
Corporate Overview November 2024 Exhibit 99.2

Disclaimer This presentation and the accompanying slides (this “Presentation”) which have been prepared by Inmagene Biopharmaceuticals (“Inmagene,” the “Company” or together with its subsidiaries, collectively referred to as the “Group”) are being delivered to a limited number of parties for discussion purposes only, and shall not form the basis for or be relied on in connection with any contract or binding commitment whatsoever. By accepting this Presentation, each recipient agrees (i) to maintain the strict confidentiality of all information that is contained in this Presentation and not already in the public domain and not to photocopy, reproduce or distribute such information in whole or in part to any other persons at any time without the prior written consent of the Group, and (ii) to use this Presentation for information purposes only and not as the basis for any investment decision with respect to the Group, Ikena Oncology, Inc. ("Ikena") or the combined company. This Presentation is being distributed solely to qualified institutional buyers and accredited investors with sufficient knowledge and experience in investment, financial and business matters and the capability to conduct their own due diligence investigation and evaluation. This Presentation has been prepared by the Group based on information and data which the Group considers reliable, but no reliance shall be placed on, and no representation or warranty, express or implied, whatsoever is or will be given by the Group or any of its affiliates, directors, officers, employees or advisers or any other person as to the truth, accuracy, completeness, fairness and reasonableness of the contents of this Presentation. This Presentation may not be all inclusive and does not purport to contain all of the information that may be required to evaluate a possible investment decision with respect to the Group. The recipient agrees and acknowledges that (i) this Presentation is not intended to form the basis of any investment decision by the recipient and does not constitute investment, tax or legal advice, and (ii) the information contained in this Presentation is subject to change, and any such changes may be material. Any liability in respect of the contents of or any omission from this Presentation is expressly excluded. Certain matters discussed in this Presentation may contain forward-looking statements that are, by their nature, subject to significant risks and uncertainties. Forward-looking statements can be identified by words such as “may,” “will,” “should,” “would,” “could,” “believe,” “expect,” “anticipate,” “intend,” “plan,” “continue,” “seek,” “estimate,” “potential” or the negative of these terms or other similar terms. Forward-looking statements in this Presentation include, but are not limited to, statements about: the Groups expectations with respect to the proposed transaction, the timing thereof, the use of proceeds therefrom and the expected post-closing ownership of the combined company; the Group’s product candidates and the potential benefits thereof and potential new indications; planned and ongoing pre-clinical and clinical studies; and estimated milestones for out-licensed product candidates; Such forward-looking statements reflect the current views of the Group’s management regarding future events; they are not guarantees of future performance. Thes forward-looking statements involve significant risks and uncertainties that could cause actual results to differ materially and adversely from results expressed or implied by this Presentation, including, amongst others: the inability to complete the proposed transaction, including due to the inability to concurrently close the merger and the private placement or due to a failure to obtain stockholder approval from Ikena’s stockholders; the outcome of any legal proceedings that may be instituted against Ikena or the Group following announcement of the proposed transaction; costs related to the proposed transaction; the ability of the combined company to obtain sufficient additional capital to advance its clinical programs; the ability of the Group’s clinical trials to demonstrate acceptable safety and efficacy of its product candidates and other positive results; the progress of the Group’s preclinical studies and clinical trials; risks related to clinical development and regulatory approval of the Group's product candidates, including potential delays in the commencement, enrollment and completion of clinical trials; the size of the market opportunities for the Group’s product candidates; changes in applicable laws or regulations; and other risks and uncertainties from time to time described in Ikena’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended June 30, 2024 and the proxy statement/registration statement, once available, relating to the proposed transaction, including those under the “Risk Factors” section therein, and in Ikena’s other filings with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission. The Group assumes no obligation to update any forward-looking information contained in this Presentation. Any forward-looking statements and projections made by third parties included in this Presentation are based on publicly available information. While the Group believes that such information is reliable, there can be no assurance as to the accuracy or completeness of the indicated information. The Group has not independently verified the information provided by such third-party sources. This Presentation may contain trademarks, service marks, trade names and copyrights of other companies, which are the property of their respective owners. Solely for convenience, some of the trademarks, service marks, trade names and copyrights referred to in this Presentation may be listed without the TM, SM or © or ® symbols, but the Group will assert, to the fullest extent under applicable law, the rights of the owners to these trademarks, service marks, trade names and copyrights. This Presentation shall also not constitute an offer to sell or the solicitation of an offer to buy any securities, or a solicitation of any vote or approval, nor shall there be any sale of securities in any states or jurisdictions in which such offer, solicitation or sale would be unlawful prior to registration or qualification under the securities laws of any such jurisdiction or an exemption therefrom. ANY SECURITIES TO BE OFFERED IN ANY TRANSACTION CONTEMPLATED HEREBY HAVE NOT BEEN REGISTERED UNDER THE SECURITIES ACT OF 1933, AS AMENDED (THE “SECURITIES ACT”), OR ANY APPLICABLE STATE OR FOREIGN SECURITIES LAWS. ANY SECURITIES TO BE OFFERED IN ANY TRANSACTION CONTEMPLATED HEREBY HAVE NOT BEEN APPROVED OR DISAPPROVED BY THE SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION (THE “SEC”), ANY STATE SECURITIES COMMISSION OR OTHER UNITED STATES OR FOREIGN REGULATORY AUTHORITY, AND WILL BE OFFERED AND SOLD SOLELY IN RELIANCE ON THE EXEMPTION FROM THE REGISTRATION REQUIREMENTS PROVIDED BY THE SECURITIES ACT AND RULES AND REGULATIONS PROMULGATED THEREUNDER (INCLUDING REGULATION D) OR REGULATION S UNDER THE SECURITIES ACT. Exhibit 99.2

Transaction summary Overview Ikena Oncology, Inc. (Nasdaq: IKNA) to acquire 100% of outstanding equity interests of Inmagene Biopharmaceuticals, structured as a public / private merger Surviving entity name: ImageneBio Inc. Issuer of unregistered common stock in PIPE: Ikena Oncology, Inc. Leerink Partners LLC as placement agent Transaction Summary Planned $50 million PIPE from new and existing investors Estimated $320 million pro forma value of the combined company Inmagene: $150 million Ikena: $120 million PIPE: $50 million CVR to legacy Inmagene shareholders for proceeds from any partnering or disposition deal involving the non-OX40 assets CVR to legacy Ikena shareholders for proceeds from any partnering or disposition deal involving IK-595 assets or any other assets used or owned by Ikena pre-merger Estimated pro forma cash at close: ~$150 million1 Estimated pro forma ownership split: 46.9% Inmagene, 37.5% Ikena, 15.6% PIPE investors Use of Proceeds To fund the combined company into 2027 and support the development of its pipeline through several key inflection points, including phase 2b data in atopic dermatitis, as well as working capital and other general corporate purposes Timing Merger and financing expected to sign in Q4 2024 and close in H1 2025 Estimated pro forma cash at close does not include transaction expenses PIPE: private investment in public equity Exhibit 99.2

Inmagene overview Clinical stage biopharmaceutical company developing potentially differentiated therapies for the treatment of immunology and inflammatory disorders Lead program, IMG-007, is an ADCC-silenced, half-life extended, non-depleting anti-OX40 mAb Inmagene owns exclusive license for global rights1 Initially being developed as a treatment for atopic dermatitis (AD); potential to address other I & I indications Results from Phase 2a AD trial where IMG-007 was administered every other week for 4 weeks: Rapid and marked improvement from baseline in EASI, O-SCORAD and BSA scores as early as week 1 Progressive improvement over 20 weeks after the last dose2 Well-tolerated without pyrexia or chills observed to date3 – potentially due to ADCC silencing Phase 1 PK study demonstrated a half life for SC formulation of IMG-007 that supports potential for Q24W4 dosing for maintenance therapy Seeking strategic partner for IMG-004, an oral, non-covalent, reversible and brain permeable BTK inhibitor with extended half-life and durable pharmacodynamic effect potentially enabling once-daily dosing5 Founded in 2019; headquartered in San Diego, CA, and raised $140 million to date ADCC: antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity, AD: atopic dermatitis, BSA: body surface area, BTK: Bruton tyrosine kinase, CSU: chronic spontaneous urticaria, EASI: eczema area and severity index, I&I: Immunology and Inflammation, IV: intravenous, mAb: monoclonal antibody, SC: subcutaneous, SCORAD: SCORing atopic dermatitis; O-SCOARD: Objective SCOARD Licensor: Hutchison MediPharma Limited (Hutchmed) Shen Y et al. Revolutionizing Atopic Dermatitis (RAD) annual conference 2024; Shen Y et al, the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology (EADV) annual conference 2024 Shen Y et al. American College of Allergy Asthma and Immunology (ACAAI) annual conference 2023, sources under footnote 2, and Inmagene data on file Q24W (every 24 weeks) for maintenance therapy is projected based on data for IMG-007 from the Phase 1 studies in healthy adults and Phase 2a study in adult patients with moderate-to-severe AD (see sources under footnotes 2 & 3) and published data for rocatinlimab (Guttman-Yassky E, et al. Lancet. 2023;401[10372]:204-214) and amlitelimab (Weidinger S et al. EADV annual conference 2023, Weidinger S, et al. American Academy of Dermatology [AAD] annual conference 2024.) Based on data from a phase 1 single and multiple ascending dose study in healthy adults, Shen Y et al. EADV annual conference 2023. Exhibit 99.2

Inmagene leadership team Chief Medical Officer Yufang Lu, MD, PhD 20+ years in drug development and medical affairs Founder and CEO Jonathan Wang, PhD, MBA 30+ years in biotech entrepreneurship, investment and research Chief Strategic Advisor Sheila Gujrathi, MD 25+ years in drug development, biotech entrepreneurship and general management VP, Finance & Administration Erin Butler 20+ years in finance/accounting; 10+ years in public biotech companies SVP, Business and Corporate Development Anna Vardanyan, MD, PhD 16+ years in business development and R&D Exhibit 99.2

Market potential for IMG-007 estimated at ~ $5bn1 Source: Inmagene analyses, GlobalData, Sanofi R&D Day and Epidemiology Appendix (12/7/23) 1. U.S., EU5 (France, Germany, UK, Spain, Italy) and Japan 2. Including celiac disease, systemic sclerosis and alopecia areata IMG-007 Indication(s) Eligible Population Current Status Atopic dermatitis (AD) ~3.0M Phase 2 Other Indications2 ~1.0M Expansion Opportunity ~ $5bn Peak Sales ~6.3M Patients Total Opportunity Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) ~0.4M Expansion Opportunity Asthma ~1.9M Expansion Opportunity Exhibit 99.2

Addressing unmet need in treatment of atopic dermatitis AD patients present with diverse clinical phenotypes due to heterogenous molecular endotypes Currently approved biologics target Th2 pathway (IL13, IL4), which may explain their suboptimal efficacy and safety profiles1 AD is a chronic relapsing disease that requires long-term management Currently approved biologics require frequent injections (Q2W or Q4W)1 Agents modulating broader T cell pathways without increased safety risks are desirable Agents that require less frequent dosing, especially for maintenance therapy, are desirable OX40/OX40L antagonists may potentially address this gap by uniquely targeting diverse T cell subtypes Molecular engineering (e.g., half-life extension) may address this gap 1. Dupixent Prescribing information, Regeneron Sanofi; ADBRY Prescribing information, LEO Pharma Inc.; EBGLYSS Prescribing information, Eli Lily and Company. Exhibit 99.2
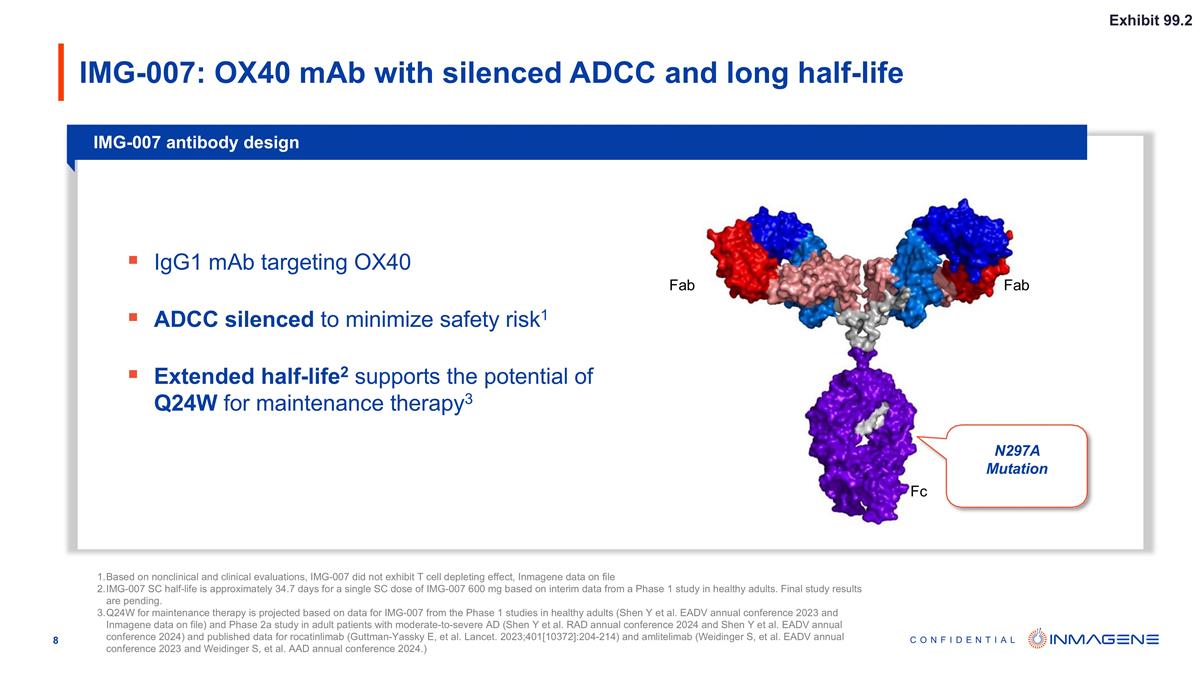
IMG-007: OX40 mAb with silenced ADCC and long half-life IMG-007 antibody design Fab Fab Fc N297A Mutation Based on nonclinical and clinical evaluations, IMG-007 did not exhibit T cell depleting effect, Inmagene data on file IMG-007 SC half-life is approximately 34.7 days for a single SC dose of IMG-007 600 mg based on interim data from a Phase 1 study in healthy adults. Final study results are pending. Q24W for maintenance therapy is projected based on data for IMG-007 from the Phase 1 studies in healthy adults (Shen Y et al. EADV annual conference 2023 and Inmagene data on file) and Phase 2a study in adult patients with moderate-to-severe AD (Shen Y et al. RAD annual conference 2024 and Shen Y et al. EADV annual conference 2024) and published data for rocatinlimab (Guttman-Yassky E, et al. Lancet. 2023;401[10372]:204-214) and amlitelimab (Weidinger S, et al. EADV annual conference 2023 and Weidinger S, et al. AAD annual conference 2024.) IgG1 mAb targeting OX40 ADCC silenced to minimize safety risk1 Extended half-life2 supports the potential of Q24W for maintenance therapy3 Exhibit 99.2
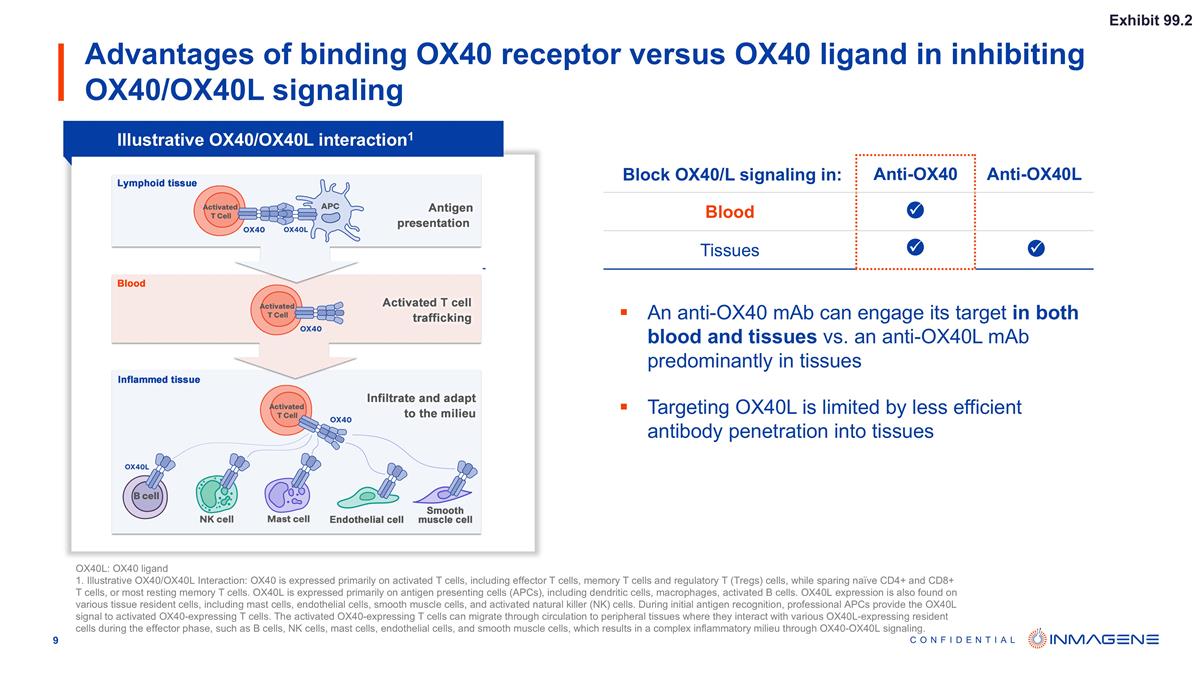
Advantages of binding OX40 receptor versus OX40 ligand in inhibiting OX40/OX40L signaling Block OX40/L signaling in: Anti-OX40 Anti-OX40L Blood Tissues An anti-OX40 mAb can engage its target in both blood and tissues vs. an anti-OX40L mAb predominantly in tissues Targeting OX40L is limited by less efficient antibody penetration into tissues ü ü ü Illustrative OX40/OX40L interaction1 OX40L: OX40 ligand 1. Illustrative OX40/OX40L Interaction: OX40 is expressed primarily on activated T cells, including effector T cells, memory T cells and regulatory T (Tregs) cells, while sparing naïve CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, or most resting memory T cells. OX40L is expressed primarily on antigen presenting cells (APCs), including dendritic cells, macrophages, activated B cells. OX40L expression is also found on various tissue resident cells, including mast cells, endothelial cells, smooth muscle cells, and activated natural killer (NK) cells. During initial antigen recognition, professional APCs provide the OX40L signal to activated OX40-expressing T cells. The activated OX40-expressing T cells can migrate through circulation to peripheral tissues where they interact with various OX40L-expressing resident cells during the effector phase, such as B cells, NK cells, mast cells, endothelial cells, and smooth muscle cells, which results in a complex inflammatory milieu through OX40-OX40L signaling. Exhibit 99.2

IMG-007’s potential advantages compared to anti-Th2 mAbs Th1 Th2 Th17 Th22 Memory T Regulatory T Anti-OX40 mAb IMG-007 IMG-007 has the potential: to address more diverse clinical phenotypes by targeting a broader range of T cell subtypes than Th2 targeting biologics to provide durable pharmacodynamic effect that supports favorable Q24W1 treatment regimen for maintenance therapy (vs. Q2W or Q4W), and could be disease modifying Target pathway ü ü ü ü ü ü ü Th: T-helper, MOA: mechanism of action, Q2W: every two weeks, Q4W: every four weeks Q24W for maintenance therapy is projected based on data for IMG-007 from the Phase 1 studies in healthy adults (Shen Y et al. EADV annual conference 2023 and Inmagene data on file) and Phase 2a study in adult patients with moderate-to-severe AD (Shen Y et al. RAD annual conference 2024 and Shen Y et al. EADV annual conference 2024) and published data for rocatinlimab (Guttman-Yassky E, et al. Lancet. 2023;401[10372]:204-214) and amlitelimab (Weidinger S, et al. EADV annual conference 2023 and Weidinger S, et al. AAD annual conference 2024) Anti-Th2 (IL-4, IL-13, IL-31) mAbs Exhibit 99.2

IMG-007 Ph2a trial in adult patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis Mean Age, years (SD): 49.8 (15.0) Sex: Female 30.8%, Male 69.2% Mean BMI (SD): 31.4 (8.7) Race: Caucasian: 46.2%, Non-Caucasian: 53.8% Mean duration of AD, years (SD): 29.6 (19.8) Mean EASI (SD): 29.5 (13.7) Mean BSA % (SD): 52.0 (25.5) IGA=3 / IGA=4: 61.5% / 38.5% Monotherapy study, topical or systemic AD medications were prohibited 13 patients enrolled; open label 3 IV doses of 300 mg at Week 0, 2 and 42 Follow up to 24 weeks Trial design1 Baseline characteristics1 1. Shen Y et al. Revolutionizing Atopic Dermatitis (RAD) annual conference 2024; Shen Y et al, the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology (EADV) annual conference 2024. 2. The same open-label design and IV dose regimen were used in the rocatinlimab AD proof-of-concept study (H. Nakagawa et al. Journal of Dermatological Science 99 (2020) 82–89 BMI: body mass index Shen Y et al. Revolutionizing Atopic Dermatitis (RAD) annual conference 2024; Shen Y et al, the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology (EADV) annual conference 2024, EASI: eczema area and severity index, IGA: Investigator's Global Assessment SD: Standard deviation Exhibit 99.2

IMG-007 was generally well-tolerated in Ph2a atopic dermatitis trial Participants with at least one TEAE 9 (69.2%) Study treatment related TEAEs 0 Serious AE 0 TEAE by CTCAE grade Grade 1 (Mild) 3 (23.1%) Grade 2 (Moderate) 5 (38.5%) Grade 3 (Severe) 1 (7.7%) TEAE that are infusion-related reactions 0 TEAE of pyrexia or chills 0 TEAE leading to 4-week dosing period discontinuation 0 There were no serious adverse events, no treatment-related AEs, no infusion-related reactions, no reports of pyrexia or chills All AEs were of mild or moderate intensity, except for one patient who experienced a severe AE of AD flare AEs by preferred terms that were reported by ≥ 2 participants included: dermatitis atopic (4 of 13), hypertension (2 of 13) and urticaria (2 of 13) The well-tolerated profile, potentially due to silenced ADCC function Overall summary of treatment-emergent adverse events1 1. AE: adverse event; CTCAE: Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events; TEAE: treatment-emergent adverse event Inmagene data on file. Shen Y et al. Revolutionizing Atopic Dermatitis (RAD) annual conference 2024; Shen Y et al, the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology (EADV) annual conference 2024 Exhibit 99.2

IMG-007: well-tolerated profile, potentially due to ADCC silencing (in AD POC studies) IMG-007 and rocatinlimab tolerability observations1 Rocatinlimab tolerability observations2 (in AD Ph2b study) Pyrexia Chills Pyrexia Chills IMG-007’s well tolerated profile may allow optimizing the dose regimens 1. Pyrexia and chills are common symptoms of cytokine releases due to cytotoxicity (Fajgenbaum, DC and June CH. N Engl J Med 2020;383:2255-2273). Rocatinlimab was engineered to enhance ADCC to induce T cell cytotoxicity thereby depleting T cells (Matsushita T. Korean J Hematol, 2011,46[3]:148-50 and. https://investors.amgen.com/static-files/04c3667d-c0e1-4f4b-a181-a99d275aa750 A Phase 1 Study of KHK4083 in Subjects with Atopic Dermatitis, Kyowa Kirin, December 3, 2018). Incidences of pyrexia and chills for rocatinlimab are based on Nakagawa H et al. J Dermatol Science 2020;99(2020):82–89. IMG-007 data is based on Shen Y et al. RAD annual conference 2024, Shen Y et al. EADV annual conference 2024, and Inmagene data on file. Comparison of historical data; rocatinlimab data is not from the same study. The results are presented from different clinical trials at different points in time with differences in trial design. No head-to-head trials have been conducted among the results shown and cross-trial comparisons must be interpreted with caution. As a result, conclusive cross-trial comparisons cannot be made. Data for rocatinlimab is based on Nakagawa H et al. J Dermatol Sci 2020;99(2):82-89 2. Rocatinlimab data is based on Guttman-Yassky, E et al. Lancet 2023; 401:204-214. POC: proof of concept Exhibit 99.2

IMG-007 Ph2a in atopic dermatitis: PK sustained well above EC90 for 24 weeks 1. EC90: The 90% maximal effective concentration for the inhibition of OX40/OX40L signaling is ~1.2 ug/mL based on in vitro assays. Inmagene data on file N numbers for Day 1, Day 8, wk2 pre-dose, wk2 post-dose, wk4 pre-dose, wk4 post-dose, wk 6, 8, 12, 16, 20 and 24 were 12, 12, 13, 13, 12, 10, 9, 9, 8, 6, 6, and 6, respectively. PK: pharmacokinetic EC90: 90% maximal effective concentration 3 IV doses @Q2W Drug concentration in the blood1 EC90 for inhibiting OX40/OX40Lsignaling1 With 3x 300 mg IV doses over 4 weeks, the mean serum drug concentration was maintained well above the EC90, concentration needed for OX40 target engagement in the blood, for 24 weeks The robust PK profile supports a potential for differentiated SC dose regimens in future late phase studies Exhibit 99.2

IMG-007 Ph2a in atopic dermatitis: rapid onset of clinical activity, maintained after the last dose at week 4 Percent (%) change from baseline in EASI score Percent (%) change from baseline in O-SCORAD score Percent (%) change from baseline in BSA score The above charts show Mean ± Standard Error N=13. Mixed-effect model with repeated measures (MMRM) was utilized for the analysis EASI: Eczema Area and Severity Index; EASI is a composite scoring system used in clinical trials to measure the extent (area) and severity of atopic eczema (dermatitis) SCORAD: SCORing Atopic Dermatitis; O-SCOARD: Objective SCOARD. SCORAD and O-SCORAD are composite scoring systems used in clinical trials to measure the extent and severity of atopic dermatitis BSA: Body Surface Area; BSA is a tool used in clinical trials to measure the extent of atopic dermatitis 0 1 2 4 6 8 12 16 20 24 0 1 2 4 6 8 12 16 20 24 0 1 2 4 6 8 12 16 20 24 Source: Inmagene data on file. Shen Y et al. Revolutionizing Atopic Dermatitis (RAD) annual conference 2024; Shen Y et al, the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology (EADV) annual conference 2024 % change from baseline in EASI score % change from baseline in EASI score % change from baseline in EASI score Analysis time point (week) Analysis time point (week) Analysis time point (week) Exhibit 99.2

Comparison of rocatinlimab’s historical POC data and IMG-007’s Ph2a data1 IMG-007 (~4 mg/kg)2 Rocatinlimab (10 mg/kg) 3 IV doses @Q2W % change from baseline in EASI score 1. Rocatinlimab’s historical AD proof-of-concept (POC) trial: Nakagawa H et al. J Dermatol Science 2020;99(2020):82–89. Comparison is made because the overall study design, the formulation (IV) and the dose regimen (3 doses Q2W over 4 weeks) evaluated in rocatinlimab’s historical POC study and IMG-007 Phase 2a POC study are sufficiently similar for cross-study comparison. The results are presented from different clinical trials at different points in time with differences in trial design. No head-to-head trials have been conducted among the results shown and cross-trial comparisons must be interpreted with caution. As a result, conclusive cross-trial comparisons cannot be made. The above chart shows Mean ± Standard Deviation. 2. In IMG-007’s AD Ph2a study, 300 mg flat dosing was used, which is equivalent to ~4 mg/kg based on an average patient body weight of 75 kg. Inmagene data on file. Shen Y et al. Revolutionizing Atopic Dermatitis (RAD) annual conference 2024 Exhibit 99.2

IMG-007 Ph2a in atopic dermatitis: durable activity based on EASI responder endpoints N=13; Patients who received rescue therapies were counted as “non-responders”. Last observation carried forward (LOCF) imputation was used for missing data, except for missing data that arises following study discontinuation with reason ‘lack of efficacy’ (none in the study). EASI-75: proportion of patients achieving ≥ 75% reduction from baseline in EASI EASI-90: proportion of patients achieving ≥ 90% reduction from baseline in EASI Proportion of patients achieving EASI-75 and EASI-90 3 IV doses 300 mg Q2W Proportion of patients achieving response (%) W0 W1 W2 W4 W6 W8 W12 W16 W20 W24 Exhibit 99.2
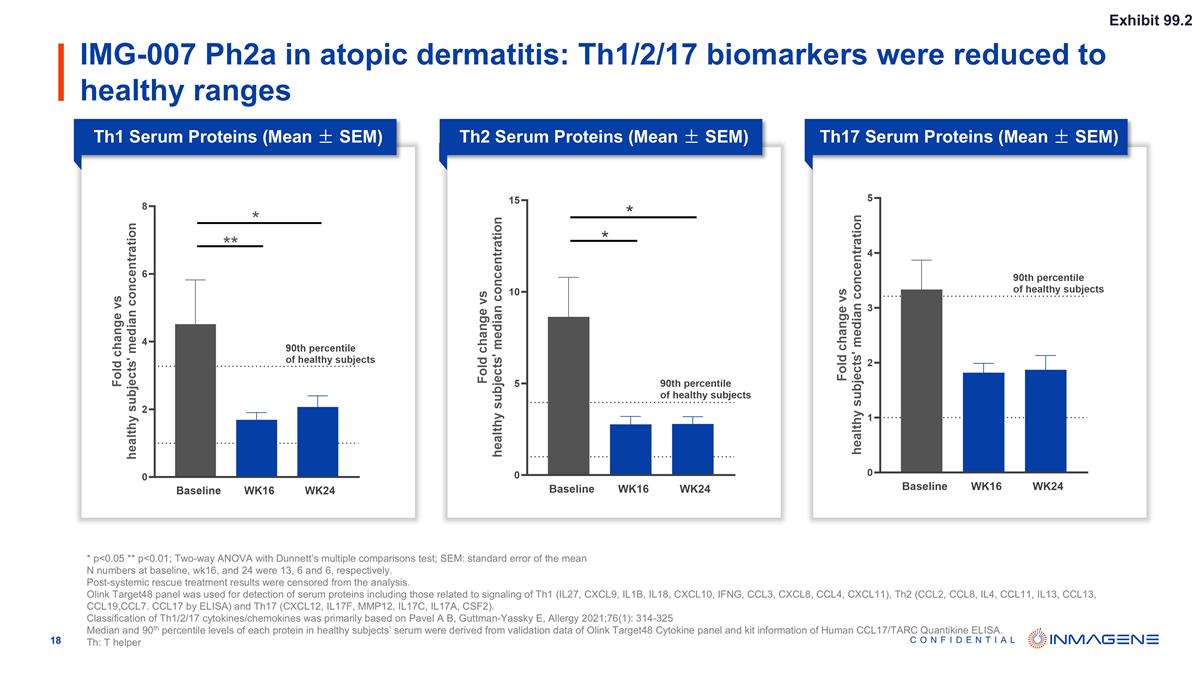
IMG-007 Ph2a in atopic dermatitis: Th1/2/17 biomarkers were reduced to healthy ranges Th1 Serum Proteins (Mean ± SEM) Th2 Serum Proteins (Mean ± SEM) Th17 Serum Proteins (Mean ± SEM) * p<0.05 ** p<0.01; Two-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test; SEM: standard error of the mean N numbers at baseline, wk16, and 24 were 13, 6 and 6, respectively. Post-systemic rescue treatment results were censored from the analysis. Olink Target48 panel was used for detection of serum proteins including those related to signaling of Th1 (IL27, CXCL9, IL1B, IL18, CXCL10, IFNG, CCL3, CXCL8, CCL4, CXCL11), Th2 (CCL2, CCL8, IL4, CCL11, IL13, CCL13, CCL19,CCL7. CCL17 by ELISA) and Th17 (CXCL12, IL17F, MMP12, IL17C, IL17A, CSF2). Classification of Th1/2/17 cytokines/chemokines was primarily based on Pavel A B, Guttman-Yassky E, Allergy 2021;76(1): 314-325 Median and 90th percentile levels of each protein in healthy subjects’ serum were derived from validation data of Olink Target48 Cytokine panel and kit information of Human CCL17/TARC Quantikine ELISA. Th: T helper Exhibit 99.2

IMG-007 Ph2a in atopic dermatitis: inhibition of Th1/2/17 serum markers FC: fold change, Log10 (FC vs Baseline): Log10 transform of fold change vs baseline Ns at baseline, wk 1, 4, 16, and 24 were 13, 12, 11, 6 and 6, respectively Post-systemic rescue treatment results were censored from the analysis ELISA assay for CCL17 and OLINK T48 panels were used for quantification of serum protein levels Classification of Th1/2/17 cytokines/chemokines was primarily based on Pavel A B, Guttman-Yassky E, Allergy 2021;76(1): 314-325 Th1 Th2 Th17 Exhibit 99.2

IMG-007 subcutaneous formulation has been developed Inmagene has developed a subcutaneous formulation. SC formulation is expected to be used in Ph2b and later studies A SC/IV PK bridging study in healthy adults is expected to be completed in December 2024 The SC formulation is at a concentration of 150 mg/mL GMP manufacturing process has been validated Stability data support anticipated shelf life of 2 years at 2-8°C Could be readily developed into a commercialization format, such as pre-filled syringe or autoinjector SC: subcutaneous IV: intravenous GMP: Good Manufacturing Practices Exhibit 99.2

IMG-007 SC PK study (interim data): robust PK profile IMG-007’s SC formulation showed a robust PK profile, similar to the IV formulation A single 600 mg SC dose showed a long half-life, estimated to be ~34.7 days3 IMG-007 was well-tolerated with no reports of pyrexia or chills (Mean ±SD; semi-log scale) Interim concentration-time profile1 (single dose) Based on interim data (as of October 22, 2024) from a Phase 1 study in healthy adults. Final study results are pending. N=6 in each dose group EC90: The 90% maximal effective concentration for the inhibition of OX40/OX40L signaling is ~1.2 ug/mL based on in vitro assays. Inmagene data on file. IMG-007 SC half-life of approximately 34.7 days is estimated for a single SC dose of IMG-007 600 mg based on interim data from a Phase 1 study in healthy adults. Final study results are pending. EC90 for inhibiting OX40/OX40L signaling2 Exhibit 99.2

IMG-007 (Inmagene) Rocatinlimab (Amgen) Amlitelimab (Sanofi) Half-life2,3 (days) 34.7 (SC) 12.0 (SC) 20.3 (IV) IMG-007 SC: long half-life enabling potential Q24W dosing1 1. Q24W for maintenance therapy is projected based on data for IMG-007 from the Phase 1 studies in healthy adults (Shen Y et al. ACAAI annual conference 2023 and Inmagene data on file) and Phase 2a study in adult patients with moderate-to-severe AD (Shen Y et al. RAD annual conference 2024 and Shen Y et al. EADV annual conference 2024) and published data for rocatinlimab (Guttman-Yassky E, et al. Lancet. 2023;401[10372]:204-214) and amlitelimab (Weidinger S, et al. EADV annual conference 2023 and Weidinger S, et al. AAD annual conference 2024.) 2. Since SC formulation is intended for late-phase development, half-life data for the SC formulation, available for IMG-007 and rocatinlimab, are presented. Half-life data for amlitelimab SC is not available, therefore data from the IV PK study is presented. The data for rocatinlimab and IMG-007 are based on single-dose studies in healthy adults; half-life data for amlitelimab is based on a multiple dose study in healthy adults; showing mean half-life results for rocatinlimab 3 mg/kg SC (Furihata K et al. Clin Pharm Drug Dev 2021;10[8]:870-883), amlitelimab 4 mg/kg IV at baseline followed with 2 mg/kg at Weeks 4 and 8 (Sagari M et al 2022; Clin Pharmacol & Therapeutics 111[5]:1121-1132). IMG-007 SC half-life of approximately 34.7 days is estimated for a single SC dose of IMG-007 600 mg based on interim data (as of October 22, 2024) from a Phase 1 study in healthy adults. Final study results are pending. 3. Results are presented from different clinical trials at different points in time with differences in trial design. No head-to-head trials have been conducted among the results shown and cross-trial comparisons must be interpreted with caution. As a result, conclusive cross-trial comparisons cannot be made. 4. Dose frequencies in phase 3 maintenance trials for rocatinlimab and amlitelimab or dose frequency approved for DUPIXENT®. Compound Company Dosing Frequency Potential (Maintenance Therapy) IMG-007 Q24W1 Rocatinlimab Q4W or Q8W4 Amlitelimab Q4W or Q12W4 DUPIXENT® (dupilumab) Q2W4 / Exhibit 99.2

IMG-007 low dose IMG-007 low dose Randomization (1:1:1:1) Enter a separate long-term extension study or safety follow-up Placebo W-5 Screening W0 Baseline W68 W52 Primary analysis Screening Period Period 1: Placebo-controlled Treatment Period 2: Active Treatment Follow-up Period IMG-007 high dose IMG-007 high dose IMG-007 high dose IMG-007 medium dose IMG-007 medium dose W20 IMG-007 atopic dermatitis Ph2b planned study design1 W: week 1. Tentative design, further refinement may be made Study population: Adult patients with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis who are candidates for systemic therapy (i.e., with or without prior systemic agents such as biologics, Jak inhibitors) A monotherapy study: Topical and systemic AD medications will be prohibited Exhibit 99.2
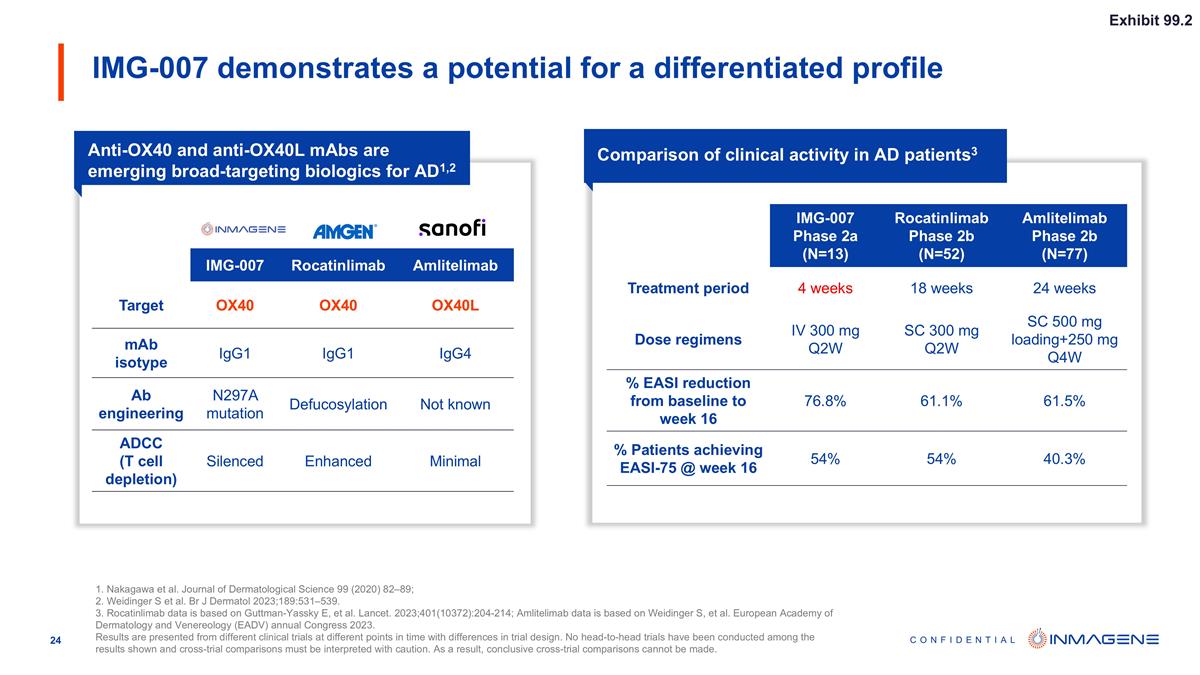
IMG-007 demonstrates a potential for a differentiated profile 1. Nakagawa et al. Journal of Dermatological Science 99 (2020) 82–89; 2. Weidinger S et al. Br J Dermatol 2023;189:531–539. 3. Rocatinlimab data is based on Guttman-Yassky E, et al. Lancet. 2023;401(10372):204-214; Amlitelimab data is based on Weidinger S, et al. European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology (EADV) annual Congress 2023. Results are presented from different clinical trials at different points in time with differences in trial design. No head-to-head trials have been conducted among the results shown and cross-trial comparisons must be interpreted with caution. As a result, conclusive cross-trial comparisons cannot be made. Anti-OX40 and anti-OX40L mAbs are emerging broad-targeting biologics for AD1,2 Comparison of clinical activity in AD patients3 IMG-007 Rocatinlimab Amlitelimab Target OX40 OX40 OX40L mAb isotype IgG1 IgG1 IgG4 Ab engineering N297A mutation Defucosylation Not known ADCC (T cell depletion) Silenced Enhanced Minimal IMG-007 Phase 2a (N=13) Rocatinlimab Phase 2b (N=52) Amlitelimab Phase 2b (N=77) Treatment period 4 weeks 18 weeks 24 weeks Dose regimens IV 300 mg Q2W SC 300 mg Q2W SC 500 mg loading+250 mg Q4W % EASI reduction from baseline to week 16 76.8% 61.1% 61.5% % Patients achieving EASI-75 @ week 16 54% 54% 40.3% Exhibit 99.2

IMG-007 has a potential for a differentiated profile IMG-007 vs. rocatinlimab (Amgen)1 IMG-007 vs. amlitelimab (Sanofi) 1 Ph2a data suggests IMG-007 could potentially drive greater clinical activity than rocatinlimab Longer half-life With fewer safety concerns, IMG-007 clinical activity could potentially be improved via increased exposure IMG-007 could potentially achieve improved clinical activity with more robust target engagement IMG-007 can block the OX40L by engaging the target in both blood and tissues vs. predominantly in tissues for amlitelimab IMG-007: No pyrexia or chills, potentially due to ADCC silencing, observed to date2 Rocatinlimab: Common occurrence of pyrexia and chills in clinical trials3 No pyrexia or chills reported to date for IMG-007 (potentially due to ADCC silencing)2 or amlitelimab (potentially due to IgG4 isotype)4 Q24W5 (IMG-007) vs Q4W or Q8W (rocatinlimab)6 Q24W5 (IMG-007) vs Q4W or Q12W (amlitelimab)6 Safety & tolerability Clinical activity Convenience Results are presented from different clinical trials at different points in time with differences in trial design. No head-to-head trials have been conducted among the results shown and cross-trial comparisons must be interpreted with caution. As a result, conclusive cross-trial comparisons cannot be made. Shen Y et al. Revolutionizing Atopic Dermatitis (RAD) annual conference 2024; Shen Y et al, the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology (EADV) annual conference 2024, Shen Y et al. American College of Allergy Asthma and Immunology (ACAAI) annual conference 2023, and Inmagene data on file. Furihata K et al. Clin Pharm Drug Dev 2021;10(8):870-883, Nakagawa H et al. J Dermatol Science 2020;99(2020):82–89, Guttman-Yassky E, et al. Lancet. 2023;401(10372):204-214 Weidinger S et al. EADV annual conference 2023, Weidinger S, et al. AAD annual conference 2024. Q24W for maintenance therapy is projected based on data for IMG-007 from the Phase 1 studies in healthy adults (Shen Y et al. ACAAI annual conference 2023 and Inmagene data on file) and Phase 2a study in adult patients with moderate-to-severe AD (Shen Y et al. RAD annual conference 2024 and Shen Y et al. EADV annual conference 2024) and published data for rocatinlimab (Guttman-Yassky E, et al. Lancet. 2023;401[10372]:204-214) and amlitelimab (Weidinger S, et al. EADV annual conference 2023 and Weidinger S, et al. AAD annual conference 2024.) Based on dose regimens for phase 3 maintenance trials. Exhibit 99.2
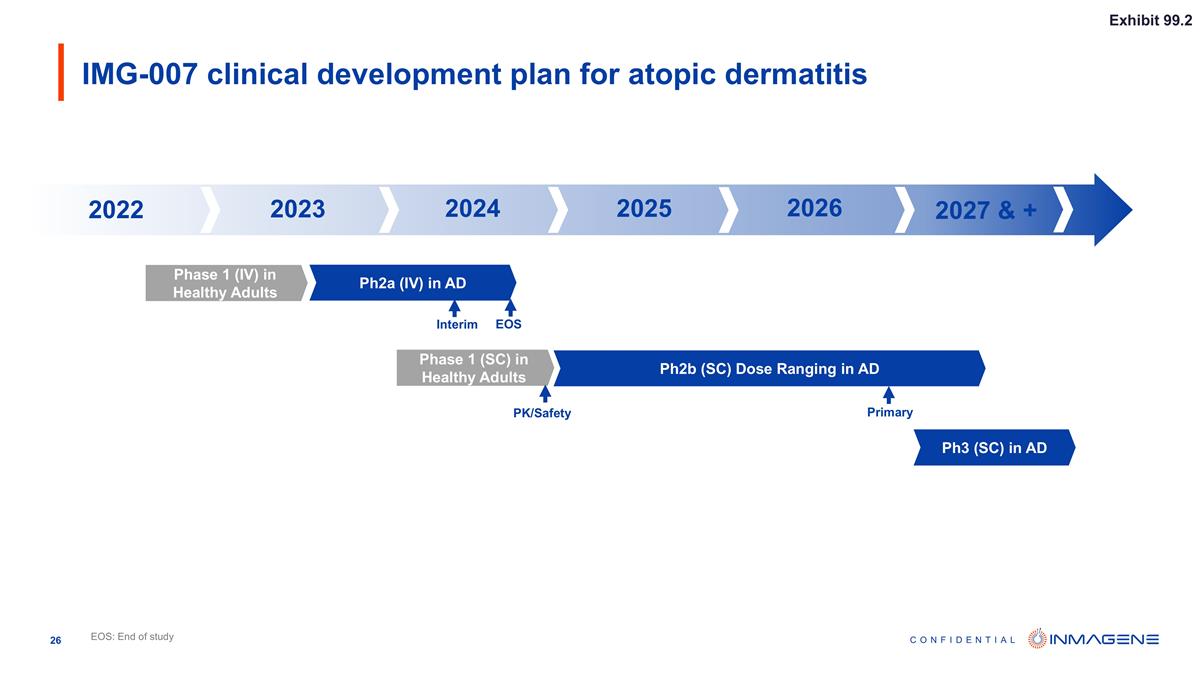
IMG-007 clinical development plan for atopic dermatitis Phase 1 (IV) in Healthy Adults Ph2b (SC) Dose Ranging in AD Interim EOS Primary Ph3 (SC) in AD Ph2a (IV) in AD Phase 1 (SC) in Healthy Adults PK/Safety EOS: End of study 2023 2024 2025+ 2022 2023 2024 2025 2026 2027 & + Exhibit 99.2

Exhibit 99.2


























