | 3,552 | | | (87) | % |
Interest income increased by $103.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2023 compared to the year ended December 31, 2022. The increase was primarily due to rising interest rates.
Interest expense was relatively flat for the year ended December 31, 2023 compared to the year ended December 31, 2022.
Other income/(expense), net changed by $5.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2023 compared to the year ended December 31, 2022. The change was primarily driven by a $5.0 million business interruption insurance recovery recognized during the second quarter of 2023 related to a fourth quarter 2021 Platform outage.
Provision for/(benefit from) income taxes changed by $(3.1) million for the year ended December 31, 2023 as compared to prior year ended December 31, 2022. The change was primarily due to a decrease in state income tax expense in certain states.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
As of December 31, 2023 and 2022, our principal sources of liquidity were cash and cash equivalents, short-term and long-term investments of $3.2 billion and $3.0 billion, respectively, which were primarily held for working capital purposes, capital expenditures, and acquisitions. Our investment policy and strategy are focused on the preservation of capital and supporting our liquidity requirements. We do not enter into investments for trading or speculative purposes.
Since our inception, we have financed our operations primarily through cash generated from operations and, to a lesser extent, sales of convertible preferred stock, borrowings under our credit facilities, and the sale of our 2030 Notes. We require payment upfront for substantially all of our bookings.
On October 29, 2021, we issued the 2030 Notes, which will mature on May 1, 2030, unless earlier repurchased or redeemed. Interest is payable semi-annually in arrears on May 1 and November 1 of each year, commencing on May 1, 2022. The net proceeds from the 2030 Notes issuance were approximately $987.5 million and we intend to use the net proceeds for general corporate purposes, which may include working capital purposes, capital expenditures, and acquisitions.
The 2030 Notes are unsecured obligations and the Indenture contains covenants limiting the Company and its subsidiaries’ ability to: (i) create certain liens and enter into sale and lease-back transactions; (ii) create, assume, incur or guarantee indebtedness; or (iii) consolidate or merge with or into, or sell or otherwise dispose of all of substantially all of the Company and its subsidiaries’ assets to another person, all of which are limited to amounts not to exceed the greater of $4.0 billion and 3.5x “Consolidated EBITDA” (as defined in the Indenture and referred to as “Covenant Adjusted EBITDA” throughout this section). Non-compliance with these covenants may result in the acceleration of repayment of the 2030 Notes and any accrued and unpaid interest.
Accordingly, the Company presents Covenant Adjusted EBITDA calculated in accordance with “Consolidated EBITDA” as that term is defined in the Indenture, which is not calculated in accordance with GAAP and may not conform to the calculation of Adjusted EBITDA by other companies. Covenant Adjusted EBITDA should not be considered as a substitute for a measure of our financial performance or other liquidity measures prepared in accordance with GAAP and is also not indicative of income or loss calculated in accordance with GAAP. Management believes that this calculation is useful to investors for purposes of analyzing our compliance with certain covenants specified in the Indenture.
The following table presents the calculation of Covenant Adjusted EBITDA in accordance with the terms of the Indenture, for each of the periods presented (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, |
| | 2023 | | 2022 |
| Calculation of Covenant Adjusted EBITDA: | | | |
| Consolidated net loss | $ | (1,158,937) | | | $ | (934,141) | |
| Add (deduct): | | | |
| Interest income | (141,818) | | | (38,842) | |
| Interest expense | 40,707 | | | 39,903 | |
| Other (income)/expense, net | 527 | | | 5,744 | |
| Provision for/(benefit from) income taxes | 454 | | | 3,552 | |
| Depreciation and amortization | 208,142 | | | 130,083 | |
| Stock-based compensation expense | 867,967 | | | 589,498 | |
RTO severance charge(1) | 5,228 | | | — | |
Other non-cash charges(2) | 6,988 | | | — | |
| Change in deferred revenue | 742,308 | | | 662,378 | |
| Change in deferred cost of revenue | (139,879) | | | (101,719) | |
| Covenant Adjusted EBITDA | $ | 431,687 | | | $ | 356,456 | |
(1)Relates to cash severance costs associated with the Company’s return-to-office (“RTO”) plan announced in October 2023, which requires a subset of the Company’s remote employees to begin working from the San Mateo headquarters for three days a week, beginning in the summer of 2024.
(2)Includes impairment expense related to certain operating lease right-of-use assets and related property and equipment.
As of December 31, 2023, contractual obligations related to the 2030 Notes are remaining payments of $38.8 million each year from 2024 through 2029 and $1,019.4 million due in 2030. These amounts represent principal and interest cash payments over the term of the 2030 Notes based on the stated maturity date. Any future redemption of the 2030 Notes could impact the amount or timing of our cash payments. For more information regarding the 2030 Notes, refer to Note 8, “Debt” to the notes to consolidated financial statements.
For all periods presented, we have generated losses from our operations and positive cash flows from operating activities. A substantial source of our cash provided by operating activities is our deferred revenue, which is included in our consolidated balance sheet as a liability. Deferred revenue consists of the unearned portion of bookings for which we have not yet satisfied our performance obligation. Our deferred revenue obligation is recognized as revenue over the estimated average lifetime of a paying user or as the virtual items are consumed.
We also expect to continue making investments in our business, including, but not limited, capital expenditures related to our technology infrastructure.
We believe our existing cash and cash equivalents and short-term investments, together with expected cash to be provided by future operations, will be sufficient to meet our needs for the next 12 months. Our future capital requirements, however, will depend on many factors, including our growth rate, investment in our headcount, capital expenditures to build out new facilities and purchase hardware for infrastructure, timing and extent of spending to support our efforts to develop our Platform, and the effects of inflation on these various expenses, amongst other factors. We may in the future enter into arrangements to acquire or invest in complementary businesses, services, and technologies, including intellectual property rights. In the event that additional financing is required from outside sources, we may seek to raise additional funds at any time through equity, equity-linked arrangements, or debt. If we are unable to raise additional capital when desired and at reasonable rates, our business, results of operations, and financial condition would be adversely affected. See Part 1, Item 1A. “Risk Factors” for more information.
Cash Flows
The following table summarizes our cash flows for the periods presented:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2023 | | 2022 |
| | | |
| (dollars in thousands) |
| Consolidated Statements of Cash Flow Data: | | | |
| Net cash and cash equivalents provided by operating activities | $ | 458,180 | | | $ | 369,296 | |
| Net cash and cash equivalents used in investing activities | $ | (2,825,099) | | | $ | (441,051) | |
| Net cash and cash equivalents provided by financing activities | $ | 67,176 | | | $ | 43,642 | |
Operating activities
Our largest source of operating cash is cash collection from sales of Robux and monthly subscriptions. Our primary uses of cash from operating activities are for payment processing fees, personnel-related expenses, data center and infrastructure-related operations, developer exchange fees, and other operating expenses.
During the year ended December 31, 2023, cash and cash equivalents provided by operating activities was $458.2 million, which consisted of a consolidated net loss of $1,158.9 million, adjusted by non-cash charges of $1,110.3 million and net cash inflows from the change in net operating assets and liabilities of $506.8 million. The non-cash charges were primarily comprised of stock-based compensation of $868.0 million and depreciation and amortization of $208.1 million. The net cash and cash equivalent inflows from the change in our net operating assets and liabilities were primarily due to a $742.3 million increase in deferred revenue, primarily due to bookings generated in the current period, and a $83.2 million increase in our developer exchange liability, primarily driven by the increase in bookings generated in the current period, coupled with the timing of payments. The overall increase was offset by a $139.9 million increase in deferred cost of revenue, primarily due to payment process fees associated with bookings generated in the current period, a $126.2 million increase in our accounts receivable balance, net due to the timing of cash receipts on bookings generated in the current period and a $50.5 million decrease in our operating lease liabilities.
Investing activities
During the year ended December 31, 2023, cash and cash equivalents used in investing activities was $2,825.1 million, primarily consisting of $2,487.1 million of investment purchases – net of sales and maturities, $320.7 million of capital expenditures, and $13.5 million of payments related to the purchase of intangible assets.
Financing activities
During the year ended December 31, 2023, cash and cash equivalents provided by financing activities was $67.2 million, primarily consisting of $53.2 million from the exercise of stock options and purchase of shares under our employee stock purchase plan and $14.7 million of proceeds from debt issued by the Company’s fully consolidated subsidiary Roblox China Holding Corp. For more information regarding the debt issued by Roblox China Holding Corp., see Note 15, “Joint Venture” in the notes to consolidated financial statements.
Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements
As of December 31, 2023, we had $11.6 million in letters of credit outstanding related to our office facilities in San Mateo, California and data center facilities in Ashburn, Virginia and Chicago, Illinois. We did not have any relationships with unconsolidated entities or financial partnerships, such as structured finance or special purpose entities that were established for the purpose of facilitating off-balance sheet arrangements or other purposes.
Contractual Obligations and Commitments
As of December 31, 2023, we have non-cancellable lease arrangements for office facilities and space for data center operations expiring in various years through 2035. As of December 31, 2023, the Company had fixed lease payment obligations of $1,008.1 million, with $97.5 million payable within 12 months. For more information regarding the operating lease commitments, refer to Note 3, “Leases” to the notes to consolidated financial statements.
Our other purchase obligations primarily consist of non-cancellable obligations with our data center hosting providers and software vendors. As of December 31, 2023, we had other purchase obligations of $459.8 million, with $223.2 million payable within 12 months. For more information regarding our contractual obligations, refer to Note 9, “Commitments and Contingencies” to the notes to consolidated financial statements.
Critical Accounting Policies and Estimates
The preparation of these financial statements in accordance with U.S. GAAP requires us to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts in our consolidated financial statements and related notes. Our estimates are based on various factors that we believe are reasonable. Actual results may differ from these estimates. To the extent that there are differences between our estimates and actual results, our future financial statement presentation, financial condition, results of operations, and cash flows will be affected.
An accounting policy is considered to be critical if it requires an accounting estimate to be made based on assumptions about matters that are highly uncertain at the time the estimate is made, and if different estimates that reasonably could have been used, or changes in the accounting estimates that are reasonably likely to occur periodically, could materially impact the consolidated financial statements.
Refer to Note 1, “Overview and Summary of Significant Accounting Policies”, to our consolidated financial statements included in this Annual Report on Form 10-K for a full description of our revenue recognition and stock-based compensation expense policies.
Revenue Recognition
In accordance with ASC 606, Revenue from Contracts with Customers, revenue is recognized when control of the service is transferred to the customer. The amount of revenue recognized reflects the consideration that the Company expects to be entitled to in exchange for these services. To achieve the core principle of this standard, the Company determines revenue recognition by:
•identifying the contract, or contracts, with the customer;
•identifying the performance obligations in the contract;
•determining the transaction price;
•allocating the transaction price to performance obligations in the contract; and
•recognizing revenue when, or as, the Company satisfies performance obligations by transferring the promised services.
The Company derives substantially all of its revenue from the sale of virtual items on the Roblox Platform.
Roblox Platform
The Company operates the Roblox Platform as live services that allow users to play and socialize with others for free. Within the experience, however, users can purchase virtual currency (“Robux”) to ultimately obtain virtual items to enhance their social experience. Proceeds from the sale of Robux are initially recorded in deferred revenue and recognized as revenue as a user purchases and uses virtual items. The Company’s identified performance obligation is to provide users with the ability to acquire, use, and hold virtual items on the Roblox Platform over the estimated period of time the virtual items are available to the user or until the virtual items are consumed.
Users can purchase Robux as one-time purchases or through monthly subscriptions via payment processors or through prepaid cards. Payments from users are non-refundable and relate to non-cancellable contracts for a fixed price that specify Company’s obligations. Revenue is recorded net of taxes assessed by government authorities that are both imposed on and concurrent with specific revenue transactions between the Company and its users, and estimated chargebacks and refunds.
The satisfaction of the Company’s performance obligation is dependent on the nature of the virtual item purchased and as a result, the Company categorizes its virtual items as either consumable or durable.
•Consumable virtual items represent items that can be consumed by a specific user action. Common characteristics of consumable virtual items may include items that are no longer displayed on the user’s inventory after a short period of time or do not provide the user any continuing benefit following consumption. For the sale of consumable virtual items, the Company recognizes revenue as the items are consumed.
•Durable virtual items represent items which result in a persistent change to a users’ character or item set (e.g., virtual hat, pet, or house). These items are generally available to the customer to hold, use, or display for as long as they are on the Roblox Platform. The Company recognizes revenue from the sale of durable virtual items ratably over the estimated period of time the items are available to the user which is estimated as the average lifetime of a paying user.
To separately account for consumable and durable virtual items, the Company specifically identifies each purchase for the majority of virtual items purchased on the Roblox Platform. For the remaining population, the Company estimates the amount of consumable and durable virtual items purchased based on data from specifically identified purchases and the expected behavior of the users within similar experiences. The estimation of consumable and durable virtual items purchased for the population of purchases not specifically identified requires management’s judgment as the Company evaluates and estimates the expected behavior of users in the population using information from known purchases in similar experiences.
The average lifetime of a paying user estimate is calculated based on historical monthly retention data for each user cohort to project future participation on the Roblox Platform. Determining the estimated average lifetime of a paying user requires management’s judgment as the Company analyzes the most recent trends in player cohort activity and other qualitative factors, including paying user behavior (e.g. impacts due to macroeconomic factors such as COVID-19), existing and new competition from a variety of entertainment resources for our users, the availability of the Roblox Platform across markets and user demographics, and other factors. The Company also considers results from prior analyses in determining the estimated average lifetime of a paying user. The Company believes this estimate is the best representation of the average life of the durable virtual items. The estimated paying user life was 28 months, 28 months, and 23 months as of December 31, 2023, 2022, and 2021, respectively. The increase in the estimated average lifetime of a paying user from 23 months as of December 31, 2021 to 28 months as of December 31, 2022 was in part attributable to the change in our paying users’ behavior as a result of the shelter-in-place and similar restrictions due to the COVID-19 pandemic, as these restrictions led to increased developer, creator, and user engagement and user experiences on the Roblox Platform relative to historical trends. Further we believe the improved content created by our developers and creators, the multitude and variety of experiences available to our users, and the way our users interacted with their peers and social network on the Roblox Platform in recent years resulted in an increase in the retention period of our paying users. Refer to the heading “Change in Accounting Estimate” for discussion on the quantitative amount of the change in accounting estimates for the respective periods impacted.
The Company offers prepaid cards through online and physical retailers, as well as on the Company website. The Company estimates expected breakage by taking into consideration historical patterns of redemption and escheatment laws as applicable.
Stock-Based Compensation Expense
The Company measures and recognizes stock-based compensation expense for all stock-based awards, including stock options, unregistered restricted stock awards (“RSAs”), restricted stock units (“RSUs”), and performance stock units (“PSUs”) granted to employees, directors, and non-employees, and stock purchase rights granted under the 2020 ESPP to employees, based on the estimated grant date fair value of the awards. The Company records forfeitures when they occur for all stock-based awards.
The fair value of each stock option and stock purchase right granted is estimated using the Black-Scholes option-pricing model and is recognized as compensation expense on a straight-line basis over the requisite service period of the awards. The Black-Scholes option pricing model requires certain subjective inputs and assumptions, including the fair value of the Company’s Class A common stock, the expected term, risk-free interest rates, expected stock price volatility, and expected dividend yield of our Class A common stock. The assumptions used to determine the fair value of the option awards represent management’s best estimates. These estimates involve inherent uncertainties and the application of management’s judgment. These assumptions and estimates are as follows:
•Fair value of Class A common stock—Prior to the direct listing of our Class A common stock on the NYSE (the “Direct Listing”), we estimated the fair value of Class A common stock, as discussed below in the section titled “Common Stock Valuations.” After the completion of the Direct Listing, the fair value of our Class A common stock is determined based on the NYSE closing price on the date of grant.
•Expected term—The expected term represents the period that stock-based awards are expected to be outstanding. The expected term assumptions are determined based on the vesting terms, estimated exercise behavior, post-vesting cancellations, and contractual lives of the awards.
•Risk-free interest rates—The risk-free interest rate is based on the implied yields in effect at the time of the grant of U.S. Treasury notes with terms approximately equal to the expected term of the award.
•Expected stock price volatility—Prior to the Direct Listing, we used the historical volatility of the Class A common stock price of similar publicly-traded peer companies. After the completion of the Direct Listing, we continue to use the historical volatility of the stock price of similar publicly traded peer companies since we have not established sufficient public trading history.
•Expected dividend yield—We utilize a dividend yield of zero, as we have no history or plan of declaring dividends on its common stock.
The fair value of RSUs is estimated based on the fair value of our common stock on the date of grant. Prior to the Direct Listing, we estimated the fair value of Class A common stock, as discussed below in the section titled “Common Stock Valuations.” For RSUs granted subsequent to the Direct listing, the fair value of our Class A common stock is determined based on the NYSE closing price on the date of grant.
CEO Long-Term Performance Award
In February 2021, the Leadership Development and Compensation Committee of the Company’s Board of Directors granted the CEO a Long-Term Performance Award (“CEO Long-Term Performance Award”), an RSU award that includes a service and a market condition. The fair value of the CEO Long-Term Performance Award was determined using a Monte Carlo simulation model. The fair value of the common stock underlying the award was determined by the Company’s Board of Directors along with management by considering a number of objective and subjective factors. The Company estimated the expected term based on the time period from the valuation date to the end of the performance period. The risk-free interest rate is based on the U.S. Treasury yield curve in effect at the time of grant for zero-coupon U.S. Treasury notes. The expected volatility is derived from the historical stock volatility of selected peers over a period equivalent to the expected term of the CEO Long-Term Performance Award. The associated stock-based compensation is recorded over the derived service period, using the accelerated attribution method. If the stock price goals are met sooner than the derived service period, the Company will adjust the stock-based compensation expense to reflect the cumulative expense associated with the vested portion of the CEO Long-Term Performance Award. Provided that David Baszucki continues to be the CEO of the Company, stock-based compensation expense is recognized over the derived service period, regardless of whether the stock price goals are achieved.
Common Stock Valuations
Prior to the Direct Listing, due to the absence of a public trading market for our common stock, and in accordance with the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants Accounting and Valuation Guide: Valuation of Privately-Held Company Equity Securities Issued as Compensation, our Board of Directors along with management exercised its reasonable judgment and considered numerous objective and subjective factors to determine the best estimate of fair value of our common stock, including:
•the prices at which we or other holders sold our common and convertible preferred stock to outside investors in arms-length transactions;
•contemporaneous valuations performed by an unrelated third-party valuation firm;
•our operating and financial performance;
•the lack of marketability of our common stock;
•the valuation of comparable companies;
•the industry outlook;
•the likelihood of achieving a liquidity event, such as an initial public offering or a sale of our company given prevailing market conditions; and
•the U.S. and global economic and capital market conditions and outlook.
We determined the fair value of our common stock using the most observable inputs available to us, including income approaches as well as recent sales of our stock. The income approach estimated the value of our business based on the future cash flows we expected to generate discounted to their present value using an appropriate discount rate to reflect the risk of achieving the expected cash flows.
We also considered any secondary transactions involving our capital stock. In our evaluation of those transactions, we considered the facts and circumstances of each transaction to determine the extent to which they represented a fair value exchange. Factors considered include transaction volume, timing, whether the transactions occurred among willing and unrelated parties, and whether the transactions involved investors with access to our financial information.
Recent Accounting Pronouncements
See section “Recent Accounting Pronouncements” within Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Information, Note 1, “Overview and Summary of Significant Accounting Policies”, for discussion of recent accounting pronouncements.
Item 7A. Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk
We are exposed to market risks in the ordinary course of our business. Market risk represents the risk of loss that may impact our financial position due to adverse changes in financial market prices and rates. Our market risk exposure is primarily the result of fluctuations in interest rates and foreign currency exchange rates.
Foreign Currency Exchange Risk
The majority of our revenue is generated in U.S. dollars, with revenue generated in Euros, Canadian dollars, Australian dollars, and the British pound primarily comprising the remainder of our revenue. Our expenses are generally denominated in the currencies of the jurisdictions in which we conduct our operations, which are primarily in the U.S., United Kingdom, Canada, Europe, and China. Our results of current and future operations and cash flows are, therefore, subject to fluctuations due to changes in foreign currency exchange rates. We have not entered into derivative or hedging transactions, but we may do so in the future if our exposure to foreign currency becomes more significant.
Due to fluctuations in exchange rates resulting from the current macroeconomic environment, we have, and may in the future, experience negative impacts to our revenue and operating expenses denominated in currencies other than the U.S. dollar.
Interest Rate Risk
As of December 31, 2023, our short-term and long-term investments primarily consist of debt securities, including corporate debt securities, commercial paper, U.S. Treasury securities, U.S. agency securities, and foreign government securities totaling $2.6 billion. Our debt securities are subject to market risk due to changes in prevailing interest rates that may cause their fair values to fluctuate in the future. Based on a sensitivity analysis, we have determined that a hypothetical 100 basis points increase in interest rates would have resulted in a decrease in the fair values of our short-term and long-term debt securities of approximately $20.7 million as of December 31, 2023. Such losses would only be realized if we sold the investments prior to maturity.
We do not enter into investments for trading or speculative purposes. Our investment policy and strategy are focused on the preservation of capital and supporting our liquidity requirements.
In October 2021, we issued $1.0 billion aggregate principal amount of the 2030 Notes. The 2030 Notes were issued at par and we incurred approximately $12.5 million in debt issuance costs. Interest on the 2030 Notes is payable semiannually in arrears on May 1 and November 1 of each year, beginning on May 1, 2022, and the entire outstanding principal amount of the 2030 Notes is due at maturity on May 1, 2030. The 2030 Notes have a fixed interest rate; therefore, we have no financial statement risk associated with changes in interest rates with respect to the 2030 Notes. Additionally, on our balance sheet we carry the 2030 Notes at face value less unamortized discount and debt issuance cost, and we present the fair value for disclosure purposes only. The fair value of our 2030 Notes will fluctuate with movements in interest rates, increasing in periods of declining rates of interest and declining in periods of increasing rates of interest.
Inflation Risk
Inflationary factors, such as increases in overhead costs, may adversely affect our results of operations. We do not believe that inflation has had a material effect on our business, financial condition or results of operations to date. If our costs were to become subject to significant inflationary pressures, we may not be able to fully offset such higher costs through price increases. Our inability or failure to do so could harm our business, financial condition or results of operations. Additionally, increased inflation rates may reduce consumer discretionary spending, which could affect the buying power of our users, developers, and creators and lead to a reduced demand for our Platform.
Item 8. Consolidated Financial Statements and Supplementary Data
ROBLOX CORPORATION
INDEX TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the stockholders and the Board of Directors of Roblox Corporation
Opinion on the Financial Statements
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of Roblox Corporation and subsidiaries (the “Company”) as of December 31, 2023 and 2022, the related consolidated statements of operations, comprehensive income/(loss), convertible preferred stock and stockholders’ equity/(deficit), and cash flows, for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2023, and the related notes (collectively referred to as the “financial statements”). In our opinion, the financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company as of December 31, 2023 and 2022, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2023, in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America.
We have also audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB), the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2023, based on criteria established in Internal Control — Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission and our report dated February 21, 2024, expressed an unqualified opinion on the Company's internal control over financial reporting.
Basis for Opinion
These financial statements are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s financial statements based on our audits. We are a public accounting firm registered with the PCAOB and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud. Our audits included performing procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures that respond to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. Our audits also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the financial statements. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
Critical Audit Matter
The critical audit matter communicated below is a matter arising from the current-period audit of the financial statements that was communicated or required to be communicated to the Audit and Compliance Committee and that (1) relates to accounts or disclosures that are material to the financial statements and (2) involved especially challenging, subjective, or complex judgments. The communication of critical audit matters does not alter in any way our opinion on the financial statements, taken as a whole, and we are not, by communicating the critical audit matter below, providing a separate opinion on the critical audit matter or on the accounts or disclosures to which it relates.
Revenue Recognition — Refer to Note 1 to the financial statements.
Critical Audit Matter Description
The Company derives substantially all of its revenue from the sale of virtual items on the Roblox platform. The Company’s performance obligation when selling virtual items to users is to provide those users with the ability to acquire, use, and hold virtual items on the Roblox platform over the estimated period of time the virtual items are available to the user, which is estimated as the average lifetime of a paying user (“customer life” for durable virtual items) or until the virtual items are consumed (for consumable virtual items). To separately identify, and account for consumable and durable virtual items, the Company specifically categorizes each purchase for the majority of virtual items purchased on the Roblox platform. For the remaining population, the Company estimates the amount of consumable and durable virtual items purchased based on data from specifically categorized purchases and the expected behavior of the users within similar experiences.
Significant judgement is exercised by management when (1) estimating the customer life, which includes analyzing the most recent trends in player cohort activities and (2) estimating the amount of consumable and durable virtual items purchased for the remaining population of purchases that are not specifically categorized (“remaining population allocation”), which includes evaluating and estimating the expected behavior of users in the population using information from known purchases in similar experiences.
Given the complexity of estimating the customer life and the remaining population allocation, auditing these estimates required a high degree of auditor judgement and increased extent of effort when performing audit procedures to evaluate the Company’s judgements and conclusions.
How the Critical Audit Matter Was Addressed in the Audit
Our audit procedures related to the Company’s estimated customer life and remaining population allocation included the following, among others:
•We obtained an understanding of the Company’s methodology for developing the estimated customer life and remaining population allocation.
•We tested the effectiveness of internal controls related to the review of the methodology and assumptions used in estimating the customer life and remaining population allocation, including the review of inputs and assumptions.
•For the customer life estimate, we (1) tested the accuracy and completeness of the historical monthly retention data for player cohorts, (2) tested the mathematical accuracy of the Company’s calculations to project future retention, and (3) assessed the impact of qualitative factors to evaluate management’s judgement on future retention utilizing competitor information that is publicly available and most recent historical trends in cohort activity.
•For the remaining population allocation estimate, we (1) tested the underlying data for specifically categorized purchases used in management’s analysis by selecting a sample of virtual items that were purchased as well as a sample of items from the Roblox platform and tested that such items were properly categorized between a consumable or a durable virtual item, (2) tested the mathematical accuracy of the percentage of consumable and durable goods for the specifically categorized purchases, (3) compared the composition of the virtual items purchased that were specifically categorized to those that were not specifically categorized to evaluate if the nature of the goods are similar, and (4) tested that the percentage of consumable and durable virtual items for the specifically categorized purchases was applied to the remaining population.
/s/ DELOITTE & TOUCHE LLP
San Jose, California
February 21, 2024
We have served as the Company’s auditor since 2019.
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the stockholders and the Board of Directors of Roblox Corporation
Opinion on Internal Control over Financial Reporting
We have audited the internal control over financial reporting of Roblox Corporation and subsidiaries (the “Company”) as of December 31, 2023, based on criteria established in Internal Control — Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO). In our opinion, the Company maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2023, based on criteria established in Internal Control — Integrated Framework (2013) issued by COSO.
We have also audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB), the consolidated financial statements as of and for the year ended December 31, 2023, of the Company and our report dated February 21, 2024, expressed an unqualified opinion on those financial statements.
Basis for Opinion
The Company’s management is responsible for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting, included in the accompanying Management’s Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s internal control over financial reporting based on our audit. We are a public accounting firm registered with the PCAOB and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects. Our audit included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk, and performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
Definition and Limitations of Internal Control over Financial Reporting
A company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company’s internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (1) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (2) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (3) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
/s/ DELOITTE & TOUCHE LLP
San Jose, California
February 21, 2024
ROBLOX CORPORATION
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
(in thousands, except par values)
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| As of December 31, |
| 2023 | | 2022 |
| Assets | | | |
| Current assets: | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 678,466 | | | $ | 2,977,474 | |
| Short-term investments | 1,514,808 | | | — | |
| Accounts receivable—net of allowances | 505,769 | | | 379,353 | |
| Prepaid expenses and other current assets | 74,549 | | | 61,641 | |
| Deferred cost of revenue, current portion | 501,821 | | | 420,136 | |
| Total current assets | 3,275,413 | | | 3,838,604 | |
| Long-term investments | 1,043,399 | | | — | |
| Property and equipment—net | 695,360 | | | 592,346 | |
| Operating lease right-of-use assets | 665,107 | | | 526,030 | |
| Deferred cost of revenue, long-term | 283,326 | | | 225,132 | |
| Intangible assets, net | 53,060 | | | 54,717 | |
| Goodwill | 142,129 | | | 134,335 | |
| Other assets | 10,284 | | | 4,323 | |
| Total assets | $ | 6,168,078 | | | $ | 5,375,487 | |
| Liabilities and Stockholders’ equity | | | |
| Current liabilities: | | | |
| Accounts payable | $ | 60,087 | | | $ | 71,182 | |
| Accrued expenses and other current liabilities | 271,121 | | | 236,006 | |
| Developer exchange liability | 314,866 | | | 231,704 | |
| Deferred revenue—current portion | 2,406,292 | | | 1,941,943 | |
| Total current liabilities | 3,052,366 | | | 2,480,835 | |
| Deferred revenue—net of current portion | 1,373,250 | | | 1,095,291 | |
| Operating lease liabilities | 646,506 | | | 494,590 | |
| Long-term debt, net | 1,005,000 | | | 988,984 | |
| Other long-term liabilities | 22,330 | | | 10,752 | |
| Total liabilities | 6,099,452 | | | 5,070,452 | |
| Commitments and contingencies (Note 9) | | | |
| Stockholders’ equity | | | |
| Common stock, $0.0001 par value; 5,000,000 authorized as of December 31, 2023 and December 31, 2022, 631,221 and 604,674 shares issued and outstanding as of December 31, 2023 and December 31, 2022, respectively; Class A common stock—4,935,000 shares authorized as of December 31, 2023 and December 31, 2022, 581,135 and 553,337 shares issued and outstanding as of December 31, 2023 and December 31, 2022, respectively; Class B common stock—65,000 shares authorized as of December 31, 2023 and December 31, 2022, 50,086 and 51,337 shares issued and outstanding as of December 31, 2023 and December 31, 2022, respectively | 61 | | | 59 | |
| Additional paid-in capital | 3,134,946 | | | 2,213,603 | |
| Accumulated other comprehensive income/(loss) | 1,536 | | | 671 | |
| Accumulated deficit | (3,060,253) | | | (1,908,307) | |
| Total Roblox Corporation Stockholders’ equity | 76,290 | | | 306,026 | |
| Noncontrolling interests | (7,664) | | | (991) | |
| Total Stockholders’ equity | 68,626 | | | 305,035 | |
| Total Liabilities and Stockholders’ equity | $ | 6,168,078 | | | $ | 5,375,487 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
ROBLOX CORPORATION
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS
(in thousands, except per share amounts)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| Revenue | $ | 2,799,274 | | | $ | 2,225,052 | | | $ | 1,919,181 | |
| Cost and expenses: | | | | | |
Cost of revenue (1) | 649,115 | | | 547,658 | | | 496,870 | |
| Developer exchange fees | 740,752 | | | 623,855 | | | 538,321 | |
| Infrastructure and trust & safety | 878,361 | | | 689,081 | | | 456,498 | |
| Research and development | 1,253,598 | | | 873,477 | | | 533,207 | |
| General and administrative | 390,055 | | | 297,317 | | | 303,020 | |
| Sales and marketing | 146,460 | | | 117,448 | | | 86,363 | |
| Total cost and expenses | 4,058,341 | | | 3,148,836 | | | 2,414,279 | |
| Loss from operations | (1,259,067) | | | (923,784) | | | (495,098) | |
| Interest income | 141,818 | | | 38,842 | | | 92 | |
| Interest expense | (40,707) | | | (39,903) | | | (6,998) | |
| Other income/(expense), net | (527) | | | (5,744) | | | (1,796) | |
| Loss before income taxes | (1,158,483) | | | (930,589) | | | (503,800) | |
| Provision for/(benefit from) income taxes | 454 | | | 3,552 | | | (320) | |
| Consolidated net loss | (1,158,937) | | | (934,141) | | | (503,480) | |
| Net loss attributable to noncontrolling interests | (6,991) | | | (9,775) | | | (11,829) | |
| Net loss attributable to common stockholders | $ | (1,151,946) | | | $ | (924,366) | | | $ | (491,651) | |
| Net loss per share attributable to common stockholders, basic and diluted | $ | (1.87) | | | $ | (1.55) | | | $ | (0.97) | |
| Weighted-average shares used in computing net loss per share attributable to common stockholders—basic and diluted | 616,445 | | | 595,559 | | | 505,858 | |
_______________
(1)Depreciation of servers and infrastructure equipment included in infrastructure and trust & safety.
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
ROBLOX CORPORATION
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF COMPREHENSIVE INCOME/(LOSS)
(in thousands)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| Consolidated net loss | $ | (1,158,937) | | | $ | (934,141) | | | $ | (503,480) | |
| Other comprehensive income/(loss), net of tax: | | | | | |
| Foreign currency translation adjustments | 1,089 | | | 1,287 | | | (55) | |
| Net change in unrealized gains/(losses) on available-for-sale marketable securities | 94 | | | — | | | — | |
| Other comprehensive income/(loss), net of tax | 1,183 | | | 1,287 | | | (55) | |
| Total comprehensive loss, including noncontrolling interests | (1,157,754) | | | (932,854) | | | (503,535) | |
| Less: net loss attributable to noncontrolling interests | (6,991) | | | (9,775) | | | (11,829) | |
| Less: cumulative translation adjustments attributable to noncontrolling interests | 318 | | | 678 | | | (27) | |
| Other comprehensive loss attributable to noncontrolling interests, net of tax | (6,673) | | | (9,097) | | | (11,856) | |
| Total comprehensive loss attributable to common stockholders | $ | (1,151,081) | | | $ | (923,757) | | | $ | (491,679) | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
ROBLOX CORPORATION
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CONVERTIBLE PREFERRED STOCK AND STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY/(DEFICIT)
(in thousands)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Convertible
Preferred Stock | | | Class A and Class B Common Stock | | Additional Paid-In Capital | | Accumulated
Other
Comprehensive
Income/(Loss) | | Accumulated Deficit | | Non-
Controlling Interest | | Total Stockholders’
Equity/(Deficit) |
| Shares | | Amount | | | Shares | | Amount | | | | | |
| Balance at January 1, 2021 | 337,235 | | $ | 344,827 | | | | 201,327 | | $ | 20 | | | $ | 239,792 | | | $ | 90 | | | $ | (492,290) | | | $ | 20,007 | | | $ | (232,381) | |
| Issuance of common stock upon exercise of stock options | — | | — | | | | 33,372 | | 3 | | | 65,284 | | | — | | | — | | | (45) | | | 65,242 | |
| Issuance of unregistered restricted stock awards granted in conjunction with a business combination | — | | — | | | | 487 | | — | | | 31,274 | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 31,274 | |
| Issuance of common stock under Employee Stock Purchase Plan | — | | — | | | | 191 | | — | | | 11,268 | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 11,268 | |
| Issuance of Series H preferred stock, net | 11,889 | | 534,286 | | | | — | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | |
| Conversion of convertible preferred stock to common stock in connection with the direct listing | (349,124) | | (879,113) | | | | 349,124 | | 35 | | | 879,078 | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 879,113 | |
| Vesting of restricted stock units | — | | — | | | | 1,376 | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Stock-based compensation expense | — | | — | | | | — | | — | | | 341,942 | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 341,942 | |
| Other | — | | — | | | | 1 | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | |
| Other comprehensive income/(loss) | — | | — | | | | — | | — | | | — | | | (28) | | | — | | | (27) | | | (55) | |
| Net loss | — | | — | | | | — | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (491,651) | | | (11,829) | | | (503,480) | |
| Balance at December 31, 2021 | — | | $ | — | | | | 585,878 | | $ | 58 | | | $ | 1,568,638 | | | $ | 62 | | | $ | (983,941) | | | $ | 8,106 | | | $ | 592,923 | |
| Issuance of common stock upon exercise of stock options | — | | | — | | | | 9,615 | | | 1 | | | 22,777 | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 22,778 | |
| Issuance of unregistered restricted stock awards granted in conjunction with a business combination | — | | | — | | | | 385 | | | — | | | 10,138 | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 10,138 | |
| Issuance of common stock under Employee Stock Purchase Plan | — | | | — | | | | 575 | | | — | | | 22,702 | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 22,702 | |
| Vesting of restricted stock units | — | | | — | | | | 8,169 | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | |
| Withholding taxes related to net share settlement of restricted stock units | — | | | — | | | | (3) | | | — | | | (150) | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (150) | |
| Stock-based compensation expense | — | | | — | | | | — | | | — | | | 589,498 | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 589,498 | |
| Other | — | | | — | | | | 55 | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | |
| Other comprehensive income/(loss) | — | | | — | | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 609 | | | — | | | 678 | | | 1,287 | |
| Net loss | — | | | — | | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (924,366) | | | (9,775) | | | (934,141) | |
| Balance at December 31, 2022 | — | | $ | — | | | | 604,674 | | $ | 59 | | | $ | 2,213,603 | | | $ | 671 | | | $ | (1,908,307) | | | $ | (991) | | | $ | 305,035 | |
| Issuance of common stock upon exercise of stock options | — | | — | | | | 10,670 | | | 2 | | | 23,747 | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 23,749 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Issuance of common stock under Employee Stock Purchase Plan | — | | — | | | | 1,065 | | | — | | | 29,629 | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 29,629 | |
| Vesting of restricted stock units | — | | — | | | | 14,812 | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | |
| Stock-based compensation expense | — | | — | | | | — | | | — | | | 867,967 | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 867,967 | |
| Other comprehensive income/(loss) | — | | — | | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 865 | | | — | | | 318 | | | 1,183 | |
| Net loss | — | | — | | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (1,151,946) | | | (6,991) | | | (1,158,937) | |
| Balance at December 31, 2023 | — | | $ | — | | | | 631,221 | | $ | 61 | | | $ | 3,134,946 | | | $ | 1,536 | | | $ | (3,060,253) | | | $ | (7,664) | | | $ | 68,626 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
ROBLOX CORPORATION
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
(in thousands)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Twelve Months Ended December 31, |
| 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| Cash flows from operating activities: | | | | | |
| Consolidated net loss | $ | (1,158,937) | | | $ | (934,141) | | | $ | (503,480) | |
| Adjustments to reconcile net loss including noncontrolling interests to net cash and cash equivalents provided by operations: | | | | | |
| Depreciation and amortization | 208,142 | | | 130,083 | | | 75,622 | |
| Stock-based compensation expense | 867,967 | | | 589,498 | | | 341,942 | |
| Operating lease non-cash expense | 97,063 | | | 69,100 | | | 43,794 | |
| (Accretion)/amortization on marketable securities, net | (73,162) | | | — | | | — | |
| Amortization of debt issuance costs | 1,316 | | | 1,261 | | | 216 | |
| Impairment expense, (gain)/loss on investment and other asset sales, and other, net | 8,969 | | | 361 | | | 680 | |
| Changes in operating assets and liabilities, net of effect of acquisitions: | | | | | |
| Accounts receivable | (126,172) | | | (72,479) | | | (61,044) | |
| Accounts payable | (3,475) | | | 10,302 | | | 23,369 | |
| Prepaid expenses and other current assets | (12,770) | | | (33,769) | | | (13,593) | |
| Other assets | (5,961) | | | (1,221) | | | (1,367) | |
| Developer exchange liability | 83,162 | | | 67,798 | | | 82,994 | |
| Accrued expenses and other current liabilities | 8,680 | | | 19,560 | | | 58,809 | |
| Other long-term liability | 11,397 | | | 10,159 | | | (1,189) | |
| Operating lease liabilities | (50,454) | | | (47,875) | | | (34,743) | |
| Deferred revenue | 742,294 | | | 662,378 | | | 819,927 | |
| Deferred cost of revenue | (139,879) | | | (101,719) | | | (172,828) | |
| Net cash and cash equivalents provided by operating activities | 458,180 | | | 369,296 | | | 659,109 | |
| Cash flows from investing activities: | | | | | |
| Acquisition of property and equipment | (320,667) | | | (426,163) | | | (93,273) | |
| Payments related to business combination, net of cash acquired | (3,859) | | | (13,388) | | | (45,692) | |
| Purchases of intangible assets | (13,500) | | | (1,500) | | | (7,856) | |
| Purchases of investments | (4,591,974) | | | — | | | — | |
| Maturities of investments | 1,642,719 | | | — | | | — | |
| Sales of investments | 462,182 | | | — | | | — | |
| Net cash and cash equivalents used in investing activities | (2,825,099) | | | (441,051) | | | (146,821) | |
| Cash flows from financing activities: | | | | | |
| Proceeds from issuance of common stock | 53,226 | | | 45,752 | | | 76,177 | |
| Net proceeds from issuance of preferred stock | — | | | — | | | 534,286 | |
| Payment of withholding taxes related to net share settlement of restricted stock units | — | | | (150) | | | — | |
| Proceeds from debt issuances | 14,700 | | | — | | | 990,000 | |
| Payment of debt issuance costs | — | | | (154) | | | (2,339) | |
| Payments related to business combination, after acquisition date | (750) | | | (150) | | | — | |
| Other financing activities | — | | | (1,656) | | | — | |
| Net cash and cash equivalents provided by financing activities | 67,176 | | | 43,642 | | | 1,598,124 | |
| Effect of exchange rate changes on cash and cash equivalents | 735 | | | 1,287 | | | (55) | |
| Net increase/(decrease) in cash and cash equivalents | (2,299,008) | | | (26,826) | | | 2,110,357 | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | | | | | |
| Beginning of year | 2,977,474 | | | 3,004,300 | | | 893,943 | |
| End of year | $ | 678,466 | | | $ | 2,977,474 | | | $ | 3,004,300 | |
| Supplemental disclosure of cash flow information: | | | | | |
| Cash paid for interest | $ | 38,750 | | | $ | 38,965 | | | — | |
| Cash paid for income taxes, net | $ | 3,145 | | | $ | 953 | | | — | |
| Supplemental disclosure of noncash investing and financing activities: | | | | | |
| Property and equipment additions in accounts payable and accrued expenses and other current liabilities | $ | 31,340 | | | $ | 57,199 | | | $ | 50,388 | |
| Intangible asset purchases in accounts payable | $ | 1,200 | | | — | | | — | |
| Fair value of unregistered restricted stock awards issued as consideration for a business combination | — | | | $ | 10,138 | | | $ | 31,274 | |
| | | | | |
| Conversion of convertible preferred stock to common stock upon direct listing | — | | | — | | | $ | 879,113 | |
| Unpaid debt issuance costs | — | | | — | | | $ | 154 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
ROBLOX CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
1. Overview and Summary of Significant Accounting Policies
Organization and Description of Business—Roblox Corporation (the “Company” or “Roblox”) was incorporated under the laws of the state of Delaware in March 2004. The Company operates a free to use immersive platform for connection and communication (the “Roblox Platform” or “Platform”) where people come to create, play, work, learn, and connect with each other in experiences built by our global community of creators. Users are free to immerse themselves in experiences on the Roblox Platform and can acquire experience-specific enhancements or avatar items by using purchased Robux, our virtual currency. Any user can be a developer or creator on the Platform using Roblox Studio, a set of free software tools. Developers and creators build the experiences that are published on Roblox and can earn Robux by monetizing their experience, creating and selling or reselling avatar items, or creating and selling Roblox Studio plugins.
Direct Listing—On March 10, 2021, the Company completed a direct listing of its Class A common stock (“Direct Listing”) on the New York Stock Exchange (“NYSE”). The Company incurred fees primarily related to financial advisory service, audit and legal expenses, in connection with the Direct Listing and recorded general and administrative expenses of $50.7 million during the first quarter of the fiscal year ended March 31, 2021. Immediately prior to the Direct Listing, all shares of outstanding convertible preferred stock were converted into an equivalent number of shares of Class A common stock.
Basis of Presentation and Summary of Significant Accounting Policies
Fiscal Year—The Company’s fiscal year ends on December 31. For example, references to fiscal 2023, 2022, and 2021 refer to the fiscal year ending December 31, 2023, December 31, 2022, and December 31, 2021, respectively.
Basis of Presentation—The accompanying consolidated financial statements have been prepared in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles in the United States (“U.S. GAAP”), and applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission (“SEC”).
Principles of Consolidation—The consolidated financial statements include the accounts of the Company and subsidiaries over which the Company has control. All intercompany transactions and balances have been eliminated. The consolidated financial statements include 100% of the accounts of wholly owned and majority owned subsidiaries, and the ownership interest of minority investors is recorded as noncontrolling interest.
Use of Estimates—The preparation of consolidated financial statements in conformity with U.S. GAAP requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the amounts reported in the consolidated financial statements and accompanying notes. Significant estimates and assumptions reflected in the consolidated financial statements include, but are not limited to, the estimated period of time the virtual items are available to the user, which is estimated as the average lifetime of a paying user, and the estimated amount of consumable and durable virtual items purchased for which the Company lacks specific information that is used for revenue recognition, the estimated amount of expected breakage related to prepaid card sales, useful lives of property and equipment and intangible assets, fair value of assets and liabilities acquired through acquisitions, accrued liabilities (including accrued developer exchange fees), contingent liabilities, valuation of deferred tax assets and liabilities, stock-based compensation expense, the discount rate used in measuring our operating lease liabilities, the carrying value of operating lease right-of-use assets, evaluation of recoverability of goodwill, intangible assets and long-lived assets, and as necessary, estimates of fair value to measure impairment losses. Management believes that the estimates, and judgments upon which they rely, are reasonable based upon information available to them at the time that these estimates and judgments are made. Actual results could differ from those estimates and any such differences may be material to the consolidated financial statements. To the extent that there are material differences between these estimates and actual results, the Company’s consolidated financial statements will be affected.
Foreign Currency Transactions—The functional currency of the Company’s international subsidiaries is the U.S. dollar, with the exception of a Chinese subsidiary wholly owned by Roblox China Holding Corp., as discussed in Note 15, “Joint Venture” to the notes to these consolidated financial statements. We translate the financial statements of our non-U.S. dollar functional subsidiary to U.S. dollars using the period-end exchange rate for assets and liabilities and the average exchange rate for the period for revenues and expenses. The effects of foreign currency translation are included in stockholders’ equity/(deficit) and periodic movements are summarized as a line item in the consolidated statements of comprehensive income.
We reflect foreign exchange transaction gains and losses resulting from the conversion of the transaction currency to the functional currency, which includes gains and losses from the remeasurement of assets and liabilities, as a component of other income/(expense), net.
Segments—The Company operates as a single operating and reportable segment, which is at the consolidated entity level. The chief operating decision maker of the Company is its chief executive officer (“CEO”), who makes resource allocation decisions and assesses performance based on financial information presented on a consolidated basis.
Revenue Recognition
Revenue Recognition Policy
In accordance with ASC 606, Revenue from Contracts with Customers, revenue is recognized when control of the service is transferred to the customer. The amount of revenue recognized reflects the consideration that the Company expects to be entitled to in exchange for these services. To achieve the core principle of this standard, the Company determines revenue recognition by:
•identifying the contract, or contracts, with the customer;
•identifying the performance obligations in the contract;
•determining the transaction price;
•allocating the transaction price to performance obligations in the contract; and
•recognizing revenue when, or as, the Company satisfies performance obligations by transferring the promised services.
The Company derives substantially all of its revenue from the sale of virtual items on the Roblox Platform.
Roblox Platform
The Company operates the Roblox Platform as live services that allow users to play and socialize with others for free. Within the experience, however, users can purchase virtual currency (“Robux”) to ultimately obtain virtual items to enhance their social experience. Proceeds from the sale of Robux are initially recorded in deferred revenue and recognized as revenue as a user purchases and uses virtual items. The Company’s identified performance obligation is to provide users with the ability to acquire, use, and hold virtual items on the Roblox Platform over the estimated period of time the virtual items are available to the user or until the virtual items are consumed.
Users can purchase Robux as one-time purchases or through monthly subscriptions via payment processors or through prepaid cards. Payments from users are non-refundable and relate to non-cancellable contracts for a fixed price that specify Company’s obligations. Revenue is recorded net of taxes assessed by government authorities that are both imposed on and concurrent with specific revenue transactions between the Company and its users, and estimated chargebacks and refunds.
The satisfaction of the Company’s performance obligation is dependent on the nature of the virtual item purchased and as a result, the Company categorizes its virtual items as either consumable or durable.
•Consumable virtual items represent items that can be consumed by a specific user action. Common characteristics of consumable virtual items may include items that are no longer displayed on the user’s inventory after a short period of time or do not provide the user any continuing benefit following consumption. For the sale of consumable virtual items, the Company recognizes revenue as the items are consumed.
•Durable virtual items represent items which result in a persistent change to a users’ character or item set (e.g., virtual hat, pet, or house). These items are generally available to the customer to hold, use, or display for as long as they are on the Roblox Platform. The Company recognizes revenue from the sale of durable virtual items ratably over the estimated period of time the items are available to the user which is estimated as the average lifetime of a paying user.
To separately account for consumable and durable virtual items, the Company specifically identifies each purchase for the majority of virtual items purchased on the Roblox Platform. For the remaining population, the Company estimates the amount of consumable and durable virtual items purchased based on data from specifically identified purchases and the expected behavior of the users within similar experiences. The estimation of consumable and durable virtual items purchased for the population of purchases not specifically identified requires management’s judgment as the Company evaluates and estimates the expected behavior of users in the population using information from known purchases in similar experiences.
The average lifetime of a paying user estimate is calculated based on historical monthly retention data for each user cohort to project future participation on the Roblox Platform. Determining the estimated average lifetime of a paying user requires management’s judgment as the Company analyzes the most recent trends in player cohort activity and other qualitative factors, including paying user behavior (e.g. impacts due to macroeconomic factors such as COVID-19), existing and new competition from a variety of entertainment resources for our users, the availability of the Roblox Platform across markets and user demographics, and other factors. The Company also considers results from prior analyses in determining the estimated average lifetime of a paying user. The Company believes this estimate is the best representation of the average life of the durable virtual items. The estimated paying user life was 28 months, 28 months, and 23 months as of December 31, 2023, 2022, and 2021, respectively.
As part of the process above, in the first quarter of 2022, the Company updated its estimated paying user life from 23 months to 25 months, which was subsequently updated again to 28 months in the third quarter of 2022, where it stayed for the entire year ended December 31, 2023. Based on the carrying amount of deferred revenue and deferred cost of revenue as of December 31, 2021, these changes in estimates resulted in a decrease in revenue of $344.9 million and a decrease in cost of revenue of $79.3 million during the year ended December 31, 2022.
The Company offers prepaid cards through online and physical retailers, as well as on the Company website. The Company estimates expected breakage by taking into consideration historical patterns of redemption and escheatment laws as applicable.
Principal Agent Considerations
The Company evaluates the sales of Robux via third-party payment processors to determine whether its revenues should be reported gross or net of fees either retained by the payment processor or paid to the developers and creators (“Developer Exchange Fees”). The Company is the principal in the transaction with the end user as a result of controlling, hosting, and integrating the delivery of the virtual items to the end user. The Company records revenue gross as a principal and records fees paid to payment processors as a component of cost of revenue and fees paid to developers and creators as a component of developer exchange fees expense.
Other Revenue
Other revenue primarily consists of revenue from advertising, licenses, and royalties. The Company recognizes revenue based on the performance obligations of the underlying agreements, in an amount that reflects the consideration that the Company expects to be entitled to.
Cost of Revenue—Cost of revenue primarily consists of payment processing fees charged by various distribution channels, as well as costs associated with the printing of prepaid cards.
Deferred Cost of Revenue—The Company defers contract costs that are direct and incremental to obtaining user contracts (i.e., sales of Robux). Deferred cost of revenue consists of payment processing fees charged by third-party payment processors. Payment processing fees are amortized over the estimated period of time the virtual items are available to the user on the Roblox Platform (based on the nature of the virtual item as either consumable or durable) in proportion to the revenue recognized. The Company classifies deferred cost of revenue as short-term or long-term based on when the Company expects to recognize the expense. Deferred cost of revenue is periodically reviewed for impairment.
Concentration of Credit Risk and Significant Customers—Financial instruments that potentially subject the Company to concentrations of credit risk consist primarily of cash and cash equivalents, short-term investments, long-term investments and accounts receivables. Cash is deposited with high quality financial institutions and may, at times, exceed federally insured limits. Management believes that the financial institutions that hold the Company’s cash deposits are financially creditworthy and, accordingly, minimal credit risk exists with respect to those balances. Generally, these deposits may be redeemed upon demand and, therefore, bear minimal interest rate risk. As it relates to cash equivalents, short-term investments, and long-term investments, the Company’s investment policy limits the amount of credit exposure in its portfolio by imposing credit rating minimums and limiting purchases by security type and sector.
The Company uses various distribution channels to collect and remit payments from users. As of December 31, 2023 and 2022, one distribution channel accounted for 30% and 37% of our accounts receivable, respectively, while a second distribution channel accounted for 26% and 19% of our accounts receivable, respectively.
For the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022, and 2021, one distribution channel processed 30%, 32%, and 35% of our overall revenue transactions, respectively, and a second distribution channel processed 17%, 18%, and 19% of our overall revenue transactions, respectively.
Fair Value Hierarchy—Assets and liabilities recorded at fair value in the consolidated financial statements are categorized based upon the level of judgment associated with the inputs used to measure their fair value. Hierarchical levels, which are directly related to the amount of subjectivity, associated with the inputs to the valuation of these assets or liabilities are as follows:
Level 1—Inputs that are unadjusted, quoted prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilities at the measurement date.
Level 2—Inputs (other than quoted prices included in Level 1) that are either directly or indirectly observable for the asset or liability through correlation with market data at the measurement date and for the duration of the instrument’s anticipated life.
Level 3—Unobservable inputs that are supported by little or no market activity and that are significant to the fair value of the assets or liabilities and which reflect management’s best estimate of what market participants would use in pricing the asset or liability at the measurement date. Consideration is given to the risk inherent in the valuation technique and the risk inherent in the inputs to the model.
In determining fair value, the Company utilizes valuation techniques that maximize the use of observable inputs and minimize the use of unobservable inputs to the extent possible as well as considers counterparty credit risk in its assessment of fair value.
Cash, Cash Equivalents and Restricted Cash—Cash and cash equivalents primarily consisted of cash in hand and money market instruments with maturities of 90 days or less from the date of purchase.
We had no restricted cash balances as of December 31, 2023 and 2022.
Short-Term and Long-Term Investments—Realized gains and losses for all investments are determined using the specific-identification method and are reflected as a component of other income/(expense), net in the consolidated statements of operations.
Debt Securities
Short-term and long-term investments include corporate debt securities, commercial paper, U.S. Treasury securities, U.S. agency securities, foreign government securities, and certificates of deposits. Based on our intentions, all debt investments are classified as available-for-sale and are reported at fair value with unrealized gains and losses recorded as a separate component of other comprehensive income, net of tax. The Company determines the appropriate classification of its investments as short-term or long-term at the time of purchase and reevaluates such determination at each reporting period based on their respective maturity dates and the Company’s reasonable expectation with regard to those investments (e.g. expectations of future sales or redemptions).
For debt securities in an unrealized loss position, we first consider whether we intend to or it is more likely than not that we will be required to sell the individual security prior to recovery of its amortized cost basis and if so, we adjust the carrying value of security down to its fair value, with the amount of the write-down recorded as a realized loss within other income/(expense), net.
Otherwise, we determine whether a decline in fair value is attributable to a partial or full credit loss by reviewing factors such as the extent to which the fair value is less than the amortized cost basis, changes in interest rates since the purchase of the security, the financial condition of the issuer, including changes in credit ratings, the remaining payment terms of the security, as well as any adverse conditions specifically related to the security, the issuer’s industry or its geographic area. If a credit loss exists, we adjust the carrying value by recording expense within other income/(expense), net equal to the amount of the credit loss, with such amount limited to the amount of the unrealized loss. Subsequent recoveries of fair value originally attributed to a credit loss are subsequently recognized as income within other income/(expense), net. Finally, any unrealized loss not deemed to be attributable to a credit loss is recognized as component of other comprehensive income/(loss), net of tax.
For purposes of identifying and measuring credit losses, the Company excludes any related accrued interest from both the fair value and amortized cost basis of the investment. Accrued interest receivable, net of the allowance for credit losses (if any), is recorded as a component of prepaid expenses and other current assets in our consolidated financial statements.
Equity Securities with Readily Determinable Fair Value
Short-term investments include mutual fund investments related to the Company’s nonqualified deferred compensation plan, which are held in a rabbi trust. The Company classifies these investments as trading securities as the rabbi trust actively manages the asset allocation to match the participants’ hypothetical fund allocations. The Company considers investments held in the rabbi trust to be restricted given their withdrawal and general use is legally restricted.
All equity investments are reported at fair value, with unrealized gains and losses recorded within other income/(expense), net in our consolidated statement of operations.
Accounts Receivable and Related Allowances—Accounts receivable represent amounts due to us based on contractual obligations with our customers. Payments made by the Company’s users are collected by payment processors and remitted to the Company generally within 30 days of invoicing. The Company maintains allowances for potential credit losses when deemed necessary. The Company has not experienced any material credit losses to date. In cases where the Company is aware of circumstances that may impair a specific customer’s ability to meet its financial obligations, it records a specific allowance as a reduction to the accounts receivable balance to reduce it to its net realizable value. In addition, the Company holds a reserve for chargebacks and refunds based on historical data and current trends and projections. Specific allowances, chargeback, and refund reserves have not been material for any of the periods presented.
Property and Equipment—Net—Property and equipment are recorded at historical cost less accumulated depreciation and amortization. Depreciation and amortization are recorded on a straight line basis over the estimated useful lives of the respective assets. Repair and maintenance costs are expensed as incurred. The estimated useful life for each asset category is as follows:
| | | | | |
| Property and Equipment | Estimated Useful Life |
| Servers and related equipment | 5 years |
| Computer hardware and software | 2 - 5 years |
| Furniture and fixtures | 2 years |
| Leasehold improvements | Shorter of remaining lease term or estimated useful life |
Goodwill and Intangible Assets—Goodwill represents the excess of the purchase price over the fair value of net assets acquired in a business combination and is allocated to reporting units expected to benefit from the business combination. Goodwill is not amortized but rather tested for impairment annually in the fourth quarter, or more frequently if events or changes in circumstances indicate that goodwill may be impaired. When conducting our annual goodwill impairment assessment, we perform a quantitative evaluation by comparing the estimated fair value of our single reporting unit, determined using the Company’s market capitalization as of the testing date, to its carrying value. Goodwill impairment is recognized when the quantitative assessment results in the carrying value exceeding the fair value, in which case an impairment charge is recorded to the extent the carrying value exceeds the fair value. There were no impairment charges to goodwill during any of the periods presented.
Intangible assets with finite lives are carried at cost, less accumulated amortization. Intangible assets with finite lives are generally amortized on a straight-line basis over the estimated useful life of the respective asset, generally up to 5 years, or in the case of acquired patents, up to 10 years.
Business Combinations and Asset Acquisitions —To determine whether a transaction is accounted for as an asset acquisition or business combination, the Company applies a screen test to evaluate if substantially all of the fair value of the gross assets acquired is concentrated in a single identifiable asset or group of similar identifiable assets. If the screen test does not result in substantially all of the fair value concentrated in a single identifiable asset or group of similar identifiable assets, the Company performs a second test to evaluate whether the assets and activities transferred include inputs and substantive processes that together, significantly contribute to the ability to create outputs, which would constitute a business. If the result of the second test indicates that the acquired assets and activities constitute a business, the Company accounts for the transaction as a business combination.
For business combinations, the purchase consideration is allocated to the tangible assets acquired, liabilities assumed, and intangible assets acquired based on their respective estimated fair values. The excess of the fair value of purchase consideration over their fair values is recorded as goodwill. The Company’s estimates of fair value are based upon assumptions believed to be reasonable, but which are inherently uncertain and unpredictable, and as a result, actual results may differ from estimates. As a result, during the measurement period, which may be up to one year following the acquisition date, if new information is obtained about facts and circumstances that existed as of the acquisition date, the Company may record adjustments to the fair value of these assets and liabilities, with the corresponding offset to goodwill. Upon the conclusion of the measurement period or final determination of the values of assets acquired or liabilities assumed, whichever comes first, any subsequent adjustments are recorded within the accompanying consolidated statements of operations.
The Company accounts for a transaction as an asset acquisition when substantially all of the fair value of the gross assets acquired is concentrated in a single identifiable asset or group of similar identifiable assets, or otherwise does not meet the definition of a business. Asset acquisition-related costs are capitalized as part of the asset or assets acquired.
Software Development Costs—The Company incurs costs related to developing the Roblox Platform and related support systems. The Company capitalizes development costs when preliminary development efforts are successfully completed, management has authorized and committed project funding, and it is probable that the project will be completed and the software will be used as intended. Development costs meeting the Company’s capitalization criteria were not material during the periods presented.
Impairment of Long-Lived Assets—The Company periodically evaluates the carrying value of long-lived assets to be held and used when indicators of impairment exist. The carrying value of a long-lived asset to be held and used is considered impaired when the estimated separately identifiable undiscounted cash flows expected to result from the use of the asset and its eventual disposition are less than the carrying value of the asset. In that event, an impairment loss is recognized based on the amount by which the carrying value exceeds the fair value of the long-lived asset.
Significant judgment is required to estimate the amount and timing of future cash flows and the relative risk of achieving those cash flows. Assumptions and estimates about future values and remaining useful lives are complex and often subjective. They can be affected by a variety of factors, including external factors such as industry and economic trends, and internal factors such as changes in the Company’s business strategy and internal forecasts.
Developer Exchange Fees Expense —The Company has established an incentive program for developers and creators to build and operate virtual experiences within the Roblox environment. Developers and creators can earn Robux through the sale of access to their experiences and enhancements in their experiences, the sale of content and tools between developers through the Creator Store, and the sale of items to users through the Marketplace. Developers can also earn Robux through our engagement-based reward program that rewards developers based on the share of time that Roblox Premium subscribers engage in their experience. Under certain conditions, and in compliance with applicable law, these developers and creators are eligible to receive a cash payout based on the amount of accumulated earned Robux through our Developer Exchange Program. In order to be qualified for our Developer Exchange Program and eligible to exchange earned Robux for real-world currency, developers and creators must meet certain conditions, such as having earned the minimum amount of Robux required to qualify for the program, a verified developer account, and an account in good standing. On January 31, 2022, we reduced the minimum amount of earned Robux required to qualify for the program from 100,000 Robux to 50,000 Robux and subsequently on January 31, 2023, we further reduced the minimum requirement from 50,000 Robux to 30,000 Robux.
The Company recognizes the expense associated with the Developer Exchange Program as Robux are earned by developers and creators that are qualified and registered in the Developer Exchange Program.
Infrastructure and Trust & Safety Expense—Infrastructure and trust & safety expense consists primarily of expenses related to the operation of our data centers and technical infrastructure in order to deliver our Platform to our users and are expensed as incurred. Infrastructure expenses also include personnel costs and allocated overhead for employees and team members whose primary responsibilities relate to supporting our infrastructure and trust & safety initiatives.
Research and Development Cost— Research and development costs consist primarily of personnel costs and allocated overhead and are expensed as incurred. Research and development costs also include expenses associated with our Game Fund program, which funds certain developers up front to develop new types of experiences for the Platform.
Stock-Based Compensation Expense—The Company measures and recognizes stock-based compensation expense for all stock-based awards, including stock options, unregistered restricted stock awards (“RSAs”), restricted stock units (“RSUs”), and performance stock units (“PSUs”) granted to employees, directors, and non-employees, and stock purchase rights granted under the 2020 ESPP to employees, based on the estimated grant date fair value of the awards.
The fair value of each stock option and stock purchase right granted is estimated using the Black-Scholes option-pricing model and is recognized as compensation expense on a straight-line basis over the requisite service period of the awards. The Black-Scholes option pricing model requires certain subjective inputs and assumptions, including the fair value of the Company’s Class A common stock, the expected term, risk-free interest rates, expected stock price volatility, and expected dividend yield of our Class A common stock. The assumptions used to determine the fair value of the option awards represent management’s best estimates. These estimates involve inherent uncertainties and the application of management’s judgment. These assumptions and estimates are as follows:
•Fair value of Class A common stock— Prior to the Direct Listing, the fair value of the shares of Class A common stock underlying the stock options and RSUs has historically been determined by the Company’s Board of Directors along with management as there was no public market for the underlying common stock. The Company’s Board of Directors along with management determined the fair value of the Company’s common stock by considering a number of objective and subjective factors including: contemporaneous third-party valuations of its common stock, the valuation of comparable companies, sales of the Company’s common and convertible preferred stock to outside investors in arms-length transactions, the Company’s operating and financial performance, the lack of marketability, and the general and industry specific economic outlook, amongst other factors. After the completion of the Direct listing, the fair value of the Company’s Class A common stock is determined based on the NYSE closing price on the date of grant.
•Expected term—The expected term represents the period that stock-based awards are expected to be outstanding. The expected term assumptions are determined based on the vesting terms, estimated exercise behavior, post-vesting cancellations and contractual lives of the awards.
•Risk-free interest rates—The risk-free interest rate is based on the implied yields in effect at the time of the grant of U.S. Treasury notes with terms approximately equal to the expected term of the award.
•Expected stock price volatility— Prior to the Direct Listing, the Company used the historical volatility of the Class A common stock price of similar publicly-traded peer companies. After the completion of the Direct Listing, the Company continues to use the historical volatility of the stock price of similar publicly traded peer companies since it has not established sufficient public trading history.
•Expected dividend yield—The Company utilizes a dividend yield of zero, as it has no history or plan of declaring dividends on its common stock.
RSUs granted by the Company prior to March 2021 vest upon the satisfaction of both a service-based vesting condition, which is typically four years, and a liquidity event-related performance vesting condition. The liquidity event-related performance vesting condition was satisfied on March 2, 2021 (the “Effective Date”) and the Company recorded a cumulative stock-based compensation expense as of the Direct Listing date for those RSUs for which the service-based vesting condition has been satisfied. Stock-based compensation related to the remaining service-based period after the liquidity event-related performance vesting condition was satisfied is recorded over the remaining requisite service period using the accelerated attribution method. For RSUs granted subsequent to the Direct Listing, we recognize stock-based compensation expense based on grant date fair value on a straight-line basis over the requisite service period for the entire award. The grant date fair value of our Class A common stock associated with our RSUs granted subsequent to the Direct Listing is determined based on the NYSE closing price on the date of grant.
In February 2021, the Leadership Development and Compensation Committee of the Company’s Board of Directors granted the CEO a Long-Term Performance Award (“CEO Long-Term Performance Award”), an RSU award that includes a service and a market condition. The fair value of the CEO Long-Term Performance Award was determined using a Monte Carlo simulation model. The fair value of the common stock underlying the award was determined by the Company’s Board of Directors along with management by considering a number of objective and subjective factors. The Company estimated the expected term based on the time period from the valuation date to the end of the performance period. The risk-free interest rate is based on the U.S. Treasury yield curve in effect at the time of grant for zero-coupon U.S. Treasury notes. The expected volatility is derived from the historical stock volatility of selected peers over a period equivalent to the expected term of the CEO Long-Term Performance Award. The associated stock-based compensation is recorded over the derived service period, using the accelerated attribution method. If the stock price goals are met sooner than the derived service period, the Company will adjust the stock-based compensation expense to reflect the cumulative expense associated with the vested portion of the CEO Long-Term Performance Award. Provided that David Baszucki continues to be the CEO of the Company, stock-based compensation expense is recognized over the derived service period, regardless of whether the stock price goals are achieved.
The Company records forfeitures when they occur for all stock-based awards.
Advertising Expense—Costs for advertising are primarily expensed as incurred and are included in sales and marketing expense in our consolidated statement of operations. Advertising costs totaled $38.3 million, $36.2 million, and $26.8 million during the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022, and 2021, respectively.
Basic and Diluted Net Loss Per Common Share—For the year ended December 31, 2021, basic and diluted net loss per share attributable to common stockholders is computed in conformity with the two-class method required for participating securities. The Company considers all series of its convertible preferred stock to be participating securities as the holders of such stock have the right to receive nonforfeitable dividends on a pari passu basis in the event that a dividend is paid on common stock. Under the two-class method, the net loss attributable to common stockholders is not allocated to the convertible preferred stock as the preferred stockholders do not have a contractual obligation to share in the Company’s losses.
For all years presented, basic net loss per share is computed by dividing net loss attributable to common stockholders by the weighted-average number of shares of common stock outstanding during the period. Diluted net loss per share is computed by giving effect to all potentially dilutive common stock equivalents to the extent they are dilutive. For purposes of this calculation, convertible preferred stock, stock options, RSUs, RSAs, convertible preferred stock warrants, and common stock warrants, as applicable, are considered to be common stock equivalents but have been excluded from the calculation of diluted net loss per share attributable to common stockholders as their effect is anti-dilutive for all periods presented.
Income Taxes—The Company accounts for income taxes using the asset and liability method. Deferred income taxes are recognized by applying enacted statutory tax rates applicable to future years to differences between the consolidated financial statement carrying amounts of existing assets and liabilities and their respective tax bases and operating loss and tax credit carryforwards. The effect on deferred tax assets and liabilities of a change in tax rates is recognized in the statement of operations in the period that includes the enactment date. The measurement of deferred tax assets is reduced, if necessary, by a valuation allowance for any tax benefit for which the future realization is uncertain.
The tax effects of a position are recognized only if it is more likely than not to be sustained based solely on its technical merits as of the reporting date. The Company considers many factors when evaluating and estimating its tax positions and tax benefits, which may require periodic adjustments.
Leases—The Company accounts for lessee and lessor arrangements as follows:
Lessee Arrangements
The Company leases facilities under non-cancellable operating lease agreements. These leases have varying terms up to 12 years and generally contain leasehold improvement incentives, rent holidays, and escalation clauses. In addition, some of these leases have renewal options for up to five years after expiration of the initial term. The Company determines if an arrangement contains a lease at inception. The Company determines if a contract contains a lease based on whether we have the right to obtain substantially all of the economic benefits from the use of an identified asset and whether we have the right to direct the use of an identified asset in exchange for consideration.
Operating lease right-of-use (“ROU”) assets represent our right to use an underlying asset for the lease term. Operating lease liabilities represent our obligation to make lease payments arising from the lease at the commencement date and are recognized based on the present value of lease payments over the lease term at the lease commencement date. Operating lease ROU assets are recognized as the lease liability, adjusted for lease incentives received, initial direct costs, and prepayments made, if any.
In determining the present value of lease payments, the Company discounts future lease payments using its incremental borrowing rate (“IBR”) since the implicit rate in our various leases is unknown. The IBR represents the rate of interest the Company would have to pay to borrow on a collateralized basis over a similar term at an amount equal to the lease payments in a similar economic environment. The Company utilizes a market-based approach to estimate the IBR, which requires significant judgment. The Company primarily considers the current economic environment, lease term and currency in which the lease is denominated, as well as (i) yields on corporate bond with a credit rating similar to the Company; (ii) yields on our outstanding unsecured debt; and (iii) indicative pricing on both secured and unsecured debt received from potential lenders (if any). Certain lease agreements include options to renew or early terminate the lease, and we include such extension periods when it is reasonably certain that they will be exercised and include such periods beyond the early termination date when it is reasonably certain the early terminations will not be exercised.
Lease expense is recognized on a straight-line basis over the lease term.
Variable lease payments are expensed when the underlying uncertainty is resolved, which is generally when the obligation for those costs are incurred and are excluded from the measurement of the right-of-use assets and lease liabilities. Variable lease payments primarily include common-area maintenance, utilities, taxes or other operating costs, which are generally based on a percentage of actual expenses incurred or a fluctuating rate which is unknown at the inception of the contract.
Leases with an initial term of 12 months or less (“short-term leases”) are not recognized on the balance sheet. The Company recognizes lease expense for short-term leases on a straight-line basis over the lease term. The Company does not account for lease components (e.g., fixed payments including rent) separately from the non-lease components (e.g., common-area maintenance costs).
Lessor Arrangements
We do not separate lease components from non-lease components and therefore allocate the entire consideration in our contracts to the lease components. All of the lease and non-lease components qualify for accounting under ASC Topic 842 Leases.
Recent Accounting Pronouncements
Accounting Pronouncements Recently Adopted
In October 2021, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) issued Accounting Standards Update (“ASU”) 2021-08, “Business Combinations (Topic 805): Accounting for Contract Assets and Contract Liabilities from Contracts with Customers”. Under ASU 2021-08, an acquirer must recognize and measure contract assets and contract liabilities acquired in a business combination in accordance with Topic 606, as if it had originated the contracts. Prior to this ASU, an acquirer generally recognized contract assets acquired and contract liabilities assumed that arose from contracts with customers at fair value on the acquisition date. The Company adopted the ASU on January 1, 2023 and the adoption did not have a material impact on the Company’s consolidated financial statements.
Recent Accounting Pronouncements Not Yet Adopted
In November 2023, the FASB issued ASU 2023-07, “Segment Reporting (Topic 280): Improvements to Reportable Segment Disclosures,” which requires public entities to disclose expanded information about their reportable segment(s)’ significant expenses and other segment items on an interim and annual basis. The ASU is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2023, and interim periods within fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2024, with early adoption permitted. The ASU is required to be applied retrospectively to all prior periods presented in the financial statements once adopted. The Company is evaluating the disclosure requirements related to the new standard.
In December 2023, the FASB issued ASU 2023-09, “Income Taxes (Topic 740): Improvements to Income Tax Disclosures,” which requires public entities to disclose specific tax rate reconciliation categories, as well as income taxes paid disaggregated by jurisdiction, amongst other disclosure enhancements. The ASU is effective for financial statements issued for annual periods beginning after December 15, 2024, with early adoption permitted. The ASU can be adopted on a prospective or retrospective basis. The Company is evaluating the disclosure requirements related to the new standard.
2. Revenue from Contracts with Customers
Disaggregation of Revenue
The following table summarizes revenue by region based on the billing country of users (in thousands, except percentages):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| Amount | | Percentage
of
Revenue | | Amount | | Percentage
of
Revenue | | Amount | | Percentage
of
Revenue |
United States and Canada (1) | $ | 1,803,812 | | | 64 | % | | $ | 1,465,955 | | | 66 | % | | $ | 1,298,938 | | | 68 | % |
| Europe | 505,633 | | | 18 | | | 404,431 | | | 18 | | | 357,656 | | | 19 | |
| Asia-Pacific, including Australia and New Zealand | 286,930 | | | 10 | | | 204,261 | | | 8 | | | 145,464 | | | 7 | |
| Rest of world | 202,899 | | | 7 | | | 150,405 | | | 7 | | | 117,123 | | | 6 | |
| Total | $ | 2,799,274 | | | 100 | % | | $ | 2,225,052 | | | 100 | % | | $ | 1,919,181 | | | 100 | % |
(1)The Company’s revenues in the U.S. were 60%, 62%, and 63% of consolidated revenues for each of the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022, and 2021, respectively.
No individual country, other than the United States, exceeded 10% of the Company’s total revenue for any period presented.
Durable virtual items accounted for 91%, 90%, and 89% of virtual item-related revenue in the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022, and 2021, respectively. Consumable virtual items accounted for 9%, 10%, and 11% of virtual item-related revenue in the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022, and 2021, respectively.
Deferred Revenue
The Company receives payments from its users based on the payment terms established in its contracts. Such payments are initially recorded to deferred revenue and are recognized into revenue as the Company satisfies its performance obligations. The aggregate amount of revenue allocated to unsatisfied performance obligations is included in our deferred revenue balances.
The increase in deferred revenue for the year ended December 31, 2023 was driven by sales during the period exceeding revenue recognized from the satisfaction of our performance obligations, which includes the revenue recognized during the period that was included in the current portion of deferred revenue at the beginning of the period. During the year ended December 31, 2023, we recognized all of the revenue that was included in the $1,941.9 million current deferred revenue balance as of December 31, 2022.
3. Leases
The Company has operating leases for real estate and co-located data centers. The components of lease expense were as follows (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| Operating lease expense | $ | 139,482 | | | $ | 90,933 | | | $ | 53,442 | |
| Variable and short-term lease expense | $ | 31,655 | | | $ | 11,586 | | | $ | 3,860 | |
As of December 31, 2023, and December 31, 2022, we had short-term operating lease liabilities totaling $111.3 million and $73.2 million, respectively, included within accrued expenses and other current liabilities on our consolidated balance sheets.
The following table presents future lease payments under the Company’s non-cancellable operating leases as of December 31, 2023 (in thousands):
| | | | | |
| Year ending December 31, | |
| 2024 | $ | 97,524 | |
| 2025 | 146,863 | |
| 2026 | 133,076 | |
| 2027 | 112,626 | |
| 2028 | 96,542 | |
| Thereafter | 421,443 | |
| Total lease payments | $ | 1,008,074 | |
Less: imputed interest (1) | (250,275) | |
| Present value of lease liabilities | $ | 757,799 | |
(1)Calculated using each lease’s incremental borrowing rate.
In addition, the Company has executed operating leases for real estate and co-located data centers which have not commenced as of December 31, 2023. The non-cancellable lease payments for these leases totaled $188.0 million as of December 31, 2023, with lease terms ranging between 7 to 10 years.
The following table presents the weighted average remaining lease term and discount rates as of December 31, 2023, and December 31, 2022:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| As of December 31, |
| 2023 | | 2022 |
| Weighted average remaining lease term (years) | 7.9 | | 7.8 |
| Weighted average discount rate | 6.3 | % | | 5.5 | % |
Supplemental cash and noncash information related to operating leases is as follows (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year ended December 31, |
| 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
Cash paid for amounts included in the measurement of lease liabilities(1) | $ | 105,337 | | | $ | 70,515 | | | $ | 52,942 | |
| Lease liabilities arising from obtaining new right-of-use assets (noncash) | $ | 256,500 | | | $ | 373,844 | | | $ | 70,068 | |
(1)The years ended December 31, 2023, 2022, and 2021 excludes $16.6 million, $1.8 million, and $9.1 million, respectively, of leasehold incentives received from the landlord.
On February 11, 2023, the Company executed a sublease as sub-lessor pursuant to which it subleased a total of approximately 78,911 square feet of its San Mateo, California corporate headquarters (the “San Mateo Headquarters”) to the sub-lessee for a lease term of approximately four years (the “2023 Sub-Lessor Agreement”). The total lease payments due to the Company under the 2023 Sub-Lessor Agreement are $22.2 million over the lease term and the Company provided possession to the sub-lessee to one of the floors in the second quarter of 2023 and the remaining floor in the third quarter of 2023.
As a result of the 2023 Sub-Lessor Agreement, the Company recognized a $7.0 million impairment loss within general and administrative expenses in its consolidated financial statements during the year ended December 31, 2023, which included $4.8 million related to the San Mateo Headquarters’ operating lease right-of-use asset and $2.2 million related to property and equipment, net associated with the San Mateo Headquarters.
4. Cash Equivalents and Investments
Financial Assets
The following is a summary of the Company’s cash equivalents and short-term and long-term investments (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | As of December 31, 2023 |
| | Amortized Cost | | Gross Unrealized Gains | | Gross Unrealized Losses | | Fair Value | | Cash Equivalents | | Short-Term Investments | | Long-Term Investments |
| Debt Securities | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Level 1 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Money market funds | | $ | 614,888 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | 614,888 | | | $ | 614,888 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | |
| U.S. Treasury securities | | 1,692,700 | | | 2,007 | | | (2,547) | | | 1,692,160 | | | — | | | 1,155,218 | | | 536,942 | |
| Subtotal | | 2,307,588 | | | 2,007 | | | (2,547) | | | 2,307,048 | | | 614,888 | | | 1,155,218 | | | 536,942 | |
| Level 2 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| U.S. agency securities | | 286,007 | | | 27 | | | (197) | | | 285,837 | | | — | | | 137,151 | | | 148,686 | |
| Foreign government securities | | 12,866 | | | 74 | | | (28) | | | 12,912 | | | — | | | 1,489 | | | 11,423 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Commercial paper | | 184,465 | | | — | | | — | | | 184,465 | | | 14,827 | | | 169,638 | | | — | |
| Corporate debt securities | | 396,171 | | | 1,992 | | | (1,234) | | | 396,929 | | | — | | | 50,581 | | | 346,348 | |
| Subtotal | | 879,509 | | | 2,093 | | | (1,459) | | | 880,143 | | | 14,827 | | | 358,859 | | | 506,457 | |
| Total Debt Securities | | $ | 3,187,097 | | | $ | 4,100 | | | $ | (4,006) | | | $ | 3,187,191 | | | $ | 629,715 | | | $ | 1,514,077 | | | $ | 1,043,399 | |
| Equity Securities | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Level 1 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Mutual funds (1) | | | | | | | | $ | 731 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 731 | | | $ | — | |
| Total Equity Securities | | | | | | | | $ | 731 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 731 | | | $ | — | |
| Total Investments | | $ | 3,187,097 | | | $ | 4,100 | | | $ | (4,006) | | | $ | 3,187,922 | | | $ | 629,715 | | | $ | 1,514,808 | | | $ | 1,043,399 | |
(1)The equity securities relate to the Company’s nonqualified deferred compensation plan and are held in a rabbi trust. Refer to Note 14, “Employee and Director Benefits”, to the notes to the consolidated financial statements for more information.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | As of December 31, 2022 |
| | Amortized Cost | | Gross Unrealized Gains | | Gross Unrealized Losses | | Fair Value | | Cash Equivalents | | Short-Term Investments | | Long-Term Investments |
| Debt Securities | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Level 1 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Money market funds | | $ | 1,903,880 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | 1,903,880 | | | $ | 1,903,880 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | |
| Total Investments | | $ | 1,903,880 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | 1,903,880 | | | $ | 1,903,880 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | |
As of December 31, 2023, all of the Company’s short-term debt investments have contractual maturities of one year or less and all of the Company’s long-term debt investments have contractual maturities of between one and three years.
Changes in market interest rates, credit risk of borrowers and overall market liquidity, amongst other factors, may cause our short-term and long-term debt investments to fall below their amortized cost basis, resulting in unrealized losses. For those debt securities in an unrealized loss position as of December 31, 2023, the unrealized losses were primarily driven by increases in interest rates following the date of purchase and the Company does not intend to sell, nor is it more likely than not it will be required to sell, such securities before recovering the amortized cost basis.
The following table presents fair values and gross unrealized losses, aggregated by investment category and the length of time that individual securities have been in a continuous loss position (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | As of December 31, 2023 |
| | Less Than 12 Months | | 12 Months or Greater | | Total |
| | Fair Value | | Unrealized Losses | | Fair Value | | Unrealized Losses | | Fair Value | | Unrealized Losses |
| U.S. Treasury securities | | $ | 486,424 | | | $ | (2,547) | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | 486,424 | | | $ | (2,547) | |
| U.S. agency securities | | 182,475 | | | (197) | | | — | | | — | | | 182,475 | | | (197) | |
| Foreign government securities | | 7,374 | | | (28) | | | — | | | — | | | 7,374 | | | (28) | |
| Corporate debt securities | | 240,913 | | | (1,234) | | | — | | | — | | | 240,913 | | | (1,234) | |
| Total | | $ | 917,186 | | | $ | (4,006) | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | 917,186 | | | $ | (4,006) | |
5. Acquisitions
Speechly, Inc.
On September 18, 2023 (the “Speechly Acquisition Date”), the Company acquired all outstanding equity interests of Speechly, Inc. and its wholly owned Finnish subsidiary Speechly Oy (together, “Speechly”). Speechly is a privately held company, that operates a speech recognition software focused on voice moderation. The acquisition has been accounted for as a business combination. The consideration totaled $10.1 million, which included (i) $4.8 million of cash paid on the Speechly Acquisition Date and (ii) $5.3 million of cash held back until certain post-acquisition conditions are satisfied.
The following table summarizes the Company’s preliminary allocation of the purchase consideration based on the fair value of assets acquired and liabilities assumed at the Speechly Acquisition Date (in thousands):
| | | | | |
| | September 18, 2023 |
| Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 970 | |
| Other current assets acquired | 111 | |
| Intangible assets, net | |
| Developed technology, useful life of five years | 2,800 | |
| Goodwill | 7,536 | |
| Other current liabilities assumed | $ | (1,117) | |
| Other long-term liabilities assumed | (182) | |
| Total purchase price | $ | 10,118 | |
Goodwill is attributable to the assembled workforce and anticipated synergies arising from the acquisition. The goodwill recognized is not expected to be deductible for income tax purposes.
Byfron Technologies, LLC Acquisition
On October 11, 2022 (the “Byfron Acquisition Date”), the Company acquired all outstanding equity interests of Byfron Technologies, LLC (“Byfron”), a privately-held company that operates a security and anti-cheat software for game publishers. The acquisition has been accounted for as a business combination. The consideration totaled $9.6 million, which included $2.0 million of cash to be held back for 18 months following the Byfron Acquisition Date. The aggregate purchase consideration comprised of the following (in thousands):
| | | | | |
| |
| | Fair Value |
| Cash paid | $ | 7,603 | |
| Cash holdback | 2,000 | |
| Total purchase price | $ | 9,603 | |
In connection with the acquisition, the Company also entered into agreements with the Byfron founders, which provide them $9.6 million over a three year service period following the Byfron Acquisition Date, subject to their continued service with the Company during that period. The agreements were determined to primarily benefit the Company and were recognized separate from the business combination. The expense associated with these agreements is being recognized ratably over the requisite service period of three years as a component of research and development expense.
The following table summarizes the Company’s allocation of the purchase consideration based on the fair value of assets acquired and liabilities assumed at the Byfron Acquisition Date (in thousands):
| | | | | |
| | October 11, 2022 |
| Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 380 | |
| Goodwill | 3,882 | |
| Identified intangible assets | 5,500 | |
| Other assets | 169 | |
| Other current liabilities | $ | (328) | |
| Total purchase price | $ | 9,603 | |
The following table presents details of the identifiable assets acquired (in thousands, except estimated useful life):
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Carrying
Amount | | Estimated Useful Life (Years) |
| Developed technology | $ | 5,500 | | | 5 |
| Total | $ | 5,500 | | | |
Goodwill is primarily attributable to the assembled workforce and anticipated synergies arising from the acquisition. The goodwill recorded in the acquisition is expected to be deductible for income tax purposes.
Hamul, Inc. Acquisition
On April 1, 2022 (the “Hamul Acquisition Date”), the Company acquired all outstanding equity interests of Hamul, Inc. (“Hamul”) a privately-held company that provides a platform for connecting gaming communities. The acquisition has been accounted for as a business combination. The fair value of the consideration transferred was $19.3 million, which consisted of $9.2 million paid in cash and 0.4 million shares of Class A common stock with a fair value of $4.0 million. The aggregate purchase consideration was comprised of the following (in thousands):
| | | | | |
| |
| | Fair Value |
| Cash paid | $ | 9,185 | |
| Common stock issued | 4,009 | |
| Replacement awards attributable to pre-acquisition service | 6,129 | |
| Total purchase price | $ | 19,323 | |
In connection with the acquisition, the Company entered into a stock-based consideration revesting agreement with the Hamul founders. The portion of the fair value of the common stock associated with pre-acquisition service of the Hamul founders represented a component of the total purchase consideration, as presented above. The remaining fair value of $7.6 million of these issued shares was excluded from the purchase price. These shares, which are subject to the recipients’ continued service with the Company, are being recognized ratably as stock-based compensation expense as a component of research and development expense over the requisite service period of three years following the Hamul Acquisition Date.
The total purchase consideration was allocated to the tangible and intangible assets acquired, and liabilities assumed, based upon their respective fair values as of the date of the acquisition. Management determined the fair values based on a number of factors. The excess of the purchase price over the net assets acquired was recorded as goodwill. Goodwill is attributable to the assembled workforce and anticipated synergies arising from the acquisition. The goodwill recognized is not expected to be deductible for income tax purposes.
The following table summarizes the Company’s allocation of the purchase consideration based on the fair value of assets acquired and liabilities assumed at the Hamul Acquisition Date (in thousands):
| | | | | |
| | April 1, 2022 |
| Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 3,020 | |
| Goodwill | 12,382 | |
| Identified intangible assets | 4,500 | |
| Deferred tax liabilities | (579) | |
| Total purchase price | $ | 19,323 | |
The following table presents details of the identifiable assets acquired (in thousands, except estimated useful life):
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Carrying
Amount | | Estimated Useful Life (Years) |
| Developed technology | $ | 4,500 | | | 5 |
| Total | $ | 4,500 | | | |
Guilded Acquisition
On August 16, 2021 (the “Guilded Acquisition Date”), the Company acquired all outstanding equity interests of Guilded, Inc., (“Guilded”), a privately-held company that operates a communications platform for connecting gaming communities. The acquisition has been accounted for as a business combination. The fair value of the consideration transferred was $77.6 million, which consisted of $46.3 million paid in cash and 0.5 million shares of Roblox’s Class A common stock with a fair value of $31.3 million. The aggregate purchase consideration for Guilded was comprised of the following (in thousands):
| | | | | |
| | Fair Value |
| Cash paid | $ | 46,285 | |
| Roblox Class A common stock issued | 22,744 | |
| Replacement awards attributable to pre-acquisition service | 8,530 | |
| Total purchase price | $ | 77,559 | |
The acquisition-related costs were not material and were recorded as general and administrative expenses in the Company’s consolidated statements of operations for the year ended December 31, 2021.
In connection with the acquisition, the Company entered into a stock-based consideration revesting agreement with the Guilded founder. The portion of the fair value of the common stock associated with pre-acquisition service of the Guilded founder represented a component of the total purchase consideration, as presented above. The remaining fair value of $8.5 million of these issued shares was excluded from the purchase price. These shares, which are subject to the recipients’ continued service with the Company, are being recognized ratably as stock-based compensation expense as a component of research and development expense over the requisite service period of three years.
The total purchase consideration of the Guilded acquisition was allocated to the tangible and intangible assets acquired, and liabilities assumed, based upon their respective fair values as of the date of the acquisition. Management determined the fair values based on a number of factors, including a valuation from an independent third-party valuation firm. The excess of the purchase price over the net assets acquired was recorded as goodwill. Goodwill is attributable to the assembled workforce and anticipated synergies arising from the acquisition. The goodwill recorded in the acquisition is not deductible for income tax purposes.
The following table summarizes the Company’s allocation of the purchase consideration based on the fair value of assets acquired and liabilities assumed at the Guilded Acquisition Date (in thousands):
| | | | | |
| | August 16, 2021 |
| Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 593 | |
| Goodwill | 58,503 | |
| Identified intangible assets | 19,600 | |
| Deferred tax liabilities | (999) | |
| Accrued expenses and other current liabilities | (138) | |
| Total purchase price | $ | 77,559 | |
The following table presents details of the identifiable intangible assets acquired at the Guilded Acquisition Date (in thousands, except estimated useful life):
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Carrying Amount | | Estimated Useful Life (Years) |
| Developed technology | $ | 19,100 | | | 5 |
| Trade name | 500 | | | 5 |
| Total | $ | 19,600 | | | |
Other Acquisitions
During the year ended December 31, 2021, the Company completed two individually immaterial acquisitions. These transactions were accounted for as asset acquisitions as they did not meet the definition of a business. The acquired assets consisted entirely of assembled workforce and had a fair value of $8.5 million with an estimated useful life of 3 years. The aggregate purchase consideration consisted of $8.5 million, paid in cash.
All of the acquisitions described above are not material to the Company for the periods presented and therefore pro forma information has not been presented.
6. Goodwill and Intangible Assets
Goodwill
The following table represents the changes to goodwill from December 31, 2021 to December 31, 2023 (in thousands):
| | | | | |
| Carrying Amount |
| Balance as of December 31, 2021 | $ | 118,071 | |
| Additions from acquisitions | 16,264 | |
| Balance as of December 31, 2022 | $ | 134,335 | |
| Additions from acquisitions | 7,536 | |
| Foreign currency translation adjustments | 258 | |
| Balance as of December 31, 2023 | $ | 142,129 | |
There are no accumulated impairment losses for any period presented.
Intangible Assets
The following tables present details of the Company’s finite-lived intangible assets as of December 31, 2023 and December 31, 2022 (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| As of December 31, 2023 |
| Gross Carrying Amount | | Accumulated Amortization | | Net Carrying Amount |
| Developed technology | $ | 75,455 | | | $ | (39,411) | | | $ | 36,044 | |
| Patents | 14,200 | | | (650) | | | 13,550 | |
| Assembled workforce | 10,000 | | | (7,374) | | | 2,626 | |
| Trade name | 500 | | | (233) | | | 267 | |
| Total intangible assets | $ | 100,155 | | | $ | (47,668) | | | $ | 52,487 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| As of December 31, 2022 |
| Gross Carrying Amount | | Accumulated Amortization | | Net Carrying Amount |
| Developed technology | $ | 72,059 | | | $ | (24,240) | | | $ | 47,819 | |
| Assembled workforce | 10,000 | | | (4,042) | | | 5,958 | |
| Trade name | 500 | | | (133) | | | 367 | |
| Total intangible assets | $ | 82,559 | | | $ | (28,415) | | | $ | 54,144 | |
The above tables do not include $0.6 million of indefinite lived intangible assets as of December 31, 2023 and December 31, 2022.
As of December 31, 2023, the weighted-average remaining useful lives of our finite-lived intangible assets were 2.4 years for developed technology, 8.7 years for patents, 0.8 years for assembled workforce, 2.7 years for trade names, and 3.2 years in total, for all finite-lived intangible assets.
Amortization expense related to our finite-lived intangible assets was $19.3 million, $16.4 million, and $10.8 million for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022, and 2021, respectively.
Expected future amortization expenses related to the intangible assets as of December 31, 2023 are as follows (in thousands):
| | | | | |
| Year ending December 31: | |
| 2024 | $ | 18,954 | |
| 2025 | 15,727 | |
| 2026 | 6,692 | |
| 2027 | 3,129 | |
| 2028 | 1,934 | |
| Thereafter | 6,051 | |
| Total remaining amortization | $ | 52,487 | |
7. Other Balance Sheet Components
Prepaid expenses and other current assets
Prepaid expenses and other current assets consisted of the following (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| As of December 31, |
| 2023 | | 2022 |
| Prepaid expenses | $ | 48,555 | | | $ | 45,173 | |
| Accrued interest receivable | 14,697 | | | 6,026 | |
| Other current assets | 11,297 | | | 10,442 | |
| Total prepaid expenses and other current assets | $ | 74,549 | | | $ | 61,641 | |
Property and equipment, net
Property and equipment, net, consisted of the following (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| As of December 31, |
| 2023 | | 2022 |
| Servers and related equipment and software | $ | 914,989 | | | $ | 741,418 | |
| Computer hardware and software licenses | 43,732 | | | 23,647 | |
| Furniture and fixtures | 520 | | | 446 | |
| Leasehold improvements | 101,785 | | | 69,311 | |
| Construction in progress | 77,043 | | | 24,306 | |
| Total property and equipment | 1,138,069 | | | 859,128 | |
| Less accumulated depreciation and amortization | (442,709) | | | (266,782) | |
| Property and equipment—net | $ | 695,360 | | | $ | 592,346 | |
Construction in progress primarily relates to leasehold improvements for the Company’s leased office buildings and network equipment infrastructure to support the Company’s data centers.
Depreciation and amortization expense of property and equipment was $188.9 million, $113.7 million, and $64.9 million for years ended December 31, 2023, 2022, and 2021, respectively.
Accrued expenses and other current liabilities
Accrued expenses and other current liabilities consisted of the following (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| As of December 31, |
| 2023 | | 2022 |
| Accrued operating expenses | $ | 51,921 | | | $ | 80,122 | |
| Short term operating lease liabilities | 111,293 | | | 73,235 | |
| Accrued interest on the 2030 Notes | 6,458 | | | 6,458 | |
| Taxes payable | 59,632 | | | 49,361 | |
| Accrued compensation and other employee related liabilities | 32,125 | | | 21,003 | |
| Other current liabilities | 9,692 | | | 5,827 | |
| Total accrued expenses and other current liabilities | $ | 271,121 | | | $ | 236,006 | |
8. Debt
2030 Notes
On October 29, 2021, the Company issued $1.0 billion aggregate principal amount of its 3.875% Senior Notes due 2030 (the “2030 Notes”). The 2030 Notes mature on May 1, 2030. The 2030 Notes bear interest at a rate of 3.875% per annum. Interest on the 2030 Notes is payable semi-annually in arrears on May 1 and November 1 of each year, commencing on May 1, 2022.
The aggregate proceeds from offering of the 2030 Notes were approximately $987.5 million, after deducting lenders costs and other issuance costs incurred by the Company. The issuance costs of $12.5 million are amortized into interest expense using the effective interest method over the term of the 2030 Notes.
The Company may voluntarily redeem the 2030 Notes, in whole or in part, under the following circumstances:
(1)at any time prior to November 1, 2024, the Company may on any one or more occasions redeem up to 40% of the aggregate principal amount of the 2030 Notes at a redemption price of 103.875% of the principal amount including accrued and unpaid interest, if any, with the net cash proceeds of certain equity offerings; provided that (1) at least 50% of the aggregate principal amount of 2030 Notes originally issued remains outstanding immediately after the occurrence of such redemption (excluding 2030 Notes held by the Company and its subsidiaries); and (2) the redemption occurs within 180 days of the date of the closing of such equity offerings.
(2)on or after November 1, 2024, the Company may redeem all or a part of the 2030 Notes at the following redemption prices (expressed as percentages of principal amount), plus accrued and unpaid interest, if any, to, but excluding, the applicable redemption date:
| | | | | | | | |
| Year | | Percentage |
| 2024 | | 101.938 | % |
| 2025 | | 100.969 | % |
| 2026 and thereafter | | 100.000 | % |
(3)at any time prior to November 1, 2024, the Company may redeem all or a part of the 2030 Notes at a redemption price equal to 100% of the principal amount of 2030 Notes redeemed, including accrued and unpaid interest, if any, plus the applicable “make-whole” premium set forth in the indenture governing the 2030 Notes (the “Indenture”) as of the date of such redemption; and
(4)in connection with any tender offer for the 2030 Notes, including an offer to purchase (as defined in the Indenture), if holders of not less than 90% in aggregate principal amount of the outstanding 2030 Notes validly tender and do not withdraw such notes in such tender offer and the Company (or any third party making such a tender offer in lieu of the Company) purchases all of the 2030 Notes validly tendered and not withdrawn by such holders, the Company (or such third party) will have the right, upon not less than 10, but not more than 60 days’ prior notice, given not more than 30 days following such purchase date to the holders of the 2030 Notes and the trustee, to redeem all of the 2030 Notes that remain outstanding following such purchase at a redemption price equal to the price offered to each holder of 2030 Notes (excluding any early tender or incentive fee) in such tender offer plus to the extent not included in the tender offer payment, accrued and unpaid interest, if any.
In certain circumstances involving a change of control triggering event (as defined in the Indenture), the Company will be required to make an offer to repurchase all, or at the holder’s option, any part, of each holder’s 2030 Notes at a repurchase price equal to 101% of the principal amount, plus accrued and unpaid interest, if any, to the applicable repurchase date.
The 2030 Notes are unsecured obligations and the Indenture contains covenants limiting the Company and its subsidiaries’ ability to: (i) create certain liens and enter into sale and lease-back transactions; (ii) create, assume, incur or guarantee certain indebtedness; or (iii) consolidate or merge with or into, or sell or otherwise dispose of all of substantially all of the Company and its subsidiaries’ assets to another person. These covenants are subject to a number of limitations and exceptions set forth in the Indenture and non-compliance with these covenants may result in the accelerated repayment of the 2030 Notes and any accrued and unpaid interest.
As of December 31, 2023, the Company was in compliance with all of its covenants under the Indenture.
The net carrying amount of the 2030 Notes, which is presented as a component of long-term debt in the Company’s consolidated financial statements, was as follows (in thousands): | | | | | | | | | | | |
| As of December 31, |
| 2023 | | 2022 |
| 2030 Notes | | | |
| Principal | $ | 1,000,000 | | | $ | 1,000,000 | |
| Unamortized issuance costs | (9,700) | | | (11,016) | |
| Net carrying amount | $ | 990,300 | | | $ | 988,984 | |
Interest expense related to the 2030 Notes was as follows (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| Contractual interest expense | $ | 38,750 | | | $ | 38,642 | | | $ | 6,781 | |
| Amortization of debt issuance costs | 1,316 | | | 1,261 | | | 216 | |
| Total interest expense | $ | 40,066 | | | $ | 39,903 | | | $ | 6,997 | |
The debt issuance costs for the 2030 Notes are amortized to interest expense over the term of the 2030 Notes using an annual effective interest rate of 4.05%.
As of December 31, 2023, and 2022, the estimated fair value of the 2030 Notes was approximately $891.8 million and $788.2 million, respectively, determined based on the last trading price of the 2030 Notes during the reporting period (a Level 2 input).
Future interest and principal payments related to the 2030 Notes, as of December 31, 2023, were as follows (in thousands):
| | | | | |
| Year ending December 31, | |
| 2024 | $ | 38,750 | |
| 2025 | 38,750 | |
| 2026 | 38,750 | |
| 2027 | 38,750 | |
| 2028 | 38,750 | |
| Thereafter | 1,058,120 | |
| Total future interest and principal payments related to the 2030 Notes | $ | 1,251,870 | |
Joint Venture Financing
Refer to Note 15, “Joint Venture”, in the notes to the consolidated financial statements for additional information on debt issued by the Company’s consolidated subsidiary, Roblox China Holding Corp.
9. Commitments and Contingencies
Purchase Obligations—Non-cancellable contractual purchase obligations, primarily related to the Company’s data center hosting providers and software vendors, as of December 31, 2023, are as follows (in thousands):
| | | | | |
| Year ending December 31, | |
| 2024 | $ | 223,201 | |
| 2025 | 157,973 | |
| 2026 | 78,117 | |
| 2027 | 261 | |
| 2028 | 209 | |
| Thereafter | — | |
| Total non-cancellable contractual purchase obligations | $ | 459,761 | |
Letters of Credit—The Company has letters of credit in connection with its operating leases which are not reflected in the Company’s consolidated balance sheets as of December 31, 2023 and 2022. The Company has not drawn down from the letters of credit and had $11.6 million and $9.9 million available in aggregate as of December 31, 2023 and 2022, respectively.
Legal Proceedings—The Company is and, from time to time may in the future become, involved in legal proceedings, claims and litigation in the ordinary course of business.
As of December 31, 2023 and 2022, the Company accrued for immaterial losses related to litigation matters that the Company believes to be probable and for which an amount of loss can be reasonably estimated. The Company considered the progress of these cases, the opinions and views of its legal counsel and outside advisors, its experience and settlements in similar cases, and other factors in arriving at the conclusion that a potential loss was probable. The Company cannot determine a reasonable estimate of the maximum possible loss or range of loss for all of these matters given that they are at various stages of the litigation process and each case is subject to the inherent uncertainties of litigation. The Company may incur substantial legal fees, which are expensed as incurred, in defending against these legal proceedings. The maximum amount of liability that may ultimately result from any of these matters cannot be predicted with absolute certainty and the ultimate resolution of one or more of these matters could ultimately have a material adverse effect on our operations.
Indemnification—In the ordinary course of business, the Company enters into agreements that may include indemnification provisions. Pursuant to such agreements, the Company may indemnify, hold harmless and defend an indemnified party for losses suffered or incurred by the indemnified party. Some of the provisions will limit losses to those arising from third-party actions. In some cases, the indemnification will continue after the termination of the agreement. The maximum potential amount of future payments the Company could be required to make under these provisions is not determinable. To date, the Company has not incurred material costs to defend lawsuits or settle claims related to these indemnification provisions.
The Company has also entered into indemnification agreements with its directors and officers that may require the Company to indemnify its directors and officers against liabilities that may arise by reason of their status or service as directors or officers to the fullest extent permitted by Delaware corporate law. To date, the Company has not incurred any material costs and has not accrued any liabilities related to such obligations. The Company also has directors’ and officers’ insurance.
10. Convertible Preferred Stock
In January 2021, the Company issued 11,888,886 shares of Series H convertible preferred stock to certain institutional accredited investors in a private placement at a purchase price of $45.00 per share for aggregate net proceeds of approximately $534.3 million. There was no underwriter or placement agent used in connection with this sale.
The Company previously issued Series A, Series B, Series C, Series D, Series D-1, Series E, Series F, and Series G prior to 2021. In November 2020, pursuant to a conversion notice and an exchange agreement with entities affiliated with the Company’s Founder, President, CEO and Chair of the Company’s Board of Directors, all outstanding convertible preferred stock held by those entities were converted into our Class A common stock and thereafter all 57.3 million outstanding shares of Class A common stock held by those entities were exchanged for 57.3 million shares of Class B common stock. The rights of the holders of Class A common stock and Class B common stock are identical, except with respect to voting and conversion.
Immediately prior to the completion of the direct listing of the Company’s Class A common stock (the “Direct Listing”) on the New York Stock Exchange, all outstanding shares of the Company’s convertible preferred stock converted into an aggregate of 349,123,976 shares of Class A common stock.
The following table summarizes the convertible preferred stock outstanding immediately prior to the conversion into common stock, and the rights and preferences of the Company’s respective series preceding the Direct Listing in March 2021 (in thousands except per share data):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Series | Shares | | Per share
price
at issuance | | Per share
conversion
price | | Aggregate
Liquidation
Preference | | Carrying
Value of
Preferred |
| Authorized | | Outstanding | |
| A | 28,000 | | | 16,358 | | | $ | 0.02 | | | $ | 0.02 | | | $ | 327 | | | $ | 313 | |
| B | 45,532 | | | 45,532 | | | $ | 0.03 | | | $ | 0.03 | | | 1,070 | | | 1,054 | |
| C | 95,290 | | | 95,290 | | | $ | 0.03 | | | $ | 0.03 | | | 2,935 | | | 4,150 | |
| D | 54,860 | | | 54,215 | | | $ | 0.04 | | | $ | 0.04 | | | 2,150 | | | 2,097 | |
| D-1 | 44,706 | | | 44,706 | | | $ | 0.09 | | | $ | 0.09 | | | 4,172 | | | 12,998 | |
| E | 24,340 | | | 24,340 | | | $ | 1.03 | | | $ | 1.03 | | | 25,000 | | | 24,906 | |
| F | 33,149 | | | 33,149 | | | $ | 4.53 | | | $ | 4.53 | | | 150,000 | | | 149,640 | |
| G | 23,645 | | | 23,645 | | | $ | 6.34 | | | $ | 6.34 | | | 150,000 | | | 149,669 | |
| H | 12,222 | | | 11,889 | | | $ | 45.00 | | | $ | 45.00 | | | 535,000 | | | 534,286 | |
| Total | 361,744 | | | 349,124 | | | | | | | $ | 870,654 | | | $ | 879,113 | |
The following table summarizes the convertible preferred stock outstanding prior to the conversion into common stock, and the rights and preferences of the Company’s respective series as of December 31, 2020 (in thousands except per share data):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Series |
Shares | | Per share
price
at issuance | | Per share
conversion
price | | Aggregate
Liquidation
Preference | | Carrying
Value of
Preferred |
| Authorized | | Outstanding | |
| A | 28,000 | | | 16,358 | | | $ | 0.02 | | | $ | 0.02 | | | $ | 327 | | | $ | 313 | |
| B | 45,532 | | | 45,532 | | | $ | 0.03 | | | $ | 0.03 | | | 1,070 | | | 1,054 | |
| C | 95,290 | | | 95,290 | | | $ | 0.03 | | | $ | 0.03 | | | 2,935 | | | 4,150 | |
| D | 54,860 | | | 54,215 | | | $ | 0.04 | | | $ | 0.04 | | | 2,150 | | | 2,097 | |
| D-1 | 44,706 | | | 44,706 | | | $ | 0.09 | | | $ | 0.09 | | | 4,172 | | | 12,998 | |
| E | 24,340 | | | 24,340 | | | $ | 1.03 | | | $ | 1.03 | | | 25,000 | | | 24,906 | |
| F | 33,149 | | | 33,149 | | | $ | 4.53 | | | $ | 4.53 | | | 150,000 | | | 149,640 | |
| G | 23,645 | | | 23,645 | | | $ | 6.34 | | | $ | 6.34 | | | 150,000 | | | 149,669 | |
| Total | 349,522 | | | 337,235 | | | | | | | $ | 335,654 | | | $ | 344,827 | |
11. Stockholders’ Equity (Deficit)
Preferred Stock —The Company’s amended and restated certificate of incorporation authorizes the issuance of 100.0 million shares of convertible preferred stock with a par value of $0.0001 per share.
Common Stock —The Company’s amended and restated certificate of incorporation authorizes the issuance of Class A common stock and Class B common stock. As of December 31, 2023, the Company is authorized to issue 4,935.0 million shares of Class A common stock and 65.0 million shares of Class B common stock. Holders of Class A common stock and Class B common stock are entitled to dividends on a pro rata basis, when, as, and if declared by the Company’s Board of Directors, subject to the rights of the holders of the Company’s convertible preferred stock. Holders of Class A common stock are entitled to one vote per share, and holders of Class B common stock are entitled to 20 votes per share. Each share of our Class B common stock is convertible into one share of our Class A common stock at any time and will convert automatically upon certain transfers and upon the earliest of (i) the date that is specified by the affirmative vote of the holders of two-thirds of the then-outstanding shares of Class B common stock, (ii) the date on which less than 30% of the Class B common stock that was outstanding on March 2, 2021 continues to remain outstanding, (iii) March 10, 2036, (iv) nine months after the death or permanent disability of Mr. David Baszucki, and (v) nine months after the date on which Mr. Baszucki no longer serves as our CEO or as a member of our Board of Directors. Class A common stock and Class B common stock are not redeemable at the option of the holder.
During the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2021, 1.3 million and 6.0 million shares of Class B common stock held by entities affiliated with Mr. Baszucki, Founder, President, CEO, and Chair of our Board of Directors were converted to Class A common stock, respectively.
Class A and Class B common stock are referred to as common stock throughout the notes to the consolidated financial statements, unless otherwise noted.
The Company reserved shares of common stock for future issuance as follows (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| As of December 31, |
| 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| Stock options outstanding | 40,159 | | | 51,591 | | | 63,267 | |
| RSUs outstanding | 39,846 | | | 30,322 | | | 14,684 | |
| PSUs | 905 | | | 415 | | | — | |
| CEO Long-Term Performance Award | 11,500 | | | 11,500 | | | 11,500 | |
| 2020 Equity Incentive Plan | 66,114 | | | 59,945 | | | 52,811 | |
| 2020 Employee Stock Purchase Plan | 16,075 | | | 11,093 | | | 5,809 | |
| Stock warrants outstanding | 264 | | | 264 | | | 324 | |
| RSAs outstanding | 149 | | | 500 | | | 468 | |
| Total | 175,012 | | | 165,630 | | | 148,863 | |
12. Stock-Based Compensation Expense
2004 Incentive Stock Plan
In 2004, the Company approved the 2004 Incentive Stock Plan (the “2004 Plan”), under which the Board of Directors may grant incentive stock options to employees and nonstatutory stock options to employees, members of the Board of Directors and consultants of the Company and its subsidiaries.
Under the 2004 Plan, incentive stock options and nonstatutory stock options may be granted at a price not less than fair value and 85% of the fair value, respectively (110% of fair value for incentive stock options granted to holders of 10% or more of voting stock). Fair value is determined by the Board of Directors. Options are exercisable over periods not to exceed 10 years (five years for incentive stock options granted to holders of 10% or more of the voting stock) from the date of grant.
The 2004 Plan was terminated on the effective date of the 2017 Amended and Restated Equity Incentive Plan, and accordingly, no shares are available for issuance under the 2004 Plan. The 2004 Plan continues to govern outstanding awards granted thereunder.
2017 Amended and Restated Equity Incentive Plan
In 2017, the Company approved the 2017 Amended and Restated Equity Incentive Plan (the “2017 Plan”), under which the Board of Directors may grant incentive stock options to employees and nonstatutory stock options, stock appreciation rights, restricted stock, and RSUs, to employees, members of the Board of Directors and consultants of the Company and its subsidiaries.
Under the 2017 Plan, incentive stock options and nonstatutory stock options may be granted at a price not less than fair value (110% of fair value for options issued to holders of 10% or more of voting stock). Stock appreciation rights may be granted at a price not less than fair value. Fair value is determined by the Board of Directors. Options are exercisable over periods not to exceed 10 years (five years for incentive stock options granted to holders of 10% or more of the voting stock) from the date of grant.
In connection with the Direct Listing, the 2017 Plan was terminated effective immediately prior to the effectiveness of the 2020 Equity Incentive Plan, and accordingly, no shares are available for issuance under the 2017 Plan. The 2017 Plan continues to govern outstanding awards granted thereunder.
2020 Equity Incentive Plan
In 2020, the Company’s Board of Directors adopted, and its stockholders approved, the 2020 Equity Incentive Plan (the “2020 Plan”), which became effective on the business day immediately prior to the effective date of the registration statement for the Company’s Direct Listing. Under the 2020 Plan, the Board of Directors may grant incentive stock options to employees and stock appreciation rights, RSAs, and RSUs, performance units and performance shares to employees, members of the Board of Directors and consultants of the Company and its subsidiaries.
Under the 2020 Plan, incentive stock options, nonstatutory stock options, and stock appreciation rights may be granted at a price not less than 100% of the fair market value of the underlying common stock on the date of grant (110% of fair value for incentive stock options issued to holders of 10% or more of voting stock). Options and stock appreciation rights are exercisable over a period not to exceed 10 years (five years for incentive stock options granted to holders of 10% or more of the voting stock) from the date of grant.
Under the 2020 Plan, 60.0 million shares of Class A common stock were initially reserved for future issuance. The number of shares of our Class A common stock reserved for future issuance under our 2020 Plan automatically increases on January 1 of each year by the least of (i) 75.0 million shares; (ii) five percent (5%) of the outstanding shares of all classes of the Company’s common stock as of December 31 of the preceding fiscal year; or (iii) a number of shares that may be determined by the Company’s Board of Directors. Stock-based awards under the 2020 Plan that expire or are forfeited, cancelled, or repurchased generally are returned to the pool of shares of Class A common stock available for issuance under the 2020 Plan. In addition, subject to the adjustment provisions of the 2020 Plan, the shares reserved for issuance under the 2020 Plan also includes (i) any shares that, as of the day immediately prior to the effective date of the registration statement, have been reserved but not issued pursuant to any awards granted under the 2017 Plan and are not subject to any awards thereunder and (ii) any shares subject to stock options, RSUs or similar awards granted under our 2017 Plan and 2004 Plan that, after the effective date of the registration statement, expire or otherwise terminate without having been exercised or issued in full, are tendered to or withheld by the Company for payment of an exercise price or for tax withholding obligations, or are forfeited to or repurchased by the Company due to failure to vest.
Employee Stock Purchase Plan
In 2020, the Company’s Board of Directors adopted, and its stockholders approved, the 2020 Employee Stock Purchase Plan (the “2020 ESPP”), which became effective in connection with the Direct Listing. The 2020 ESPP authorizes the issuance of shares of common stock pursuant to purchase rights granted to employees. At inception, 6.0 million shares of the Company’s Class A common stock were reserved for future issuance under the 2020 ESPP. The number of shares of our Class A common stock reserved for future issuance under our 2020 ESPP automatically increases on January 1 of each year by the least of (i) 15.0 million shares; (ii) one percent (1%) of the outstanding shares of all classes of the Company’s common stock as of December 31 of the preceding fiscal year; or (iii) a number of shares that may be determined by the Company’s Board of Directors
The 2020 ESPP plan is a compensatory plan and includes two components: a component that allows the Company to make offerings intended to qualify under Section 423 of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986 (the “Code”) and a component that allows the Company to make offerings not intended to qualify under Section 423 of the Code. Subject to any limitations contained therein, the 2020 ESPP allows eligible employees to contribute (in the form of payroll deductions or otherwise to the extent permitted by the administrator) an amount established by the administrator from time to time in its discretion to purchase Class A common stock at a discounted price per share. The price at which Class A common stock is purchased under the 2020 ESPP is equal to 85% of the fair market value of a share of the Company’s Class A common stock on the enrollment date or exercise date, whichever is lower. Offering periods are generally 24 months long and begin on the first trading day on or after February 25 and August 25 of each year with each offering period having four purchase periods of approximately six months each.
Stock-based compensation expense
Stock-based compensation expense included in the consolidated statements of operations was as follows (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| Infrastructure and trust & safety | $ | 92,147 | | | $ | 56,197 | | | $ | 35,255 | |
| Research and development | 607,593 | | | 398,899 | | | 219,851 | |
| General and administrative | 131,577 | | | 109,607 | | | 72,929 | |
| Sales and marketing | 36,650 | | | 24,795 | | | 13,907 | |
| Total stock-based compensation expense | $ | 867,967 | | | $ | 589,498 | | | $ | 341,942 | |
Stock Options
The following table summarizes the Company’s stock option activity (in thousands, except per option data and remaining contractual term):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Options Outstanding |
| Number of
Shares
Subject to
Options | | Weighted-
Average
Exercise
Price (per Option) | | Weighted-Average Remaining
Contractual
Term
(Years) | | Aggregate Intrinsic Value |
| Balances as of December 31, 2020 | 98,502 | | | $ | 2.55 | | | 7.76 | | $ | 3,838,994 | |
| Granted | — | | | — | | | | | |
| Cancelled, forfeited, and expired | (1,862) | | | $ | 3.95 | | | | | |
| Exercised | (33,373) | | | $ | 1.95 | | | | | |
| Balances as of December 31, 2021 | 63,267 | | | $ | 2.82 | | | 6.97 | | $ | 6,348,395 | |
| Granted | — | | | — | | | | | |
| Cancelled, forfeited, and expired | (2,061) | | | $ | 4.06 | | | | | |
| Exercised | (9,615) | | | $ | 2.37 | | | | | |
| Balances as of December 31, 2022 | 51,591 | | | $ | 2.85 | | | 6.00 | | $ | 1,321,183 | |
| Granted | — | | | — | | | | | |
| Cancelled, forfeited, and expired | (762) | | | $ | 4.60 | | | | | |
| Exercised | (10,670) | | | $ | 2.23 | | | | | |
| Balances as of December 31, 2023 | 40,159 | | | $ | 2.98 | | | 5.16 | | $ | 1,716,171 | |
| Exercisable as of December 31, 2023 | 37,753 | | | $ | 2.86 | | | 5.08 | | $ | 1,618,078 | |
| Vested and expected to vest at December 31, 2023 | 40,159 | | | $ | 2.98 | | | 5.16 | | $ | 1,716,171 | |
The aggregate intrinsic value of options exercised for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022, and 2021 was $373.4 million, $423.3 million, and $2,548.3 million, respectively. Aggregate intrinsic value represents the difference between the exercise price of the options and the estimated fair value of the Company’s Class A common stock at the time of exercise. The aggregate grant-date fair value of options that vested during the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022, and 2021 was $51.9 million, $64.1 million, and $79.9 million, respectively.
As of December 31, 2023, the Company had $26.9 million of unrecognized stock-based compensation related to unvested options, which is expected to be recognized over a weighted-average remaining requisite service period of 1.0 year.
RSUs and RSAs
The following table summarizes the Company’s RSU and RSA activity (in thousands, except per share data):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Restricted Stock Units | | Unregistered Restricted Stock Awards |
| Number of
Shares | | Weighted-
Average
Grant Date
Value per Share | | Number of
Shares | | Weighted-
Average
Grant Date
Value per Share |
| Unvested as of December 31, 2020 | 3,061 | | | $ | 31.55 | | | 388 | | | $ | 37.75 | |
| Granted | 13,382 | | | $ | 78.92 | | | 209 | | | $ | 81.67 | |
| Vested and released | (1,376) | | | $ | 38.46 | | | (129) | | | $ | 37.75 | |
| Cancelled | (383) | | | $ | 52.78 | | | — | | | — | |
| Unvested as of December 31, 2021 | 14,684 | | | $ | 68.03 | | | 468 | | | $ | 57.37 | |
| Granted | 25,540 | | | $ | 41.09 | | | 298 | | | $ | 46.00 | |
| Vested and released | (8,169) | | | $ | 57.65 | | | (266) | | | $ | 53.67 | |
| Cancelled | (1,733) | | | $ | 57.58 | | | — | | | — | |
| Unvested as of December 31, 2022 | 30,322 | | | $ | 48.73 | | | 500 | | | $ | 52.55 | |
| Granted | 27,377 | | | $ | 37.59 | | | — | | | — | |
| Vested and released | (14,812) | | | $ | 45.97 | | | (351) | | | $ | 55.31 | |
| Cancelled | (3,041) | | | $ | 46.79 | | | — | | | — | |
| Unvested as of December 31, 2023 | 39,846 | | | $ | 42.25 | | | 149 | | | $ | 46.00 | |
As of December 31, 2023, the Company had $1,588.0 million of unrecognized stock-based compensation related to RSUs, which is expected to be recognized over the weighted-average remaining requisite service period of 2.2 years.
RSUs granted prior to our Direct Listing vest upon the satisfaction of both the service condition and a liquidity event-related performance vesting condition which was satisfied on the Effective Date. In the first quarter of 2021, we recorded cumulative stock-based compensation expense of $21.3 million related to all then-outstanding RSUs for which the service-based vesting condition had been satisfied. Stock-based compensation related to the remaining service-based period after the liquidity event-related performance vesting condition was satisfied is being recorded over the remaining requisite service period using the accelerated attribution method.
RSUs granted subsequent to our Direct Listing only have service conditions, which historically have been satisfied generally over four years. For grants made during and subsequent to July 2022, the service condition is satisfied generally over three years.
As of December 31, 2023, the Company had $3.2 million of unrecognized stock-based compensation related to RSAs, which is expected to be recognized over the weighted average remaining requisite service period of 1.3 years.
CEO Long-Term Performance Award
In February 2021, the Leadership Development and Compensation Committee granted the CEO Long-Term Performance Award under the 2017 Plan, which provides him the opportunity to earn a maximum number of 11,500,000 shares of Class A common stock. The CEO Long-Term Performance Award vests upon the satisfaction of a service condition and achievement of certain Class A common stock price targets (referred to as a “Company Stock Price Hurdle”), as described below.
The CEO Long-Term Performance Award is eligible to vest based on the Company’s stock price performance over various performance periods, with the first performance period beginning two years after the Effective Date and ending on the seventh anniversary of the Effective Date. The CEO Long-Term Performance Award is divided into seven performance periods that are eligible to vest based on the achievement of various Company Stock Price Hurdles, measured based on an average of our stock price over a consecutive 90-day trading period applicable to the performance period. In addition, Mr. Baszucki must remain employed as our CEO through the date a Company Stock Price Hurdle is achieved in order to earn the RSUs that relate to the applicable Company Stock Price Hurdle. The following table summarizes the various Company Stock Price Hurdles and associated RSUs eligible to vest over each performance period (in thousands, except Company Stock Price Hurdles):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Company Stock Price Hurdle | | Number of RSUs Eligible to Vest | | Performance Period Commencement Dates as Measured from the Effective Date |
| 1 | $ | 165.00 | | | 750 | | | 2 years |
| 2 | $ | 200.00 | | | 750 | | | 3 years |
| 3 | $ | 235.00 | | | 2,000 | | | 4 years |
| 4 | $ | 270.00 | | | 2,000 | | | 5 years |
| 5 | $ | 305.00 | | | 2,000 | | | 5 years |
| 6 | $ | 340.00 | | | 2,000 | | | 5 years |
| 7 | $ | 375.00 | | | 2,000 | | | 5 years |
If the Company Stock Price Hurdle fails to reach $165.00 prior to the seventh anniversary of the Effective Date, no portion of the CEO Long-Term Performance Award will vest. Further, any RSUs associated with a Company Stock Price Hurdle not achieved by the seventh anniversary of the Effective Date will terminate and be cancelled for no additional consideration to Mr. Baszucki. The Company Stock Price Hurdles and number of RSUs eligible to vest will be adjusted to reflect any stock splits, stock dividends, combinations, reorganizations, reclassifications, or similar events under the 2017 Plan. Each vested RSU under the CEO Long-Term Performance Award will be settled in a share of our Class A common stock on the next company quarterly settlement date occurring on or after the date on which the RSU vests, regardless of whether Mr. Baszucki remains the CEO as of such date. Company quarterly settlement dates for this purpose are February 20, May 20, August 20, and November 20.
The Company estimated the grant date fair value of the CEO Long-Term Performance Award using a model based on multiple stock price outcomes developed through the use of a Monte Carlo simulation that incorporates into the valuation the possibility that the Company Stock Price Hurdles may not be satisfied. A Monte Carlo simulation model requires use of various assumptions, including the underlying stock price, volatility, and the risk-free interest rate as of the valuation date, corresponding to the length of time remaining in the performance period, and expected dividend yield. The weighted-average grant date fair value of the CEO Long-Term Performance Award was estimated to be $20.19 per share, and the Company estimates that as of the grant date, it will recognize total stock-based compensation expense of approximately $232.2 million over the derived service period of each of the seven separate tranches which is between 3.45 – 5.38 years, using the accelerated attribution method. If the Company Stock Price Hurdles are met sooner than the derived service period, the stock-based compensation expense will be adjusted to reflect the cumulative expense associated with the vested award. The stock-based compensation expense will be recognized over the requisite service period if Mr. Baszucki provides service as the Company’s CEO, regardless of whether the Company Stock Price Hurdles are achieved.
The Company recorded $48.9 million, $48.9 million, and $42.0 million of stock-based compensation expense related to the CEO Long-Term Performance Award during the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022, and 2021, respectively, within general and administrative expenses. As of December 31, 2023, unrecognized stock-based compensation expense related to the CEO Long-Term Performance Award was $92.4 million which will be recognized over the remaining derived service period of each respective tranche.
PSUs
2023 PSU Grants
During the second quarter of 2023, the Leadership Development and Compensation Committee granted performance-based restricted stock unit awards (the “2023 PSU Grants”), to certain members of management. The number of shares that can be earned will range from 0% to 200% of the target number of shares, based on the Company’s performance against two independent performance measures relative to pre-established thresholds during a two-year performance period ending on December 31, 2024. The two independent performance measures include the Company’s cumulative (i) bookings and (ii) Covenant Adjusted EBITDA during the performance period, as those performance measures are defined in the respective grant agreements with each employee. Further, the awards are subject to continuous employment, with the first vesting to occur in the first quarter of 2025 (in which 50% of any awards earned will vest) and the second vesting to occur in the second quarter of 2026 (in which the remaining 50% of any awards earned will vest).
As of December 31, 2023, the number of shares under the 2023 PSU Grants that can be earned at target performance totaled 277,361, with 80% of the target number of shares allocated to the cumulative bookings performance measure and 20% of the target number of shares allocated to the Covenant Adjusted EBITDA performance measure.
The Company recognizes stock-based compensation expense for the 2023 PSU Grants based upon the per-share grant date fair value of $45.70 on an accelerated attribution method over the requisite service period of each separately vesting tranche. At each reporting period, the amount of stock-based compensation is determined based on the probability of achievement against the pre-established performance measures and if necessary, a cumulative catch-up adjustment is recorded to reflect any revised estimates regarding the probability of achievement.
The Company recorded $6.4 million of stock-based compensation expense related to the 2023 PSU Grants during the year ended December 31, 2023. Based on the expected probability of achievement against the pre-established performance measures as of December 31, 2023, unrecognized stock-based compensation expense related to the 2023 PSU Grants was $12.8 million as of December 31, 2023, which is expected to be recognized over the remaining derived service period of each respective tranche.
2022 PSU Grants
During the second quarter of 2022, the Leadership Development and Compensation Committee granted performance-based restricted stock unit awards (the “2022 PSU Grants”), to certain members of management. On the grant date, the target number of 2022 PSU Grants was 207,284. The number of shares that can be earned will range from 0% to 200% of the target number of shares, based on the Company’s stock price performance and achievement of certain stock price hurdles during the last quarter of the second year through the end of the third year of a three-year performance period (the “2022 PSU Grant Stock Price Hurdles”) and subject to continuous employment through such date.
The Company estimated the grant date fair value of the 2022 PSU Grants using a model based on multiple stock price outcomes developed through the use of a Monte Carlo simulation which incorporates into the valuation the possibility that the 2022 PSU Grant Stock Price Hurdles may not be satisfied. The grant date fair value of the 2022 PSU Grants was estimated to be $43.13 per share, and the Company estimates that it will recognize total stock-based compensation expense of approximately $7.5 million using the accelerated attribution method over the derived service period of each tranche which is equal to five measurement periods commencing with the last quarter of the second year and ending with the last quarter of the third year. If the 2022 PSU Grant Stock Price Hurdles are met sooner than the derived service period, the stock-based compensation expense will be adjusted to reflect the cumulative expense associated with the vested award. Stock-based compensation expense will be recognized over the requisite service period if the members of management continue to provide service to the Company, regardless of whether the 2022 PSU Grant Stock Price Hurdles are achieved.
The Company recorded $3.2 million and $3.0 million of stock-based compensation expense related to the 2022 PSU Grants during the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022, respectively. As of December 31, 2023, unrecognized stock-based compensation expense related to the 2022 PSU grants was $1.3 million which will be recognized over the remaining derived service period of each of five tranches.
Employee Stock Purchase Plan
The following table presents the assumptions used in estimating the grant date fair value of purchase rights granted under the 2020 ESPP for the offerings made in the respective years including reset and rollover:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, |
| | 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| Risk-free interest rate | 4.78% | - | 5.61% | | 0.71% | - | 3.35% | | 0.06% | - | 0.25% |
| Expected volatility | 47.92% | - | 75.99% | | 54.16% | - | 81.51% | | 46.97% | - | 56.91% |
| Dividend yield | —% | | —% | | —% |
| Expected terms (in years) | 0.49 | - | 2.00 | | 0.50 | - | 2.01 | | 0.44 | - | 2.00 |
The Company recorded $32.0 million, $25.7 million, and $9.9 million of stock-based compensation expense related to the 2020 ESPP during the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022, and 2021, respectively.
13. Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income (Loss)
The following table shows a summary of changes in accumulated other comprehensive income/(loss) by component for the periods presented (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Foreign Currency Translation | | Unrealized Gains/(Losses) on Available-For-Sale Debt Securities | | Total |
| Balance as of December 31, 2021 | $ | 62 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 62 | |
| Other comprehensive income/(loss) before reclassifications | 609 | | | — | | | 609 | |
| Amounts reclassified from accumulated other comprehensive income/(loss) | — | | | — | | | — | |
| Change in accumulated other comprehensive income/(loss), net of tax | 609 | | | — | | | 609 | |
| Balance as of December 31, 2022 | $ | 671 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 671 | |
| Other comprehensive income/(loss) before reclassifications | 771 | | | (1,845) | | | (1,074) | |
| Amounts reclassified from accumulated other comprehensive income/(loss) | — | | | 1,939 | | | 1,939 | |
| Change in accumulated other comprehensive income/(loss), net of tax | 771 | | | 94 | | | 865 | |
| Balance as of December 31, 2023 | $ | 1,442 | | | $ | 94 | | | $ | 1,536 | |
14. Employee and Director Benefits
Defined Contribution Plan
The Company sponsors a 401(k) defined contribution retirement plan for eligible employees. For the year ended December 31, 2023, the Company matched 100% of all employee contributions, up to 50% of the Internal Revenue Service (“IRS”) deferral limit. For the years ended December 31, 2022 and 2021, the Company matched 100% of the first 3% of employee contributions and 50% of the next 2% for each employee, subject to the maximum total contribution mandated by the IRS.
The Company made matching contributions in the amount of $24.9 million, $14.6 million, and $9.3 million for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022, and 2021, respectively.
Deferred Compensation Plan
The Company established the Roblox Corporation Nonqualified Deferred compensation Plan (as amended, the “NQDC Plan”) for its non-employee directors and a select group of management employees. Eligible participants may voluntarily elect to participate in the NQDC Plan. Unless otherwise determined by the committee that administers the NQDC Plan, eligible employee participants may elect annually to defer up to 90% of their base salary, up to 100% of their cash bonus compensation (if any), and up to 65% of any RSUs or PSUs granted under the Company’s 2020 Plan (if any), and eligible non-employee director participants may elect annually to defer up to 100% of their cash director fees and any RSUs granted under the Company’s 2020 Plan. Obligations of the Company under the NQDC Plan represent at all times unsecured general obligations of the Company to pay deferred compensation in the future in accordance with the terms of the NQDC Plan.
Cash amounts deferred under the plan may only later be settled in cash and are credited or charged with the performance of investment options offered under the NQDC Plan as elected by the participants. The amount credited or charged to each participant’s cash deferrals are based on the performance of a hypothetical portfolio of investments which are tracked by an administrator, with such credits or charges included as a component of operating expenses in the Company’s consolidated statements of operations. The cash obligations due to participants are presented as other long-term liabilities on the Company’s consolidated balance sheet.
The Company generally funds the cash obligations associated with the NQDC Plan by purchasing investments that match the hypothetical investment choices made by the plan participants. The investments (and any uninvested cash) are held in a rabbi trust in order to receive certain tax benefits. The rabbi trust is subject to creditor claims in the event of insolvency, but the assets held in the rabbi trust are not available for general corporate purposes. The investments held in the rabbi trust are presented as short-term investments and any uninvested cash is presented as cash and cash equivalents on the Company’s consolidated balance sheet.
As it relates to any deferred RSUs and PSUs, the Company ensures enough shares of its Class A common stock are reserved to settle all obligations under the NQDC Plan. These obligations are settled on the date(s) elected by the participant. The accounting for the RSUs and PSUs deferred under the NQDC Plan is consistent with the accounting for non-deferred RSUs and PSUs.
15. Joint Venture
Background
In February 2019, the Company entered into a joint venture agreement with Songhua River Investment Limited (“Songhua”), an affiliate of Tencent Holdings Ltd. (“Tencent Holdings”), to create Roblox China Holding Corp. (in which Roblox holds a 51% ownership interest as it relates to the voting shares). Songhua contributed $50.0 million in capital in exchange for a 49% ownership interest in Roblox China Holding Corp. The business of the joint venture (either directly or indirectly through the joint venture’s wholly owned subsidiaries) is to engage in the (i) development, localization, and licensing of the Roblox application to Shenzhen Tencent Computer Systems Co., Ltd. for operation and publication as a game in China, and (ii) development, localization, and licensing to creators of a Chinese version of the Roblox Studio and to oversee relations with local Chinese developers.
The joint venture is consolidated into the Company’s consolidated financial statements as the Company maintains a controlling financial interest through voting rights, while the minority member of the joint venture does not have substantive participating rights or veto rights. The Company classifies the 49% ownership interest held by Songhua as a noncontrolling interest on its consolidated balance sheet.
Joint Venture Financing
On May 10, 2023, Roblox China Holding Corp. (the “Borrower”) issued $30.0 million aggregate principal debt which matures on May 10, 2026 (the “2026 Notes”), unless earlier prepaid by the Borrower or converted by the holders into the Borrower’s voting shares. Further, the Borrower, at its sole election, may extend the maturity date by two years.
The 2026 Notes were funded by the Company and Songhua (the “Lenders”) in the amount of $15.3 million and $14.7 million, respectively. The 2026 Notes bear interest at a rate of 6.0% per annum, with accrued interest payable on the final maturity date.
At any point, the Lenders may voluntarily convert the 2026 Notes into voting shares of the Borrower, provided that immediately after such conversion, the Lenders continue to own the same percentage of voting shares in the Borrower as they did immediately prior to the conversion. The conversion ratio will be determined at the time of such conversion (if any), and will be determined by dividing the then fair value of the Borrower’s voting shares (as mutually agreed to by the Lenders and Borrower) into the sum of the unpaid principal and accrued interest.
The portion of the 2026 Notes outstanding to Songhua is reflected in the Company’s consolidated financial statements as long-term debt, net, at its principal amount, while the portion outstanding to the Company – including any related interest expense – is eliminated upon consolidation. Interest expense related to the 2026 Notes was $0.5 million for the year ended December 31, 2023.
16. Income Taxes
The components of loss before income taxes were as follows (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| Domestic | $ | (1,151,493) | | | $ | (916,592) | | | $ | (472,141) | |
| Foreign | (6,990) | | | (13,997) | | | (31,659) | |
| $ | (1,158,483) | | | $ | (930,589) | | | $ | (503,800) | |
The components of the provision for/(benefit from) income taxes were as follows (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| Current provision: | | | | | |
| Federal | $ | (144) | | | $ | 144 | | | $ | — | |
| State | (561) | | | 2,405 | | | 678 | |
| Foreign | 1,255 | | | 1,582 | | | — | |
| Total current provision | 550 | | | 4,131�� | | | 678 | |
| Deferred provision: | | | | | |
| Federal | — | | | (474) | | | (878) | |
| State | — | | | (105) | | | (120) | |
| Foreign | (96) | | | — | | | — | |
| Total deferred provision | (96) | | | (579) | | | (998) | |
| Provision for/(benefit from) income taxes | $ | 454 | | | $ | 3,552 | | | $ | (320) | |
The provision for/(benefit from) income taxes differs from the amount estimated by applying the statutory income (loss) before taxes as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| Federal tax at statutory rate | 21 | % | | 21 | % | | 21 | % |
| State tax at statutory rate, net of federal benefit | 2 | | | 2 | | | 2 | |
| Research and development credits | 6 | | | 2 | | | 10 | |
| Change in valuation allowance | (27) | | | (21) | | | (117) | |
| Stock-based compensation | (3) | | | (4) | | | 84 | |
| Other | 1 | | | 0 | | | 0 | |
| Provision for/(benefit from) income taxes | 0 | % | | 0 | % | | 0 | % |
Deferred income taxes reflect the net tax effects of temporary differences between the carrying amounts of assets and liabilities for financial reporting purposes and the amounts used for income tax purposes. The following table presents the components of the Company’s deferred tax assets (liabilities) for the periods presented (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| Deferred tax assets: | | | | | |
| Accrued expenses | $ | 14,231 | | | $ | 13,593 | | | $ | 11,466 | |
| Deferred revenue | 246,144 | | | 198,130 | | | 107,221 | |
| Net operating loss carryforwards | 599,804 | | | 490,309 | | | 505,668 | |
| Tax credit carryforwards | 155,246 | | | 85,527 | | | 65,855 | |
| Stock-based compensation | 29,083 | | | 28,238 | | | 35,368 | |
| Operating lease liabilities | 176,007 | | | 130,688 | | | 56,897 | |
| Capitalized research and development | 366,898 | | | 178,488 | | | — | |
| Interest | — | | | — | | | 1,556 | |
| Other | 2,914 | | | 1,988 | | | 1,369 | |
| Total gross deferred tax asset | 1,590,327 | | | 1,126,961 | | | 785,400 | |
| Less: valuation allowance | (1,222,211) | | | (907,226) | | | (711,297) | |
| Net deferred tax assets | 368,116 | | | 219,735 | | | 74,103 | |
| Deferred tax liabilities: | | | | | |
| Fixed assets | (28,645) | | | (92,009) | | | (13,889) | |
| Intangible assets | (2,735) | | | (6,694) | | | (9,060) | |
| Operating lease right-of-use assets | (154,334) | | | (121,032) | | | (51,154) | |
| Deferred cost of revenue | (182,495) | | | — | | | — | |
| Total deferred tax liabilities | (368,209) | | | (219,735) | | | (74,103) | |
| Net deferred tax liabilities | $ | (93) | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | |
We have not provided U.S. income taxes or foreign withholding taxes on the undistributed earnings of our profitable foreign subsidiaries because we intend to permanently reinvest such earnings in foreign operations. As of December 31, 2023 and 2022, the cumulative amount of earnings upon which income taxes have not been provided is not material.
The Company accounts for deferred taxes under ASC 740, Income Taxes, which requires a reduction of the carrying amounts of deferred tax assets by a valuation allowance if, based on available evidence, it is more likely than not that such assets will not be realized. Accordingly, the need to establish valuation allowances for deferred tax assets is assessed periodically based on the ASC 740 more-likely-than-not realization threshold criterion. This assessment considers matters such as future reversals of existing taxable temporary differences, projected future taxable income, tax-planning strategies and results of recent operations. The evaluation of the recoverability of the deferred tax assets requires that we weigh all positive and negative evidence to reach a conclusion that it is more likely than not that all or some portion of the deferred tax assets will not be realized. The weight given to the evidence is commensurate with the extent to which it can be objectively verified. Due to our lack of U.S. earnings history, the net U.S. deferred tax assets have been fully offset by a valuation allowance. There are immaterial deferred tax assets and deferred tax liabilities in our foreign jurisdictions without valuation allowance.
The Company’s valuation allowance increased by $315.0 million, $195.9 million, and $589.0 million, in the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022, and 2021, respectively.
As of December 31, 2023, we had federal net operating loss carryforwards of $2,382.3 million, which do not expire, federal net operating loss carryforwards of $52.2 million, which begin to expire in 2035, state net operating loss carryforwards of $1,261.4 million, which begin to expire in 2024, and foreign net operating loss carryforwards of $66.8 million, which begin to expire in 2024.
As of December 31, 2023, we had U.S. federal and California research and development tax credits of approximately $201.3 million and $139.3 million, respectively. The federal research and development credits begin to expire in 2030, while California credits do not expire.
Under Internal Revenue Code Section 382 (“Section 382”), an ownership change generally occurs if one or more stockholders or groups of stockholders who own at least 5% of our stock increase their ownership by more than 50 percentage points over their lowest ownership percentage within a rolling three-year period. Similar rules may apply under state tax laws. The Company did experience one or more ownership changes in financial periods ending on or before December 31, 2023. In this regard, the Company has determined that based on the timing of the ownership change and the corresponding Section 382 limitations, none of its net operating losses or other tax attributes appear to expire subject to such limitation.
A reconciliation of the beginning and ending amounts of unrecognized tax benefits is as follows (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| As of December 31, |
| 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| Unrecognized tax benefits at beginning of year | $ | 96,372 | | | $ | 72,919 | | | $ | 19,386 | |
| Increases related to current year tax positions | 59,917 | | | 25,458 | | | 53,440 | |
| Increases related to prior year tax positions | 16,100 | | | 865 | | | 93 | |
| Decreases related to prior year tax positions | — | | | (2,870) | | | — | |
| Unrecognized tax benefits at end of year | $ | 172,389 | | | $ | 96,372 | | | $ | 72,919 | |
We classify uncertain tax positions as non-current liabilities unless expected to be paid within one year or otherwise directly related to an existing deferred tax asset, in which case the uncertain tax position is recorded as an offset to the deferred tax asset on the consolidated balance sheet. As of December 31, 2023, we had gross unrecognized tax benefits of approximately $172.4 million, of which $1.4 million would impact income tax expense if recognized. As of December 31, 2022, we had gross unrecognized tax benefits of approximately $96.4 million. The Company does not anticipate any significant change within twelve months of this reporting date.
Our policy is to recognize interest and penalties related to income taxes as components of interest expense and other expense, respectively. The Company accrued interest and penalties of $0.4 million and $0.2 million in the years ended December 31, 2023 and December 31, 2022, respectively. The Company did not accrue interest and penalties related to unrecognized tax benefits as of December 31, 2021.
The Company is subject to taxation in the United States, various states, and foreign jurisdictions. All tax years for U.S. federal and California tax returns currently remain open for examination by the tax authorities. As of December 31, 2023, we are no longer subject to foreign examinations by tax authorities for years before 2019. As of December 31, 2023, the Company is under examination in a foreign jurisdiction and is not under examination by the Internal Revenue Service or any state tax jurisdictions.
On January 1, 2022, a provision of the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017 eliminated the option to deduct research and development expenditures and instead requires taxpayers to amortize such costs over five years. This change did not have a significant impact to the Company’s provision for income tax for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 as the Company has net operating loss carryforwards to offset the impact of the change and maintains a full valuation allowance against its deferred tax assets. Further, the Company does not anticipate this change to have a significant impact to the provision for income tax for the year ended December 31, 2024 and will continue to evaluate the impact on its business in future periods.
17. Basic and Diluted Net Loss Per Common Share
The following table presents the calculation of basic and diluted net loss per share (in thousands, except per share data):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year ended December 31, |
| 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| Basic and diluted net loss per share | | | | | |
| Numerator | | | | | |
| Consolidated net loss | $ | (1,158,937) | | | $ | (934,141) | | | $ | (503,480) | |
| Less: net loss attributable to noncontrolling interests | (6,991) | | | (9,775) | | | (11,829) | |
| Net loss attributable to common stockholders | $ | (1,151,946) | | | $ | (924,366) | | | $ | (491,651) | |
| Denominator | | | | | |
| Weighted-average common shares used in computing net loss per share attributable to common stockholders, based and diluted | 616,445 | | | 595,559 | | | 505,858 | |
| Net loss per share attributable to common stockholders, basic and diluted | $ | (1.87) | | | $ | (1.55) | | | $ | (0.97) | |
The potential shares of common stock that were excluded from the computation of diluted net loss per share because including them would have been anti-dilutive are as follows (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year ended December 31, |
| 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| Stock options outstanding | 40,159 | | | 51,591 | | | 63,267 | |
| RSUs outstanding | 39,846 | | | 30,322 | | | 14,684 | |
| 2020 ESPP | 3,347 | | | 2,311 | | | 523 | |
2023 PSUs Grants based on performance target achievement at period-end(1) | 9 | | | — | | | — | |
| Stock warrants outstanding | 264 | | | 264 | | | 324 | |
| RSAs outstanding | 149 | | | 500 | | | 468 | |
| Total | 83,774 | | | 84,988 | | | 79,266 | |
(1)Represents the hypothetical number of shares that would have been earned under the Company’s 2023 PSU Grants had the performance period ended on the balance sheet date.
The CEO Long-Term Performance Award and 2022 PSU Grants were excluded from the above table because the respective stock price targets had not been met as of the periods presented.
18. Geographic Information
Long-lived assets, comprising property and equipment, net, by geographic area were as follows (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| As of December 31, |
| 2023 | | 2022 |
| United States | $ | 646,572 | | | $ | 553,127 | |
| Rest of world | 48,788 | | | 39,219 | |
| Total | $ | 695,360 | | | $ | 592,346 | |
19. Subsequent Events
On February 7, 2024, the Company executed a lease assignment as sub-lessee pursuant to which the Company will sublease approximately 133,137 square feet of office space in San Mateo, California for a lease term of approximately five years (the “2024 Sub-Lessee Agreement”). Concurrent with the execution of the 2024 Sub-Lessee Agreement, the Company executed a sublease as sub-lessor pursuant to which it will sublease approximately 61,773 square feet of its San Mateo, California corporate headquarters to the sub-lessee for a lease term of approximately 3 years (the “2024 Sub-Lessor Agreement”). Both the 2024 Sub-Lessee Agreement and 2024 Sub-Lessor Agreement are contingent upon each respective landlord’s consent, amongst other contingencies.
The initial annual base rent under the 2024 Sub-Lessee Agreement ranges from approximately $8.0 million to $9.0 million over the lease term and the Company expects to take possession in the first half of 2024. The initial annual base rent due to the Company under the 2024 Sub-Lessor Agreement ranges from approximately $4.0 million to $5.0 million over the lease term and the Company expects to provide possession in the first half of 2024.
Item 9. Changes in and Disagreements With Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosures
None.
Item 9A. Controls and Procedures
Evaluation of Disclosure Controls and Procedures
Our management, with the participation of our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, has evaluated the effectiveness of our disclosure controls and procedures as of the end of the period covered by this Annual Report on Form 10-K. The term “disclosure controls and procedures,” as defined in Rules 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e) under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the Exchange Act), means controls and other procedures of a company that are designed to ensure that information required to be disclosed by a company in the reports that it files or submits under the Exchange Act is recorded, processed, summarized, and reported within the time periods specified in the SEC’s rules and forms. Disclosure controls and procedures include, without limitation, controls and procedures designed to ensure that information required to be disclosed by a company in the reports that it files or submits under the Exchange Act is accumulated and communicated to the company’s management, including its principal executive and principal financial officers, or persons performing similar functions, as appropriate to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosure. In designing and evaluating our disclosure controls and procedures, our management recognizes that disclosure controls and procedures, no matter how well conceived and operated, can provide only reasonable assurance that the objectives of the disclosure controls and procedures are met. Based on the evaluation of our disclosure controls and procedures as of December 31, 2023, our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer concluded that, as of such date, our disclosure controls and procedures were effective at the reasonable assurance level.
Management’s Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting
Our management is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting, as defined in Rule 13a-15(f) of the Exchange Act. Under the supervision and with the participation of our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer and oversight of our Audit & Compliance Committee, our management conducted an evaluation of the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting based on the framework in Internal Control—Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (2013 Framework). Based on this evaluation, management concluded that our internal control over financial reporting was effective as of December 31, 2023. Deloitte & Touche LLP, an independent registered public accounting firm, has issued an audit report with respect to the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2023, which is included in Item 8 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Changes in Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
There were no changes in our internal control over financial reporting identified in connection with the evaluation required by Rule 13a-15(d) and 15d-15(d) of the Exchange Act that occurred during the three months ended December 31, 2023, that have materially affected, or are reasonably likely to materially affect, our internal control over financial reporting.
Inherent Limitations on Effectiveness of Controls and Procedures
In designing and evaluating the disclosure controls and procedures and internal control over financial reporting, management recognizes that any controls and procedures, no matter how well designed and operated, can provide only reasonable assurance of achieving the desired control objectives. In addition, the design of disclosure controls and procedures and internal control over financial reporting must reflect the fact that there are resource constraints and that management is required to apply judgment in evaluating the benefits of possible controls and procedures relative to their costs.
Item 9B. Other Information
During our last fiscal quarter, the following directors and officers, as defined in Rule 16a-1(f), adopted a “Rule 10b5-1 trading arrangement” or a “non-Rule 10b5-1 trading arrangement” as defined in Regulation S-K Item 408:
On November 29, 2023, David Baszucki, our Chief Executive Officer and member of our Board of Directors, adopted a Rule 10b5-1 trading arrangement as an individual, as trustee of The Baszucki Family Foundation, and as a representative of the Bessemer Trust Company of Delaware who serves as trustee for the 2020 Jan Baszucki Gift Trust, dated April 3, 2020 and the 2020 David Baszucki Gift Trust, dated April 3, 2020. The trading arrangement provides for the sale from time to time of an aggregate of up to 10,581,062 shares of Class A Common Stock and the gift of an aggregate of up to 2,364,016 shares of Class A Common Stock to a charitable organization. The trading arrangement expires on February 24, 2025, or earlier if all transactions under the trading arrangement are completed. The trading arrangement is intended to satisfy the affirmative defense in Rule 10b5-1(c).
On November 20, 2023, Anthony Lee, a member of our Board of Directors, adopted a Rule 10b5-1 trading arrangement, as a trustee of the Fallen Leaf Revocable Trust. The trading plan provides for the sale from time to time of an aggregate of up to 500,000 shares of Class A Common Stock. The trading arrangement expires on March 31, 2025, or earlier if all transactions under the trading arrangement are completed. The trading arrangement is intended to satisfy the affirmative defense in Rule 10b5-1(c).
On November 28, 2023, Greg Baszucki, a member of our Board of Directors, adopted a Rule 10b5-1 trading arrangement as trustee of the Greg & Christina Baszucki Living Trust, dated August 18, 2016. The trading plan arrangement provides for the sale from time to time of an aggregate of up to 468,000 shares of Class A Common Stock. The trading arrangement expires on March 7, 2025, or earlier if all transactions under the trading arrangement are completed. The trading arrangement is intended to satisfy the affirmative defense in Rule 10b5-1(c).
On November 18, 2023, Michael Guthrie, our Chief Financial Officer, adopted a Rule 10b5-1 trading arrangement providing for the sale from time to time of an aggregate of up to 500,000 shares of Class A Common Stock. The trading arrangement expires on December 13, 2024, or earlier if all transactions under the trading arrangement are completed. The trading arrangement is intended to satisfy the affirmative defense in Rule 10b5-1(c).
No other officers or directors, as defined in Rule 16a-1(f), adopted or terminated a “Rule 10b5-1 trading arrangement” or a “non-Rule 10b5-1 trading arrangement” as defined in Regulation S-K Item 408, during the last fiscal quarter.
Item 9C. Disclosure Regarding Foreign Jurisdictions that Prevent Inspection
Not applicable.
Part III
Item 10. Directors, Executive Officers and Corporate Governance
Information responsive to this item is incorporated herein by reference to our definitive proxy statement with respect to our 2024 Annual Meeting of Stockholders to be filed with the SEC within 120 days after the end of the fiscal year covered by this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Item 11. Executive Compensation
Information responsive to this item is incorporated herein by reference to our definitive proxy statement with respect to our 2024 Annual Meeting of Stockholders to be filed with the SEC within 120 days after the end of the fiscal year covered by this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Item 12. Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owner and Management and Related Stockholder Matters
Information responsive to this item is incorporated herein by reference to our definitive proxy statement with respect to our 2024 Annual Meeting of Stockholders to be filed with the SEC within 120 days after the end of the fiscal year covered by this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Item 13. Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence
Information responsive to this item is incorporated herein by reference to our definitive proxy statement with respect to our 2024 Annual Meeting of Stockholders to be filed with the SEC within 120 days after the end of the fiscal year covered by this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Item 14. Principal Accounting Fees and Services
Information responsive to this item is incorporated herein by reference to our definitive proxy statement with respect to our 2024 Annual Meeting of Stockholders to be filed with the SEC within 120 days after the end of the fiscal year covered by this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Part IV
Item 15. Exhibits and Financial Statement Schedules
Exhibits
The exhibits listed below are filed as part of this Annual Report on Form 10-K or are incorporated herein by reference, in each case as indicated below.
Financial Statement Schedules
All financial statement schedules are omitted because the information called for is not required or is shown either in the consolidated financial statements or in the notes thereto.
EXHIBIT INDEX
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Exhibit
Number | | | | Incorporated by Reference |
| Description | | Form | | File No. | | Exhibit | | Filing Date |
| 3.1 | | | | 10-Q | | 001-39763 | | 3.1 | | May 13, 2021 |
| 3.2 | | | | 8-K | | 001-39763 | | 3.1 | | September 14, 2023 |
| 4.1 | | | | S-1/A | | 333-250204 | | 4.1 | | January 8, 2021 |
| 4.2 | | | | S-1/A | | 333-250204 | | 4.2 | | January 8, 2021 |
| 4.3 | | | | S-1/A | | 333-250204 | | 4.3 | | January 8, 2021 |
| 4.4 | | | | 8-K | | 001-39763 | | 4.1 | | October 29, 2021 |
| 4.5 | | | | 8-K | | 001-39763 | | 4.2 | | October 29, 2021 |
| 4.6 | | | | 10-K | | 001-39763 | | 4.8 | | February 25, 2022 |
| 10.1+ | | | | S-1/A | | 333-250204 | | 10.1 | | January 8, 2021 |
| 10.2*+ | | | | | | | | | | |
| 10.3+ | | | | S-1/A | | 333-250204 | | 10.4 | | January 8, 2021 |
| 10.4+ | | | | S-1/A | | 333-250204 | | 10.5 | | January 8, 2021 |
| 10.5+ | | | | S-1/A | | 333-250204 | | 10.6 | | January 8, 2021 |
| 10.6 | | | | S-1/A | | 333-250204 | | 10.7 | | January 8, 2021 |
| 10.7+ | | | | 10-K | | 001-39763 | | 10.7 | | February 25, 2022 |
| 10.8 | | | | 10-Q | | 001-39763 | | 10.2 | | May 10, 2023 |
| 10.9+ | | | | 10-Q | | 001-39763 | | 10.6 | | May 13, 2021 |
| 10.10+ | | | | S-1/A | | 333-250204 | | 10.12 | | January 8, 2021 |
| 10.11+ | | | | S-1/A | | 333-250204 | | 10.13 | | January 8, 2021 |
| 10.12+ | | | | S-1/A | | 333-250204 | | 10.14 | | January 8, 2021 |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 10.13+ | | | | S-1/A | | 333-250204 | | 10.15 | | January 8, 2021 |
| 10.14+ | | | | 10-Q | | 001-39763 | | 10.4 | | May 13, 2021 |
| 10.15+ | | | | 10-Q | | 001-39763 | | 10.1 | | November 9, 2022 |
| 19.1* | | | | | | | | | | |
| 21.1* | | | | | | | | | | |
| 23.1* | | | | | | | | | | |
| 24.1* | | | | | | | | | | |
| 31.1* | | | | | | | | | | |
| 31.2* | | | | | | | | | | |
| 32.1† | | | | | | | | | | |
| 97.1* | | | | | | | | | | |
| 101.INS* | | XBRL Instance Document - the instance document does not appear in the Interactive Data File because its XBRL tags are embedded within the Inline XBRL document. | | | | | | | | |
| 101.SCH* | | Inline XBRL Taxonomy Extension Schema Document. | | | | | | | | |
| 101.CAL* | | Inline XBRL Taxonomy Extension Calculation Linkbase Document. | | | | | | | | |
| 101.DEF* | | Inline XBRL Taxonomy Extension Definition Linkbase Document. | | | | | | | | |
| 101.LAB* | | Inline XBRL Taxonomy Extension Label Linkbase Document. | | | | | | | | |
| 101.PRE* | | Inline XBRL Taxonomy Extension Presentation Linkbase Document. | | | | | | | | |
| 104* | | Cover Page Interactive Data File (formatted as inline XBRL and contained in Exhibit 101). | | | | | | | | |
___________* Filed herewith.
+ Indicates management contract or compensatory plan.
† The certifications furnished in Exhibit 32.1 hereto are deemed to accompany this Annual Report on Form 10-K are not deemed filed with the SEC and are not to be incorporated by reference into any filing of the Registrant under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended (the “Exchange Act”), whether made before or after the date of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Item 16. Form 10-K Summary
None.
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized, in San Mateo, California, on the 21st day of February, 2024.
| | | | | | | | |
| Roblox Corporation |
| | |
| By: | /s/ David Baszucki |
| | David Baszucki |
| | Founder, President and Chief Executive Officer |
POWER OF ATTORNEY
KNOW ALL PERSONS BY THESE PRESENTS, that each person whose signature appears below constitutes and appoints David Baszucki, Michael Guthrie, and Mark Reinstra, and each one of them, as their true and lawful attorneys-in-fact and agents, with full power of substitution and resubstitution, for them and in their name, place, and stead, in any and all capacities, to sign any and all amendments to this Annual Report on Form 10-K, and to file the same, with all exhibits thereto and other documents in connection therewith, with the Securities and Exchange Commission, granting unto said attorneys-in-fact and agents, and each of them, full power and authority to do and perform each and every act and thing requisite and necessary to be done in connection therewith, as fully to all intents and purposes as he or she might or could do in person, hereby ratifying and confirming all that said attorneys-in-fact and agents or any of them, or his or her substitute or substitutes, may lawfully do or cause to be done by virtue hereof.
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this Annual Report on Form 10-K has been signed by the following persons on behalf of the registrant and in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Signature | | Title | | Date |
| | | | |
| /s/ David Baszucki | | Founder, President, Chief Executive Officer and Chair of Board of Directors | | |
| David Baszucki | | (Principal Executive Officer) | | February 21, 2024 |
| | | | |
| /s/ Michael Guthrie | | Chief Financial Officer | | |
| Michael Guthrie | | (Principal Financial Officer) | | February 21, 2024 |
| | | | |
| /s/ Amy Rawlings | | Chief Accounting Officer | | |
| Amy Rawlings | | (Principal Accounting Officer) | | February 21, 2024 |
| | | | |
| /s/ Gregory Baszucki | | Director | | |
| Gregory Baszucki | | | | February 21, 2024 |
| | | | |
| /s/ Christopher Carvalho | | Director | | |
| Christopher Carvalho | | | | February 21, 2024 |
| | | | |
| /s/ Jason Kilar | | Director | | |
| Jason Kilar | | | | February 21, 2024 |
| /s/ Anthony P. Lee | | Director | | |
| Anthony P. Lee | | | | February 21, 2024 |
| | | | |
| /s/ Gina Mastantuono | | Director | | |
| Gina Mastantuono | | | | February 21, 2024 |
| | | | |
| /s/ Andrea Wong | | Director | | |
| Andrea Wong | | | | February 21, 2024 |