
Exhibit 99.1 Corporate Presentation June 2024

Legal Disclosure This presentation contains forward-looking statements, all of which are qualified in their entirety by this cautionary statement. Many of the forward-looking statements contained herein can be identified by the use of forward-looking words such as may , anticipate , believe , could', expect , should , plan , intend , estimate , will , potential and ongoing , among others, although not all forward-looking statements contain these identifying words. These forward-looking statements include statements about the initiation, timing, progress, results and cost of our research and development programs and our current and future preclinical studies and clinical trials, including statements regarding the timing of initiation and completion of studies or trials and related preparatory work, the period during which the results of the trials will become available and our research and development programs; our ability to successfully manufacture our drug substances and product candidates for preclinical use, for clinical trials and on a larger scale for commercial use, if approved; the ability and willingness of our third-party strategic collaborators to continue research and development activities relating to our development candidates and product candidates; our ability to commercialize our products, if approved; our ability to obtain funding for our operations necessary to complete further development and commercialization of our product candidates; our ability to obtain and maintain regulatory approval of our product candidates; the size and growth potential of the markets for our product candidates and our ability to serve those markets; our financial performance; our expected cash runway into the second half of 2026; and the implementation of our business model, including strategic plans for our business and product candidates. Except as otherwise noted, these forward-looking statements speak only as of the date of this presentation, and we undertake no obligation to update or revise any of such statements to reflect events or circumstances occurring after this presentation. Because forward-looking statements are inherently subject to risks and uncertainties, some of which cannot be predicted or quantified and some of which are beyond our control, you should not rely on these forward-looking statements as predictions of future events. For a discussion of these and other risks and uncertainties, and other important factors, any of which could cause our actual results to differ from those contained in the forward- looking statements, see the section entitled Risk Factors in our most recent Annual Report on Form 10-K and Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), as well as discussions of potential risks, uncertainties, and other important factors in our other subsequent filings with the SEC, which are available on the SEC's website at www.sec.gov. The events and circumstances reflected in our forward-looking statements may not be achieved or occur and actual results could differ materially from those projected in the forward-looking statements. We caution you not to place undue reliance on the forward-looking statements contained in this presentation. This presentation discusses product candidates that are under preclinical or clinical evaluation and that have not yet been approved for marketing by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) or any other regulatory authority. Until finalized in a clinical study report, clinical trial data presented herein remain subject to adjustment as a result of clinical site audits and other review processes. No representation is made as to the safety or effectiveness of these product candidates for the use for which such product candidates are being studied. This presentation shall not constitute an offer to sell or the solicitation of an offer to buy, nor shall there be any sale of these securities in any state or other jurisdiction in which such offer, solicitation or sale would be unlawful prior to registration or qualification under the securities laws of any such state or other jurisdiction. 2

Well Positioned with Multiple Near-Term Clinical Catalysts Precision Late-Stage Large Market Opportunity Key Upcoming Catalysts Therapy Clinical Development In Areas of Unmet Need Platform • Direct tumor cell killing • Phase 3 in Primary • Ocular Oncology• Multiple clinical data and immune activation Uveal Melanoma >60,000 patients/yr readouts expected within 2 Ongoing (US/EU) next 6-12 months, • Focal treatment approach including early Phase 1 1 • FDA SPA Agreement to deliver durable • Urologic Oncology bladder data response ~500,000 patients/yr 3 (globally)• Cash expected to fund operations into 2H 2026 1. Special Protocol Assessment (SPA). 2. See sources on slide 8 of this presentation. 3 3 3. Bladder cancer. Putnam & Assoc. Epidemiology Analysis.

Clinical Pipeline Across Multiple Solid Tumor Indications Planned Program Preclinical Phase 1 Phase 2 Phase 3 Milestones OCULAR ONCOLOGY 2024 – Phase 3 enrollment ongoing Primary Uveal Melanoma YE 2024 – Phase 2 12-month data Metastases to the Choroid 2024 – Phase 2 initiation (Multiple primary cancers with metastasis to YE 2024 – Initial Phase 2 data the choroid, e.g., Breast and Lung) Ocular Surface Cancers OTHER SOLID TUMORS Bladder Cancer (Non-Muscle Invasive (NMIBC) and Muscle Mid-2024 – Early Phase 1 data Invasive (MIBC)) Other HSPG* Expressing Tumors *Virus-like drug conjugates (VDCs) bind to a subset of modified tumor associated glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) that are part of the heparan sulphate chain of heparan sulfate proteoglycans 4 (HSPGs). Schiller et al. Viruses 2022, 14(8), 1656

Bel-sar is a Potential First-in-Class Therapy for Multiple Solid Tumors

Reactive oxygen species disrupts cell membrane and organelles Bel-sar has a novel dual mechanism of action Disruption of the tumor cell membrane and pro-immunogenic cell death by necrosis leads to T cell activation and immune- mediated tumor cell killing Kines RC, et al. Int J Cancer. 2016;138(4):901–11. Kines RC, et al. Mol Cancer Ther. 2018;17(2):565–74. Kines RC, et al. Cancer Immunol Res. 2021;9:693–706. 6 DAMPs, damage-associated molecular patterns; HSPG, heparan sulfate proteoglycan; VDC, virus-like drug conjugate; VLP, virus-like particle. Bel-sar, AU-011

Bel-sar Ocular Oncology Target Indications: Therapeutic Area • Primary Uveal Melanoma • Metastases to the Choroid • Ocular Surface Cancers

Bel-sar Opportunities in Ocular Oncology Represent a Multi-billion- dollar Addressable Market ~66,000 patients/year ~80% Ocular Oncology Total Addressable Market (US/EU) of patients are diagnosed at the early stage (indeterminate lesions (ILs) and small tumors) Current radiotherapy Primary Uveal Melanoma Ocular Surface Cancers treatment 3 1 ~35,000 patients/year ~11,000 patients/year Leaves up to 87% of patients with major irreversible vision loss ~100 Ocular Oncologists in US/EU — focused call 4 point opportunity <20 Metastases to the Choroid Field Based Team — Retinoblastoma Intend to add small sales 4 2 1 force to launch globally ~500 patients/year ~20,000 patients/year 1. ClearView & Putnam & Assoc. Epidemiology Analysis Choroidal Melanoma and Choroidal Metastasis 2. American Cancer Society- Retinoblastoma statistics 3. Includes Conjunctival Melanoma, Primary Acquired Melanosis, Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Ocular Surface Squamous Neoplasia (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12788119/; https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19628487/; https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8676629/; https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29511061/; https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9037556/) 8 4. Bel-sar is an investigational product candidate. Subject to regulatory approval.

Primary Uveal Melanoma—High Unmet Medical Need Most common primary 2 Uvea: Choroid, Ciliary Body and Iris intraocular cancer in adults Choroid is 90% 1 of the uvea choroid Impacts ~11,000 3 50% of patients patients in US/EU per year develop metastasis within 15 years (metastatic uveal ~80% patients diagnosed 2 melanoma) 3 with early-stage disease Primary Uveal Melanoma is a Rare and Life-Threatening Ocular Cancer with No Drugs Approved 1. Heiting, G. Iris/uvea of the eye. Accessed Oct. 3, 2023. https://www.allaboutvision.com/en-gb/resources/uvea-iris-choroid/ 2. Kaliki S, Shields CL. Uveal melanoma: relatively rare but deadly cancer. Eye (Lond). 2017;31(2):241-257. doi:10.1038/eye.2016.275 3. Clearview & Putnam & Assoc. Market Research 9

Current Treatment Paradigm for Uveal Melanoma Small Medium Large Metastatic SIZE 1 2.5–3 >10 Indeterminate Small (mm): Lesions Melanomas Risk Factors Growth Small CM Enuc. Observation Systemic Chemotherapy Radiotherapy Radiotherapy ® (KIMMTRAK ) Local – Early (~8,000) Local – Late (~2,300) Metastatic (~2,000) 1. Each figure represents ~250 persons. Shields CL et al. Choroidal and ciliary body melanoma. Available at: https://eyewiki.aao.org/Choroidal_and_Ciliary_Body_Melanoma. Accessed May 2, 2024. Epidemiology analysis for choroidal melanoma and choroidal metastasis by ClearView Healthcare Partners and Putman. 10 10 Enuc., enucleation. CM, Choroidal Melanoma. Incidence: Patients 1 US/EU

High Morbidity Associated with Current Standard of Care 3–7 Radiotherapy Up to 87% of Primary Uveal Melanoma Patients Become Legally Blind Over Time in the Eye Adverse Event Proportion of patients 1,2 Treated with Radiotherapy Surgeries secondary to AEs legally blind (BCVA 40%+ (e.g., cataracts) ≤20/200) after Brachy Radiation retinopathy 40%+ 1, 2 Therapy Neovascular glaucoma 10% 100% Dry eye syndrome 20% 80% Strabismus 2%+ 60% Retinal detachment 1-2% 40% Vision loss (≥15 letters) ~70% 20% Long-term legal blindness ~90% (≤20/200) 0% Serious Adverse Event Baseline Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Long Term Scleral necrosis 0-5% Enucleation/eye loss 10-15% Severe vision loss (≥30 ~90% letters) in HRVL 1. Jarczak J, Karska-Basta I, Romanowska-Dixon B. Deterioration of visual acuity after brachytherapy and proton therapy of uveal melanoma, and methods of counteracting this complication based on recent publications. Medicina (Kaunas). 2023;59(6):1131. 2. Tsui I, Beardsley RM, McCannel TA, Oliver SC, et al. Visual acuity, contrast sensitivity and color vision three years after iodine-125 brachytherapy for choroidal and ciliary body melanoma. Open Ophthalmol J. 2015;9:131-5. 3. Shields CL et al. Arch Ophthalmol. 2000;118(9):1219-1228. 4. Peddada KV et al. J Contemp Brachytherapy. 2019;11(4):392-397. 5. Jarczak J et al. Medicina (Kaunas). 2023;59(6):1131. 6. Shields CL et al. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2019;30(3):206-214. 7. Kaliki S, Shields CL. Eye 2017;31(2):241-257. AE, adverse event; BCVA, best-corrected 11 visual acuity; HRVL, high-risk for vision loss.

Bel-sar has the Potential to be the First Approved Therapy in Primary Uveal Melanoma Bel-sar is Delivered by Simple Light Activation with Goals of Suprachoroidal Injection Standard Ophthalmic Laser Treatment Local tumor control Preservation of vision c No radiation-related morbidity Opportunity to treat early and reduce risk of metastases Two ~2 minute Two ~5 minute Injections Lasers Improvement in safety and quality of life In-Office Procedure Bel-sar is an investigational product candidate. Subject to regulatory approval. 12

Phase 2 Trial – Dose Escalation and Expansion with Suprachoroidal Administration Patient Population Representative of Early-Stage Disease: Small Choroidal Melanoma and Indeterminate Lesions Trial Design – Enrollment Complete (n=22) Endpoint Endpoint Definitions Growth in Tumor Height 6-9 doses- 40 μg 9 doses- 80 μg 2 doses- 40 μg x 2 Lasers 1 dose- 20 μg 1 dose- 40 μg 1 dose- 40 μg x 2 Lasers Tumor Progression ≥0.5mm or ≥1.5 mm in Largest x 2 Lasers QWx3 x 1 Laser x 1 Laser x 2 Lasers QWx3 QWx2 Up to 3 cycles Basal Diameter (LBD) 3 cycles Cohort 1 Cohort 2 Cohort 3 Cohort 4 Cohort 5 Cohort 6 (n=1) (n=3*) (n=2) (n=3) 2 Cycles (n=1) (n=up to 10) Decrease from Baseline: 3 Cycles (n=2) Visual Acuity Loss ≥15 letters Change in Rate of Growth Subtherapeutic Regimens Therapeutic Regimen Tumor Thickness Growth Rate of Tumor Thickness N=10 N=11** 3 Cycles (9 doses) 1- 2 Doses (n=9); 2 cycles-6 doses (n=1) One Cycle = Doses on days 1, 8 and 15 Goal: To Determine Safety, Optimal Dose and Therapeutic Regimen with Suprachoroidal Administration *Cohort 2: 2 subjects were planned; third subject was additionally enrolled due to dose error in 1 subject **12 patients enrolled, 1 subject who discontinued after 1 cycle due to unrelated SAEs is not included in data analysis (n=11). Data that follows will be based on a cohort of 11 13 ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT04417530 ; AU-011-202

Phase 2 Interim Data Demonstrates Tumor Control, Vision Preservation and an Excellent Safety Profile 80% Tumor Control Rate 90% Visual Acuity Preservation Rate <20% Grade 1 AEs Aura Biosciences, Inc. Protocol AU-011-202 Exctraction 9/18/2023 Data Cut 3 Aug 2023 Open-Label Data Review Median Change in BCVA in Phase 3 Eligible Median Vision Graph Change Over Time Cycle 3 N=10 Patients with Therapeutic Regimen (n=10) Safety Analysis Set new window 100% Subtherapeutic Therapeutic 3 80% 1 80% -1 60% -3 -5 40% -7 20% 20% -9 -11 0% -13 Up to 2 Cycle Regimens 3 Cycle Regimens (n=10) (n=10) -15 0 3 6 9 12 Tumor Progression: change from baseline in thickness ≥0.5mm; or in LBD Months Vision Loss (15 letters) ≥1.5mm confirmed by at least one repeat assessment wind August 3, 2023, data on file Aura Biosciences Vision acuity loss definition based on ETDRS BCVA letter Change from Baseline score (≥ 15 letters from baseline) ' PROGRAM fVA2chgm.sas Outputs are not QCed Programmatically or by Prometrika 14 % Subjects with Tumor Control Change from Baseline

SPA Agreement with FDA Supports Global Phase 3 Trial Design Fast Track and Orphan Drug Designations 80 µg bel-sar treatment arm (n=40) SPA Agreement 15 Month Primary Efficacy Analysis Randomize 40 µg bel-sar treatment arm (n=20) (2:1:2) Sham control arm (n=40) Enrollment (N=~100) Primary Endpoint First Key Secondary Endpoint £ Time to Tumor Progression£ Time to Composite Endpoint: Tumor Progression or Visual Acuity Failure An SPA Indicates Concurrence by the FDA that the Design of the Trial can Adequately Support a Regulatory Submission 15 SPA – Special Protocol Assessment

1.0 + Censored Time to tumor 0.8 Kaplan-Meier analysis progression simulation of Phase 2 0.6 Change from baseline in thickness Log-rank test interim data support ≥0.5 mm or in LBD ≥1.5 mm 0.4 confirmed by at least one repeat P = 0.0012 assumptions for the assessment potential success of 0.2 Phase 3 trial with high 0.0 statistical significance Subtherapeutic 0 100 200 300 400 500 (≤2 cycles), n=10 3 cycles, n=10 1.0 + Censored 0.8 Time to composite 0.6 endpoint 0.4 Time to tumor progression or vision Log-rank test acuity failure (≥15 letter loss in P = 0.0023 ETDRS-BCVA), whichever occurs 0.2 earlier 0.0 0 100 200 300 400 500 Days Study duration 12 months. Participants either had an event or were censored at the last visit; some had their Week 52 visit after 365 days. Any events at the final visit are assigned to the actual time of that visit. Log-rank test p-value based on unsimulated original Kaplan-Meier curves. BCVA, best-corrected visual acuity; ETDRS, Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Study; LBD, largest basal diameter. August 3, 2023 data on file, Aura 16 Biosciences. ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT04417530; AU-011-202. Progression-free probability Progression-free probability

Phase 2 Interim Data Support Phase 3 Assumptions Robustness Analysis of Phase 2 interim tumor control rates 100% Overall rate P < 0.05 P < 0.005 in Phase 2 80% 2x “worse” than Phase 2 Actual data Actual data 60% 2x “worse” 94% 93% (Δ60) (Δ60) than Phase 2 power power >99% >99% (Δ30) (Δ20) power 40% Overall rate power in Phase 2 Actual rate with 20% documented growth in Phase 2 0% Sham Bel-sar Same dose, regimen, route of administration, range of tumor sizes and reading center as Phase 2 trial Phase 3 • Similar population to Phase 2 participants receiving the therapeutic regimen trial design • Enriching for early documented growth; Phase 3 randomization stratified by growth rate 17 ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT06007690; AU-011-301.

Bel-sar Opportunities in Ocular Oncology Represent a Multi-billion- dollar Addressable Market ~66,000 patients/year Majority originate from breast and Ocular Oncology Total Addressable Market (US/EU) lung cancer Burdensome Standard Primary Uveal Melanoma Ocular Surface Cancers of Care with Radiation 3 1 ~35,000 patients/year ~11,000 patients/year Morbidities Daily treatments of radiotherapy for 4 weeks ~100 Ocular Oncologists in US/EU — focused call 4 point opportunity <20 Metastases to the Choroid Field Based Team — Retinoblastoma Intend to add small sales 4 2 1 force to launch globally ~500 patients/year ~20,000 patients/year 1. ClearView & Putnam & Assoc. Epidemiology Analysis Choroidal Melanoma and Choroidal Metastasis 2. American Cancer Society- Retinoblastoma statistics 3. Includes Conjunctival Melanoma, Primary Acquired Melanosis, Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Ocular Surface Squamous Neoplasia (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12788119/; https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19628487/; https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8676629/; https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29511061/; https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9037556/) 18 4. Bel-sar is an investigational product candidate. Subject to regulatory approval.

Metastases to the Choroid – Phase 2 Trial Expected to Begin in 2024 Planned Study Design (n=12*) Cohort 1 Cohort 2 Cohort 3 Cohort 4 N=3 patients N=3 patients N=3 patients N=3 patients 80µg 160µg 200µg 200µg 1 cycle 1 cycle 2 cycles 1 cycle Study Objectives Study Population • Patients with Unilateral, Unifocal • Safety/Dose-limiting Toxicity Metastases to the Choroid • Efficacy • Breast or Lung Primary • Change in Tumor Size • No Changes in Concurrent Systemic • Change in Vision Letter Score Medications Planned Highlights: Primary Endpoint at One-month Post-treatment; Possibility to See Tumor Shrinkage and Vision Improvement 19 *3+3 Design. Each cohort to have a minimum of 3 and a maximum of 6 patients.

Bel-sar Urologic Oncology Target Indications: Therapeutic Area • Non-muscle invasive bladder cancer • Muscle invasive bladder cancer

Bladder Cancer is a Global High Unmet Medical Need Non-Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer ~500,000 1 New cases/ year globally >200,000 NMIBC 1 New cases/year US, Europe & Asia >60,000 Unmet Need Unmet Need MIBC 1 New cases/year US, Europe & Asia Recurrence, multiple TURBT surgeries, Progression of Disease, Loss of Bladder/Cystectomy, Progression of Disease, Loss of Metastasis and Survival Bladder/Cystectomy 1. Bladder cancer. Putnam & Assoc. Epidemiology Analysis. 21

Current Treatment Paradigm for Non-Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer Low grade – Low & intermediate risk High risk papillary disease CIS – BCG unresponsive Progression Adjuvant therapy Intermediate risk High risk adjuvant therapy adjuvant therapy Intravesical gene therapy ® (Adstiladrin ) BCG >6 tx BCG >6 tx TURBT TURBT Systemic immunotherapy ® (Keytruda ) Intravesical Intravesical Chemotherapy Chemotherapy Intravesical immunotherapy recurrence recurrence ® (Anktiva ) Cystectomy (~80,000) (~20,000) (~4,000) 1. Each figure represents 1000 persons. 2. Holzbeierlein JM et al. J Urol. 2024 Apr 25:101097JU0000000000003981 [epub ahead of print]. Holzbeierlein JM et al. J Urol. 2024 Apr;211(4):533-538. Internal Aura epidemiology of market size data on file. 22 BCG, Bacillus Calmette-Guérin; TURBT, transurethral resection of the bladder. Prevalence 1,2 Patients (US)

Bel-sar as Potential Front-Line Therapy in NMIBC may be Optimized for In Office-based Procedure Bel-sar’s Local Administration Goals of Treatment Aligned with with Bel-sar Current Urologic Oncology Practice Focal Treatment with Direct Tumor Cell Killing No Virus Replication or Viral Shedding Stimulate Anti-tumor Specific T Cell Response Lasers and Bladder Injections Reduce Risk of Recurrence (e.g. Botox) are Commonly Used Avoid TURBT /Operating Room Bel-sar has a Dual Mechanism of Action and its Local Administration is Aligned with Clinical Practice 23

21 participants TURBT and cystectomy patients NMIBC and MIBC patients Phase 1 trial for bladder cancer designed to Part 1 (n=5) Part 2 (n=16) evaluate safety, Bel-sar alone Bel-sar + focal light activation feasibility and MoA NMIBC MIBC n=10 n=6 Completed No treatment-related AEs, SAEs, or dose-limiting toxicities were seen in Ongoing the 5 patients Study objectives Safety & dose- Feasibility of Focal distribution Markers of Focal necrosis limiting toxicity technique of bel-sar immune activation AE, adverse event; MIBC, muscle invasive bladder cancer; MoA, mechanism of action; NMIBC, non–muscle invasive bladder cancer; SAE, serious adverse event; TURBT, transurethral resection of bladder tumor. 24 Clinicaltrials.gov identifier: NCT05483868; AU-011-102.

Clinical Complete Response with Immune Activation after Single Dose Confirmed by Histopathology in Part 2 First Patient Evidence of complete Immune response by absence of tumor infiltrate cells, as well as immune activation, after single dose Example of papillary treatment in first patient carcinoma (Ta) Necrosis Papillary 7 days after urothelial bel-sar treatment carcinoma H&E stain Pre-injection bladder biopsy demonstrating low-grade papillary urothelial carcinoma; non-invasive. Post-treatment TURBT demonstrating necrosis, inflammatory infiltrate, and no residual carcinoma. Circled region shows area of necrosis; arrow indicates edge of inflammatory infiltrate. 25 H&E, hematoxylin and eosin; TURBT, transurethral resection of the bladder. Clinicaltrials.gov identifier: NCT05483868; AU-011-102.

Company Highlights Ocular Oncology Therapeutic Area Urologic Oncology Therapeutic Area • Primary Uveal Melanoma – Global Phase 3 • Bladder Cancer – Phase 1 Trial CoMpass Trial: • Clinical complete response in first patient with • Trial actively enrolling single dose • Special Protocol Assessment (SPA) • Early data expected mid-year 2024 Agreement with FDA • Phase 3 assumptions supported by Phase 2 Corporate data • Metastases to the Choroid – Phase 2 trial • Strong cash position – expected to fund planned to initiate in 2024 operations into 2H 2026 • Second ocular indication potentially • Experienced leadership team across functions 1 doubles market opportunity • Initial data expected by year end 2024 1. ClearView & Putnam & Assoc. Epidemiology Analysis Choroidal Melanoma and Choroidal Metastasis. 26 26 Bel-sar is an investigational product candidate. Subject to regulatory approval.


Appendix: Phase 2 Primary Uveal Melanoma Trial – Interim Data

High Local Complete Response Rate at 12 months Follow-up* Dose Response: >90% Completed 12 Months Subtherapeutic vs Therapeutic Regimen Total Patients Tumor Control 100% Dose/Regimen Subtherapeutic Therapeutic (n) Rate 80% Subtherapeutic Regimens 80% Single dose up to 2 cycles 10 20% (2/10) 60% Therapeutic Regimen 40% 3 Cycles (n=11) 11 73% (8/11) 20% 20% 3 Cycles and Phase 3 eligible (n=10)* 10 80% (8/10) 0% * One subject with circumpapillary tumor that did not meet Phase 3 criteria is not included Up to 2 Cycle Regimens (n=10) 3 Cycle Regimens (n=10) Tumor Progression: change from baseline in thickness ≥0.5mm; or in LBD ≥1.5mm confirmed by at least one repeat assessment August 3, 2023, data on file Aura Biosciences High Tumor Control Rates with Therapeutic Regimen in Phase 3 Eligible Patients with Active Growth *A local complete response, or CR, in early-stage choroidal melanoma is described as tumor control and complete arrest of tumor growth by ocular oncologists. 29 Based on Phase 2 interim data, August 3, 2023. % Subjects with Tumor Control

High Tumor Control Rates Observed in Phase 3 Population Treated with Therapeutic Regimen in Phase 2* Aura Biosciences, Inc. Protocol AU-011-202 Exctraction 9/18/2023 Data Cut 3 Aug 2023 Subtherapeutic Regimens (n=10) Active Growth and 3 Cycle Regimens (n=10) Open-Label Data Review Figure Tumor Thickness Change or Grow Over Time Cycle 3 N=10 Safety Analysis Set Change from Baseline in Tumor Thickness Over 12 Months Change from Baseline in Tumor Thickness Over 12 Months 2.00 1.75 1.50 1.25 1.00 0.75 0.50 0.25 0.00 -0.25 -0.50 0 90 180 270 360 450 Analysis Day Treatment Treatment Follow-up Timeframe Follow-up Timeframe Timeframe Timeframe Subject Identifier for the Study Patients who had documented growth at entry (n=6) 002-2045 004-2019 004-2028 011-2024 All patients with documented growth at entry (n=10) Patients who did not have documented growth at entry (n=4) 012-2038 015-2031 022-2044 030-2035 Progressio 0n 3 1 D -2 e0 fi4 n 0 ition based on 0 T 31 u-m 20 o4 r 1 Thickness (Increase ≥0.5mm) Progression Definition based on Tumor Thickness (Increase ≥0.5mm) ' August 3, 2023, data on file Aura Biosciences PROGRAM fthickchg2.sas Phase 2 Interim Data Demonstrated Tumor Control Rate of 80%, with 90% of Patients at 12 Months of Follow Up *Based on Phase 2 interim data, August 3, 2023. 30 Change from Baseline in Tumor Thickness (mm) Change from Baseline Change from Baseline in Tumor Thickness (mm)

Phase 2 Interim Data Demonstrated Complete Cessation of Growth Among Responders Successful Treatment with 3 Cycle Regimen in Phase 3 Eligible Tumors with Active Growth Change in Tumor Growth (mm/yr) (n=8) P < 0.0001 + 0.383 - 0.001 August 3, 2023, data on file Aura Biosciences Tumor thickness growth rates/ slopes estimated using Mixed Models for Repeat Measures (random intercept and slope model for Historical and Study periods) Interim Data Showed Negative Growth Rate Among Responders in Planned Phase 3 Population (P <0.0001) 31 31 Rate of Tumor Growth (mm/yr)

90% Visual Acuity Preservation Despite 80% of These Phase 2 Patients Being at High Risk for Vision Loss* >90% Patients Completed 12 months Aura Biosciences, Inc. Protocol AU-011-202 Exctraction 9/18/2023 Data Cut 3 Aug 2023 Open-Label Data Review Total Vision Vision Median Change in BCVA in Phase 3 Eligible Patients with Median Vision Graph Change Over Time Cycle 3 N=10 Populations Patients Failures Preservation Therapeutic Regimen (n=10) Safety Analysis Set new window (n) (n) Rate 3 All Dose Cohorts 1 -1 All Treated Patients 22 1 96% -3 Subtherapeutic -5 -7 Single dose up to 2 cycles 10 0 100% -9 -11 Therapeutic Regimens -13 3 Cycles (n=11) 11 1 91% -15 0 3 6 9 12 3 Cycles and Phase 3 eligible (n=10)* 10 1 90% Months wind Vision acuity loss definition based on ETDRS BCVA *One subject with circumpapillary tumor that doesn’t meet Phase 3 criteria is not included Vision Loss (15 letters) letter score (≥ 15 letters from baseline) Change from Baseline ' August 3, 2023, data on file Aura Biosciences PROGRAM fVA2chgm.sas Outputs are not QCed Programmatically or by Prometrika 90% Visual Acuity Preservation Data Supports Potential to be Front Line Therapy for Early-Stage Disease *Based on Phase 2 interim data, August 3, 2023. 32 Change from Baseline
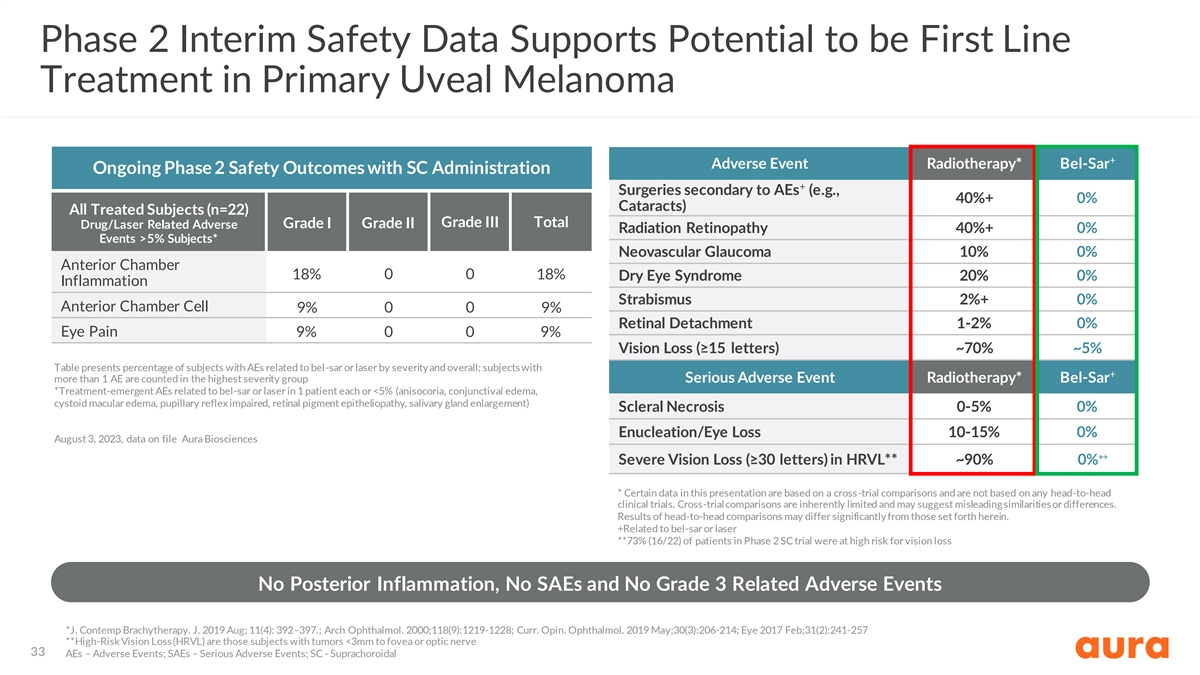
Phase 2 Interim Safety Data Supports Potential to be First Line Treatment in Primary Uveal Melanoma + Adverse Event Radiotherapy* Bel-Sar Ongoing Phase 2 Safety Outcomes with SC Administration + Surgeries secondary to AEs (e.g., 40%+ 0% Cataracts) All Treated Subjects (n=22) Grade III Total Drug/Laser Related Adverse Grade I Grade II Radiation Retinopathy 40%+ 0% Events >5% Subjects* Neovascular Glaucoma 10% 0% Anterior Chamber 18% 0 0 18% Dry Eye Syndrome 20% 0% Inflammation Strabismus 2%+ 0% Anterior Chamber Cell 9% 0 0 9% Retinal Detachment 1-2% 0% Eye Pain 9% 0 0 9% Vision Loss (≥15 letters) ~70% ~5% Table presents percentage of subjects with AEs related to bel-sar or laser by severity and overall; subjects with + more than 1 AE are counted in the highest severity group Serious Adverse Event Radiotherapy* Bel-Sar *Treatment-emergent AEs related to bel-sar or laser in 1 patient each or <5% (anisocoria, conjunctival edema, cystoid macular edema, pupillary reflex impaired, retinal pigment epitheliopathy, salivary gland enlargement) Scleral Necrosis 0-5% 0% Enucleation/Eye Loss 10-15% 0% August 3, 2023, data on file Aura Biosciences ++ Severe Vision Loss (≥30 letters) in HRVL** ~90% 0% * Certain data in this presentation are based on a cross-trial comparisons and are not based on any head-to-head clinical trials. Cross-trial comparisons are inherently limited and may suggest misleading similarities or differences. Results of head-to-head comparisons may differ significantly from those set forth herein. +Related to bel-sar or laser **73% (16/22) of patients in Phase 2 SC trial were at high risk for vision loss No Posterior Inflammation, No SAEs and No Grade 3 Related Adverse Events *J. Contemp Brachytherapy. J. 2019 Aug; 11(4): 392–397.; Arch Ophthalmol. 2000;118(9):1219-1228; Curr. Opin. Ophthalmol. 2019 May;30(3):206-214; Eye 2017 Feb;31(2):241-257 **High-Risk Vision Loss (HRVL) are those subjects with tumors <3mm to fovea or optic nerve 33 AEs – Adverse Events; SAEs – Serious Adverse Events; SC - Suprachoroidal
































