As filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on February 9, 2024
Registration No. 333-
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
Form F-1
REGISTRATION STATEMENT
UNDER
THE SECURITIES ACT OF 1933
Psyence Biomedical Ltd.
(Exact Name of Registrant as Specified in Its Charter)
| Canada | | 2834 | | Not Applicable |
(State or Other Jurisdiction of
Incorporation or Organization) | | (Primary Standard Industrial
Classification Code Number) | | (I.R.S. Employer
Identification Number) |
21 Richmond Street West
Penthouse Suite 1300
Toronto, Ontario MK5 2K1
Telephone: + 1 (416) 346-7764
(Address, including zip code, and telephone number, including area code, of Registrant’s principal executive offices)
Puglisi & Associates
850 Library Ave., Suite 204
Newark, Delaware 19711
Telephone: (302) 738-6680
(Name, address, including zip code, and telephone number, including area code, of agent for service)
Copies to:
Douglas S. Ellenoff
Stuart Neuhauser
Benjamin S. Reichel
Ellenoff Grossman & Schole LLP
1345 Avenue of the Americas
New York, New York 10105
(212) 370-1300
Approximate date of commencement of proposed sale of the securities to the public: As soon as practicable after this Registration Statement becomes effective and business combination described in the prospectus is completed.
If this form is filed to register additional securities for an offering pursuant to Rule 462(b) under the Securities Act, check the following box and list the Securities Act registration statement number of the earlier effective registration statement for the same offering. ¨
If this form is a post-effective amendment filed pursuant to Rule 462(c) under the Securities Act, check the following box and list the Securities Act registration statement number of the earlier effective registration statement for the same offering. ¨
If this Form is a post-effective amendment filed pursuant to Rule 462(d) under the Securities Act, check the following box and list the Securities Act registration statement number of the earlier effective registration statement for the same offering. ¨
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is an emerging growth company as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act of 1933.
Emerging growth company x
If an emerging growth company that prepares its financial statements in accordance with U.S. GAAP, indicate by check mark if the registrant has elected not to use the extended transition period for complying with any new or revised financial accounting standards† provided pursuant to Section 7(a)(2)(B) of the Securities Act. ☐
† The term “new or revised financial accounting standard” refers to any update issued by the Financial Accounting Standards Board to its Accounting Standards Codification after April 5, 2012.
The registrant hereby amends this registration statement on such date or dates as may be necessary to delay its effective date until the registrant shall file a further amendment which specifically states that this registration statement shall thereafter become effective in accordance with Section 8(a) of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, or until the registration statement shall become effective on such date as the Securities and Exchange Commission, acting pursuant to said Section 8(a), may determine.
The information in this prospectus is not complete and may be changed. We may not issue these securities until the registration statement filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission is effective. This prospectus is not an offer to sell these securities and it is not soliciting an offer to buy these securities in any state where the offer or sale is not permitted.
| PRELIMINARY PROSPECTUS, SUBJECT TO COMPLETION, DATED FEBRUARY 9, 2024 |
Psyence Biomedical Ltd.
22,496,000 Common Shares
This prospectus relates to the public offering of an aggregate of 22,496,000 common shares, no par value (“Common Shares”), of Psyence Biomedical Ltd., a corporation organized under the laws of Ontario, Canada (“Psyence,” the “Company,” “we,” “us” or “our”) which may be sold from time to time by the selling shareholders named in this prospectus (each, a “Selling Shareholder”), consisting of (i) an aggregate of up to 18,750,000 Common Shares issuable pursuant to those certain First Tranche Notes (as defined herein) issued to certain investors (the “Investors”) by the Company on January 25, 2024, which First Tranche Notes had an initial conversion price of $10.00; provided, however, that such conversion price is subject to certain adjustments according to the terms and reset dates included in the First Tranche Notes and may be reduced to a conversion floor of $1.00, until the First Reset Date (as such term is defined in the First Tranche Notes), then to $0.50 on the Second Reset Date (as such term is defined in the First Tranche Notes) and lower thereafter; (ii) 150,000 Common Shares (the “CCM Fee Shares”) that were issued to J.V.B. Financial Group, LLC (“J.V.B.”), acting through its Cohen & Company Capital Markets Division (“CCM”), in lieu of payment of deferred underwriting commissions and transaction fees in connection with the Business Combination (as defined herein) at an effective price of $10.00 per share; (iii) 150,000 Common Shares (the “Cantor Fee Shares”) that were issued to Cantor Fitzgerald & Co. (“Cantor”) in lieu of payment of deferred underwriting commissions at an effective price of $10.00 per share; (iv) 150,000 Common Shares (the “Maxim Fee Shares”) that were issued to Maxim Group, LLC (“Maxim”) in lieu of payment of transaction fees in connection with the Business Combination at an effective price of $6.67 per share; (v) 125,000 Common Shares (the “MWE Fee Shares”) that were issued to McDermott Will & Emery LLP (“MWE”) in connection with payment for services in connection with the Business Combination at an effective price of $10.00 per share; (vi) 150,000 Common Shares (the “EGS Fee Shares”) that the Company is contractually bound to issue to Ellenoff Grossman & Schole LLP (“EGS”) in connection with payment for services in connection with the Business Combination at an effective price of approximately $1.50 per share; (vii) 21,000 Common Shares (the “RNA Fee Shares” and, together with the CCM Fee Shares, the Cantor Fee Shares, the Maxim Fee Shares, the MWE Fee Shares and the EGS Fee Shares, the “Advisory Fee Shares”) that were issued to RNA Advisors, LLC (“RNA”) in connection with payment for services in connection with the Business Combination at an effective price of $10.00 per share; and (viii) 3,000,000 Common Shares (the “Founder Shares”) issued by the Company to Newcourt SPAC Sponsor LLC (the “Sponsor”) upon the Closing (as defined herein) in exchange for shares of NCAC originally issued for a nominal fee in a private placement prior to NCAC’s IPO, 1,396,071 of which were distributed to the members of the Sponsor upon the Closing.
The Selling Shareholders may offer, sell or distribute all or a portion of the Common Shares registered hereby publicly or through private transactions at prevailing market prices or at negotiated prices. We will not receive any of the proceeds from such sales of the Common Shares. We will bear all costs, expenses and fees in connection with the registration of these securities. The Selling Shareholders will bear all commissions and discounts, if any, attributable to their sale of Common Shares. See “Plan of Distribution.”
You should read this prospectus and any prospectus supplement or amendment carefully before investing in our securities. Our Common Shares trade on the Nasdaq Global Market under the symbol “PBM,” and certain of our warrants (the “Public Warrants”) trade on the Nasdaq Capital Market under the symbol “PBMWW.”
We are a “foreign private issuer,” and an “emerging growth company” each as defined under the federal securities laws, and, as such, we are subject to reduced public company reporting requirements. See the section entitled “Prospectus Summary — Implications of Being an Emerging Growth Company and a Foreign Private Issuer” for additional information.
Investing in our Common Shares involves a high degree of risk. You should purchase our Common Shares only if you can afford to lose your entire investment. See the section entitled “Risk Factors,” which begins on page 16.
Neither the Securities and Exchange Commission nor any state securities commission has approved or disapproved of these securities or determined whether this prospectus is truthful or complete. Any representation to the contrary is a criminal offense.
The date of this Prospectus is , 2024
TABLE OF CONTENTS
ABOUT THIS PROSPECTUS
This prospectus is part of a registration statement on Form F-1 filed by Psyence with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (the “SEC”), pursuant to which the Selling Shareholders may, from time to time, sell up to an aggregate of 22,496,000 Common Shares from time to time through any means described in the section entitled “Plan of Distribution.” More specific terms of any securities that the Selling Shareholders offer and sell may be provided in a prospectus supplement that describes, among other things, the specific amounts and prices of the Common Shares being offered and the terms of the offering. We will not receive any proceeds from the sale by such Selling Shareholders of the securities offered by them described in this prospectus.
A prospectus supplement may also add, update or change information included in this prospectus. Any statement contained in this prospectus will be deemed to be modified or superseded for purposes of this prospectus to the extent that a statement contained in such prospectus supplement modifies or supersedes such statement. Any statement so modified will be deemed to constitute a part of this prospectus only as so modified, and any statement so superseded will be deemed not to constitute a part of this prospectus. You should rely only on the information contained in this prospectus and any applicable prospectus supplement. See the section entitled “Where You Can Find More Information.”
We have not authorized anyone to provide any information or to make any representations other than those contained in this prospectus or any accompanying prospectus supplement we have prepared. We take no responsibility for, and can provide no assurance as to the reliability of, any other information that others may give you. This prospectus is an offer to sell only the Common Shares offered hereby and only under circumstances and in jurisdictions where it is lawful to do so. No dealer, salesperson or other person is authorized to give any information or to represent anything not contained in this prospectus or any applicable prospectus supplement. This prospectus is not an offer to sell our securities, and it is not soliciting an offer to buy our securities, in any jurisdiction where the offer or sale is not permitted. You should assume that the information appearing in this prospectus or any prospectus supplement is accurate only as of the date on the front of those documents, regardless of the time of delivery of this prospectus or any applicable prospectus supplement. Our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects may have changed since those dates.
This prospectus contains summaries of certain provisions contained in some of the documents described herein, but reference is made to the actual documents for complete information. All of the summaries are qualified in their entirety by the actual documents. Copies of some of the documents referred to herein have been filed, will be filed or will be incorporated by reference as exhibits to the registration statement of which this prospectus is a part, and you may obtain copies of those documents as described below under “Where You Can Find More Information.”
On January 25, 2024 (the “Closing Date”), we consummated the transactions contemplated by that certain Amended and Restated Business Combination Agreement, dated as of July 31, 2023 (as amended, the “Business Combination Agreement”), by and among the Company, NCAC, Newcourt SPAC Sponsor LLC, a Delaware limited liability company (the “Sponsor”), Psyence Group Inc., a corporation organized under the laws of Ontario, Canada (“Parent”), Psyence (Cayman) Merger Sub, a Cayman Islands exempted company and a direct and wholly owned subsidiary of the Company (“Merger Sub”), Psyence Biomed Corp., a corporation organized under the laws of British Columbia, Canada (“Psyence Biomed Corp.”), and Biomed II (collectively, the “Business Combination”). The following transactions occurred at the closing of the Business Combination (the “Closing”): (i) Parent contributed Biomed II to the Company in a share for share exchange (the “Company Exchange”), (ii) following the Company Exchange, Merger Sub merged with and into NCAC, with NCAC being the surviving company in the merger (the “Merger”) and each outstanding ordinary share of NCAC was converted into the right to receive one Common Share of the Company, and (iii) each outstanding warrant to purchase NCAC Class A Ordinary Shares was converted into a warrant to acquire one Common Share (the “warrants”) on substantially the same terms as were in effect immediately prior to the effective time of the Merger (the “Effective Time”) under their terms.
On January 15, 2024, in connection with the Business Combination, the Company and Biomed II entered into the Securities Purchase Agreement with the Investors and the Sponsor, relating to up to four senior secured convertible notes (collectively, the “Notes” and the transactions pursuant to the Securities Purchase Agreement, the “Financing”), obligations under which are guaranteed by certain assets of the Company and Biomed II, issuable to the Investors at or after the Closing, as the case may be, for the aggregate principal amount of up to $12,500,000 in exchange for up to $10,000,000 in subscription amounts. The Notes for the first tranche of the Financing (the “First Tranche Notes”), for an aggregate of $3,125,000, were delivered by the Company to the Investors on January 25, 2024, in exchange for an aggregate of $2,500,000 in financing, which occurred substantially concurrently with, and was contingent upon, the consummation of the Business Combination.
In connection with the Closing of the Business Combination, the Company agreed to issue the Advisory Fee Shares to certain third party advisors as payment for transaction fees incurred in connection with the Business Combination.
FUNCTIONAL AND REPORTING CURRENCY
A substantial portion of Psyence’s activity, including transactions with customers, as well as equity transactions and cash investments, are incurred in Canadian dollars. Psyence’s management believes that the U.S. dollar is the currency of the primary economic environment in which it operates. Thus, the functional and reporting currency for Psyence is the U.S. dollar.
INDUSTRY AND MARKET DATA
In this prospectus, we present industry data, information and statistics regarding Psyence’s industry, business and the markets in which Psyence competes as well as publicly available information, industry and general publications and research and studies conducted by third parties. This information is supplemented where necessary with Psyence’s own internal estimates and information obtained from discussions with its customers, taking into account publicly available information about other industry participants and Psyence’s management’s judgment where information is not publicly available. This information appears in “Prospectus Summary,” “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations,” “Business” and other sections of this prospectus.
Unless otherwise expressly stated, we obtained this industry, business, market and other data from reports, research surveys, studies and similar data prepared by market research firms and other third parties, industry and general publications, government data and similar sources that we believe to be reliable. In some cases, we do not expressly refer to the sources from which this data is derived. In that regard, when we refer to one or more sources of this type of data in any paragraph, you should assume that other data of this type appearing in the same paragraph is derived from the same sources, unless otherwise expressly stated or the context otherwise requires. While we have compiled, extracted and reproduced industry data from these sources, we have not independently verified the data. Industry publications, research, studies and forecasts generally state that the information they contain has been obtained from sources believed to be reliable, but that the accuracy and completeness of such information is not guaranteed. Forecasts and other forward-looking information obtained from these sources are subject to the same qualifications and uncertainties as the other forward-looking statements in this prospectus. These forecasts and forward-looking information are subject to uncertainty and risk due to a variety of factors, including those described under “Risk Factors.” These and other factors could cause results to differ materially from those expressed in any forecasts or estimates.
TRADEMARKS, TRADE NAMES AND SERVICE MARKS
This prospectus includes trademarks, tradenames and service marks, certain of which belong to Psyence and others that are the property of other organizations. Solely for convenience, trademarks, tradenames and service marks referred to in this prospectus appear without the ®, TM and SM symbols, but the absence of those symbols is not intended to indicate, in any way, that we will not assert our or their rights or that the applicable owner will not assert its rights to these trademarks, tradenames and service marks to the fullest extent under applicable law. We do not intend our use or display of other parties’ trademarks, trade names or service marks to imply, and such use or display should not be construed to imply, a relationship with, or endorsement or sponsorship of us by, these other parties.
FREQUENTLY USED TERMS
Unless otherwise stated or unless the context otherwise requires in this document:
“Articles of Incorporation” means the Company’s Articles of Incorporation, as registered on June 29, 2023.
“Board” means the board of directors of the Company.
“Biomed II” means Psyence Biomed II Corp., a corporation organized under the laws of Ontario, Canada.
“Business Combination” means the business combination transaction pursuant to which, among other things, (i) Parent contributed Biomed II to the Company in a share for share exchange and (ii) immediately thereafter, Merger Sub merged with and into NCAC, with NCAC being the surviving company in the merger and each outstanding NCAC Ordinary Share being converted into the right to receive one Common Share.
“Business Combination Agreement” means the Amended and Restated Business Combination Agreement, dated as of July 31, 2023, as amended on November 9, 2023, by and among NCAC, Sponsor, Parent, the Company, Merger Sub, Psyence Biomed Corp. and Biomed II.
“Cantor” means Cantor Fitzgerald & Co.
“CCM” means Cohen & Company Capital Markets, a division of J.V.B. Financial Group LLC, an affiliate of a passive member of the Sponsor.
“Closing” means the consummation of the Business Combination.
“Closing Date” means January 25, 2024.
“Code” means the Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended.
“Common Shares” means the common shares of the Company.
“Company Exchange” means the exchange in which Parent contributed Biomed II to the Company in a share for share exchange.
“Continental” means Continental Stock Transfer & Trust Company, our transfer agent and warrant agent.
“Effective Time” means the effective time of the Merger.
“Exchange Act” means the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended.
“IFRS” means the International Financial Reporting Standards issued by the International Accounting Standards Board.
“IPO” means NCAC’s initial public offering of NCAC Public Units, consummated on October 22, 2021.
“JOBS Act” means the Jumpstart Our Business Startups Act of 2012, as amended.
“Lock-Up Agreement” means the lock-up agreement, dated as of January 25, 2024, by and among the Company, NCAC and certain shareholders of the Company.
“Merger” means the merger in which Merger Sub merged with and into NCAC, with NCAC being the surviving company in the merger and each outstanding NCAC Ordinary Share being converted into the right to receive one Common Share.
“Merger Sub” means Psyence (Cayman) Merger Sub, a Cayman Islands exempted company and a direct and wholly owned subsidiary of the Company.
“Nasdaq” means The Nasdaq Stock Market LLC.
“NCAC” means Newcourt Acquisition Corp, a Cayman Islands exempted company.
“NCAC Class A Ordinary Shares” means NCAC’s Class A Ordinary Shares, par value $0.0001 per share.
“NCAC Class B Ordinary Shares” means NCAC’s Class B Ordinary Shares, par value $0.0001 per share, which were converted into NCAC Class A Ordinary Shares on a one-for-one-basis on October 20, 2023.
“NCAC Ordinary Shares” means the NCAC Class A Ordinary Shares.
“NCAC Private Placement Shares” means the NCAC Class A Ordinary Shares included in the NCAC Private Placement Units.
“NCAC Private Placement Units” means the units, each unit consisting of one NCAC Private Placement Share and one-half of one NCAC Private Placement Warrant, purchased in a private placement in connection with the IPO.
“NCAC Private Placement Warrants” means the warrants to purchase NCAC Ordinary Shares underlying the NCAC Private Placement Units.
“NCAC Public Shareholders” means the holders of NCAC Public Shares.
“NCAC Public Shares” means NCAC Class A Ordinary Shares issued as part of the NCAC Public Units sold in the IPO.
“NCAC Public Units” means the 25,000,000 units issued in connection with the IPO, each of which consists of one NCAC Class A Ordinary Share and one-half of one NCAC Public Warrant.
“NCAC Public Warrants” means the warrants included in the NCAC Public Units sold in the IPO, each of which is exercisable for one NCAC Class A Ordinary Share, in accordance with its terms.
“NCAC Units” means the NCAC Public Units and the NCAC Private Placement Units, collectively.
“NCAC Warrants” means the NCAC Public Warrants and the NCAC Private Placement Warrants, collectively.
“OBCA” means the Business Corporations Act (Ontario).
“Original Business Combination Agreement” means that certain Business Combination Agreement entered into on January 9, 2023 by and among, NCAC, the Sponsor, Parent and Psyence Biomed Corp.
“Parent” means Psyence Group Inc., a corporation organized under the laws of Ontario, Canada.
“PCAOB” means the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board.
“Private Warrants” means the former NCAC Private Placement Warrants, which were converted at the Effective Time into a right to acquire one Common Share on substantially the same terms as were in effect immediately prior to the Effective Time under the terms of the Warrant Agreement.
“Psyence” or the “Company” means Psyence Biomedical, Ltd., a corporation organized under the laws of Ontario, Canada, and where context warrants, including its subsidiaries.
“Public Warrants” means the former NCAC Public Warrants, which were converted at the Effective Time into a right to acquire one Common Share on substantially the same terms as were in effect immediately prior to the Effective Time under the terms of the Warrant Agreement.
“Securities” means Common Shares and Public Warrants, collectively.
“SEC” means the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission.
“Securities Act” means the Securities Act of 1933, as amended.
“Sponsor” means Newcourt SPAC Sponsor LLC, a Delaware limited liability company.
“Sponsor Support Agreement” means the support agreement, dated as of January 18, 2024, by and among the Sponsor and the officers and directors of NCAC, in their capacities as shareholders of NCAC, NCAC and Psyence, pursuant to which such shareholders of NCAC agreed to, among other things, vote in favor of the Business Combination and other related matters.
“Structuring Shares” means the up to 3,000,000 Common Shares that are payable to the Investors as a structuring fee pursuant the Securities Purchase Agreement.
“Treasury Regulations” means the regulations, including proposed and temporary regulations, promulgated under the Code.
“Trust Account” means the trust account that held the net proceeds of the sale of the NCAC Public Units in the IPO and the sale of the NCAC Private Placement Units.
“Underwriting Agreement” means the Underwriting Agreement, dated October 19, 2021, entered into at the time of the IPO by and between NCAC and Cantor.
“U.S. GAAP” means generally accepted accounting principles in the United States of America.
“Warrant Agreement” means the warrant agreement, dated October 19, 2021, by and between NCAC and Continental Stock Transfer & Trust Company, as warrant agent, governing NCAC’s warrants.
PROSPECTUS SUMMARY
This summary highlights selected information that is presented in greater detail elsewhere in this prospectus. This summary does not contain all of the information you should consider before investing in our Common Shares. You should read this entire prospectus carefully, including the sections titled “Risk Factors” and “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” and our consolidated financial statements and the related notes included elsewhere in this prospectus, before making an investment decision.
Business
Overview
We are a life science biotechnology company that, through our operating subsidiary, Biomed II, is developing natural psilocybin medicinal formulations and treatment protocols for the treatment of adjustment disorder in patients with an incurable cancer diagnosis. We have commenced the clinical trial process to evaluate the safety and efficacy of our product candidates.
Our Lead Product Candidate
Our lead product candidate is PEX010, a capsule containing 25mg naturally sourced psilocybin and which is being used in our Phase IIb Study. Psyence has entered into two IP licensing agreements (the “Filament Licensing Agreements”) with Filament Health Corp., a Canadian company that produces natural psilocybin capsules and the proprietary owner of PEX010 (“Filament”), for the licensing of PEX010 with respect to Psyence’s designated fields of use: anxiety and depression, including associated ailments, such as PTSD, stress, grief, and adjustment disorder within the context of palliative care.
Psyence has not performed any pre-clinical or clinical trials on PEX010. PEX010 is owned and has undergone clinical trials directed by Filament and its licensees. PEX010 has received regulatory approval to proceed into Phase I and II clinical trials in several jurisdictions worldwide. The FDA, Health Canada, MHRA, and the EMA have reviewed the chemistry, manufacturing, and controls and quality information of PEX010 through its associated filed DMFs/ IMPDs. The DMF for PEX010 is also on file with the Therapeutic Goods Administration (the “TGA”) in Australia. In addition to clinical trials, PEX010 is also already being administered to real-world patients via the Health Canada Special Access Program (“SAP”). Through the SAP, PEX010 is being prescribed for end-of-life distress as well as Major Depressive Disorder. As of June 23, 2023, 79 doses of PEX010 have been administered to 67 patients. Despite the serious condition of many of these patients, no serious adverse events or unexpected adverse events have been reported in any SAP administration.
Palliative Care Clinical Trial
We have contracted iNGENū Pty Ltd (“iNGENū ”), a contract research organization (“CRO”) in Australia that specializes in the study of psychedelics, to conduct a Phase IIb double-blind, randomized, low-dose controlled clinical trial to assess the efficacy and safety of PEX010 in psilocybin- assisted psychotherapy for the treatment of Adjustment Disorder (“AjD”) due to incurable cancer (the “Phase IIb Study”). Outsourcing the study to a CRO assists the company in operating in a more capital efficient manner without the overhead of handling in-house.
On January 9, 2023, Psyence and iNGENū signed a letter of intent to further develop Psyence’s licensed natural psilocybin drug product, starting with a Phase IIb Study in order to lead a pre-IND meeting with the FDA. The product to be used in this Phase IIb Study will be the proprietary botanical drug candidate PEX010 (25mg), which Psyence sources from Filament. The planned randomized double-blind study will evaluate the use of psilocybin-assisted psychotherapy versus psychotherapy alone and will test 84 patients utilizing the HAM A scale as the primary endpoint, which is an FDA validated endpoint, and safety data will be collected throughout the study.
The 84-patient Phase IIb Study is in the late planning stage, and estimated to commence enrollment in H1Q4 2024.
In addition, the Phase IIb Study adds a dose-finding arm, which allows us to accelerate our development strategy, seeking input from the FDA with our pre-IND application. If the outcome of the Phase II Study is positive, we believe we may be able to proceed directly to a Phase III trial in the United States, subject to FDA review and the opening of an IND; however, there is no guarantee that the FDA will accept data from trials conducted outside of the United States.
Psyence’s R&D capabilities
Psyence’s CEO (Dr. Neil Maresky) and Medical Director (Dr. Clive Ward-Able) are both medically trained physicians with close to 60 years of experience between them within the pharmaceutical industry related to R&D and the commercialization of new products. This experience provides the foundations for an excellent understanding of the clinical development, regulatory and commercialization needs of various pharmaceutical markets to design the optimal development program.
Psyence plans on working with various CROs and consultancy agencies to prepare and operationalize their protocols for the various phases of the clinical development program.
Competitive Environment
There are currently no pharmaceutical agents with regulatory approval for the treatment of AjD within palliative care or any other arena. The current treatment of AjD is empirical, with either psychotherapy or off- label pharmacological agents, such as anti-depressants or anxiolytics, or a combination of both.
We believe that the competitive landscape analysis of other commercial psychedelic-assisted treatments in clinical trials strongly suggests that Psyence’s clinical asset has a first-mover advantage in both the palliative care and cancer-related AjD market upon approval. PEX010 and its associated IP has been licensed to Psyence, giving it exclusivity for the indications of anxiety and depression within the context of palliative care in the UK and exclusive commercialization rights in the same indications and fields of use in the UK, EU and US. Psyence plans to expand their targeted indication of cancer-related AjD to address different types of AjD and other secondary indications both in a palliative and non-palliative context.
Recent Developments
Consummation of the Business Combination
On January 25, 2024, we consummated the transactions contemplated by the Business Combination Agreement, pursuant to which (i) Parent contributed Biomed II to the Company in a share for share exchange, (ii) following the Company Exchange, Merger Sub merged with and into NCAC, with NCAC being the surviving company in the Merger, and each outstanding ordinary share of NCAC was converted into the right to receive one Common Share of the Company, and (iii) each outstanding warrant to purchase NCAC Class A Ordinary Shares was converted into a warrant to acquire one Common Share on substantially the same terms as were in effect immediately prior to the Effective Time under their terms.
Securities Purchase Agreement
On January 15, 2024, in connection with the Business Combination, the Company and Biomed II entered into the Securities Purchase Agreement with the Investors and the Sponsor, relating to up to four senior secured convertible notes obligations under which are guaranteed by certain assets of the Company and Biomed II, issuable to the Investors at or after the Closing, as the case may be, for the aggregate principal amount of up to $12,500,000 in exchange for up to $10,000,000 in subscription amounts.
The two First Tranche Notes, for an aggregate of $3,125,000, were delivered by the Company to the Investors on January 25, 2024, in exchange for an aggregate of $2,500,000 in financing, which occurred substantially concurrently with, and was contingent upon, the consummation of the Business Combination. On the original issuance date of the First Tranche Notes, interest began accruing at 8.0% per annum based on the outstanding principal amount of the First Tranche Notes, and is payable monthly in arrears in cash or in Common Shares (at the Conversion Price). The initial Conversion Price of the First Tranche Notes was $10.00; provided, however, that such Conversion Price is subject to certain adjustments according to the terms and reset dates included in the First Tranche Notes and may be reduced to a Conversion Floor of $1.00, until the First Reset Date (as such term is defined in the First Tranche Notes), then to $0.50 on the Second Reset Date (as such term is defined in the First Tranche Notes) and to $0 thereafter.
Two Second Tranche Notes, in an aggregate principal amount of $3,125,000, will be delivered by Psyence Biomedical to the Investors in exchange for an aggregate of an additional $2,500,000 in financing (the “Second Tranche Financing”), subject to certain conditions. The Investors’ obligation to provide the Second Tranche Financing is contingent upon the Initial Resale Registration Statement (defined below) having been declared effective by the SEC and certain other conditions described in the Securities Purchase Agreement.
Providing any financing with respect to the Third Tranche Notes and the Fourth Tranche Notes is at the sole discretion of the Investors. With respect to any financing relating to the Third Tranche Notes, the Investors may issue a commitment letter to the Company on or before the 30th day following the last funding of the Second Tranche Financing, assuming that the Second Tranche Financing has been provided. With respect to the Fourth Tranche Notes, the Investors may issue a commitment letter to the Company on or before the 90th day after the last funding of the Second Tranche Financing, assuming that the Second Tranche Financing is provided. The Third Tranche Notes would be in an aggregate principal amount of $3,125,000 and would be delivered in exchange for an additional $2,500,000 in financing. This would be the same for the Fourth Tranche Notes. Additionally, in consideration of the willingness of the Investors to enter into the transactions that are the subject of the Securities Purchase Agreement and the Notes, including providing the financing, Psyence Biomedical agreed that it or certain of its shareholders would pay the Investors a structuring fee by delivering to the Investors an aggregate of 3,000,000 Common Shares (the “Structuring Shares”). At the initial closing of the financing under the terms of the Securities Purchase Agreement, and concurrent with the closing of the Business Combination, 1,300,000 of the Structuring Shares were delivered to the Investors. The remaining 1,700,000 are subject to the terms of Call Option Agreements, by and among the Investors and certain members of the Sponsor, pursuant to which such Common Shares are deliverable to the Investors no later than two business days after requested by the Investors; provided that no amounts shall be requested at any time that the Investors own in excess of 9.9% of the Company.
In order to secure the repayment of the Notes by the Company and Psyence II, pursuant to the terms and conditions of a General Security Agreement, dated January 25, 2024 (the “Security Agreement”), each agreed to grant to the Investors a security interest, subject to certain exceptions, in all of the Collateral (as such term is defined in the Security Agreement) in each of their possessions, including a pledge of all equity securities owned by either of them, provided that no Common Shares are pledged equity securities.
Pursuant to a Guaranty, dated January 25, 2024. Psyence II also agreed to guaranty all of the Company’s obligations to the Investors under the Notes including, without limitation, payment of all installments of principal and interest thereunder.
In connection with the foregoing, on January 25, 2024, the Company and the Investors entered into a registration rights agreement (the “Registration Rights Agreement”), pursuant to which the Company has agreed to file a registration statement covering the resale of the Common Shares issuable upon conversion of the First Tranche Notes (the “Initial Resale Registration Statement”) and any additional registration statements required to be filed to register the resale of the Common Shares issuable upon any of the other Notes, as applicable, and to use its best efforts to have the Initial Resale Registration Statement and such registration statement(s), as applicable, declared effective by the SEC as soon as practicable, but in no event later than the applicable Effectiveness Deadline (as defined in the Registration Rights Agreement for such applicable registration statement). The registration statement of which this prospectus forms a part qualifies as the Initial Resale Registration Statement. The Registration Rights Agreement contains certain penalty provisions, subject to certain conditions and cure periods, for the Company failing to (i) file a registration statement by certain deadlines set forth in the Registration Rights Agreement, (ii) cause a registration statement to be declared effective by certain deadlines set forth in the Registration Rights Agreement, (iii) maintain certain circumstances and conditions allowing the resale of certain securities or (iv) satisfy the requirements of Rule 144(c)(1) under the Exchange Act if a registration statement is not effective. The Registration Rights Agreement also provides the Investors with customary piggyback registration rights under certain circumstances.
In connection with the foregoing, on January 25, 2024, NCAC and the Company entered into a lock-up agreement with certain shareholders of the Company (the “Lock-Up Agreement”), pursuant to which such shareholders agreed not to, during the period (the “Lock-Up Period”) commencing from the Closing and ending on the earliest of (x) one hundred eighty (180) days after the Closing; provided, however, that in the event that the Investors delay investment of the Subscription Amounts (as defined in the Securities Purchase Agreement) with respect to the Second Tranche Note (as defined in the Securities Purchase Agreement) due to the occurrence of an event outlined in Section 2.1(b) of the Securities Purchase Agreement, such period shall be extended by 60 days or such earlier date as the deficiency is resolved, and (y) subsequent to the Closing, the date on which the Company consummates a liquidation, merger, share exchange or other similar transaction with an unaffiliated third party that results in all of Psyence Biomedical’s shareholders having the right to exchange the Common Shares for cash, securities or other property, (i) lend, offer, pledge, hypothecate, encumber, donate, assign, sell, contract to sell, sell any option or contract to purchase, purchase any option or contract to sell, grant any option, right or warrant to purchase, or otherwise transfer or dispose of, directly or indirectly, any shares issued or issuable to the applicable shareholder pursuant to their respective agreements (“Restricted Securities”), (ii) enter into any swap or other arrangement that transfers to another, in whole or in part, any of the economic consequences of ownership of the Restricted Securities, or (iii) publicly disclose the intention to do any of the foregoing, whether any such transaction described in clauses (i), (ii) or (iii) above is to be settled by delivery of Restricted Securities or other securities, in cash or otherwise (any of the foregoing described in clauses (i), (ii) or (iii), a “Prohibited Transfer”). The lock-up provisions provide for certain exemptions for transfers to permitted transferees.
The foregoing descriptions of the Securities Purchase Agreement, the Guaranty, the Registration Rights Agreement, the General Security Agreement, the Lock-Up Agreement and the Note are qualified in their entirety by the full text of such agreements (or their forms), which are filed as Exhibit 2.3, Exhibit 10.1, Exhibit 10.12, Exhibit 10.13, Exhibit 10.14 and Exhibit 10.15 hereto, respectively and are incorporated herein by reference.
Amendment to CCM Engagement Letter
On January 25, 2024, NCAC and CCM, entered into an amendment to engagement letter (the “CCM Amendment”), which amended that certain Engagement Letter dated as of February 9, 2023, by and among NCAC and CCM (the “Initial Engagement Letter”). Pursuant to the CCM Amendment, NCAC agreed to pay CCM a revised transaction fee, in lieu of (i) $982,500 owed to CCM as deferred underwriting commission and (ii) fees outstanding under the Initial Engagement Letter, in connection with the Business Combination in an amount equal to 150,000 CCM Fee Shares, plus reimbursable expenses incurred as of the Closing Date, which was paid from NCAC’s trust account at the Closing of the Business Combination.
In addition to the obligation to deliver the CCM Fee Shares to CCM, the terms of the CCM Amendment also include registration rights obligations on the part of the Company, which include obligations to use reasonable best efforts to file a resale registration statement covering the CCM Fee Shares and to maintain the effectiveness thereof while CCM continues to hold the CCM Fee Shares, in accordance with the terms of the CCM Amendment.
The foregoing description of the CCM Amendment is qualified in its entirety by the full text of the CCM Amendment, which is filed as Exhibit 10.9 hereto and is incorporated herein by reference.
Modified Cantor Deferred Underwriting Fee Payment Obligations
Pursuant to the Underwriting Agreement, dated as of October 19, 2021 (as amended or modified, the “Underwriting Agreement”), entered into in connection with NCAC’s IPO, NCAC previously agreed to pay to Cantor, in Cantor’s capacity as representative of the underwriters, deferred underwriting commissions in an aggregate amount of $5,567,500 (reflecting Cantor’s portion of the $6,550,000 deferred underwriting commission, after giving effect to the waiver of 50% of the original $13,100,000 deferred underwriting fee) (the “Cantor Deferred Fee”).
On January 25, 2024, NCAC and Cantor, in consideration of redemption levels by NCAC public shareholders, among other factors, entered into that certain fee modification agreement (the “Cantor Fee Modification Agreement”), pursuant to which, among other things, Cantor agreed to accept, in lieu of payment of the Cantor Deferred Fee in cash at the Closing, an aggregate of 150,000 Cantor Fee Shares, payable and delivered, at Closing at an effective price of $10.00 resulting from a waiver of a portion of the Cantor Deferred Fee.
In addition to the Company’s obligation to deliver the Cantor Fee Shares to Cantor, free and clear of specified restrictions, the terms of the Cantor Fee Modification Agreement also include registration rights obligations on the part of the Company, which include obligations to use commercially reasonable efforts to file a resale registration statement covering the Cantor Fee Shares and to maintain the effectiveness thereof while Cantor continues to hold the Cantor Fee Shares, in each case in accordance with the terms of the Cantor Fee Modification Agreement. The Cantor Fee Modification Agreement also includes a penalty provision that will require the Company to deliver to Cantor $5,567,500 in cash in the event that Cantor is unable to timely sell or transfer Cantor Fee Shares or the shares and warrants purchased in the private placement by Cantor in connection with NCAC’s IPO, due to continuing restrictions thereunder resulting from a failure by the Company to satisfy certain post-closing registration-related covenants and agreements in accordance with terms of the Cantor Fee Modification Agreement, following notice and reasonable opportunity to cure on the part of the Company.
The foregoing description of the Cantor Fee Modification Agreement is qualified in its entirety by the full text of the Cantor Fee Modification Agreement, which is filed as Exhibit 10.10 hereto and is incorporated herein by reference.
MWE Fee Agreement
On January 25, 2024, NCAC and MWE entered into that certain fee agreement (the “MWE Fee Agreement”). Pursuant to the MWE Fee Agreement, NCAC agreed to pay MWE a fee (the “MWE Amended Fee”) for the legal services provided by MWE to NCAC, in lieu of outstanding legal fees due to MWE. The MWE Fee Agreement provides that the MWE Amended Fee is comprised of (i) $100,000 due upon the Closing, (ii) an additional $100,000, payable on or prior to the 90th day after the Closing and (iii) 125,000 MWE Fee Shares, payable and delivered, at Closing.
In addition to the obligation to deliver the MWE Amended Fee, the terms of the MWE Fee Agreement also include registration rights obligations on the part of the Company, which include obligations to use commercially reasonable efforts to file a resale registration statement covering the MWE Fee Shares and to maintain the effectiveness thereof while MWE continues to hold the MWE Fee Shares, in accordance with the terms of the MWE Fee Agreement.
EGS Fee Modification Agreement
On January 26, 2024, the Company and EGS entered into that certain fee modification agreement (the “EGS Fee Modification Agreement”), pursuant to which the Company agreed to pay to EGS, for services provided prior to the Closing, (i) $50,000 upon the Closing, (ii) $50,000 payable to EGS within ninety (90) days following the Closing, and (iii) 100,000 Common Shares to be issued promptly following the date upon which the SEC declares the registration statement of which this prospectus forms a part effective (the “Issuance Date”). Additionally, the Company agreed to pay EGS (i) $25,000 in connection with the filing of the registration statement of which this prospectus forms a part and (ii) 50,000 Common Shares, to be issued upon the Issuance Date.
Amendments to RNA Engagement Letter
On January 25, 2024, NCAC and RNA Advisors, LLC, entered into that certain amendment to engagement letter (the “RNA Amendment”), which amended that certain Engagement Letter dated as of February 2, 2023, by and among NCAC and RNA. Pursuant to the RNA Amendment, NCAC agreed to pay RNA a revised transaction fee (the “RNA Amended Fee”) in connection with the Business Combination, comprised of (i) $25,000 due upon the Closing, (ii) an additional $25,000, payable on or prior to the 90th day after the Closing and (iii) 21,000 RNA Fee Shares, payable and delivered, at Closing.
In addition to the obligation to deliver the RNA Amended Fee, the terms of the RNA Amendment also include registration rights obligations on the part of the Company, which include obligations to use reasonable best efforts to file a resale registration statement covering the RNA Fee Shares and to maintain the effectiveness thereof while RNA continues to hold the RNA Fee Shares, in accordance with the terms of the RNA Amendment.
Amendments to Maxim Engagement Letter
On January 25, 2024, NCAC and Maxim entered into that certain amendment to engagement letter (the “Maxim Amendment”), which amended that certain Engagement Letter dated as of April 28, 2023, by and among Parent and Maxim. Pursuant to the Maxim Amendment, Parent agreed to pay Maxim a revised transaction fee in connection with the Business Combination in an amount equal to 150,000 Maxim Fee Shares.
In addition to the obligation to deliver the Maxim Fee Shares to Maxim, the terms of the Maxim Amendment also include registration rights obligations on the part of the Company, which include obligations to use reasonable best efforts to file a resale registration statement covering the Maxim Fee Shares and to maintain the effectiveness thereof while Maxim continues to hold the Maxim Fee Shares, in accordance with the terms of the Maxim Amendment.
The foregoing description of the Maxim Amendment is qualified in its entirety by the full text of the Maxim Amendment, which is filed as Exhibit 10.11 hereto and is incorporated herein by reference.
Lock-Ups
In connection with the Closing, including the Securities Purchase Agreement, the following parties are subject to lock-ups as set forth below: MWE, NCAC, J.V.B., Cantor and RNA (each, a “Lock-Up Party”) entered into lock-up arrangements which are substantially identical to each other, pursuant to which the applicable Lock-Up Party agreed not to, during the period (the “Lock-Up Period”) commencing from the Closing and ending on the earliest of (x) one hundred eighty (180) days after the Closing; provided, however, that in the event that the Investors delay investment of the Subscription Amounts (as defined in the Securities Purchase Agreement) with respect to the Second Tranche Note (as defined in the Securities Purchase Agreement) due to the occurrence of an event outlined in Section 2.1(b) of the Securities Purchase Agreement, such period shall be extended by 60 days or such earlier date as the deficiency is resolved, and (y) subsequent to the Closing, the date on which the Company consummates a liquidation, merger, share exchange or other similar transaction with an unaffiliated third party that results in all of the Company’s shareholders having the right to exchange the Common Shares for cash, securities or other property, (i) lend, offer, pledge, hypothecate, encumber, donate, assign, sell, contract to sell, sell any option or contract to purchase, purchase any option or contract to sell, grant any option, right or warrant to purchase, or otherwise transfer or dispose of, directly or indirectly, any shares issued or issuable to the applicable Lock-Up Party pursuant to their respective agreements (“Restricted Securities”), (ii) enter into any swap or other arrangement that transfers to another, in whole or in part, any of the economic consequences of ownership of the Restricted Securities, or (iii) publicly disclose the intention to do any of the foregoing, whether any such transaction described in clauses (i), (ii) or (iii) above is to be settled by delivery of Restricted Securities or other securities, in cash or otherwise (any of the foregoing described in clauses (i), (ii) or (iii), a “Prohibited Transfer”). The lock-up provisions provide for certain exemptions for transfers to permitted transferees.
Further, pursuant to documents entered into by NCAC upon the IPO of NCAC, certain shares are restricted until: (i) in the case of the founder shares, the earlier of (a) one year after the Closing and (b) subsequent to the Closing, (x) the date on which the Company completes a liquidation, merger, share exchange, reorganization or other similar transaction that results in all of the Company’s public shareholders having the right to exchange their Common Shares for cash, securities or other property or (y) if the last reported sale price of the Common Shares equals or exceeds $12.00 per share (as adjusted for share sub-divisions, share capitalizations, reorganizations, recapitalizations and the like) for any 20 trading days within any 30-trading day period commencing at least 150 days after the Closing, and (ii) in the case of placement units, placement shares, placement warrants issued in connection with NCAC’s initial public offering, as well as any Common Shares issued upon exercise thereof, 30 days after the Closing.
Headquarters and Operational Office
Psyence’s headquarters address is 121 Richmond Street West, Penthouse Suite 1300, Toronto, Ontario, M5H 2K1, Canada. The Company has an operational office in South Africa at Unit A210 The Old Biscuit Mil, 373-375 Albert Road, Woodstock, Cape Town, 7925.
Foreign Private Issuer Status
We are a foreign private issuer within the meaning of the rules under the Exchange Act. As such, we are exempt from certain provisions applicable to United States domestic public companies. For example:
| · | we are not required to provide as many Exchange Act reports, or as frequently, as a domestic public company; |
| | | |
| · | for interim reporting, we are permitted to comply solely with our home country requirements, which are less rigorous than the rules that apply to domestic public companies; |
| · | we are not required to provide the same level of disclosure on certain issues, such as executive compensation; |
| · | we are exempt from provisions of Regulation FD aimed at preventing issuers from making selective disclosures of material information; |
| · | we are not required to comply with the sections of the Exchange Act regulating the solicitation of proxies, consents or authorizations in respect of a security registered under the Exchange Act; and |
| · | we are not required to comply with Section 16 of the Exchange Act requiring insiders to file public reports of their share ownership and trading activities and establishing insider liability for profits realized from any “short-swing” trading transaction. |
We will be required to file an annual report on Form 20-F within four months of the end of each fiscal year. In addition, we intend to publish our results on a semi-annual basis as press releases, distributed pursuant to the rules and regulations of the Nasdaq. Press releases relating to financial results and material events will also be furnished to the SEC on Form 6-K. However, the information we are required to file with or furnish to the SEC will be less extensive and less timely compared to that required to be filed with the SEC by U.S. domestic issuers. As a result, you may not be afforded the same protections or information that would be made available to you were you investing in a U.S. domestic issuer.
The Nasdaq listing rules provide that a foreign private issuer may follow the practices of its home country, which for us is Canada, rather than the Nasdaq rules as to certain corporate governance requirements, including the requirement that the issuer have a majority of independent directors and certain audit committee, compensation committee and nominating and corporate governance committee requirements, the requirement to disclose third party director and nominee compensation and the requirement to distribute annual and interim reports. A foreign private issuer that follows a home country practice in lieu of one or more of the listing rules shall disclose in its annual reports filed with the SEC each requirement that it does not follow and describe the home country practice followed by the issuer in lieu of such requirements. Currently, the Company does not plan to rely on the home country practice exemption with respect to its corporate governance other than the quorum requirement for shareholder meetings and with respect to Nasdaq shareholder approval rules. Our bylaws provide that two shareholders holding 25% of the voting shares constitutes a quorum, as contrasted with the Nasdaq requirement of one-third of a company’s outstanding voting securities. If the Company chooses to take advantage of other home country practice in the future, its shareholders may be afforded less protection than they otherwise would enjoy under Nasdaq corporate governance listing standards applicable to U.S. domestic issuers.
Implications of Being an Emerging Growth Company
As a company with less than US$1.235 billion in revenue for the last fiscal year, we qualify as an “emerging growth company” pursuant to the Jumpstart Our Business Startups Act of 2012, as amended (the “JOBS Act”). An emerging growth company may take advantage of specified reduced reporting and other requirements that are otherwise applicable generally to public companies. These provisions include exemption from the auditor attestation requirement under Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, or Section 404, in the assessment of the emerging growth company’s internal control over financial reporting. The JOBS Act also provides that an emerging growth company does not need to comply with any new or revised financial accounting standards until such date that a private company is otherwise required to comply with such new or revised accounting standards. We intend to take advantage of certain of these exemptions.
We will remain an emerging growth company until the earliest of (i) the last day of our fiscal year during which we have total annual gross revenues of at least US$1.235 billion; (ii) the last day of our fiscal year following the fifth anniversary of the date of the first sale of our common equity securities pursuant to an effective registration statement under the Securities Act; (iii) the date on which we have, during the previous three year period, issued more than $1.0 billion in non-convertible debt; or (iv) the date on which we are deemed to be a “large accelerated filer” under the Exchange Act, which would occur if the market value of our Common Shares that are held by non-affiliates exceeds $700 million as of the last business day of our most recently completed second fiscal quarter and we have been publicly reporting for at least 12 months. Once we cease to be an emerging growth company, we will not be entitled to the exemptions provided in the JOBS Act discussed above.
Risk Factor Summary
Our business is subject to numerous risks and uncertainties, including those highlighted in the section entitled “Risk Factors,” that represent challenges that we face in connection with the successful implementation of our strategy and the growth of our business. In particular, the following considerations, among others, may offset our competitive strengths or have a negative effect on our business strategy, which could cause a decline in the price of shares of our Common Shares or warrants and result in a loss of all or a portion of your investment:
| · | We are a clinical-stage biotechnology company and have incurred significant losses since our inception. We anticipate that we will incur significant losses for the foreseeable future. |
| · | Psyence has a limited operating history and expects a number of factors to cause its operating results to fluctuate on an annual basis, which may make it difficult to predict the future performance of Psyence. |
| · | Psyence has never generated revenue and may never be profitable. |
| · | The Company will require substantial additional funding to achieve its business goals, and if it is unable to obtain this funding when needed and on acceptable terms, it could be forced to delay, limit or terminate its product development efforts. |
| · | The psychedelic therapy and biotechnology industries are undergoing rapid growth and substantial change, which has resulted in an increase in competitors, consolidation and formation of strategic relationships. Acquisitions or other consolidating transactions could harm Psyence in a number of ways, including by losing strategic partners if they are acquired by or enter into relationships with a competitor, losing customers, revenue and market share, or forcing Psyence to expend greater resources to meet new or additional competitive threats, all of which could harm Psyence’s operating results. |
| · | Current and future preclinical and clinical studies will be conducted outside the United States, and the FDA may not accept data from such studies to support any NDAs submitted after completing the applicable developmental and regulatory prerequisites (absent an IND). |
| · | There is a high rate of failure for product candidates proceeding through clinical trials. |
| · | Because the results of preclinical studies and earlier clinical trials are not necessarily predictive of future results, Psyence may not have favorable results in its planned and future clinical trials. |
| · | Negative results from clinical trials or studies of others and adverse safety events involving Psyence’s psychedelic analogs could have a material adverse effect on Psyence’s business. |
| · | Supply chain interruptions could delay Psyence in the process of developing its product candidates. |
| · | We rely on third parties to conduct our clinical trials. If these third parties do not properly and successfully carry out their contractual duties or meet expected deadlines, we may not be able to obtain regulatory approval of, or commercialize, our product candidates. |
| · | We are dependent on licensed intellectual property. If we were to lose our rights to licensed intellectual property, we may not be able to continue developing or commercializing our product candidates, if approved. If we breach any of the agreements under which we license the use, development and commercialization rights to our product candidates or technology from third parties or, in certain cases, we fail to meet certain development deadlines, we could lose license rights that are important to our business. |
| · | We (or iNGENū in conducting our clinical trials) will depend on enrollment of patients in our clinical trials for our product candidates. If we encounter difficulties enrolling patients in our clinical trials, our clinical development activities could be delayed or otherwise adversely affected. |
| · | If we fail to comply with healthcare regulations, we could face substantial enforcement actions, including civil and criminal penalties and our business, operations and financial condition could be adversely affected. |
| · | Our prospective products will be subject to the various federal and state laws and regulations relating to health and safety and failure to comply with, or changes in, these laws or regulations could have an adverse impact on our business. |
| · | Clinical trials are expensive, time-consuming, uncertain and susceptible to change, delay or termination. The results of clinical trials are open to differing interpretations. |
| · | Psyence may be subject to federal, state and foreign healthcare laws and regulations and implementation of or changes to such healthcare laws and regulations could adversely affect Psyence’s business and results of operations. |
| · | Serious adverse events or other safety risks could require Psyence to abandon development and preclude, delay or limit approval of its current or future product candidates, limit the scope of any approved label or market acceptance, or cause the recall or loss of marketing approval of products that are already marketed. |
| · | Psyence may voluntarily suspend or terminate a clinical trial if at any time its believes that any of its product candidates presents an unacceptable risk to participants, if preliminary data demonstrates that the product candidate is unlikely to receive regulatory approval or unlikely to be successfully commercialized, or if sufficient funds to proceed to the next phases of clinical trials are not raised. |
| · | The success of Psyence’s product candidates and future approved products, if any, is subject to a number of constantly-evolving state and federal laws, regulations, and enforcement policies pertaining to psilocybin containing products. |
| · | We may seek fast track and breakthrough therapy designations or priority review for one or more of our product candidates, but we might not receive such designation or priority review, and even if we do, such designation or priority review may not lead to a faster development or regulatory review or approval process, and does not assure FDA approval of our product candidates. Even if a product qualifies for such designation or priority review, the FDA may later decide that the product no longer meets the conditions for qualification or decide that the time period for FDA review or approval will not be shortened. |
| · | We may seek approval of our product candidates, where applicable, under the FDA’s accelerated approval pathway. This pathway may not lead to a faster development, regulatory review or approval process and does not increase the likelihood that our product candidates will receive marketing approval. |
| · | The psychedelic therapy industry and market are relatively new, and this industry and market may not continue to exist or grow as anticipated. |
| · | Negative public opinion and perception of the psychedelic industry could adversely impact Psyence’s ability to operate and Psyence’s growth strategy. |
| · | The expansion of the use of psychedelics in the medical industry may require new clinical research into effective medical therapies. |
| · | The psychedelic therapy industry is difficult to quantify and investors will be reliant on their own estimates of the accuracy of market data. |
| · | Psyence may not be able to adequately protect or enforce its intellectual property rights, which could harm its competitive position. |
| · | If third parties claim that intellectual property owned or used by Psyence infringes upon their intellectual property, Psyence’s operating profits could be adversely affected. |
| · | We may infringe the intellectual property rights of others, which may prevent or delay our product development efforts and stop us from commercializing or increase the costs of commercializing our product candidates. |
| · | If Psyence is not able to adequately prevent disclosure of trade secrets and other proprietary information, the value of its products could be significantly diminished. |
| · | The market price and trading volume of the Common Shares may be volatile and could decline significantly following the Business Combination. |
| · | Public Warrants are exercisable for Common Shares, which would increase the number of shares eligible for future resale in the public market and result in dilution to its shareholders. |
| · | The requirements of being a public company may strain the Company’s resources, divert the Company management’s attention and affect the Company’s ability to attract and retain qualified board members. |
| · | The Company qualifies as a foreign private issuer within the meaning of the rules under the Exchange Act, and as such the Company is exempt from certain provisions applicable to United States domestic public companies. |
| · | Psyence currently reports financial results under IFRS, which differs in certain significant respects from U.S. GAAP. |
| · | You may face difficulties in protecting your interests, and your ability to protect your rights through U.S. courts may be limited, because the Company is incorporated under the laws of Canada, the Company conducts substantially all of its operations and a majority of its directors and executive officers reside outside of the United States. |
| · | It is not expected that the Company will pay dividends in the foreseeable future. |
PRICE RANGE OF SECURITIES AND DIVIDENDS
Price Range of Securities
Our Common Shares trade on the Nasdaq Global Market under the symbol “PBM,” and certain of our Public Warrants trade on the Nasdaq Capital Market under the symbol “PBMWW.”
The closing price of our Common Shares and Public Warrants as reported by Nasdaq on February 8, 2024, was $0.94 and $0.03, respectively.
Dividends
Psyence has not paid any cash dividends on its shares to date and does not intend to pay cash dividends in the foreseeable future. The payment of cash dividends in the future will be dependent upon the Company’s revenue and earnings, if any, capital requirements and general financial condition. The payment of any cash dividends is within the discretion of the Company’s board of directors (the “Board”). Further, our ability to declare dividends may be limited by the terms of financing or other agreements entered into by us or our subsidiaries from time to time.
CAPITALIZATION
The following table sets forth the capitalization of the Company on an unaudited pro forma combined basis as of September 30, 2023, after giving effect to the Business Combination and the Financing:
| Pro Forma Ownership | | Shares | | Number of Percent
Outstanding | |
| Rollover equity shares of Psyence Biomedical shareholders | | | 5,000,000 | | 37.34 | % |
| NCAC Public Shareholders | | | 119,659 | | 0.89 | % |
| Members of Sponsor | | | 3,765,071 | | 28.12 | % |
| Sponsor | | | 2,389,929 | | 17.85 | % |
| Cantor | | | 337,000 | | 2.52 | % |
| CCM | | | 183,000 | | 1.36 | % |
| Financing Investors | | | 1,300,000 | | 9.71 | % |
| Other Third Party Advisers | | | 296,000 | | 2.21 | % |
| Total shares outstanding | | | 13,390,659 | | 100 | % |
The information set forth in the section titled “Prospectus Summary – Recent Developments – Consummation of the Business Combination – Securities Purchase Agreement” is incorporated herein by reference.
RISK FACTORS
Investing in our securities involves a high degree of risk. You should carefully consider the following information about these risks, together with the other information appearing elsewhere in this prospectus, including our financial statements, the notes thereto and the section entitled “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations,” before deciding to invest in our securities. The occurrence of any of the following risks could have a material adverse effect on our business, reputation, financial condition, results of operations and future growth prospects, as well as our ability to accomplish our strategic objectives. As a result, the trading price of our securities could decline and you could lose all or part of your investment. Additional risks and uncertainties not presently known to us or that we currently deem immaterial may also impair our business operations and the market price of our securities.
Risks Related to Our Business and Industry
We are a clinical-stage biotechnology company and have incurred significant losses since our inception. We anticipate that we will incur significant losses for the foreseeable future.
Investment in biotechnology product development is highly speculative because it entails substantial upfront capital expenditures and significant risk that any potential product candidate will fail to demonstrate effectiveness or an acceptable safety profile, gain regulatory approval and become commercially viable. All of Psyence’s product candidates will require substantial additional capital expenditures and development time, including extensive clinical research and resources, before it would be able to apply for and then receive marketing authorization and begin generating revenue from product sales.
Since its inception, Psyence has invested most of its resources in establishing strategic partnerships, securing intellectual property licensing rights, building its own intellectual property portfolio, raising capital, building its management team and providing general and administrative support for these operations. Psyence has incurred losses in each year since its inception and expects to incur significant losses for the foreseeable future. Psyence’s net loss for the years ended March 31, 2022 and March 31, 2023 was USD$1.85 million and USD$3.15 million, respectively. To date, no products have been approved for commercial sale and Psyence has not generated any revenue. Psyence has financed operations solely through the sale of equity securities and convertible debt financings. Psyence continues to incur significant research and development and other expenses related to ongoing operations and expects to incur losses for the foreseeable future, including following the completion of the Business Combination.
Due to the numerous risks and uncertainties associated with the development of its product candidates, Psyence is unable to predict the timing or amount of its expenses, or when it will be able to generate any meaningful revenue or achieve or maintain profitability, if ever. In addition, its expenses could increase beyond current expectations if Psyence is required by the Therapeutic Goods Administration in Australia (“TGA”), the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (“FDA”), the European Medicines Agency (“EMA”), Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency in the UK (“MHRA”), or other comparable foreign regulatory authorities, to perform preclinical studies or clinical trials in addition to those that Psyence currently anticipates, or if there are any delays in any of Psyence’s or its future collaborators’ clinical trials or the development of the existing product candidates and any other product candidates that Psyence may identify. Even if Psyence’s existing product candidates or any future product candidates that Psyence may identify are approved for commercial sale, Psyence anticipates incurring significant costs associated with commercializing any approved product and ongoing compliance efforts.
Psyence has a limited operating history and expects a number of factors to cause its operating results to fluctuate on an annual basis, which may make it difficult to predict the future performance of Psyence.
Psyence is a clinical stage biotechnology development company with a limited operating history. Consequently, any predictions made about Psyence’s future success or viability may not be as accurate as they could be if Psyence had a longer operating history and additional definitive partnership agreements in place. Psyence’s operating results are expected to significantly fluctuate from quarter-to-quarter or year-to- year due to a variety of factors, many of which are beyond its control. Factors relating to Psyence’s business that may contribute to these fluctuations include, but are not limited to:
| · | any delays or issues in finding, and establishing successful business arrangements with, pharmaceutical and product development partners to assist in moving its product candidates through the development and commercialization processes; |
| · | delays in the commencement, enrolment and timing of clinical trials; |
| · | the success of its preclinical trials; |
| · | potential side effects of its product candidates that could delay or prevent approval or license-out agreements or cause an approved product candidate to be eliminated; |
| · | its ability to obtain additional funding to develop its product candidates; |
| · | its ability to attract and retain talented and experienced personnel to manage its business effectively; |
| · | competition from existing psychedelic analogs companies or new psychedelic analogs companies that continue to emerge; |
| · | assuming market authorization has been obtained for our product candidates, the ability of patients or healthcare providers to obtain coverage or sufficient reimbursement for such products; |
| · | its ability to adhere to clinical study requirements directly or with third parties such as clinical research organizations (“CROs”); |
| · | its dependency on third-party manufacturers to manufacture products and key ingredients; |
| · | its ability to establish or maintain collaborations, licensing or other transactions; |
| · | its ability to defend against any challenges to its intellectual property, including claims of patent infringement; |
| · | its ability to enforce its intellectual property rights against potential competitors; |
| · | its ability to secure additional intellectual property protection for its product candidates and associated manufacturing methods currently under development; |
| · | a biological or chemical effect that Psyence does not predict; |
| · | adverse economic circumstances; |
| · | potential liability claims; and |
| · | the duration and effects of COVID-19 on Psyence’s personnel, business, operations and financial condition. |
Accordingly, the results of any historical financial periods should not be relied upon as indications of future operating performance.
Psyence has never generated revenue and may never be profitable.
Psyence may never be able to develop or commercialize marketable products or achieve profitability. Revenue from the sale of any product candidate for which regulatory approval is obtained will be dependent, in part, upon the size of the markets in the territories for which Psyence gains regulatory approval, the accepted price for the product, the acceptance of the product by physicians and patients, the ability to obtain reimbursement at any price and whether Psyence owns the commercial rights for that territory. Psyence’s growth strategy depends on its ability to generate revenue. In addition, if the number of addressable patients is not as anticipated, the indication or intended use approved by regulatory authorities is narrower than expected, or the reasonably accepted population for treatment is narrowed by competition, physician choice or treatment guidelines, Psyence may not generate significant revenue from sales of such products, even if approved. Even if Psyence is able to generate revenue from the sale of any approved products, Psyence may not become profitable and may need to obtain additional funding to continue operations. Even if Psyence were to achieve profitability in the future, it may not be able to sustain profitability in subsequent periods.
Psyence’s failure to achieve sustained profitability would depress the value of the Company and could impair its ability to raise capital, expand the business, diversify its research and development pipeline, market its product candidates, if approved, and pursue or continue operations. Psyence’s prior losses, combined with expected future losses, have had and will continue to have an adverse effect on shareholders’ equity and working capital.
The Company will require substantial additional funding to achieve its business goals, and if it is unable to obtain this funding when needed and on acceptable terms, it could be forced to delay, limit or terminate its product development efforts.
Psyence’s clinical trial and product development pipeline currently consists of one active preclinical study in Canada, and one Phase IIb study currently under review in Australia. We have also obtained approval from the MHRA to conduct a Phase IIa study in the UK, which was not initiated due to certain cost-effective incentives provided by Australia. Once the Phase IIb study in Australia is completed, a Phase III pivotal study program will begin, of which the size and number of trials will depend on the results of the Phase IIb study, the advice given to Psyence from the regulatory authorities and whether the FDA will assess the program as being fast-tracked or eligible as a breakthrough therapy. If the assessment is the latter, the Phase III program could be smaller than anticipated and less than the usual required two pivotal studies to support market authorization.
Psyence intends to submit the NDA requesting assessment via the 505(b)(2) pathway. A 505(b)(2) application is an NDA that contains full reports of investigations of safety and effectiveness, where at least some of the information required for approval comes from studies not conducted by or for the applicant, and for which the applicant has not obtained a right of reference or use, including, for example, the agency’s finding of safety and/or effectiveness for a listed drug or published literature. This could potentially allow for a shorter development program along with less data that is developed by Psyence, as compared to a regular NDA submission. Despite the usage of psilocybin for decades, there have been relatively few studies pertaining to psilocybin products due to the ban on the research into psychedelics. However, recently, academic institutions have been allowed to conduct such studies.
Conducting clinical trials and developing biopharmaceutical products is expensive and time consuming, and we expect to require substantial additional capital to conduct research, preclinical studies and clinical trials for the current and future trials, seek regulatory approvals for our product candidates and launch and commercialize any products for which Psyence may receive regulatory approval, including building our own commercial sales, marketing and distribution organization. Our management and strategic decision makers have not made decisions regarding the future allocation of certain resources among Psyence’s pipeline of trials, but continue to evaluate the needs and opportunities with respect to each of these trials routinely and on a case-by-case basis. Because the outcome of any preclinical or clinical development and regulatory approval process is highly uncertain (including the size and quantum of the Phase III registrational program), Psyence cannot reasonably estimate the actual amounts necessary to successfully complete the development, regulatory approval process and potential commercialization of its product candidates and any future product candidates it may identify.
Psyence expects that the cash provided in the Business Combination, together with Psyence’s existing cash, will be sufficient to fund operations through 18 months following the Closing. However, Psyence’s operating plan may change as a result of many factors currently unknown, and Psyence may need to seek additional funds sooner than planned, through public or private equity or debt financings, sales of assets or programs, other sources, such as strategic collaborations or license and development agreements, or a combination of these approaches. Even if Psyence believes that its funds are sufficient for its current or future operating plans, it may opportunistically seek additional capital if market conditions are favorable or for specific strategic considerations. Psyence’s spending will vary based on new and ongoing product development and business development activities. Any such additional fundraising efforts for Psyence may divert management from their day-to-day activities, which may adversely affect Psyence’s ability to develop and commercialize product candidates that Psyence may identify and pursue. Moreover, such financing may result in dilution to shareholders, imposition of debt covenants and repayment obligations, or other restrictions that may affect Psyence’s business. Changing circumstances, some of which may be beyond Psyence’s control, could cause Psyence to consume capital significantly faster than currently anticipated, and Psyence may need to seek additional funds sooner than planned. Psyence’s future funding requirements, both short-term and long-term, will depend on many factors, including, but not limited to:
| · | the time and cost necessary to complete ongoing and planned clinical trials; |
| · | the outcome, timing and cost of meeting regulatory requirements established by the TGA, FDA, the EMA, the MHRA and other comparable foreign regulatory authorities; |
| · | the progress, timing, scope and costs of preclinical studies, clinical trials and other related activities for ongoing and planned clinical trials, and potential future clinical trials; |
| · | the costs of obtaining clinical and commercial supplies of raw materials and drug products for Psyence’s product candidates, as applicable, and any other product candidates Psyence may identify and develop; |
| · | Psyence’s ability to successfully identify and negotiate acceptable terms for third-party supply and contract manufacturing agreements with contract manufacturing organizations (“CMOs”); |
| · | the costs of commercialization activities for any of Psyence’s product candidates that receive marketing approval, including the costs and timing of establishing product sales, marketing, distribution and manufacturing capabilities, or entering into strategic collaborations with third parties to leverage or access these capabilities; |
| · | the amount and timing of sales and other revenues from Psyence’s product candidates, if approved, including the sales price and the availability of coverage and adequate third-party reimbursement; |
| · | the cash requirements of developing Psyence’s programs and Psyence’s ability and willingness to finance their continued development; |
| · | the cash requirements of any future acquisitions or discovery of product candidates; |
| · | the time and cost necessary to respond to technological and market developments, including other products that may compete with one or more of Psyence’s product candidates; |
| · | the costs of acquiring, licensing or investing in intellectual property rights, products, product candidates and businesses; |
| · | the costs of maintaining, expanding and protecting Psyence’s intellectual property portfolio; |
| · | its ability to attract, hire and retain qualified personnel as Psyence expands research and development and establishes a commercial infrastructure; and |
| · | the costs of operating as a public company in the United States and maintaining a listing on Nasdaq. |
Psyence cannot be certain that additional funding will be available on acceptable terms, or at all. Market volatility resulting from the COVID-19 pandemic and the related U.S. and global economic impact or other factors could also adversely impact the ability to access funds as and when needed. If adequate funds are not available to Psyence on a timely basis, Psyence may be required to delay, limit or terminate one or more research or development programs or trials or the potential commercialization of any approved products or be unable to expand operations or otherwise capitalize on business opportunities, as desired, which could materially affect Psyence’s business, prospects, financial condition and results of operations.
We depend on our current key personnel and our ability to attract and retain employees.
Our future growth and success depends on our ability to recruit, retain, manage and motivate our employees. We are highly dependent on our current management and scientific personnel, including Dr. Neil Maresky (Chief Executive Officer), Jody Aufrichtig (Executive Chairman), Warwick Corden-Lloyd (Chief Financial Officer), Dr. Clive Ward-Able (Medical Director) and Taryn Vos (General Counsel). The inability to hire or retain experienced management personnel could adversely affect our ability to execute our business plan and harm our operating results. Due to the specialized scientific and managerial nature of our business, we rely heavily on our ability to attract and retain qualified scientific, technical and managerial personnel. The competition for qualified personnel in the pharmaceutical field is intense and we may be unable to continue to attract and retain qualified personnel necessary for the development of our business or to recruit suitable replacement personnel.
The pro forma financial statements are presented for illustrative purposes only and may not be an indication of the Company’s financial condition or results of operations following the completion of the Business Combination.
The pro forma financial statements contained in this prospectus are presented for illustrative purposes only and may not be an indication of the Company’s financial condition or results of operations following the completion of the Business Combination for several reasons. The pro forma financial statements have been derived from the historical financial statements of NCAC and Psyence and adjustments and assumptions have been made regarding the Company after giving effect to the Business Combination. The information upon which these adjustments and assumptions have been made is preliminary, and these kinds of adjustments and assumptions are difficult to make with accuracy. As a result, the actual financial condition and results of operations of the Company following the completion of the Business Combination may not be consistent with, or evident from, these pro forma financial statements. The assumptions used in preparing the pro forma financial information may not prove to be accurate, and other factors may affect the Company’s financial condition or results of operations following the Business Combination. Any decline or potential decline in the Company’s financial condition or results of operations may cause significant variations in the market price of the Company’s securities.
Our historical financial results and our unaudited pro forma combined financial statements may not be representative of our results as a separate, stand-alone company.
The historical financial information we have included in this prospectus has been derived from the financial statements and accounting records of Parent and does not necessarily reflect what our financial position, results of operations or cash flows would have been had we been a separate, stand-alone company during the periods presented. The historical information does not necessarily indicate what our results of operations, financial position, cash flows or costs and expenses will be in the future. Our pro forma financial information set forth under “Unaudited Pro Forma Combined Financial Information” reflects changes to our operations as a result of the separation. However, there can be no assurances that this unaudited pro forma combined financial information will appropriately reflect our financial position or results of operations as a separate, stand-alone company.
The psychedelic therapy and biotechnology industries are undergoing rapid growth and substantial change, which has resulted in an increase in competitors, consolidation and formation of strategic relationships. Acquisitions or other consolidating transactions could harm Psyence in a number of ways, including by losing strategic partners if they are acquired by or enter into relationships with a competitor, losing customers, revenue and market share, or forcing Psyence to expend greater resources to meet new or additional competitive threats, all of which could harm Psyence’s operating results.
The psychedelic therapy and biotechnology industries are intensely competitive and subject to rapid and significant technological change. Psyence has competitors in Canada, the United States, Europe and other jurisdictions, including major multinational pharmaceutical companies, established biotechnology companies, specialty pharmaceutical and generic drug companies and universities and other research institutions. Many of its competitors have greater financial and other resources, such as larger research and development staff and more experienced marketing and manufacturing organizations than it does. Large pharmaceutical companies, in particular, have extensive experience in, and substantial capital resources for, conducting research, molecular derivative development, obtaining regulatory approvals, obtaining intellectual property protection and establishing key relationships. These companies also have significantly greater sales and marketing capabilities and experience in completing collaborative transactions in Psyence’s target markets with leading companies and research institutions.
Psyence’s competitors may introduce new psychedelic analogs or develop technological advances that compete with Psyence. Psyence cannot predict the timing or impact of competitors introducing new psychedelic analogs or technological advances. Such competing psychedelic analogs may be safer, more effective, more effectively marketed, licensed or sold or have lower prices or superior performance features than Psyence’s psychedelic analogs, and this could negatively impact Psyence’s business and results of operations. Established pharmaceutical companies may also invest heavily to accelerate discovery and development of novel compounds or to in-license novel compounds that could make the psychedelic analogs that Psyence develops obsolete. As a result of any of these factors, Psyence’s competitors may succeed in obtaining patent protection or discovering, developing and commercializing psychedelic analogs before Psyence does or may develop psychedelic analogs that are deemed to be more effective or gain greater market acceptance than those of Psyence.
Smaller or early-stage companies may also prove to be significant competitors, particularly through collaborative transactions with large, established companies. In addition, many universities and private and public research institutions may become active in the development of novel compounds. Psyence’s competitors may succeed in developing, acquiring or licensing on an exclusive basis, technologies and psychedelic analogs that are more effective or less costly than any of the psychedelic analogs that Psyence is currently developing or that it may develop, which could render its psychedelic analogs obsolete or non- competitive. If Psyence’s competitors market psychedelic analogs that are more effective, safer or less expensive or that reach the market sooner than Psyence’s psychedelic analogs, if any, Psyence may not achieve commercial success. In addition, because of its limited resources, it may be difficult for Psyence to stay abreast of the rapid changes in each technology. If Psyence fails to stay at the forefront of technological change, it may be unable to compete effectively. Technological advances or products developed by its competitors may render its technologies or psychedelic analogs obsolete, less competitive or not economical.
Current and future preclinical and clinical studies will be conducted outside the United States, and the FDA may not accept data from such studies to support any NDAs submitted after completing the applicable developmental and regulatory prerequisites (absent an IND).
Psyence is conducting a preclinical and a clinical study outside the United States. Psyence has received full approval of a study in the UK from the MHRA, which was not initiated due to certain cost-effective incentives provided by Australia. Psyence has also made a submission to the Australian Human Research Ethics Committees (HRECs) for the review of research proposals involving human participants to ensure that they are ethically acceptable. The protocol under review in Australia will be reviewed as part of a Pre-IND (Investigational New Drug) application by the FDA. To the extent Psyence does not conduct these clinical trials under an IND, the FDA may not accept data from such trials. Although the FDA may accept data from clinical trials conducted outside the United States that are not conducted under an IND, the FDA’s acceptance of these data is subject to certain conditions. For example, the clinical trial must be well designed and conducted and performed by qualified investigators in accordance with ethical principles and all applicable FDA regulations. The trial population must also adequately represent the intended U.S. population, and the data must be applicable to the U.S. population and U.S. medical practice in ways that the FDA deems clinically meaningful. There can be no guarantee that the FDA will accept data from trials conducted outside of the United States. If the FDA does not accept the data from such clinical trials, this would likely result in the need for additional trials and the completion of additional regulatory steps, which would be costly and time-consuming and could delay or permanently halt the development of Psyence’s product candidates.
There is a high rate of failure for product candidates proceeding through clinical trials.
Psyence has no registered products on the market, and its new potential psilocybin-based product candidates are currently either in the preclinical or clinical development phase. Psyence’s ability to achieve and sustain profitability with respect to its product candidates in which psilocybin is featured as the active pharmaceutical ingredient depends on obtaining regulatory approvals for and, if approved, successfully commercializing, its product candidates, either alone or with third parties. Before obtaining regulatory approval for the commercial distribution of its current or future product candidates, Psyence or an existing or future collaborator must conduct extensive preclinical tests and clinical trials to demonstrate the safety, purity and potency of its product candidates.
Generally, there is a high rate of failure for product candidates proceeding through clinical trials. Psyence may suffer significant setbacks in its clinical trials similar to the experience of a number of other companies in the pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries, even after receiving promising results in earlier trials. Further, even if Psyence views the results of a clinical trial to be positive, applicable international regulatory authorities may disagree with Psyence’s interpretation of the data. In the event that Psyence obtains negative results from clinical trials for product candidates or other problems related to potential chemistry, manufacturing and control issues or other hurdles occur and its current or future product candidates are not approved, Psyence may not be able to generate sufficient revenue or obtain financing to continue its operations, its ability to execute on its current business plan may be materially impaired and its reputation in the industry and in the investment community might be significantly damaged. In addition, Psyence’s inability to properly design, commence and complete clinical trials may negatively impact the timing and results of its clinical trials and ability to seek approvals for its product candidates.
The testing, marketing and manufacturing of any new drug product for use in the U.S. will require approval from the FDA. Psyence cannot predict with any certainty the amount of time necessary to obtain such FDA approval and whether any such approval will ultimately be granted. Preclinical and clinical trials may reveal that one or more product candidates are ineffective or unsafe, in which event further development of such product candidates could be seriously delayed or terminated. Moreover, obtaining approval for certain product candidates may require testing on human subjects of substances whose effects on humans are not fully understood or documented. Delays in obtaining FDA or any other necessary regulatory approvals of any proposed drug and failure to receive such approvals would have an adverse effect on the drug’s potential commercial success and on Psyence’s business, prospects, financial condition and results of operations. In addition, it is possible that a proposed drug may be found to be ineffective or unsafe due to conditions or facts that arise after development has been completed and regulatory approvals have been obtained. In this event, Psyence may be required to withdraw such proposed drug from the market. To the extent that its success will depend on any regulatory approvals from government authorities outside of the U.S. that perform roles similar to that of the FDA, uncertainties similar to those stated above will also exist.
Because the results of preclinical studies and earlier clinical trials are not necessarily predictive of future results, Psyence may not have favorable results in its planned and future clinical trials.
Successful development of therapeutic products is highly uncertain and is dependent on numerous factors, many of which are beyond Psyence’s control. Product candidates that appear promising in the early phases of development may fail to reach the market for several reasons, including, but not limited to:
| · | preclinical or clinical study results that may show the product to be less effective than desired (e.g., the study failed to meet Psyence’s primary objectives) or to have harmful or problematic side effects; |
| · | failure to receive the necessary regulatory approvals or a delay in receiving such approvals. Among other things, such delays may be caused by slow enrollment in clinical studies, length of time to achieve study endpoints, additional time requirements for data analysis or regulatory requests for additional preclinical or clinical data or unexpected safety or manufacturing issues; |
| · | manufacturing costs, pricing, or reimbursement issues or other factors that make the product not economical; and |
| · | the proprietary rights of others and their competing products and technologies that may prevent the product from being commercialized. |
Any positive results from preclinical testing of Psyence’s prospective product candidates may not necessarily be predictive of the results from planned or future clinical trials for such product candidates. Many companies in the pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries have suffered significant setbacks in clinical trials after achieving positive results in preclinical and early clinical development, and Psyence cannot be certain that it will not face similar setbacks. These setbacks have been caused by, among other things, preclinical findings while clinical trials were underway or safety or efficacy observations in clinical trials, including adverse events. If Psyence fails to produce positive results in its planned clinical trials for its product candidates as described in the section titled “Business”, or its future clinical trials, the development timeline and regulatory approval and commercialization prospects for such product candidates, and, correspondingly, Psyence’s business and financial prospects, would be materially adversely affected.
Negative results from clinical trials or studies of others and adverse safety events involving Psyence’s psychedelic analogs could have a material adverse effect on Psyence’s business.
From time to time, studies or clinical trials on medical-grade psilocybin mushroom products may be conducted or sponsored by academics, research institutions or others, including government agencies. The publication of negative results of studies or clinical trials related to Psyence’s proposed products or the therapeutic areas in which Psyence’s proposed products will compete could have a material adverse effect on Psyence’s business, prospects, financial condition and results of operations.
Supply chain interruptions could delay Psyence in the process of developing its product candidates.
There are few licensed suppliers of input materials for the manufacture of Psyence’s product candidates. Any loss of stored materials or facilities through fire, theft or other causes could have an adverse effect on Psyence’s ability to procure the product candidate materials and continue product development activities. Furthermore, Psyence is largely dependent on Filament, for the supply of PEX010 (a capsule containing 25mg naturally sourced psilocybin and product being used in Psyence’s Phase IIb Study), and despite Psyence’s rights to manufacture the product candidate itself or through a third-party CMO in the event that Filament is unable to meet an order or demand for product, any interruption in Filament’s supply chain will lead to delays in Psyence’s drug development timelines. Furthermore, Filament will be required to continue to meet regulatory requirements applicable to the PEX010 product candidate and maintain GMP compliant standards which dictate the minimum requirements for the methods, facilities and controls used in manufacturing, processing and packing of a drug product. There can be no assurances that Filament or any CMOs will be able to meet Psyence’s timetable and requirements or carry out their contractual obligations in accordance with the applicable regulations. In addition, the drug product supplied to Psyence may not meet its specifications and quality policies and procedures nor may they be able to supply the drug product in commercial quantities when the time comes. If Psyence is unable to arrange for alternative third-party supply sources on commercially reasonable terms or in a timely manner, it may delay the development of its product candidates and could have a material adverse effect on Psyence’s business operations and financial condition.
Further, the failure of CMOs to operate in compliance with GMP or other applicable quality related regulations could result in, among other things, certain product liability claims in the event such failure to comply results in defective products that caused injury or harm. In general, Psyence’s dependence upon third parties for the supply of Psyence’s drug product may adversely affect profit margins and Psyence’s ability o develop and deliver viable end products on a timely and competitive basis.
Psyence’s proprietary information, or that of its strategic business partners, may be lost or Psyence may suffer security breaches.
In the ordinary course of business, Psyence collects and stores sensitive data, including valuable and commercially sensitive intellectual property, clinical trial data, proprietary business information and that of Psyence’s strategic business partners, as well as the personally identifiable information of clinical trial subjects, employees and patients, in and on Psyence’s networks. Despite security measures, information technology and infrastructure may be vulnerable to attacks by hackers or breached due to employee error, malfeasance or other disruptions. Any such breach could compromise Psyence’s networks and the information stored there could be accessed, publicly disclosed, lost or stolen. Any such access, disclosure or other loss of information could result in legal claims or proceedings, liability under laws that protect the privacy of personal information, regulatory penalties, disruption of operations, damage to Psyence’s reputation, and cause a loss of confidence in Psyence’s ability to conduct clinical trials, which could adversely affect Psyence’s business, prospects, financial condition and results of operations.
Costs associated with compliance with numerous laws and regulations could impact our financial results. In addition, we could become subject to increased enforcement and/or litigation risks associated with the psychedelic therapeutics industry.
The manufacture, labeling and distribution of products containing psilocybin or other psychedelic analogs is governed by various federal, state and local agencies. To the extent we are able to successfully commercialize any of our currently contemplated product candidates via the FDA’s NDA approval pathway, the presence of psychedelic analogs as active or inactive ingredients, as applicable, may give rise to heightened regulatory scrutiny and greater risk of consumer litigation, either of which could further restrict the permissible scope of our marketing claims about such products or our ability to sell them in the United States at all. The shifting compliance environment and the need to build and maintain robust systems to comply with different psychedelic-related regulations in jurisdictions may increase costs and/or the risk that we may violate one or more applicable regulatory requirements. If our operations, or any of our activities or prospective products, are found to be in violation of any such laws or any other governmental regulations that apply to the manufacture, distribution, or sale of prescription drug products, generally, and to products containing psychedelic analogs, we may be subject to penalties, including, without limitation, civil and criminal penalties, damages, fines, the curtailment or restructuring of our operations, any of which could adversely affect our ability to operate our business or our financial results.
Failure to comply with any applicable regulatory requirements, relating to psilocybin or otherwise, may result in, among other things, injunctions, product withdrawals, recalls, product seizures, fines and criminal prosecutions. Additionally, advertising and labeling laws are often enforced by governmental officials, and any action based on potentially misleading or deceptive advertising is often followed by costly class-action complaints under consumer-protection laws.
Psyence may acquire businesses or products, or form additional strategic alliances, in the future, and may not realize the benefits of such acquisitions.
Psyence may acquire additional businesses or products, form additional strategic alliances, or create joint ventures with third parties that it believes will complement or augment its existing business. Any of these relationships may require Psyence to incur non-recurring and other charges, increase Psyence’s near and long-term expenditures, issue securities that dilute Psyence’s existing shareholders or disrupt Psyence’s management and business. In addition, we face significant competition in seeking appropriate strategic partners and the negotiation process is time-consuming and complex. If Psyence acquires businesses with promising markets or technologies, it may not be able to realize the benefit of acquiring such businesses if it is unable to successfully integrate them with its existing operations and company culture. Psyence may encounter numerous difficulties in developing, manufacturing, and marketing any new products resulting from a strategic alliance or acquisition that delay or prevent it from realizing their expected benefits or enhancing its business. There is no assurance that, following any such acquisition, Psyence will achieve the synergies expected in order to justify the transaction, which could result in a material adverse effect on its business and prospects.
We will need substantial additional financing to develop our product candidates and implement our operating plans. If we fail to obtain additional financing, we may be unable to complete the development and commercialization of our product candidates.
We expect to spend a substantial amount of capital in the development and manufacturing of our product candidates, and we will need substantial additional financing to do so. In particular, we will require substantial additional financing to enable commercial production of our product candidates and initiate and complete registrational trials for multiple products in multiple regions. Further, if approved, we will require significant additional capital in order to launch and commercialize our product candidates.
As of September 30, 2023, we had USD$605,480 in cash and cash equivalents. Changing circumstances may cause us to consume capital significantly faster than we currently anticipate, and we may need to spend more money than currently expected because of circumstances beyond our control. We may also need to raise additional capital sooner than we currently anticipate if we choose to expand more rapidly than we presently plan. In any event, we will require additional capital for the further development and commercialization of our product candidates.
We cannot be certain that additional funding will be available on acceptable terms, or at all. We have no committed source of additional capital. If we are unable to raise additional capital in sufficient amounts or on terms acceptable to us, we may have to significantly delay, scale back or discontinue the development or commercialization of our product candidates or other research and development initiatives. We could be required to seek collaborators for our product candidates at an earlier stage than otherwise would be desirable or on terms that are less favorable than might otherwise be available or relinquish or license on unfavorable terms our rights to our product candidates in markets where we otherwise would seek to pursue development or commercialization ourselves.
Any of the above events could significantly harm our business, prospects, financial condition and results of operations and cause the price of our Common Shares to decline.
In addition, future changes in regulations, changes in legal status of psilocybin-containing products, more vigorous enforcement thereof or other unanticipated events could require extensive changes to Psyence’s operations, increased compliance costs or give rise to material liabilities, which could have a material adverse effect on the business, results of operations and financial condition of Psyence.
We rely on third parties to conduct our clinical trials. If these third parties do not properly and successfully carry out their contractual duties or meet expected deadlines, we may not be able to obtain regulatory approval of, or commercialize, our product candidates.
Psyence relies on iNGENū to conduct clinical development activities with Psyence’s product candidates, which activities involve trial design, regulatory submissions, clinical patient recruitment, clinical trial monitoring, clinical data management and analysis, safety monitoring and project management.
Additionally, we expect to utilize and depend upon independent investigators and collaborators, such as medical institutions, CROs, CDMOs and strategic partners to conduct our preclinical studies under agreements with us and in connection with our clinical trials. We expect to have to negotiate budgets and contracts with CROs, trial sites and CDMOs, which may result in delays to our development timelines and increase costs. We will rely heavily on these third parties over the course of our clinical trials, and we control only certain aspects of their activities. As a result, we have less direct control over the conduct, timing and completion of these clinical trials and the management of data developed through clinical trials than would be the case if we were relying entirely upon our own staff. Nevertheless, we are responsible for ensuring that each of our studies is conducted in accordance with applicable protocol, legal and regulatory requirements and scientific standards and our reliance on third parties does not relieve us of our regulatory responsibilities. We and these third parties are required to comply with good clinical practices (“GCPs”), which are regulations and guidelines enforced by the FDA and comparable foreign regulatory authorities for product candidates in clinical development. Regulatory authorities enforce these GCPs through periodic inspections of trial sponsors, principal investigators and trial sites. If we or any of these third parties fail to comply with applicable GCP regulations, the clinical data generated in our clinical trials may be deemed unreliable and the FDA or comparable foreign regulatory authorities may require us to perform additional clinical trials before approving our marketing applications. We cannot assure you that, upon inspection, such regulatory authorities will determine that any of our clinical trials comply with the GCP regulations. Our failure or any failure by these third parties to comply with these regulations or to recruit a sufficient number of patients may require us to repeat clinical trials, which would delay the regulatory approval process. Moreover, our business may be implicated if any of these third parties violates federal or state fraud and abuse or false claims laws and regulations or healthcare privacy and security laws.
Any third parties conducting our clinical trials are not and will not be our employees and, except for remedies available to us under our agreements with such third parties, we cannot control whether or not they devote sufficient time and resources to our product candidates. These third parties may also have relationships with other commercial entities, including our competitors, for whom they may also be conducting clinical trials or other drug development activities, which could affect their performance on our behalf. If these third parties do not successfully carry out their contractual duties or obligations or meet expected deadlines, if they need to be replaced or if the quality or accuracy of the clinical data they obtain is compromised due to the failure to adhere to our clinical protocols or regulatory requirements or for other reasons, our clinical trials may be extended, delayed or terminated and we may not be able to complete development of, obtain regulatory approval of or successfully commercialize our product candidates. As a result, our financial results and the commercial prospects for our product candidates would be harmed, our costs could increase and our ability to generate revenue could be delayed.
Switching or adding third parties to conduct our clinical trials involves substantial cost and requires extensive management time and focus. In addition, changes in manufacturers often involve changes in manufacturing procedures and processes, which could require that we conduct bridging studies between our prior clinical supply used in our clinical trials and that of any new manufacturer. We may be unsuccessful in demonstrating the comparability of clinical supplies which could require the conduct of additional clinical trials. Additionally, there is a natural transition period when a new third party commences work. As a result, delays occur, which can materially impact our ability to meet our desired clinical development timelines.
We are dependent on licensed intellectual property. If we were to lose our rights to licensed intellectual property, we may not be able to continue developing or commercializing our product candidates, if approved. If we breach any of the agreements under which we license the use, development and commercialization rights to our product candidates or technology from third parties or, in certain cases, we fail to meet certain development deadlines, we could lose license rights that are important to our business.
We do not currently own any patents, and we are heavily reliant upon a number of license agreements under which we are granted rights to intellectual property that are important to our business and we may need or choose to enter into additional license agreements in the future.
Specifically, our business and active Phase IIb clinical trial are highly dependent on Research IP Agreement with Filament, which expires in April 2027. Until we develop our own product candidates, the termination, non-renewal or hinderance of use of the license granted under the Research IP Agreement would have a material adverse effect on our ability to develop its product candidates as it currently does.
Our existing license agreements impose, and we expect that future license agreements will impose on us, various development, regulatory and/or commercial diligence obligations, payment of milestones and/or royalties and other obligations. If we fail to comply with our obligations under these agreements, the licensor may have the right to terminate the license, in which event we would not be able to market products covered by the license. Our business could suffer, for example, if any current or future licenses terminate, if the licensors fail to abide by the terms of the license, if the licensed patents or other rights are found to be invalid or unenforceable, or if we are unable to enter into necessary licenses on acceptable terms.
Licensing of intellectual property is of critical importance to our business and involves complex legal, business and scientific issues. Disputes may arise between us and our licensors regarding intellectual property subject to a license agreement, including:
| · | the scope of rights granted under the license agreement and other interpretation-related issues; |
| · | whether and the extent to which our technology and processes infringe on intellectual property of the licensor that is not subject to the licensing agreement; |
| · | our right to sublicense patent and other rights to third parties; |
| · | our diligence obligations with respect to the use of the licensed technology in relation to our development and commercialization of our product candidates, and what activities satisfy those diligence obligations; |
| · | our obligation to pursue, or license others to pursue, development of indications we are not currently pursuing; |
| · | the ownership of inventions and know-how resulting from the joint creation or use of intellectual property by our licensors and us and our partners; |
| · | our right to transfer or assign the license; and |
| · | the effects of termination. |
If disputes over intellectual property that we have licensed prevent or impair our ability to maintain our current licensing arrangements on acceptable terms, we may be unable to successfully develop and commercialize the affected product candidates.
We may enter into additional licenses to third-party intellectual property that are necessary or useful to our business. Our current licenses and any future licenses that we may enter into may impose various royalty payment, milestone, and other obligations on us. Under some license agreements, we may not control prosecution of the licensed intellectual property, or may not have the first right to enforce the intellectual property. In those cases, we may not be able to adequately influence patent prosecution or enforcement, or prevent inadvertent lapses of coverage due to failure to pay maintenance fees. If we fail to comply with any of our obligations under a current or future license agreement, the licensor may allege that we have breached our license agreement, and may accordingly seek to terminate our license. Termination of any of our current or future licenses could result in our loss of the right to use the licensed intellectual property, which could materially adversely affect our ability to develop and commercialize a product candidate or product, if approved, as well as harm our competitive business position and our business prospects. Under some license agreements, termination may also result in the transfer of or granting in rights under certain of our intellectual property and information related to the product candidate being developed under the license, such as regulatory information.
The agreements under which we license intellectual property or technology to or from third parties are complex, and certain provisions in such agreements may be susceptible to multiple interpretations. The resolution of any contract interpretation disagreement that may arise could narrow what we believe to be the scope of our rights to the relevant intellectual property or technology or increase what we believe to be our financial or other obligations under the relevant agreement, either of which could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects. Moreover, if disputes over intellectual property that we have licensed prevent or impair our ability to maintain our current licensing arrangements on commercially acceptable terms, we may be unable to successfully develop and commercialize the affected product candidates.
In addition, if our licensors fail to abide by the terms of the license, if the licensors fail to prevent infringement by third parties, if the licensed patents or other rights are found to be invalid or unenforceable, or if we are unable to enter into necessary licenses on acceptable terms, our business could suffer. Moreover, our licensors may own or control intellectual property that has not been licensed to us and, as a result, we may be subject to claims, regardless of their merit, that we are infringing, misappropriating or otherwise violating the licensor’s rights.
Similarly, if we are unable to successfully obtain rights to required third-party intellectual property rights or maintain the existing intellectual property rights we have, we may have to seek alternative options, such as developing new product candidates with design-around technologies, which may require more time and investment, or abandon development of the relevant research programs or product candidates and our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects could suffer.
We (or iNGENū in conducting our clinical trials) will depend on enrollment of patients in our clinical trials for our product candidates. If we encounter difficulties enrolling patients in our clinical trials, our clinical development activities could be delayed or otherwise adversely affected.
Identifying and qualifying patients to participate in clinical trials of our product candidates will be critical to our success. We may experience difficulties in patient enrollment in our clinical trials for a variety of reasons. The timely completion of clinical trials in accordance with their protocols depends, among other things, on our ability to enroll a sufficient number of patients who remain in the study until its conclusion. The enrollment of patients depends on many factors, including:
| · | the patient eligibility criteria defined in the protocol; |
| · | the number of patients with the disease or condition being studied; |
| · | the perceived risks and benefits of the product candidate in the trial; |
| · | clinicians’ and patients’ perceptions as to the potential advantages of the product candidate being studied in relation to other available therapies, including any new drugs that may be approved for the indications we are investigating or drugs that may be used off-label for these indications; |
| · | the size and nature of the patient population required for analysis of the trial’s primary and secondary endpoints; |
| · | the proximity of patients to study sites; |
| · | the design of the clinical trial; |
| · | our ability to recruit clinical trial investigators with the appropriate competencies and experience; |
| · | competing clinical trials for similar therapies or other new therapeutics not involving psychedelic therapies; |
| · | our ability to obtain and maintain patient consents; |
| · | disruptions to health care systems caused by the coronavirus pandemic or outbreaks of other infections; |
| · | the risk that patients enrolled in clinical trials will drop out of the clinical trials before completion of their treatment; and |
| · | other public health factors, including the coronavirus pandemic or outbreaks of other infections. |
Moreover, because our product candidates represent a departure from more commonly used methods for AjD treatment, potential study participants and their doctors may be inclined to use conventional therapies, such as pure psychotherapy, rather than participate in our clinical trials.
Delays in patient enrollment may result in increased costs or may affect the timing or outcome of the planned clinical trials, which could prevent completion of these clinical trials and adversely affect our ability to advance the development of our product candidates. In addition, many of the factors that may lead to a delay in the commencement or completion of clinical trials may also ultimately lead to the denial of regulatory approval of our product candidates.
Psyence’s insurance coverage may be inadequate or expensive.
Psyence’s business is subject to a number of risks and hazards generally, including adverse clinical trial results, accidents, labor disputes and changes in the regulatory environment. Such occurrences could result in damage to assets, personal injury or death, environmental damage, delays in operations, monetary losses and possible legal liability.
Psyence’s insurance may not cover all the potential risks associated with its operations. Psyence may also be unable to maintain insurance to cover these risks at economically feasible premiums. Insurance coverage may not be available (or generally available on acceptable terms) or may not be adequate to cover any resulting liability. The successful assertion of one or more large claims against us that exceed available insurance coverage, or the occurrence of changes in our insurance policies, including premium increases or the imposition of large retention, or deductible, or co-insurance requirements, could have an adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
Certain significant personnel may allocate their time to other businesses, which may cause conflicts of interest in their determination as to how much time to devote to our affairs and potentially competitive fiduciary and pecuniary interests that conflict with our interests.
Certain of Psyence’s directors and officers do not devote their full time to the affairs of Psyence and certain of Psyence’s directors and officers are also directors, officers and shareholders of other biotechnology and research and development companies or other public companies in general, and as a result they may find themselves in a position where their duty to another company conflicts with their duty to Psyence. Although Psyence has policies which address such potential conflicts and the Business Corporations Act (Ontario) has provisions governing directors in the event of such a conflict, there is no assurance that any such conflicts will be resolved in favor of Psyence. If any such conflicts are not resolved in favor of Psyence, Psyence may be adversely affected.
Risks Related to Regulatory Matters
If we fail to comply with healthcare regulations, we could face substantial enforcement actions, including civil and criminal penalties and our business, operations and financial condition could be adversely affected.
The research and development, studying, manufacturing, packaging, labeling, advertising and distribution of Psyence’s planned product candidates are subject to regulation by one or more governmental authorities, and various agencies of the federal, provincial, state and localities in which Psyence intends to commercialize its products. These governmental authorities may attempt to regulate any of its products that fall within their jurisdiction. Such governmental authorities may not accept the evidence of safety for any ingredients that Psyence may want to market, may determine that a particular product or product ingredient presents an unacceptable health risk and may determine that a particular statement of nutritional support that Psyence wants to use is an unacceptable claim. Such a determination would prevent Psyence from marketing particular products or using certain statements of nutritional support on its products. Psyence also may be unable to disseminate third-party literature that supports its products if the third-party literature fails to satisfy certain requirements. In addition, governmental authorities could require Psyence to remove a particular product from the market. Any recall or removal would result in additional costs to Psyence, including lost revenues from any products that it is required to remove from the market, any of which could be material. Any such product recalls or removals could lead to liability, substantial costs and reduced growth prospects, all of which could be material.
Our prospective products will be subject to the various federal and state laws and regulations relating to health and safety and failure to comply with, or changes in, these laws or regulations could have an adverse impact on our business.
We are in the process of developing an investigational new drug for which we intend to pursue FDA approval via the New Drug Application (“NDA”) process.
In connection with our development and future commercialization (if applicable) of the above- described prospective products, we and each contemplated product candidate are subject to the Federal Food Drug and Cosmetic Act (FDCA). The FDCA is intended to assure the consumer, in part, that drugs and devices are safe and effective for their intended uses and that all labeling and packaging is truthful, informative, and not deceptive. The FDCA and FDA regulations define the term “drug,” in part, by reference to its intended use, as “articles intended for use in the diagnosis, cure, mitigation, treatment, or prevention of disease” and “articles (other than food) intended to affect the structure or any function of the body of man or other animals.” Therefore, almost any ingested or topical or injectable product that, through its label or labeling (including internet websites, promotional pamphlets, and other marketing material), that is claimed to be beneficial for such uses will be regulated by FDA as a drug. The definition also includes components of drugs, such as active pharmaceutical ingredients. Drugs must generally either receive premarket approval by FDA through the NDA process or conform to a “monograph” for a particular drug category, as established by FDA’s Over-the-Counter (OTC) Drug Review. If the FDA does not award premarket approval for our product candidates through the NDA process, this could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
The FDA will accept data from studies performed in other countries, as long as the study complies with GCP and ICH guidelines. FDA will review the Phase IIb protocol prior to the start of the study to provide advice on what and how aspects of the trial will be captured. Advice from a pre-IND meeting with the FDA was received in July 2023, which informed the Phase IIb study design and may also inform the phase III program we plan to do.
Clinical trials are expensive, time-consuming, uncertain and susceptible to change, delay or termination. The results of clinical trials are open to differing interpretations.
Clinical testing is expensive, time consuming, and uncertain as to outcome and may be more costly than anticipated due various factors including, but not limited to, regulatory environment, legal compliance, supply and demand of services and inflationary costs. We cannot guarantee that any clinical trials will be conducted as planned or completed on schedule, or at all. Failures in connection with one or more clinical trials can occur at any stage of testing.
Regulatory agencies may analyze or interpret the results of clinical trials differently than Psyence. Even if the results of the clinical trials are favorable, the clinical trials for the product candidates are expected to continue for several years and may take significantly longer to complete. Events that may prevent successful or timely completion of clinical development include:
| · | delays in reaching a consensus with regulatory authorities on trial design and other trial related matters; |
| · | delays in reaching agreement on acceptable terms with prospective third party service providers assisting the CROs in the conduct of the trial; |
| · | actual or perceived lack of effectiveness of the product candidate during clinical trials; |
| · | discovery of serious or unexpected toxicities or side effects experienced by trial participants or other safety issues, such as drug interactions; |
| · | slower than expected rates of subject recruitment and enrollment rates in clinical trials; |
| · | difficulty in retaining subjects for the entire duration of applicable clinical studies (as study subjects may withdraw at any time due to adverse side effects from the therapy, insufficient efficacy, fatigue with the clinical trial process, death or for any other reason; |
| · | delays or inability in manufacturing or obtaining sufficient quantities of materials for use in clinical trials due to regulatory and manufacturing constraints; |
| · | inadequacy of or changes in manufacturing process or product candidate formulation; |
| · | delays in obtaining and maintaining regulatory authorizations, including “clinical holds” or delays requiring suspension or termination of a trial by a regulatory agency, such as the TGA, before or after a trial is commenced; |
| · | changes in applicable regulatory policies and regulation, including changes to requirements imposed on the extent, nature or timing of studies; |
| · | uncertainty regarding proper dosing; |
| · | delay or failure to supply product for use in clinical trials which conforms to regulatory specification; |
| · | unfavorable results from ongoing pre-clinical studies and clinical trials; |
| · | failure of the CRO, or other third-party contractors to comply with all contractual requirements or to perform their services in a timely or acceptable manner; |
| · | failure by Psyence, its employees, the CRO or its employees to comply with all applicable regulatory requirements relating to the conduct of clinical trials; |
| · | scheduling conflicts with participating clinicians and clinical institutions; |
| · | failure to design appropriate clinical trial protocols; |
| · | regulatory concerns with administering a psychoactive product, generally, and the potential for abuse; |
| · | insufficient data to support regulatory approval; |
| · | inability or unwillingness of medical investigators to follow our clinical protocols; or difficulty in maintaining contact with patients during or after treatment, which may result in incomplete data. |
Any of the foregoing could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
Psyence may be subject to federal, state and foreign healthcare laws and regulations and implementation of or changes to such healthcare laws and regulations could adversely affect Psyence’s business and results of operations.
If Psyence successfully completes the requisite preclinical and clinical testing, makes the required regulatory submissions and obtains any corresponding authorizations or licenses (as applicable), fulfills all other applicable development-related regulatory obligations, and, eventually, obtains FDA approval to market one or more of its current or future product candidates in the United States, Psyence will be subject to certain healthcare laws and regulations. In Australia, the U.S. and certain foreign jurisdictions, there have been a number of legislative and regulatory proposals to change the healthcare system in ways that could impact Psyence’s ability to commercialize Psyence’s product candidates. If Psyence were found to be in violation of any of these laws or any other federal, state or foreign regulations, Psyence may be subject to administrative, civil and/or criminal penalties, damages, fines, individual imprisonment, exclusion from federal health care programs and the restructuring of its operations. Any of these could have a material adverse effect on its business and financial results. Since many of these laws have not been fully interpreted by the courts, there is an increased risk that Psyence may be found in violation of one or more of their provisions. Any action against Psyence for violation of these laws, even if Psyence is ultimately successful in its defense, will cause Psyence to incur significant legal expenses and divert management’s attention away from the operation of the business. In addition, in many foreign countries, particularly the countries of the European Union, the pricing of prescription drugs is subject to government control.
Serious adverse events or other safety risks could require Psyence to abandon development and preclude, delay or limit approval of its current or future product candidates, limit the scope of any approved label or market acceptance, or cause the recall or loss of marketing approval of products that are already marketed.
If any of Psyence’s current or future product candidates, prior to or after any approval for commercial sale, cause serious or unexpected side effects, or are associated with other safety risks such as misuse, abuse or diversion, a number of potentially significant negative consequences could result, including:
| · | regulatory authorities may interrupt, delay or halt clinical trials; |
| · | regulatory authorities may deny regulatory approval of future product candidates; |
| · | regulatory authorities may require certain labeling statements, such as warnings or contraindications or limitations on the indications for use, and/or impose restrictions on distribution; |
| · | regulatory authorities may withdraw their approval, require more onerous labeling statements, or require Psyence to recall any product that is approved; |
| · | Psyence may be required to change the way the product is administered or conduct additional clinical trials; |
| · | Psyence’s relationships with its collaboration partners may suffer; |
| · | Psyence could be sued and held liable for harm caused to patients; or |
| · | Psyence’s reputation could suffer. |
Any of these events could prevent us from achieving or maintaining market acceptance of our product candidates, if approved, and could significantly harm our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
Psyence may voluntarily suspend or terminate a clinical trial if at any time its believes that any of its product candidates presents an unacceptable risk to participants, if preliminary data demonstrates that the product candidate is unlikely to receive regulatory approval or unlikely to be successfully commercialized, or if sufficient funds to proceed to the next phases of clinical trials are not raised.
After obtaining the requisite regulatory authorizations to commence or advance clinical trials, Psyence may voluntarily suspend or terminate any of its clinical trials for any number of reasons, including if it believes that a product candidate’s use, or a person’s exposure to such product candidate, may cause adverse health consequences or death. In addition, regulatory agencies may at any time recommend the temporary or permanent discontinuation of a clinical trial or request that Psyence cease using investigators in the clinical trials if the agency believes that a clinical trial is not being conducted in accordance with applicable regulatory requirements, or that it presents an unacceptable safety risk to participants. If Psyence elects or is forced to suspend or terminate a clinical trial of any of its product candidates, the commercial prospects for that product will be harmed and its ability to generate product revenue from such product candidate may be delayed or eliminated. Furthermore, any of these events may result in labeling statements such as warnings or contraindications. In addition, such events or labeling could prevent Psyence or its partners from achieving or maintaining market acceptance of the affected product candidate and could substantially increase the costs of commercializing its future product candidates and impair its ability to generate revenue from the commercialization of these product candidates either by Psyence or by its collaboration partners.
The clinical trial is divided into stages and progression of each stage is dependent on governmental approval to proceed to the next stage being furnished by Psyence. Accordingly, if Psyence believes that it does not have sufficient funds to progress with the next phases of the clinical trials, or for any other reason, Psyence is entitled to exercise this discretion in accordance with applicable laws and regulatory compliance and approvals, taking patient risk and safety into account.
The success of Psyence’s product candidates and future approved products, if any, is subject to a number of constantly-evolving state and federal laws, regulations, and enforcement policies pertaining to psilocybin containing products.
Local, state, federal, and international psilocybin laws and regulations remain highly restrictive and subject to evolving interpretations, which could require Psyence to incur substantial costs associated with compliance requirements. Psyence seeks independent local legal opinions confirming the lawfulness of Psyence’s existing and proposed activities as well as its compliance with legal, regulatory and governmental developments as they pertain to and affect Psyence’s operations. In addition, violations of these laws, or allegations of such violations, could disrupt Psyence’s business and result in a material adverse effect on Psyence’s operations. In addition, it is possible that regulations may be enacted in the future that will be directly applicable to Psyence’s proposed business regarding the administration of psilocybin or psilocybin- assisted psychotherapy. Psyence cannot predict the nature of any future laws, regulations, interpretations, or applications, nor can it determine what effect additional governmental regulations or administrative policies and procedures, when and if promulgated, could have on its activities in the psychedelics industry.
There can be no assurance that Psyence’s product candidates containing psilocybin (as the active pharmaceutical ingredient) will be approved for commercialization in Australia, the U.S. or any other target jurisdiction at any time in the near or distant future. Any regulations the FDA issues relating to the sale, marketing, and/or other activities involving administration of psilocybin or psilocybin-assisted psychotherapy could have a material adverse effect on Psyence’s business, financial condition and results of operations.
We may seek fast track and breakthrough therapy designations or priority review for one or more of our product candidates, but we might not receive such designation or priority review, and even if we do, such designation or priority review may not lead to a faster development or regulatory review or approval process, and does not assure FDA approval of our product candidates. Even if a product qualifies for such designation or priority review, the FDA may later decide that the product no longer meets the conditions for qualification or decide that the time period for FDA review or approval will not be shortened.
We may seek fast track, breakthrough therapy, and/or regenerative medicine advanced therapy designations or priority review for one or more of our product candidates.
The FDA may issue a fast track designation to a product candidate if it is intended, whether alone or in combination with one or more other products, for the treatment of a serious or life-threatening disease or condition, and it demonstrates the potential to address unmet medical needs for such a disease or condition. Fast track designation applies to the combination of the product and the specific indication for which it is being studied. The sponsor of a new biologic may request that the FDA designate the biologic as a fast track product at any time during the clinical development of the product. For fast track products, sponsors may have greater interactions with the FDA during product development. A fast track product may also be eligible for rolling review, where the FDA may consider for review sections of the BLA on a rolling basis before the complete application is submitted, if the sponsor provides a schedule for the submission of the sections of the BLA, the FDA agrees to accept sections of the BLA and determines that the schedule is acceptable, and the sponsor pays any required user fees upon submission of the first section of the BLA. However, the FDA’s goal for reviewing a BLA fast track application under the Prescription Drug User Fee Act (“PDUFA”) does not begin until the last section of the application is submitted. Fast track designation may be withdrawn by the FDA if the FDA believes that the designation is no longer supported by data emerging in the clinical trial process.
A breakthrough therapy is defined as a product candidate that is intended, alone or in combination with one or more other drugs, to treat a serious or life-threatening disease or condition, and preliminary clinical evidence indicates that the product candidate may demonstrate substantial improvement over existing therapies on one or more clinically significant endpoints, such as substantial treatment effects observed early in clinical development. For product candidates that have been designated as breakthrough therapies, interaction and communication between the FDA and the sponsor of the trial can help to identify the most efficient path for clinical development while minimizing the number of patients placed in ineffective control regimens. Product candidates designated as breakthrough therapies by the FDA are also eligible for priority review if supported by clinical data at the time of the submission of the BLA.
Fast track designation, priority review, and breakthrough therapy designation are within the discretion of the FDA. Accordingly, even if we believe that one of our product candidates meets the criteria for any such designation, the FDA may disagree and instead determine not to make such designation. In any event, the receipt of such designation may expedite the development or approval process, but do not change the standards for approval. Even if a product qualifies for one or more of these programs, the FDA may later decide that the product no longer meets the conditions for qualification or decide that the time period for FDA review or approval will not be shortened.
We may seek approval of our product candidates, where applicable, under the FDA’s accelerated approval pathway. This pathway may not lead to a faster development, regulatory review or approval process and does not increase the likelihood that our product candidates will receive marketing approval.
A product may be eligible for accelerated approval if it is designed to treat a serious or life-threatening disease or condition and generally provides a meaningful advantage over available therapies upon a determination that the product candidate has an effect on a surrogate endpoint or intermediate clinical endpoint that is reasonably likely to predict clinical benefit or on a clinical endpoint that can be measured earlier than irreversible morbidity or mortality, (“IMM”) that is reasonably likely to predict an effect on IMM or other clinical benefit. The FDA considers a clinical benefit to be a positive therapeutic effect that is clinically meaningful in the context of a given disease, such as IMM. For the purposes of accelerated approval, a surrogate endpoint is a marker, such as a laboratory measurement, radiographic image, physical sign or other measure that is thought to predict clinical benefit, but is not itself a measure of clinical benefit. An intermediate clinical endpoint is a clinical endpoint that can be measured earlier than an effect on irreversible morbidity or mortality that is reasonably likely to predict an effect on irreversible morbidity or mortality or other clinical benefit. The accelerated approval pathway may be used in cases in which the advantage of a new drug over available therapy may not be a direct therapeutic advantage, but is a clinically important improvement from a patient and public health perspective. If granted, accelerated approval is usually contingent on the sponsor’s agreement to conduct, in a diligent manner, additional post-approval confirmatory studies to verity and describe the drug’s clinical benefit. Under the Food and Drug Omnibus Reform Act of 2022 (“FDORA”), the FDA is permitted to require, as appropriate, that a post-approval confirmatory study or studies be underway prior to approval or within a specified time period after the date of accelerated approval was granted. FDORA also requires sponsors to send updates to the FDA every 180 days on the status of such studies, including progress toward enrollment targets, and the FDA must promptly post this information publicly. FDORA also gives the FDA increased authority to withdraw approval of a drug or biologic granted accelerated approval on an expedited basis if the sponsor fails to conduct such studies in a timely manner, send the necessary updates to the FDA, or if such post-approval studies fail to verify the drug’s predicted clinical benefit. Under FDORA, the FDA is empowered to take action, such as issuing fines, against companies that fail to conduct with due diligence any post-approval confirmatory study or submit timely reports to the agency on their progress. In addition, the FDA currently requires, unless otherwise informed by the agency, pre-approval of promotional materials for products receiving accelerated approval, which could adversely impact the timing of the commercial launch of the product. Thus, even if we seek to utilize the accelerated approval pathway, we may not be able to obtain accelerated approval and, even if we do, we may not experience a faster development, regulatory review or approval process for that product. There can be no assurance that the FDA would allow any of the product candidates we may develop to proceed on an accelerated approval pathway, and even if the FDA did allow such pathway, there can be no assurance that such submission or application will be accepted or that any expedited development, review or approval will be granted on a timely basis, or at all. Moreover, even if we received accelerated approval, any post-approval studies required to confirm and verify clinical benefit may not show such benefit, which could lead to withdrawal of any approvals we have obtained. Receiving accelerated approval does not assure that the product’s accelerated approval will eventually be converted to a traditional approval.
Risks Relating to the Psychedelic Therapy Market and Biotechnology Industry
The psychedelic therapy industry and market are relatively new, and this industry and market may not continue to exist or grow as anticipated.
Psyence operates its business in a relatively new industry and market. In addition to being subject to general business risks, Psyence must continue to build brand awareness in this industry and market through significant investments in its strategy, operational capacity, quality assurance and compliance with regulations. In addition, there is no assurance that the industry and market will continue to exist and grow as currently estimated or anticipated or function and evolve in a manner consistent with management’s expectations and assumptions. Any event or circumstance that adversely affects the psychedelic therapy industry and market could have a material adverse effect on Psyence’s business, financial conditions and results of operations.
Psilocybin is considered scientifically to be the safest of the psychedelics and/or drugs of abuse potential. In fact, psilocybin has been described as being anti-addictive and has been studied for the use in substance addictive disorders, such as alcohol use disorder, smoking cessation and opioid addiction. Notwithstanding the foregoing, the psychedelic therapy market will face specific marketing challenges given the products’ status as a controlled substance, which has resulted in past and current public perception that the products have negative health and lifestyle effects and have the potential to cause physical and social harm due to psychoactive and potentially addictive effects. Any marketing efforts by Psyence would need to overcome this perception to build consumer confidence, brand recognition and goodwill.
Negative public opinion and perception of the psychedelic industry could adversely impact Psyence’s ability to operate and Psyence’s growth strategy.
Consumer perception of Psyence’s products may be significantly influenced by scientific research or findings, regulatory investigations, litigation, media attention and other publicity regarding the consumption of naturally derived, medicinal-grade psilocybin mushroom products. There can be no assurance that future scientific research, findings, regulatory proceedings, litigation, media attention or other research findings or publicity will be favorable to the naturally derived medicinal-grade psilocybin mushroom market or any particular product, or consistent with earlier publicity. Future research reports, findings, regulatory proceedings, litigation, media attention or other publicity that are perceived as less favorable than, or that question, earlier research reports, findings or publicity could have a material adverse effect on the demand for Psyence’s envisaged products and Psyence’s business, results of operations, financial condition and cash flows. Psyence’s dependence upon consumer perception means that adverse scientific research reports, findings, regulatory proceedings, litigation, media attention or other publicity, whether or not accurate or with merit, could have a material adverse effect on Psyence, the demand for Psyence’s products, and Psyence’s business, results of operations, financial condition and cash flows. Further, adverse publicity reports or other media attention regarding the safety, efficacy and quality of naturally derived medicinal-grade psilocybin mushroom in general, or Psyence’s products specifically, or associating the consumption of naturally derived medicinal-grade psilocybin mushroom’s negative effects or events, could have such a material adverse effect. Such adverse publicity reports or other media attention could arise even if the adverse effects associated with such products resulted from consumers’ failure to consume such products appropriately or as directed.
The expansion of the use of psychedelics in the medical industry may require new clinical research into effective medical therapies.
Research in the UK, Canada, Australia and internationally regarding the medical benefits, viability, safety, efficacy, addictiveness, dosing and social acceptance of psychedelic and psychoactive products remains in early stages. There have been relatively few clinical trials on the benefits of such products. Although Psyence believes that the articles, reports and studies support its beliefs regarding the medical benefits, viability, safety, efficacy, dosing and social acceptance of psychedelic and psychoactive products, future research and clinical trials may prove such statements to be incorrect, or could raise concerns regarding, and perceptions relating to, psychedelic and psychoactive products. Future research studies and clinical trials may draw opposing conclusions to those stated in this prospectus or reach negative conclusions regarding the medical benefits, viability, safety, efficacy, dosing, social acceptance or other facts and perceptions related to psychedelic and psychoactive products, which could have a material adverse effect on the demand for Psyence’s product candidate and psychedelic therapies and a material adverse effect on Psyence’s business, financial condition and results of operations.
The psychedelic therapy industry is difficult to quantify and investors will be reliant on their own estimates of the accuracy of market data.
Because the psychedelic therapy industry is in a nascent stage with uncertain boundaries, there is a lack of information about comparable companies available for potential investors to analyze in deciding whether to invest in Psyence and, few, if any, established companies whose business model Psyence can follow or upon whose success Psyence can build. Accordingly, investors will have to rely on their own estimates in deciding whether to invest in Psyence. There can be no assurance that Psyence’s estimates are accurate or that the market size is sufficiently large for its business to grow as projected, which may negatively impact its financial results.
Risks Related to Intellectual Property
Psyence may not be able to adequately protect or enforce its intellectual property rights, which could harm its competitive position.
Psyence relies upon a combination of patent, copyright, trademark and trade secret laws, as well as nondisclosure agreements, know-how of the scientific team, and other methods, to protect its proprietary technologies and processes. The strengths of patents in the pharmaceutical field involve complex legal and scientific questions and can be uncertain. Where appropriate, Psyence will seek patent protection for certain aspects of its products and technology. Filing, prosecuting and defending patents in a wide range of countries can be prohibitively expensive. If Psyence fails to adequately protect its intellectual property, it may face competition from companies who attempt to create a generic product to compete with its future product candidates. Psyence may also face competition from companies who develop a substantially similar product to its future product candidates that are not covered by any patents.
While Psyence will apply for a number of patents, there can be no assurances that any patents will be issued. Specifically, naturally occurring substances arising from botanical sources, e.g Psilocybin, cannot be patented. As such, we will be required to rely on other processes such as extraction, purification, or formulation in order to establish patents and such processes are not guaranteed to receive issued patents. Even if patents are issued, the claims allowed may not be sufficiently broad to protect all of Psyence’s intellectual property. In addition, any future patents issued to Psyence may be challenged, invalidated or circumvented. As such, any rights granted under these patents may not provide Psyence with meaningful protection. If Psyence’s patents do not adequately protect its intellectual property, competitors may be able to offer products similar to Psyence’s products.
Psyence will be further dependent, to an extent, on Filament’s wholly-owned subsidiary, Psilo Scientific LTD. (“Psilo”), to maintain and defend the intellectual property currently being licensed to Psyence under the Filament Licensing Agreements, and which is relevant for use in Psyence’s proposed Australian palliative care clinical trial. Any failure on the part of Psilo or Filament, as applicable, to adequately maintain or defend its intellectual property will have a direct effect on the viability of Psyence’s Australian palliative care clinical trial initiatives.
Psyence’s strategy is to patent technologies with commercial potential in jurisdictions with significant commercial opportunities. However, patent protection may not be available for some of the products or technologies Psyence is developing, such as in the areas of methods of treatment (which are not patentable in most jurisdictions).
The patent positions of pharmaceutical products are complex and uncertain. The scope and extent of patent protection for future product candidates are particularly uncertain. Protection of Psyence’s future product candidates will be sought in respect of, among other things, composition-of-matter for specific formulations, methods of use, and delivery mechanisms, bearing in mind that patent protection is not available for naturally derived psilocybin alone. If any of Psyence’s products are approved and marketed for an indication for which it does not have an issued or licensed patent, Psyence’s ability to use a patent to prevent a competitor from commercializing a non-branded version of its commercial products for that non- patented indication could be significantly impaired or even eliminated.
Many companies have encountered significant problems in protecting, defending and enforcing intellectual property rights in foreign jurisdictions. The legal systems of certain countries, particularly certain developing countries, do not favor the enforcement of patents and other intellectual property rights, particularly those relating to pharmaceuticals, which could make it difficult for Psyence to stop the infringement of patents or marketing of competing products in violation of its proprietary rights generally. Proceedings to enforce patent rights in foreign jurisdictions may not be successful, could result in substantial cost and divert Psyence’s efforts and attention from other aspects of its business.
If third parties claim that intellectual property owned or used by Psyence infringes upon their intellectual property, Psyence’s operating profits could be adversely affected.
There is a substantial amount of litigation, both within and outside the U.S., involving patent and other intellectual property rights in the pharmaceutical industry. Psyence may, from time to time, be notified of claims that Psyence is infringing upon patents, trademarks, copyrights or other intellectual property rights owned by third parties, and Psyence cannot provide assurances that other companies will not, in the future, pursue such infringement claims against it, its commercial partners or any third-party proprietary technologies it has licensed. If Psyence were found to infringe upon a patent or other intellectual property right, or if Psyence failed to obtain or renew a license under a patent or other intellectual property right from a third party, or if a third party that Psyence were licensing technologies from was found to infringe upon a patent or other intellectual property rights of another third party, Psyence may be required to pay damages, suspend the manufacture of certain products or reengineer or rebrand its products, if feasible, or it may be unable to enter certain new product markets. Any such claims could also be expensive and time-consuming to defend and divert management’s attention and resources. Psyence’s competitive position could suffer as a result. In addition, if Psyence has declined or failed to enter into a valid non-disclosure or assignment agreement for any reason, Psyence may not own the intellectual property, and its products may not be adequately protected. Thus, Psyence cannot guarantee that any of its future product candidates, or its commercialization thereof, does not and will not infringe any third party’s intellectual property.
We may infringe the intellectual property rights of others, which may prevent or delay our product development efforts and stop us from commercializing or increase the costs of commercializing our product candidates.
Our success will depend in part on our ability to operate without infringing the proprietary rights of third parties. We are not aware of any third-party proprietary rights that our planned products will infringe or misappropriate, but we have not conducted any freedom to operate study as we are in the earliest stages of development. We thus cannot guarantee that our product candidates, or manufacture or use of our product candidates, will not infringe third-party patents. Furthermore, a third party may claim that we are using inventions covered by the third party’s patent rights and may go to court to stop us from engaging in our normal operations and activities, including making or selling our product candidates. These lawsuits are costly and could affect our results of operations and divert the attention of managerial and scientific personnel. Some of these third parties may be better capitalized and have more resources than us. There is a risk that a court would decide that we are infringing the third party’s patents and would order us to stop the activities covered by the patents. In that event, we may not have a viable way around the patent and may need to halt commercialization of our product candidates. In addition, there is a risk that a court will order us to pay the other party damages for having violated the other party’s patents. In addition, we may be obligated to indemnify our licensors and collaborators against certain intellectual property infringement claims brought by third parties, which could require us to expend additional resources. The pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries have produced a proliferation of patents, and it is not always clear to industry participants, including us, which patents cover various types of products or methods of use. The coverage of patents is subject to interpretation by the courts, and the interpretation is not always uniform.
If we are sued for patent infringement, we would need to demonstrate that our product candidates or methods either do not infringe the patent claims of the relevant patent or that the patent claims are invalid, and we may not be able to do this. Proving invalidity is difficult. For example, in the U.S., proving invalidity requires a showing of clear and convincing evidence to overcome the presumption of validity enjoyed by issued patents. Even if we are successful in these proceedings, we may incur substantial costs and diversion of management’s time and attention in pursuing these proceedings, which could have a material adverse effect on us. If we are unable to avoid infringing the patent rights of others, we may be required to seek a license, which may not be available, defend an infringement action or challenge the validity of the patents in court. Patent litigation is costly and time consuming. We may not have sufficient resources to bring these actions to a successful conclusion. In addition, if we do not obtain a license, develop or obtain non-infringing technology, fail to defend an infringement action successfully or have infringed patents declared invalid, we may incur substantial monetary damages, encounter significant delays in bringing our product candidates to market and be precluded from manufacturing or selling our product candidates.
Some of our competitors may be able to sustain the costs of complex patent litigation more effectively than us or the third parties from whom we license intellectual property because they have substantially greater resources. In addition, any uncertainties resulting from the initiation and continuation of any litigation could have a material adverse effect on our ability to raise the funds necessary to continue our operations.
If Psyence is not able to adequately prevent disclosure of trade secrets and other proprietary information, the value of its products could be significantly diminished.
Psyence relies, to an extent, on trade secrets to protect its proprietary licensed intellectual property, especially where it does not believe patent protection is appropriate or obtainable. However, trade secrets are difficult to protect. Psyence relies in part on confidentiality agreements and restraints of trade with its current and former employees, consultants, outside scientific collaborators, sponsored researchers, contract manufacturers, vendors and other advisors, as well as similar confidentiality protections benefiting its strategic partners and licensors to protect Psyence’s owned and licensed trade secrets and other proprietary information. These agreements may not effectively prevent disclosure of confidential information and may not provide an adequate remedy in the event of unauthorized disclosure of confidential information. In addition, Psyence cannot guarantee that it, nor its strategic and business partners, have executed these agreements with each party that may have or have had access to owned and licensed trade secrets. Any party with whom Psyence or strategic and business partners have executed such an agreement may breach that agreement and disclose proprietary information, including owned and licensed trade secrets, and adequate remedies for such breaches may not be available.
Enforcing a claim that a party illegally disclosed or misappropriated a trade secret is difficult, expensive and time-consuming, and the outcome is unpredictable. In addition, some courts inside and outside the U.S. are less willing or unwilling to protect trade secrets. If any of Psyence’s owned or licensed trade secrets were to be lawfully obtained or independently developed by a competitor, Psyence would have no right to prevent them, or those to whom they disclose such trade secrets, from using that technology or information to compete with it. If any of Psyence’s owned and licensed trade secrets were to be disclosed to or independently developed by a competitor or other third-party, Psyence’s competitive position would be harmed.
Risks Related to Ownership of Our Securities
If we fail to meet applicable listing requirements, Nasdaq may delist our Common Shares from trading, in which case the liquidity and market price of our Common Shares could decline.
We cannot assure you that we will be able to meet the continued listing standards of Nasdaq in the future. If we fail to comply with the applicable listing standards and Nasdaq delists our Common Shares, we and our shareholders could face significant material adverse consequences, including:
· a limited availability of market quotations for our Common Shares;
· reduced liquidity for our Common Shares;
· a determination that our Common Shares are “penny stock”, which would require brokers trading in our Common Shares to adhere to more stringent rules and possibly result in a reduced level of trading activity in the secondary trading market for our Common Shares;
· a limited amount of news about us and analyst coverage of us; and
· a decreased ability for us to issue additional equity securities or obtain additional equity or debt financing in the future.
The National Securities Markets Improvement Act of 1996, which is a federal statute, prevents or preempts the states from regulating the sale of certain securities, which are referred to as “covered securities.” Because we expect that our shares will be listed on Nasdaq, such securities will be covered securities. Although the states are preempted from regulating the sale of our securities, the federal statute does allow the states to investigate companies if there is a suspicion of fraud, and, if there is a finding of fraudulent activity, then the states can regulate or bar the sale of covered securities in a particular case. Further, if we were no longer listed on Nasdaq, our securities would not be covered securities and we would be subject to regulations in each state in which we offer our securities.
The market price and trading volume of the Common Shares may be volatile and could decline significantly following the Business Combination.
The stock markets, including Nasdaq, on which the Company lists its securities, have from time to time experienced significant price and volume fluctuations. Even if an active, liquid and orderly trading market develops and is sustained for the Common Shares, the market prices of the Common Shares may be volatile and could decline significantly. In addition, the trading volumes in the Common Shares may fluctuate and cause significant price variations to occur. If the market prices of the Common Shares decline significantly, you may be unable to resell your Common Shares at or above the market price of the Common Shares as of the date immediately following the consummation of the Business Combination. There can be no assurance that the market prices of the Common Shares will not fluctuate widely or decline significantly in the future in response to a number of factors, including, among others, the following:
| · | the realization of any of the risk factors presented in this prospectus; |
| · | actual or anticipated differences in our estimates, or in the estimates of analysts, for the Company’s revenues, results of operations, cash flows, liquidity or financial condition; |
| · | announcements by the Company or its competitors of significant business developments; |
| · | acquisitions or expansion plans; |
| · | the Company’s involvement in litigation; |
| · | sale of Common Shares or other securities in the future; |
| · | market conditions in the Company’s industry; |
| · | changes in key personnel; |
| · | the trading volume of Common Shares; |
| · | actual, potential or perceived control, accounting or reporting problems; |
| · | changes in accounting principles, policies and guidelines; |
| · | other events or factors, including but not limited to those resulting from infectious diseases, health epidemics and pandemics (including but not limited to the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic), natural disasters, war, acts of terrorism or responses to these events; and |
| · | general economic and market conditions. |
In addition, the stock markets have experienced extreme price and volume fluctuations. Broad market and industry factors may materially harm the market price of the Common Shares, regardless of our operating performance. In the past, following periods of volatility in the market price of a company’s securities, securities class action litigation has often been instituted against that company. If the Company were involved in any similar litigation it could incur substantial costs and our management’s attention and resources could be diverted.
Public Warrants are exercisable for Common Shares, which would increase the number of shares eligible for future resale in the public market and result in dilution to its shareholders.
An aggregate of 13,070,000 Common Shares will become issuable upon exercise of Public Warrants in accordance with the terms of the Warrant Agreement. These warrants will become exercisable 30 days after the Closing Date, or February 24, 2024. The exercise price of these warrants will be $11.50 per share. To the extent such warrants are exercised, additional Common Shares will be issued, which will result in dilution to the holders of Common Shares and increase the number of shares eligible for resale in the public market. Sales of substantial numbers of such shares in the public market or the fact that such warrants may be exercised could adversely affect the market price of Common Shares.
If securities or industry analysts do not publish research, publish inaccurate or unfavorable research or cease publishing research about the Company, its share price and trading volume could decline significantly.
The trading market for Common Shares depends, in part, on the research and reports that securities or industry analysts publish about the Company or its business. The Company may be unable to sustain coverage by well-regarded securities and industry analysts. If either none or only a limited number of securities or industry analysts maintain coverage of the Company, or if these securities or industry analysts are not widely respected within the general investment community, the demand for Common Shares could decrease, which might cause its share price and trading volume to decline significantly. In the event that the Company obtains securities or industry analyst coverage or, if one or more of the analysts who cover the Company downgrade their assessment of the Company or publish inaccurate or unfavorable research about the Company’s business, the market price and liquidity for Common Shares could be negatively impacted.
The requirements of being a public company may strain the Company’s resources, divert the Company management’s attention and affect the Company’s ability to attract and retain qualified board members.
The Company will incur additional legal, accounting and other expenses following completion of the Business Combination. The Company is subject to the reporting requirements of the Exchange Act, the Sarbanes-Oxley Act, the Dodd-Frank Act, the Nasdaq listing requirements and other applicable securities rules and regulations. These expenses may increase even more if the Company no longer qualifies as an “emerging growth company,” as defined in Section 2(a) of the Securities Act. The Exchange Act requires that our company file annual and other material reports with respect to our businesses, financial condition, and results of operations. In addition, we must establish the corporate infrastructure necessary for operating a public company, which may divert our management’s attention from implementing our growth strategy, which could delay or slow the implementation of our business strategies, and in turn negatively impact our company’s financial condition and results of operations.
Changing laws, regulations and standards relating to corporate governance and public disclosure are creating uncertainty for public companies, increasing legal and financial compliance costs and making some activities more time-consuming. These laws, regulations and standards are subject to varying interpretations, in many cases due to their lack of specificity, and, as a result, their application in practice may evolve over time as new guidance is provided by regulatory and governing bodies. This could result in continuing uncertainty regarding compliance matters and higher costs necessitated by ongoing revisions to disclosure and governance practices. The Company expects these laws and regulations to increase its legal and financial compliance costs and to render some activities more time-consuming and costly, although the Company is currently unable to estimate these costs with any degree of certainty.
The Company’s management team has limited experience managing a publicly traded company, interacting with public company investors and complying with the increasingly complex laws pertaining to public companies. The Company’s management team may not successfully or efficiently manage the transition to being a public company subject to significant regulatory oversight and reporting obligations under the federal securities laws and regulations and the continuous scrutiny of securities analysts and investors. The need to establish the corporate infrastructure demanded of a public company may divert the management’s attention from implementing its growth strategy, which could prevent the Company from improving its business, financial condition and results of operations. Furthermore, the Company expects these rules and regulations to make it more difficult and more expensive for the Company to maintain director and officer liability insurance, and consequently the Company may be required to incur substantial costs to obtain such coverage. These additional obligations could have a material adverse effect on its business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects. These factors could also make it more difficult for the Company to attract and retain qualified members of its board of directors, particularly to serve on the Company’s audit committee, compensation committee and nominating and corporate governance committee, and qualified executive officers.
As a result of disclosure of information in this prospectus and in filings required of a public company, the Company’s business and financial condition will become more visible, which may result in threatened or actual litigation, including by competitors and other third parties. If such claims are successful, the Company’s business and operating results could be adversely affected, and, even if the claims do not result in litigation or are resolved in the Company’s favor, these claims, and the time and resources necessary to resolve them, could have an adverse effect on its business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
The Company is an “emerging growth company,” and it cannot be certain if the reduced SEC reporting requirements applicable to emerging growth companies will make the Company’s Common Shares less attractive to investors, which could have a material and adverse effect on the Company, including its growth prospects.
The Company is an “emerging growth company” as defined in the JOBS Act. The Company will remain an “emerging growth company” until the earliest to occur of (i) the last day of the fiscal year (a) following the fifth anniversary of the date of the first sale of our common equity securities pursuant to an effective registration statement under the Securities Act, (b) in which the Company has total annual gross revenue of at least $1.235 billion or (c) in which the Company is deemed to be a large accelerated filer, which means the market value of Common Shares held by non-affiliates exceeds $700 million as of the last business day of the Company’s prior second fiscal quarter, and (ii) the date on which the Company issued more than $1.0 billion in non-convertible debt during the prior three-year period. The Company intends to take advantage of exemptions from various reporting requirements that are applicable to most other non “emerging growth companies” including, but not limited to, an exemption from the provisions of Section 404(b) of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act requiring that the Company’s independent registered public accounting firm provide an attestation report on the effectiveness of its internal control over financial reporting and reduced disclosure obligations regarding executive compensation, and exemptions from the requirements of holding a non-binding advisory vote on executive compensation and shareholder approval of any golden parachute payments not previously approved.
Furthermore, even after the Company no longer qualifies as an “emerging growth company,” as long as the Company continues to qualify as a foreign private issuer under the Exchange Act, the Company will be exempt from certain provisions of the Exchange Act that are applicable to U.S. domestic public companies, including, but not limited to, (i) the rules under the Exchange Act requiring the filing of quarterly reports on Form 10-Q and current reports on Form 8-K with the SEC; (ii) the sections of the Exchange Act regulating the solicitation of proxies, consents, or authorizations in respect of a security registered under the Exchange Act; (iii) the sections of the Exchange Act requiring insiders to file public reports of their share ownership and trading activities and liability for insiders who profit from trades made in a short period of time; and (iv) the selective disclosure rules by issuers of material nonpublic information under Regulation FD As a result, the Company shareholders may not have access to certain information they deem important. The Company cannot predict if investors will find Common Shares less attractive because it relies on these exemptions. If some investors do find Common Shares less attractive as a result, there may be a less active trading market and share price for Common Shares may be more volatile.
The Company qualifies as a foreign private issuer within the meaning of the rules under the Exchange Act, and as such the Company is exempt from certain provisions applicable to United States domestic public companies.
Because the Company qualifies as a foreign private issuer under the Exchange Act, the Company is exempt from certain provisions of the securities rules and regulations in the United States that are applicable to U.S. domestic issuers, including, but not limited to: (i) the rules under the Exchange Act requiring the filing of quarterly reports on Form 10-Q and current reports on Form 8-K with the SEC; (ii) the sections of the Exchange Act regulating the solicitation of proxies, consents, or authorizations in respect of a security registered under the Exchange Act; (iii) the sections of the Exchange Act requiring insiders to file public reports of their share ownership and trading activities and liability for insiders who profit from trades made in a short period of time; and (iv) the selective disclosure rules by issuers of material nonpublic information under Regulation FD.
The Company is required to file an annual report on Form 20-F within four months of the end of each fiscal year. Press releases relating to financial results and material events will also be furnished to the SEC on Form 6-K. However, the information the Company is required to file with or furnish to the SEC will be less extensive and less timely compared to that required to be filed with the SEC by U.S. domestic issuers. Accordingly, after the Business Combination, if you continue to hold Common Shares, you may receive less or different information about the Company than you would receive about a U.S. domestic public company.
The Company may lose its foreign private issuer status which would then require it to comply with the domestic reporting regime of the Exchange Act and cause us to incur significant additional legal, accounting and other expenses.
As discussed above, the Company is a foreign private issuer and therefore is not be required to comply with all of the periodic disclosure and current reporting requirements of the Exchange Act and may take advantage of certain exemptions to Nasdaq’s corporate governance rules. The determination of foreign private issuer status is made annually on the last business day of an issuer’s most recently completed second fiscal quarter, and, accordingly, the next determination will be made with respect to the Company on September 30, 2024. In the future, the Company would lose its foreign private issuer status if (1) more than 50% of its outstanding voting securities are owned by U.S. residents and (2) a majority of its directors or executive officers are U.S. citizens or residents, or it fails to meet additional requirements necessary to avoid loss of foreign private issuer status. If the Company loses its foreign private issuer status, it will be required to file with the SEC periodic reports and registration statements on U.S. domestic issuer forms, which are more detailed and extensive than the forms available to a foreign private issuer. The Company would also have to mandatorily comply with U.S. federal proxy requirements, and its officers, directors and principal shareholders will become subject to the short-swing profit disclosure and recovery provisions of Section 16 of the Exchange Act. In addition, it would lose its ability to rely upon exemptions from certain corporate governance requirements under the listing rules of Nasdaq. As a U.S. listed public company that is not a foreign private issuer, the Company could incur significant additional legal, accounting and other expenses that it will not incur as a foreign private issuer.
Psyence currently reports financial results under IFRS, which differs in certain significant respects from U.S. GAAP.
Psyence currently reports financial results under IFRS. There are and there may in the future be certain significant material differences between IFRS and U.S. GAAP. As a result, financial information and reported earnings of Psyence for historical or future periods could be significantly different if they were prepared in accordance with U.S. GAAP. In addition, the Company does not intend to provide a reconciliation between IFRS and U.S. GAAP unless it is required under applicable law. As a result, you may not be able to meaningfully compare our financial statements under IFRS with those of companies that prepare financial statements under U.S. GAAP.
If we are classified as a passive foreign investment company, United States taxpayers who own our Common Shares may have adverse United States federal income tax consequences.
A non-U.S. corporation such as ourselves will be classified as a passive foreign investment company, which is known as a PFIC, for any taxable year if, for such year, either
· At least 75% of our gross income for the year is passive income; or
· The average percentage of our assets (determined at the end of each quarter) during the taxable year which produces passive income or which are held for the production of passive income is at least 50%.
Passive income generally includes dividends, interest, rents, royalties (other than rents or royalties derived from the active conduct of a trade or business) and gains from the disposition of passive assets.
If we are determined to be a PFIC for any taxable year (or portion thereof) that is included in the holding period of a U.S. taxpayer who holds our Common Shares, the U.S. taxpayer may be subject to increased U.S. federal income tax liability and may be subject to additional reporting requirements.
Depending on the amount of our cash and other assets held for the production of passive income, it is possible that, for our current taxable year or for any subsequent year, more than 50% of our assets may be assets which produce passive income. We will make this determination following the end of any particular tax year. Although the law in this regard is unclear, we treat our consolidated affiliated entities as being owned by us for United States federal income tax purposes, not only because we exercise effective control over the operation of such entities but also because we are entitled to substantially all of their economic benefits, and, as a result, we consolidate their operating results in our consolidated financial statements. For purposes of the PFIC analysis, in general, a non-U.S. corporation is deemed to own its pro rata share of the gross income and assets of any entity in which it is considered to own, directly or indirectly, at least 25% of the equity by value. Our status as a PFIC is a fact-intensive determination made on an annual basis, and no opinion of counsel has or will be provided regarding our classification as a PFIC.
For a more detailed discussion of the application of the PFIC rules to us and the consequences to U.S. taxpayers who own our Common Shares if we were determined to be a PFIC, see “Certain Material U.S. Federal Income Tax Considerations — Passive Foreign Investment Company.”
You may face difficulties in protecting your interests, and your ability to protect your rights through U.S. courts may be limited, because the Company is incorporated under the laws of Canada, the Company conducts substantially all of its operations and a majority of its directors and executive officers reside outside of the United States.
The Company is a corporation incorporated under the laws of Canada, and conducts a majority of its operations through its subsidiary, Biomed II, outside the United States. Substantially all of the Company’s assets are located outside the United States. A majority of the Company’s officers and directors reside outside the United States and a substantial portion of the assets of those persons are located outside of the United States. As a result, it could be difficult or impossible for you to bring an action against the Company or against these individuals outside of the United States in the event that you believe that your rights have been infringed upon under the applicable securities laws or otherwise and it will be difficult to effect service of process within the United States upon the Company’s officers or directors, or enforce judgments obtained in United States courts against the Company’s officers or directors. Even if you are successful in bringing an action of this kind, the laws of Ontario could render you unable to enforce a judgment against the Company’s assets or the assets of the Company’s directors and officers.
The Articles of Incorporation and certain Canadian legislation contain provisions that may have the effect of delaying or preventing a change in control.
Certain provisions of the Articles of Incorporation, together or separately, could discourage potential acquisition proposals, delay or prevent a change in control and limit the price that certain investors may be willing to pay for our common shares. For instance, our Articles of Incorporation contain provisions that establish certain advance notice procedures for nomination of candidates for election as directors at shareholders’ meetings.
In addition, a non-Canadian must file an application for review with the Minister responsible for the Investment Canada Act and obtain approval of the Minister prior to acquiring control of a “Canadian Business” within the meaning of the Investment Canada Act, where prescribed financial thresholds are exceeded. Finally, limitations on the ability to acquire and hold our common shares may be imposed by the Competition Act (Canada). The Competition Act (Canada) establishes a pre-merger notification regime for certain types of merger transactions that exceed certain statutory shareholding and financial thresholds. Transactions that are subject to notification cannot be closed until the required materials are filed and the applicable statutory waiting period has expired or been waived by the Commissioner. The Commissioner of Competition still retains the authority under the Competition Act (Canada) to review any acquisition or establishment, directly or indirectly, including through the acquisition of shares, of control over or of a significant interest in us, whether or not it is subject to mandatory notification. Otherwise, there are no limitations either under the laws of Canada or Ontario, or in our articles on the rights of non-Canadians to hold or vote our common shares. Any of these provisions may discourage a potential acquirer from proposing or completing a transaction that may have otherwise presented a premium to our shareholders. We cannot predict whether investors will find our company and our common shares less attractive because we are governed by foreign laws.
It is not expected that the Company will pay dividends in the foreseeable future.
It is expected that the Company will retain most, if not all, of its available funds and any future earnings to fund the development and growth of its business. In addition, the Company is a holding company and its subsidiaries are located abroad. Part of the Company’s primary internal sources of funds to meet its cash needs will be its share of the dividends, if any, paid by the Company’s subsidiaries. The distribution of dividends to the Company from the subsidiaries in certain markets where the Company operates is subject to restrictions imposed by the applicable laws and regulations in these markets. As a result, it is not expected that the Company will pay any cash dividends in the foreseeable future.
The Board has complete discretion as to whether to distribute dividends. Even if the Board decides to declare and pay dividends, the timing, amount and form of future dividends, if any, will depend on the future results of operations and cash flow, capital requirements and surplus, the amount of distributions, if any, received by the Company from subsidiaries, the Company’s financial condition, contractual restrictions and other factors deemed relevant by the Board. There is no guarantee that the Common Shares will appreciate in value after the Business Combination or that the trading price of the shares will not decline. Holders of the Common Shares should not rely on an investment in Common Shares as a source for any future dividend income.
CAUTIONARY NOTE REGARDING FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS
This prospectus contains forward-looking statements that involve substantial risks and uncertainties. All statements other than statements of historical facts contained in this prospectus, including statements regarding our future financial position, business strategy and plans and objectives of management for future operations, are forward-looking statements. In some cases, you can identify forward-looking statements by terminology such as “believe,” “may,” “estimate,” “continue,” “anticipate,” “intend,” “should,” “plan,” “expect,” “predict,” “potential” or the negative of these terms or other similar expressions. Forward-looking statements include, without limitation, the company’s expectations concerning the outlook for its business, productivity, plans and goals for future operational improvements and capital investments, operational performance, future market conditions or economic performance and developments in the capital and credit markets and expected future financial performance, as well as any information concerning possible or assumed future results of operations of the Company as set forth in this prospectus.
Forward-looking statements involve a number of risks, uncertainties and assumptions, and actual results or events may differ materially from those projected or implied in those statements. Important factors that could cause such differences include, but are not limited to: (i) the effect of the Business Combination on Psyence’s business relationships, performance, and business generally, (ii) the ability to recognize the anticipated benefits of the Business Combination, which may be affected by, among other things, competition and our ability to grow and manage growth profitably, (iii) the results of the Phase IIb Study, (iv) the ability of the Company to maintain the listing of its securities on The Nasdaq Stock Market LLC, (v) volatility in the price of the securities of the Company due to a variety of factors, including changes in the competitive and highly regulated industries in which Psyence plans to operate, variations in performance across competitors, changes in laws and regulations affecting Psyence’s business and changes in the combined capital structure, (vi) the ability to implement business plans, forecasts, and other expectations and identify and realize additional opportunities, (vii) the risk that Psyence has a limited operating history, has not yet released a commercially available product and does not have experience manufacturing or selling a commercial product at scale and (viii) the risk that Psyence may not be able to effectively manage its growth, including its design, research, development and maintenance capabilities.
The foregoing list of factors is not exhaustive. Forward-looking statements are not guarantees of future performance. You should carefully consider the foregoing factors and the other risks and uncertainties described in the Company’s Reports on Form 20-F, Current Reports on Form 6-K and other documents filed by the Company from time to time with the SEC. These filings identify and address other important risks and uncertainties that could cause actual events and results to differ materially from those contained in the forward-looking statements. The forward-looking statements in this document represent the views of the Company as of the date of this document. Subsequent events and developments may cause that view to change. Readers are cautioned not to put undue reliance on forward-looking statements, and all forward-looking statements in this document are qualified by these cautionary statements. The Company assumes no obligation and does not intend to update or revise these forward-looking statements, whether as a result of new information, future events, or otherwise. The Company does not give any assurance that it will achieve its expectations. The inclusion of any statement in this document does not constitute an admission by the Company or any other person that the events or circumstances described in such statement are material.
USE OF PROCEEDS
We will not receive any proceeds from the sale by the Selling Shareholders of their Common Shares.
SELLING SHAREHOLDERS
The following table sets forth the names of the Selling Shareholders, the number of Common Shares beneficially owned by each Selling Shareholder as of the date of this prospectus, the number of shares being sold, the number of shares beneficially owned upon completion of the offering and the percentage beneficial ownership upon completion of the offering. We have based percentage ownership on 13,390,659 Common Shares outstanding as of the date of this prospectus. The table and the other information contained under the captions “Selling Shareholder” and “Plan of Distribution” has been prepared based upon information furnished to us by or on behalf of the Selling Shareholders. Also included in the footnotes to the table is any relationship during the past three years between the Selling Shareholders and us or any of our predecessors or affiliates. Beneficial ownership is determined according to the rules of the SEC, which generally provide that a person has beneficial ownership of a security if he, she, or it possesses sole or shared voting or investment power over that security, including options and warrants that are currently exercisable or exercisable within 60 days of the date of this prospectus.
Unless otherwise indicated, the business address of each of the Selling Shareholders in this table is c/o Psyence Biomedical Ltd., 121 Richmond Street West, Penthouse Suite 1300, Toronto, Ontario, M5H 2K1, Canada.
| | | | | | | | | After Sale of Shares in Offering | |
| Name | | Shares
Beneficially
Owned | | | Shares
Being
Sold | | | Shares
Beneficially
Owned | | | Percent of
Outstanding(1) | |
| Harraden Circle Investors, LP(2) | | | 10,025,000 | | | | 9,375,000 | | | | 650,000 | | | | 4.8 | % |
| Harraden Circle Special Opportunities, LP(2) | | | 10,025,000 | | | | 9,375,000 | | | | 650,000 | | | | 4.8 | % |
| J.V.B. Financial Group, LLC(3) | | | 199,500 | | | | 150,000 | | | | 49,500 | | | | * | |
| Cantor Fitzgerald & Co.(4) | | | 430,500 | | | | 150,000 | | | | 280,500 | | | | 1.4 | % |
| Maxim Group LLC(5) | | | 150,000 | | | | 150,000 | | | | 0 | | | | - | |
| McDermott Will & Emery LLP(6) | | | 125,000 | | | | 125,000 | | | | 0 | | | | - | |
| Ellenoff Grossman & Schole LLP(7) | | | 150,000 | | | | 150,000 | | | | 0 | | | | - | |
| RNA Advisors, LLC(8) | | | 21,000 | | | | 21,000 | | | | 0 | | | | - | |
| Newcourt SPAC Sponsor LLC(9) | | | 2,515,429 | | | | 1,603,929 | | | | 911,500 | | | | 6.7 | |
| Lapus Family Trust | | | 32,500 | | | | 17,500 | | | | 15,000 | | | | * | |
| John and Maria Abbott Revocable Trust | | | 32,500 | | | | 17,500 | | | | 15,000 | | | | * | |
| Reluco Financial LLC | | | 81,250 | | | | 43,750 | | | | 37,500 | | | | * | |
| Jason Beccaris and Sally Burtle JWROS | | | 32,500 | | | | 17,500 | | | | 15,000 | | | | * | |
| JOHNSON DANZ LIVING TRUST | | | 81,250 | | | | 43,750 | | | | 37,500 | | | | * | |
| Aegis Lockwood Holding Inc. | | | 65,000 | | | | 35,000 | | | | 30,000 | | | | * | |
| FM Capital Sponsor, LLC | | | 125,000 | | | | 125,000 | | | | 0 | | | | - | |
| Dan Rogers | | | 15,000 | | | | 15,000 | | | | 0 | | | | - | |
| Rohit Bodas | | | 7,500 | | | | 7,500 | | | | 0 | | | | - | |
| Nicole Farb | | | 7,500 | | | | 7,500 | | | | 0 | | | | - | |
| Simran Aggarawal | | | 7,500 | | | | 7,500 | | | | 0 | | | | - | |
| Chris Ehrlich | | | 30,000 | | | | 30,000 | | | | 0 | | | | - | |
| Curiosum | | | 30,000 | | | | 30,000 | | | | 0 | | | | - | |
| Andrew Drake | | | 2,821 | | | | 2,821 | | | | 0 | | | | - | |
| Ananda OM LLC | | | 82,556 | | | | 44,453 | | | | 38,103 | | | | * | |
| Blind 1212, LLC | | | 165,112 | | | | 88,906 | | | | 76,206 | | | | * | |
| Clark Huang | | | 8,255 | | | | 4,445 | | | | 3,810 | | | | * | |
| Driss Benamour | | | 20,638 | | | | 11,113 | | | | 9,525 | | | | * | |
| Emerson & Ashton | | | 8,255 | | | | 4,445 | | | | 3,810 | | | | * | |
| Evo Investment Holdings LLC(10) | | | 412,784 | | | | 222,269 | | | | 190,515 | | | | 1.4 | % |
| Jane Selena Shim | | | 8,255 | | | | 4,445 | | | | 3,810 | | | | * | |
| LWB Roth 1 LLC | | | 10,732 | | | | 5,779 | | | | 4,953 | | | | * | |
| LWB Sspac 1, LLC | | | 30,547 | | | | 16,448 | | | | 14,099 | | | | * | |
| Makan Family Trust DTD 10/10/2005 | | | 165,112 | | | | 88,906 | | | | 76,206 | | | | * | |
| Olana Holdings, LLC | | | 8,255 | | | | 4,445 | | | | 3,810 | | | | * | |
| Parsec Ventures, LP | | | 20,638 | | | | 11,113 | | | | 9,525 | | | | * | |
| Randall-Palumbo Family Revocable Trust | | | 20,638 | | | | 11,113 | | | | 9,525 | | | | * | |
| Red Dawn Capital, LLC | | | 330,224 | | | | 177,813 | | | | 152,411 | | | | 1.1 | % |
| Ricardo L. Elias 2017 Revocable Trust dtd 3/30/2017 | | | 165,112 | | | | 88,906 | | | | 76,206 | | | | * | |
| Ronald and Caryn Suber Revocable Living Trust(11) | | | 20,638 | | | | 11,113 | | | | 9,525 | | | | * | |
| Shanti Family Trust Non Exempt LLC | | | 82,556 | | | | 44,453 | | | | 38,103 | | | | * | |
| Steven C. Pierson | | | 20,638 | | | | 11,113 | | | | 9,525 | | | | * | |
| The Griffith Family 2004 Trust | | | 165,112 | | | | 88,906 | | | | 76,206 | | | | * | |
| The Shamdasani Revocable Trust | | | 20,638 | | | | 11,113 | | | | 9,525 | | | | * | |
| William B. Douglas | | | 82,556 | | | | 44,453 | | | | 38,103 | | | | * | |
* Less than 1%
(1) We do not know when or in what amounts the Selling Shareholders will offer the resale securities for sale, if at all. The Selling Shareholders may sell any or all of the resale securities included in and offered by this prospectus. We cannot estimate the number of resale securities that will be held by the Selling Shareholders after completion of the offering. However, for purposes of this table, we have assumed that after completion of the offering all of the resale securities will have been sold by the Selling Shareholders.
(2) The principal business office of Harraden Circle Investors, LP and Harraden Circle Special Opportunities, LP is located at 299 Park Avenue, 21st Floor, New York, NY 10171. The Common Shares reported herein are directly beneficially owned by Harraden Circle Investors, LP (“Harraden Fund”). Harraden Circle Investors GP, LP (“Harraden GP”) is the general partner to Harraden Fund, and Harraden Circle Investors GP, LLC (“Harraden LLC”) is the general partner of Harraden GP. Harraden Circle Investments, LLC (“Harraden Adviser”) is investment manager to Harraden Fund and other high net worth individuals. Frederick V. Fortmiller, Jr. is the managing member of each of Harraden LLC and Harraden Adviser. In such capacities, each of Harraden GP, Harraden LLC, Harraden Adviser and Mr. Fortmiller may be deemed to indirectly beneficially own the Common Shares reported herein directly beneficially owned by Harraden Fund. The Common Shares represent 650,000 Common Shares received in exchange for NCAC Private Placement Shares exchanged for shares purchased in a private placement in connection with the IPO of NCAC and up to an aggregate of 9,375,000 Common Shares, which represents 300% of the maximum number of Common Shares issued or issuable pursuant to that certain First Tranche Note issued to the Selling Shareholder by the Company on January 25, 2024. Under the terms of the Notes, the Investors may not convert the Notes to the extent (but only to the extent) such Investor or any of its affiliates would beneficially own a number of our Common Shares which would exceed 9.99% of the outstanding shares of the Company.
(3) Represents (a) 150,000 CCM Fee Shares (being registered for resale), (b) 33,000 Common Shares received in exchange for NCAC Private Placement Shares at the Closingand (c) 16,500 Common Shares underlying Private Warrants. J.V.B. is the record owner of the securities. Jerry Serowick is a Managing Director of J.V.B. and has investment control over the securities held by J.V.B. As such, Mr. Serowick may be deemed to have beneficial ownership of the securities held directly by J.V.B. Mr. Serowick disclaims any beneficial ownership of the reported shares other than to the extent of any pecuniary interest he may have therein, directly or indirectly. The business address of the Selling Shareholder is 3 Columbus Circle, 17th Floor, New York, NY 10019. CCM served as an advisor to NCAC in connection with its IPO and the Business Combination.
(4) Shares owned prior to the offering represents (a) 150,000 Cantor Fee Shares (being registered for resale), (b) 187,000 Common Shares received in exchange for NCAC Private Placement Shares at the Closing and (c) 93,500 Common Shares underlying Private Warrants. Cantor Fitzgerald & Co. (“CF&CO”) is the record owner of the securities. The business address of CF&CO is 110 East 59th Street, New York, NY 10022. CF Group Management, Inc. (“CFGM”) is the managing general partner of Cantor Fitzgerald, L.P. (“CFLP”) and directly or indirectly controls the managing general partner of Cantor Fitzgerald Securities (“CFS”), which indirectly is the majority owner of CF&CO. Mr. Howard Lutnick is Chairman and Chief Executive of CFGM and trustee of CFGM’s sole stockholder. CFLP, indirectly, holds a majority of the ownership interests in CFS, and therefore also indirectly holds a majority of the ownership interests in CF&CO. As such, each of CFLP, CFGM, CFS and Mr. Lutnick may be deemed to have beneficial ownership of the securities held directly by CF&CO. Each such entity or person disclaims any beneficial ownership of the reported shares other than to the extent of any pecuniary interest they may have therein, directly or indirectly. The foregoing should not be construed in and of itself as an admission by any of CFLP, CFGM, CFS or Mr. Lutnick as to beneficial ownership of the securities beneficially owned, directly, by CF&CO. CF&CO served as the representative of the underwriters in NCAC’s IPO.
(5) Represents 150,000 Maxim Fee Shares. Maxim Group, LLC is the record and beneficial owner of the securities set forth in the table. The address of Maxim Group, LLC is 405 Lexington Avenue, 2nd FL, New York, NY 10174. Maxim served as an advisor to the Company and Parent in connection with the Business Combination.
(6) MWE is the record owner of the securities. Olivia Sengbusch may be deemed to have beneficial ownership of the securities held directly by MWE. Ms. Sengbusch disclaims any beneficial ownership of the reported shares other than to the extent of any pecuniary interest she may have therein, directly or indirectly. The business address of the Selling Shareholder is 444 West Lake Street, Suite 4000, Chicago, IL 60606. MWE served as an advisor to NCAC in connection with the Business Combination.
(7) The business address of the Selling Shareholder is 1345 Avenue of the Americas, 11th Fl., New York, NY 10105.
(8) Represents 21,000 RNA Fee Shares. The address of the Selling Shareholder is 2121 N California Blvd STE 290, Walnut Creek, CA 94596. RNA served as an advisor to the Company and Parent in connection with the Business Combination and serves as its U.S. legal counsel following the Closing.
(9) Represents (a) 2,138,929 Common Shares received at the Closing in exchange for shares purchased in a private placement prior to the IPO of NCAC (1,603,929 of which are being registered for resale), (b) 125,500 Common Shares underlying Private Warrants and (c) 251,000 Common Shares received at the Closing in exchange for NCAC Private Placement Shares at the Closing. Sponsor, a limited liability company organized under the laws of the State of Delaware, is the record holder of such shares. Tabula Rasa Limited, a British Virgin Islands company with limited liability, is the sole manager of Sponsor. Carl Linde is the director of Fiducia Trustees Limited, the sole corporate director of Tabula Rasa Limited. Consequently, Mr. Linde be deemed the beneficial owner of the shares held by our sponsor and have voting and dispositive control over such securities. Mr. Linde disclaims beneficial ownership of any shares other than to the extent he may have a pecuniary interest therein, directly or indirectly. Each of NCAC’s officers and directors is a member of the Sponsor. The address for the principal business office of the sponsor is 2201 Broadway, Suite 705, Oakland, CA 94612.
(10) Represents (a) 222,269 Common Shares received at the Closing in exchange for shares purchased in a private placement prior to the IPO of NCAC (being registered for resale), (b) 63,505 Common Shares underlying Private Warrants and (c) 127,010 Common Shares received at the Closing in exchange for NCAC Private Placement Shares at the Closing. The address of the Selling Shareholder is c/o Evolution Capital Management LLC, 10250 Constellation Blvd., Suite 2300, Los Angeles, CA 90067.
(11) Represents (a) 11,113 Common Shares received at the Closing exchange for shares purchased in a private placement in connection with the IPO of NCAC (being registered for resale), (b) 3,175 Common Shares underlying Private Warrants and (c) 6,350 Common Shares received at the Closing in exchange for NCAC Private Placement Shares at the Closing. The address of the Selling Shareholder is 740 North High Street, Denver, CO 80218.
PLAN OF DISTRIBUTION
The Selling Shareholders and any of their pledgees, donees, assignees and successors-in-interest may, from time to time, sell any or all of their Common Shares on any stock exchange, market or trading facility on which the shares are traded or in private transactions or by gift, subject to the expiration of the Lock-Up Period. The shares offered by this prospectus may be sold by the Selling Shareholders at market prices prevailing at the time of sale or at negotiated prices. The Selling Shareholders may use any one or more of the following methods when selling or otherwise transferring shares:
| · | on any national securities exchange or quotation service on which the securities may be listed or quoted at the time of sale; |
| · | in the over-the-counter market; |
| · | in transactions otherwise than on these exchanges or systems or in the over-the-counter market; |
| · | through the writing or settlement of options, whether such options are listed on an options exchange or otherwise; |
| · | ordinary brokerage transactions and transactions in which the broker-dealer solicits purchasers; |
| · | block trades in which the broker-dealer will attempt to sell the shares as agent but may position and resell a portion of the block as principal to facilitate the transaction; |
| · | purchases by a broker-dealer as principal and resale by the broker-dealer for its account; |
| · | distributions to such Selling Shareholder’s limited partners or members; |
| · | an exchange distribution in accordance with the rules of the applicable exchange; |
| · | in “at-the-market” offerings, as defined in Rule 415 under the Securities Act, at negotiated prices, at prices prevailing at the time of sale or at prices related to such prevailing market prices, including sales made directly on a national securities exchange or sale made through a market maker other than on an exchange or other similar offerings through sales agents; |
| · | privately negotiated transactions; |
| · | short sales made after the date the registration statement of which this prospectus forms a part is declared effective by the SEC; |
| · | broker-dealers may agree with a selling security holder to sell a specified number of such shares at a stipulated price per share; |
| · | a combination of any of the above methods of sale; and |
| · | any other method permitted pursuant to applicable law. |
To the extent permitted under Rule 144, the Selling Shareholders may also sell Common Shares owned by them pursuant to Rule 144 or in other transactions exempt from registration rather than pursuant to this prospectus.
Broker-dealers engaged by the Selling Shareholders may arrange for other broker-dealers to participate in sales. Broker-dealers may receive commissions or discounts from the Selling Shareholders (or, if any broker-dealer acts as agent for the purchaser of shares, from the purchaser) in amounts to be negotiated. The Selling Shareholders do not expect these commissions and discounts to exceed what is customary in the types of transactions involved.
The Selling Shareholders may from time to time pledge or grant a security interest in some or all of the shares owned by them and, if the Selling Shareholders default in the performance of the secured obligations, the pledgees or secured parties may offer and sell the Common Shares from time to time under this prospectus, or under an amendment to this prospectus under Rule 424(b)(3) or other applicable provision of the Securities Act amending the list of Selling Shareholders to include the pledgee, transferee or other successors in interest as Selling Shareholder under this prospectus.
In connection with the sale of our Common Shares or interests therein, the Selling Shareholders may enter into hedging transactions with broker-dealers or other financial institutions which may in turn engage in short sales of our Common Shares in the course of hedging the positions they assume. The Selling Shareholders may, after the date of this prospectus, also sell our Common Shares short and deliver these securities to close out their short positions, or lend or pledge its Common Shares to broker-dealers that in turn may sell these securities. The Selling Shareholders may also enter into option or other transactions with broker-dealers or other financial institutions or the creation of one or more derivative securities which require the delivery to such broker-dealer or other financial institution of Common Shares offered by this prospectus, which shares such broker-dealer or other financial institution may resell pursuant to this prospectus (as supplemented or amended to reflect such transaction).
Subject to the terms of any lock-up agreements, the Selling Shareholders also may transfer the Common Shares in other circumstances, in which case the transferees, pledgees or other successors in interest will be the selling beneficial owners for purposes of this prospectus.
The Selling Shareholders and any broker-dealers or agents that are involved in selling the shares may be deemed to be “underwriters” within the meaning of the Securities Act in connection with such sales. In such event, they will be subject to the prospectus delivery requirements of the Securities Act, any commissions received by such broker-dealers or agents and any profit on the resale of the shares purchased by them may be deemed to be underwriting commissions or discounts under the Securities Act, and federal securities laws, including Regulation M, may restrict the timing of purchases and sales of our Common Shares by the Selling Shareholders and any other persons who are involved in the distribution of the Common Shares pursuant to this prospectus. The Selling Shareholders have informed us that they do not have any agreement or understanding, directly or indirectly, with any person to distribute the Common Shares.
Lock-Ups
In connection with the Closing, including the Securities Purchase Agreement, the following parties are subject to lock-ups as set forth below: MWE, NCAC, J.V.B., Cantor and RNA entered into Lock-Up Agreements which are substantially identical to each other, pursuant to which the applicable Lock-Up Party agreed not to, during the period commencing from the Closing and ending on the earliest of (x) one hundred eighty (180) days after the Closing; provided, however, that in the event that the Investors delay investment of the Subscription Amounts (as defined in the Securities Purchase Agreement) with respect to the Second Tranche Note (as defined in the Securities Purchase Agreement) due to the occurrence of an event outlined in Section 2.1(b) of the Securities Purchase Agreement, such period shall be extended by 60 days or such earlier date as the deficiency is resolved, and (y) subsequent to the Closing, the date on which the Company consummates a liquidation, merger, share exchange or other similar transaction with an unaffiliated third party that results in all of the Company’s shareholders having the right to exchange the Common Shares for cash, securities or other property, (i) lend, offer, pledge, hypothecate, encumber, donate, assign, sell, contract to sell, sell any option or contract to purchase, purchase any option or contract to sell, grant any option, right or warrant to purchase, or otherwise transfer or dispose of, directly or indirectly, any shares issued or issuable to the applicable Lock-Up Party pursuant to their respective agreements, (ii) enter into any swap or other arrangement that transfers to another, in whole or in part, any of the economic consequences of ownership of the Restricted Securities, or (iii) publicly disclose the intention to do any of the foregoing, whether any such transaction described in clauses (i), (ii) or (iii) above is to be settled by delivery of Restricted Securities or other securities, in cash or otherwise. The lock-up provisions provide for certain exemptions for transfers to permitted transferees.
Further, pursuant to documents entered into by NCAC upon the IPO of NCAC, certain shares are restricted until: (i) in the case of the Founder Shares, the earlier of (a) one year after the Closing and (b) subsequent to the Closing, (x) the date on which the Company completes a liquidation, merger, share exchange, reorganization or other similar transaction that results in all of the Company’s public shareholders having the right to exchange their Common Shares for cash, securities or other property or (y) if the last reported sale price of the Common Shares equals or exceeds $12.00 per share (as adjusted for share sub-divisions, share capitalizations, reorganizations, recapitalizations and the like) for any 20 trading days within any 30-trading day period commencing at least 150 days after the Closing, and (ii) in the case of placement units, placement shares, placement warrants issued in connection with NCAC’s IPO, as well as any Common Shares issued upon exercise thereof, 30 days after the Closing.
We may be required to amend or supplement this prospectus in the event that (a) a Selling Shareholder transfers securities under conditions which require the purchaser or transferee to be named in the prospectus as a Selling Shareholder, in which case we will be required to amend or supplement this prospectus to name the Selling Shareholder, or (b) a Selling Shareholder sells shares to an underwriter, in which case we will be required to amend or supplement this prospectus to name the underwriter and the method of sale.
We are paying all fees and expenses incident to the registration of the shares. We have agreed to indemnify the Selling Shareholder against certain losses, claims, damages and liabilities, including liabilities under the Securities Act.
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL
CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS
Unless the context otherwise requires, all references in this section to the “Company,” “we,” “us” or “our” refer to the business of Psyence Group Inc. prior to the consummation of the Business Combination, which became the business of Psyence Biomedical Ltd. and its subsidiaries following the consummation of the Business Combination.
You should read the following discussion and analysis of our financial condition and results of operations in conjunction with the information under “Selected Historical Financial Data” and our historical condensed consolidated interim financial statements and the related notes included elsewhere in this prospectus. This discussion and analysis should also be read together with the interim financial statements of Psyence Biomedical for the three and six months periods ended September 30, 2023 and 2022 and the pro forma financial information as of September 30, 2023 and 2022 included elsewhere in this prospectus. This discussion contains forward-looking statements that involve risks, uncertainties and assumptions. Our actual results and the timing of selected events could differ materially from those anticipated in these forward-looking statements as a result of various factors, including those set forth under “Risk Factors” set forth in the prospectus.
The numbers presented here have been translated to USD and are presented in USD.
Overview
Psyence Group Inc.is a life science biotechnology company listed on the Canadian Securities Exchange (CSE: PSYG) with a focus on natural psychedelics. Psyence Biomedical, also referred to as “Psyence Therapeutics,” is a division of Psyence, which is developing natural psilocybin medicinal formulations and treatment protocols for the treatment of adjustment disorder in patients with an incurable cancer diagnosis.
Recent Developments
See “Prospectus Summary – Recent Developments” for additional information regarding the Company and the Business Combination Agreement.
Results of Operations
Sales and marketing costs
For the 3-month period ended September 30, 2023, the Company incurred sales and marketing costs of $1,095, consisting primarily of expenses for conferences, content, promotional materials and website design costs. For the 3-month period ended September 30, 2022, sales and marketing costs of $0 were incurred.
For the 6-month period ended September 30, 2023, the Company incurred sales and marketing costs of $2,122 consisting primarily of expenses for conferences, content, promotional materials and website design costs. For the 6-month period ended September 30, 2022, sales and marketing costs of $0 were incurred.
For the year ended March 31, 2023, we incurred sales and marketing costs of $7,024, consisting primarily of expenses for conferences, content, promotional materials and website design costs. For the year ended March 31, 2022, sales and marketing costs of $17,440 were incurred, consisting of costs to create awareness of the Company and its activities, due to its recent establishment.
Research and development
For the 3-month period ended September 30, 2023, the Company incurred research and development costs of ($8,530) due to foreign exchange fluctuations, as compared to $1,984 for the 3-month period ended September 30, 2022.
For the 6-month period ended September 30, 2023, the Company incurred research and development costs of $791,439, as compared to $160,676 for the 6-month period ended September 30, 2022. The costs for both periods were incurred as we commenced clinical trials. The increase in costs reflect the higher costs associated with the Company’s Phase IIb palliative care clinical trial, as opposed to costs related to Phase IIa palliative care clinical trial.
For the year ended March 31, 2023, we incurred research and development costs of $1,607,565. This consisted of $1,372,850 of costs related to the clinical trial for the treatment of adjustment disorder, $170,072 for the formulation and licensing of PEX010 and $64,644 for general research.
General and administration costs
For the 3-month period ended September 30, 2023, the Company incurred general and administrative costs of ($16,105) due to option expense reversals, which consisted of bank fees, salaries and wages and operational costs, compared with $80,604 for the year ended 3-month period ended September 30, 2022. General and administrative costs decreased during the period in comparison to the preceding period as result of a decrease in payroll related costs.
For the 6-month period ended September 30, 2023, the Company incurred general and administrative costs of $85,569, which consisted of bank fees, salaries and wages and operational costs, compared with $172,588 for the 6-month period ended September 30, 2022. General and administrative costs decreased slightly during the period in comparison to the preceding period as result of a decrease in payroll related costs.
For the year ended March 31, 2023, the Company incurred general and administrative costs of $366,132, which consisted of bank fees, salaries and wages and operational costs, compared with $384,747 for the year ended March 31, 2022. General and administrative costs decreased slightly during the year ended March 31, 2023 in comparison to the year ended March 31, 2022 as result of a decrease in payroll related costs.
Professional and consulting fees
For the 3-month period ended September 30, 2023, professional and consulting fees totaled $199,516. This consisted of $129,461 paid to consultants for product development, financial, business strategies and administrative services, legal fees of $46,413 paid to legal practitioners for various corporate matters, and $23,642 for accounting services and audit fees.
For the 3-month period ended September 30, 2022, professional and consulting fees totaled $178,767. This consisted of $178,153 paid to consultants for product development, financial, business strategies and administrative services and legal fees of $614 paid to legal practitioners for various corporate matters.
For the 6-month period ended September 30, 2023, professional and consulting fees totaled $584,427. This consisted of $248,131 paid to consultants for product development, financial, business strategies and administrative services, legal fees of $312,455 paid to legal practitioners for various corporate matters, and $23,841 for accounting services and audit fees.
For the 6-month period ended September 30, 2022, professional and consulting fees totaled $341,744. This consisted of $340,373 paid to consultants for product development, financial, business strategies and administrative services and legal fees of $1,371 paid to legal practitioners for various corporate matters.
For the year ended March 31, 2023, professional and consulting fees totaled $1,251,474. This consisted of $825,866 paid to consultants for business strategies, financial and administrative services, legal fees of $250,523 paid to legal practitioners for various corporate matters, and $175,085 for accounting services and audit fees.
The professional and consulting fees for the period increased from the preceding period due to the Business Combination.
Other gains and losses
For the 3-month period ended September 30, 2023, and 2022, the Company incurred/(received) interest of $27,906 and ($854), respectively and had a foreign exchange loss of $113,997 and loss of $1,570, respectively.
For the 6-month period ended September 30, 2023, and 2022, the Company incurred/(received) interest of $27,423 and ($1,005), respectively and had a foreign exchange loss of $115,434 and $2,890, respectively.
For the years ended March 31, 2023 and 2022, the Company earned interest income of $1,553 and $0, respectively, and had a foreign exchange gain of $26,890 and loss of $2,278, respectively.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
Since incorporation, the operations have been financed from investment by our parent, Psyence Group Inc. and a loan advance based off the Company’s eligibility to receive a rebate from the Australian Tax Office. Our main use for liquidity is funding scientific research, clinical studies, salaries and professional and consulting fees. Our ability to fund operations and to make planned cash flows are subject to prevailing economic conditions, regulatory and financial, business, and other factors, some of which are beyond the Company’s control.
As of September 30, 2023, we had a cash balance of $605,480 and negative working capital of $982,671. This is as result of the trade payables relating to the Phase IIb Clinical Study. Working capital represents the excess of current assets over current liabilities. The Company prioritizes expenditure, both capital and operational, by regularly reviewing its available cash and cash equivalent balances against the spend required to deliver on its key strategic objectives and milestones.
As of March 31, 2023, we had a cash balance of including restricted cash of $1,363,900 and negative working capital of $200,545. This is as result of the trade payables relating to the Phase IIb Clinical Study. Working capital represents the excess of current assets over current liabilities. The Company prioritizes expenditure, both capital and operational, by regularly reviewing its available cash and cash equivalent balances against the spend required to deliver on its key strategic objectives and milestones.
The Company’s current expenditure obligations include commitments for the Phase IIb palliative care clinical trial. The Company expects to continue funding these projects with available cash and cash equivalents, and therefore, is subject to risks including, but not limited to, an inability to raise additional funds through the issuance of equity, debt instruments or similar means of financing to support the Company’s continued development, including operating requirements and to meet its liabilities and commitments at they become due.
The Company has experienced operating losses and cash outflows from operations since incorporation and by nature of its business, will require ongoing financing to continue its research and development operations. The Company’s ability to access both public and private capital is dependent upon, among other things, general and sectoral market conditions and the capital markets generally, market perceptions about the Company and its business operations, and the trading prices of the Company’s securities from time to time. There can be no assurance that additional funds can be raised upon terms acceptable to the Company, or at all, as funding for early-stage companies remain challenging generally.
The Company’s primary capital needs are funds to advance its research and development activities and for working capital purposes. These activities include staffing, pre-clinical studies, clinical trials, professional and consulting fees and general and administrative costs. There are uncertainties regarding the Company’s ability to continue as a going concern. There is no assurance that additional capital or other types of financing will be available if needed or that these financings will be on terms at least as favorable for the Company as those previously obtained, or at all.
Critical Accounting Policies
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with IFRS requires management to make certain estimates, judgments and assumptions concerning the future. Actual results may differ from these estimates. The Company’s management reviews these estimates, judgments, and assumptions on an ongoing basis, based on experience and other factors, including expectations of future events that are believed to be reasonable under the circumstances. Revisions to estimates are adjusted prospectively in the period in which the estimates are revised. The following are deemed to be critical accounting policies as these require a high level of subjectivity and judgement and could have a material impact on Psyence’s financial statements.
Going concern
Our audited financial statements included elsewhere in this prospectus have been prepared on the assumption that the Company will continue as a going concern, meaning it will continue in operation for the foreseeable future and will be able to realize assets and discharge liabilities in the ordinary course of operations.
Management routinely plans future activities including forecasting future cash flows and forming judgements collectively with directors of the Company.
Judgement is required in determining if the Company’s has sufficient cash reserves, together with all other available information, to continue as a going concern for a period of at least twelve months.
As of September 30, 2023 the Company has concluded that a material uncertainty exists that casts significant doubt about the Company’s ability to continue as a going concern.
Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Financial Instruments and Financial Risk Management
In the normal course of business, the Company is exposed to a variety of financial risks: credit risk, liquidity risk, foreign exchange risk and interest rate risk. These financial risks are subject to normal credit standards, financial controls, risk management, as well as monitoring. The Psyence Board has overall responsibility for the establishment and oversight of the Company’s risk management framework.
Credit risk
Credit risk arises from cash and cash equivalents held with banks. The maximum exposure to credit risk is equal to the carrying value of the financial assets. The objective of managing counterparty credit risk is to prevent losses on financial assets. The Company minimizes the credit risk of cash and cash equivalents by depositing with only reputable financial institutions. The Company also assesses the credit quality of counterparties, taking into account their financial position, past experience and other factors.
Liquidity risk
Liquidity risk is the risk that the Company will not be able to meet its financial obligations as they fall due.
The Company manages liquidity risk through an ongoing review of future commitments and cash balances available. Historically, the Company’s main source of funding has been through investments from its parent. The Company’s access to financing is always uncertain and there can be no assurance of continued access to significant equity or debt funding on terms satisfactory to the Company, or at all.
Foreign exchange risk
Foreign currency risk is the risk that the fair values of future cash flows of a financial instrument will fluctuate because they are denominated in currencies that differ from the respective functional currency.
The Company operates internationally and is exposed to foreign exchange risk from the South African Rand, Great British Pound, Australian Dollar and United States Dollar. Foreign exchange risk arises from transactions as well as recognized financial assets and liabilities denominated in foreign currencies.
A 10% adverse change in exchange rate would have resulted in a loss of $110,468 as of September 30, 2023.
Management mitigates the risk of adverse exchange rate movements by holding funds in Canadian and US dollars.
Interest rate risk
Interest rate risk is the risk that the fair value of future cash flows of a financial instrument will fluctuate because of changes in market interest rates. The Company has no significant interest-bearing assets or liabilities and therefore its income and operating cash flows are substantially independent of changes in market interest rates.
Capital Management
The Company’s objectives when managing its capital are to safeguard its ability to continue as a going concern, to meet its capital expenditures for its continued operations, and to maintain a flexible capital structure which optimizes the cost of capital within a framework of acceptable risk. The Company manages its capital structure and adjusts it in light of changes in economic conditions and the risk characteristics of the underlying assets. To maintain or adjust its capital structure, the Company may issue new shares, issue debt, or acquire or dispose of assets. The Company is not subject to externally imposed capital requirements.
Management reviews its capital management approach on an ongoing basis. The Company considers its shareholders’ equity balance as capital.
Related Party Transactions
All related party transactions are measured at the exchange amount, which is the amount of consideration established and agreed to by the related parties. All amounts either due from or due to related parties other than specifically disclosed are non-interest bearing, unsecured and have no fixed terms of repayments. The Company incurred the following transactions with related parties during the 6 month period ended September 30, 2023 and September 30, 2022:
Compensation to key management personnel
Key management personnel are those persons having authority and responsibility for planning, directing and controlling the activities of the Company, directly or indirectly. Key management personnel include the Company’s executive officers and Board of Directors.
| Key Management Personnel | | September 30, 2023 | | | September 30, 2022 | |
| Short term benefits | | | 251,514 | | | | 327,439 | |
Short-term benefits consist of consulting fees, payroll and other benefits paid to key management personnel.
The Company incurred the following transactions with related parties during the years ended March 31, 2023 and March 31, 2022:
| Key Management Personnel | | March 31, 2023 | | | March 31, 2022 | |
| Short term benefits | | | 593,717 | | | | 610,233 | |
| Share based compensation | | | 174,778 | | | | 295,188 | |
| Total | | | 768,495 | | | | 905,421 | |
Short term benefits consist of consulting fees, payroll and other benefits paid to key management personnel. Share based compensation is options granted to key management personnel. Accounts payable included balances for related parties of $74,156 ($17,610 – March 31, 2022 & $22,366 – March 31, 2021).
Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements
We have no obligations, assets or liabilities, which would be considered off-balance sheet arrangements as of September 30, 2023. We do not participate in transactions that create relationships with entities or financial partnerships, often referred to as variable interest entities, which would have been established for the purpose of facilitating off-balance sheet arrangements. We have not entered into any off-balance sheet financing arrangements, established any special purpose entities, guaranteed any debt or commitments of other entities, or purchased any non-financial assets.
Contractual obligations
We do not have any long-term debt, capital lease obligations, operating lease obligations or long-term liabilities.
JOBS Act
On April 5, 2012, the JOBS Act was signed into law. The JOBS Act contains provisions that, among other things, relax certain reporting requirements for qualifying public companies. We qualify as an “emerging growth company” and under the JOBS Act are allowed to comply with new or revised accounting pronouncements based on the effective date for private (not publicly traded) companies. We are electing to delay the adoption of new or revised accounting standards, and as a result, we may not comply with new or revised accounting standards on the relevant dates on which adoption of such standards is required for non- emerging growth companies. As such, our financial statements may not be comparable to companies that comply with public company effective dates.
Additionally, we are in the process of evaluating the benefits of relying on the other reduced reporting requirements provided by the JOBS Act. Subject to certain conditions set forth in the JOBS Act, if, as an “emerging growth company,” we choose to rely on such exemptions we may not be required to, among other things, (i) provide an auditor’s attestation report on our system of internal control over financial reporting pursuant to Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act, (ii) provide all of the compensation disclosure that may be required of non-emerging growth public companies under the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act, (iii) comply with any requirement that may be adopted by the PCAOB regarding mandatory audit firm rotation or a supplement to the auditor’s report providing additional information about the audit and the financial statements (auditor discussion and analysis) and (iv) disclose certain executive compensation related items such as the correlation between executive compensation and performance and comparisons of executive compensation to median employee compensation. These exemptions will apply for a period of five years following the completion of our IPO or until we are no longer an “emerging growth company,” whichever is earlier
UNAUDITED PRO FORMA CONDENSED COMBINED FINANCIAL INFORMATION
Introduction
Psyence Biomedical is providing the following unaudited pro forma condensed combined financial information to aid you in your analysis of the financial aspects of the Business Combination.
The following unaudited pro forma condensed combined balance sheet as of September 30, 2023 combines the historical balance sheet of NCAC as of September 30, 2023 with the historical carve-out consolidated balance sheets of Psyence Biomed Corp. as of September 30, 2023, giving pro forma effect to the Business Combination, as if it had occurred as of September 30, 2023.
The following unaudited pro forma condensed combined statements of operations for the six months ended September 30, 2023 combine the historical statement of operations of NCAC for the nine months ended September 30, 2023 less the three months ended March 31, 2023, and the historical carve-out consolidated statements of net loss and comprehensive loss of Psyence Biomed Corp. for the six months ended September 30, 2023, giving pro forma effect to the Business Combination as if it had occurred on April 1, 2022, the beginning of the earliest period presented.
The following unaudited pro forma condensed combined statements of operations for the year ended March 31, 2023 combine the historical statement of operations of NCAC for the year ended December 31, 2022, and the historical carve-out consolidated statements of net loss and comprehensive loss of Psyence Biomed Corp. for the year ended March 31, 2023, giving pro forma effect to the Business Combination as if it had occurred on April 1, 2022, the beginning of the earliest period presented.
The unaudited pro forma condensed combined financial statements have been derived from:
| | · | the historical audited financial statements of NCAC as of December 31, 2022 and for the year ended December 31, 2022 and the related notes thereto; |
| | · | the historical unaudited financial statements of NCAC as of March 31, 2023 and for the three months ended March 31, 2023 and the related notes thereto; and |
| | · | the historical unaudited financial statements of NCAC as of September 30, 2023 and for the nine months ended September 30, 2023 and the related notes thereto; and |
| | · | the historical audited carve-out consolidated financial statements of Psyence Biomed Corp. as of September 30, 2023 and for the six months ended September 30, 2023 (the “Carve-Out interim Consolidated Financial Statements”) and the related notes thereto included elsewhere in this prospectus; and |
| | · | the historical audited carve-out consolidated financial statements of Psyence Biomed Corp. as of and for the years ended March 31, 2023 and 2022 (the “Carve-Out Consolidated Financial Statements”) and the related notes thereto included elsewhere in this prospectus. |
This information should be read together with the Carve-Out Consolidated Financial Statements of Psyence Biomed Corp. and its related notes and NCAC’s financial statements and related notes, “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations,” and other financial information included elsewhere in this prospectus.
UNAUDITED PRO FORMA CONDENSED COMBINED BALANCE SHEET AS OF SEPTEMBER 30, 2023
(In USD)
| | | Original Target | | | | | | IFRS
Conversion
and | | | Actual
Redemption | |
| | | (IFRS,
Historical) – USD
(Note 4) | | | NCAC
(U.S. GAAP
Historical) | | | Presentation
Alignment
(Note 4) | | | Transaction
Accounting
Adjustments | | | | Pro Forma
Combined | |
| ASSETS | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Current assets | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | | $ | 605,480 | | | $ | 88,174 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 1,351,130 | | A | | $ | 2,275,445 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (1,613,859 | ) | B | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (50,000 | ) | H | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 2,500,000 | | J | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (605,480 | ) | O | | | | |
| Restricted cash | | | 29,586 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (29,586 | ) | O | | | — | |
| Other receivables | | | 18,787 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | | 18,787 | |
| Interest receivable | | | — | | | | 53,659 | | | | — | | | | (53,659 | ) | A | | | — | |
| Prepaid expenses and other assets | | | 15,519 | | | | 20,683 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | | 36,202 | |
| Total current assets | | | 669,372 | | | | 162,516 | | | | — | | | | 1,499,250 | | | | | 2,330,434 | |
| Non-current assets | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Investments held in Trust Account | | | — | | | | 12,518,199 | | | | — | | | | (1,297,471 | ) | A | | | — | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (11,493,744 | ) | K | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 100,172 | | L | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 172,844 | | M | | | | |
| Total non-current assets | | | — | | | | 12,518,199 | | | | — | | | | (12,518,199 | ) | | | | — | |
| Total assets | | $ | 669,372 | | | $ | 12,680,715 | | | $ | — | | | $ | (11,019,653 | ) | | | $ | 2,330,434 | |
| LIABILITIES | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Current liabilities | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Accounts payable and accrued liabilities | | $ | 914,990 | | | $ | 1,007,704 | | | $ | — | | | $ | (618,551 | ) | B | | $ | 1,304,143 | |
| Deferred underwriting fee payable | | | — | | | | 13,100,000 | | | | — | | | | (13,100,000 | ) | I | | | — | |
| Loan to affiliate | | | 737,053 | | | | 70,000 | | | | — | | | | 1,460,657 | | B | | | 2,267,710 | |
| Loan from Sponsor | | | — | | | | 1,607,770 | | | | — | | | | (50,000 | ) | H | | | 1,657,942 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 100,172 | | L | | | | |
| Convertible Note | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 484,496 | | J | | | 484,496 | |
| Derivative warrant liability | | | — | | | | 392,100 | | | | — | | | | (392,100 | ) | O | | | 594,685 | |
| | | | — | | | | | | | | | | | | 594,685 | | P | | | | |
| Common stock subject to possible redemption | | | — | | | | — | | | | 12,571,858 | (a) | | | (1,078,114 | ) | E | | | — | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (11,493,744 | ) | K | | | | |
| Total current liabilities | | | 1,652,043 | | | | 16,177,574 | | | | 12,571,858 | | | | (24,092,499 | ) | | | | 6,308,976 | |
| Total liabilities | | | 1,652,043 | | | | 16,177,574 | | | | 12,571,858 | | | | (24,092,499 | ) | | | | 6,308,976 | |
| Class A ordinary shares subject to possible redemption | | | — | | | | 12,571,585 | | | | (12,571,858 | )(a) | | | — | | | | | — | |
| EQUITY | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net parent investment | | | (982,671 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | 982,671 | | C | | | — | |
| NCAC Class B ordinary shares | | | — | | | | 654 | | | | — | | | | (654 | ) | G | | | — | |
| NCAC Class A ordinary shares | | | — | | | | 114 | | | | — | | | | 500 | | C | | | 1,339 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 45 | | B | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 12 | | E | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 523 | | G | | | | |
| | | Original Target
| | | | | | IFRS
Conversion
and | | | Actual
Redemption | |
| | | (IFRS,
Historical) – USD
(Note 4) | | | NCAC
(U.S. GAAP
Historical) | | | Presentation
Alignment
(Note 4) | | | Transaction
Accounting
Adjustments | | | | Pro Forma
Combined | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 130 | | J | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 15 | | I | | | | |
| Additional paid-in capital | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (988,955 | ) | B | | | 71,542,872 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 4,110,908 | | C | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (3,904,541 | ) | D | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 1,078,102 | | E | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 131 | | G | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 1,499,985 | | I | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (635,066 | ) | N | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 2,015,374 | | J | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 68,366,934 | | F | | | | |
| Accumulated deficit | | | — | | | | (16,069,485 | ) | | | — | | | | (1,467,055 | ) | B | | | (75,522,753 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (5,094,079 | ) | C | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 3,904,541 | | D | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (68,366,934 | ) | F | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 392,100 | | O | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (594,685 | ) | P | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 11,600,000 | | I | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 172,844 | | M | | | | |
| Total equity | | | (982,671 | ) | | | (16,068,717 | ) | | | — | | | | 13,072,846 | | | | | (3,978,542 | ) |
| Total equity and liabilities | | $ | 669,372 | | | $ | 12,680,715 | | | $ | — | | | $ | (11,019,653 | ) | | | $ | 2,330,434 | |
See accompanying notes to the unaudited pro forma condensed combined financial information.
UNAUDITED PRO FORMA CONDENSED COMBINED STATEMENT OF OPERATIONS FOR THE SIX MONTHS ENDED SEPTEMBER 30, 2023
(in USD)
| | | Original Target
| | | | | | IFRS
Conversion
and | | | Actual
Redemption | |
| | | (IFRS,
Historical) – USD
(Note 4) | | | NCAC
(U.S. GAAP
Historical)(1) | | | Presentation
Alignment
(Note 4) | | | Transaction
Accounting
Adjustments | | | | Pro Forma
Combined | |
| Operating expenses | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Sales and marketing | | $ | (2,122 | ) | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | | $ | (2,122 | ) |
| Research and development | | | (791,439 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | | (791,439 | ) |
| General and administrative | | | (85,569 | ) | | | (290,985 | ) | | | — | | | | 60,000 | | BB | | | (316,554 | ) |
| Professional fees and consulting fees | | | (584,427 | ) | | | (778,157 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | | (1,362,584 | ) |
| Foreign exchange gain (loss) | | | (115,434 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | | (115,434 | ) |
| Interest income | | | (27,423 | ) | | | — | | | | 358,533 | (b) | | | (358,533 | ) | AA | | | (27,423 | ) |
| Total operating expense | | | (1,606,414 | ) | | | (1,069,142 | ) | | | 358,533 | | | | (298,533 | ) | | | | (2,615,556 | ) |
| Other income and (expense) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Interest income on marketable securities held in Trust Account | | | — | | | | 358,533 | | | | (358,533 | )(b) | | | — | | | | | — | |
| Profit (loss) before income tax | | | (1,606,414 | ) | | | (710,609 | ) | | | — | | | | (298,533 | ) | | | | (2,615,556 | ) |
| Income tax (expense) benefit | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | | — | |
| Net income (loss) | | $ | (1,606,414 | ) | | $ | (710,609 | ) | | $ | — | | | $ | (298,533 | ) | | | $ | (2,615,556 | ) |
| Basic and diluted net loss per share, redeemable Class A ordinary shares | | | | | | $ | 0.20 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Basic and diluted net loss per share, Class B ordinary shares | | | | | | $ | (0.08 | ) | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Pro forma weighted average number of shares outstanding – basic and diluted | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 13,390,659 | |
| Pro forma loss per share – basic and diluted | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | $ | (0.20 | ) |
| (1) | Combine the historical statement of operations of NCAC for the six months ended September 30, 2023 derived from the nine month ended September 30, 2023 less the three months ended March 31, 2023. |
UNAUDITED PRO FORMA CONDENSED COMBINED STATEMENT OF OPERATIONS FOR THE YEAR ENDED MARCH 31, 2023
(in USD)
| | | Original Target
| | | | | | IFRS
Conversion
and | | | Actual
Redemption | |
| | | (IFRS,
Historical) – USD
(Note 4) | | | NCAC
(U.S. GAAP
Historical)(1) | | | Presentation
Alignment
(Note 4) | | | Transaction
Accounting
Adjustments | | | | Pro Forma
Combined | |
| Operating expenses | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Sales and marketing | | $ | (7,024 | ) | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | | $ | (7,024 | ) |
| Research and development | | | (1,607,565 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | | (1,607,565 | ) |
| General and administrative | | | (366,132 | ) | | | (869,379 | ) | | | — | | | | 220,000 | | BB | | | (70,849,500 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (68,833,989 | ) | CC | | | | |
| Professional fees and consulting fees | | | (1,251,474 | ) | | | (424,598 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | | (1,676,072 | ) |
| Foreign exchange gain (loss) | | | 26,890 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | | 26,890 | |
| Interest income | | | 1,553 | | | | — | | | | 3,551,791 | (b) | | | (3,551,791 | ) | AA | | | 1,553 | |
| Total operating expense | | | (3,203,752 | ) | | | (1,293,977 | ) | | | 3,551,791 | | | | (73,165,780 | ) | | | | (74,111,718 | ) |
| Other income and (expense) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Change in fair value of warrants | | | — | | | | 5,756,500 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | | 5,756,500 | |
Interest income on marketable securities held in Trust
Account | | | — | | | | 3,551,791 | | | | (3,551,791 | )(b) | | | — | | | | | — | |
| Profit (loss) before income tax | | | (3,203,752 | ) | | | 8,014,314 | | | | — | | | | (73,165,780 | ) | | | | (68,355,218 | ) |
| Income tax (expense) benefit | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | | — | |
| Net income (loss) | | $ | (3,203,752 | ) | | $ | 8,014,314 | | | $ | — | | | $ | (73,165,780 | ) | | | $ | (68,355,218 | ) |
| Basic and diluted net loss per share, redeemable Class A ordinary shares | | | | | | $ | 0.38 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Basic and diluted net loss per share, Class B ordinary shares | | | | | | $ | 0.25 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Pro forma weighted average number of shares outstanding – basic and diluted | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 13,390,659 | |
| Pro forma loss per share – basic and diluted | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | $ | (5.10 | ) |
| (1) | Combine the historical statement of operations of NCAC for the year ended December 31, 2022 |
NOTES TO UNAUDITED PRO FORMA CONDENSED COMBINED FINANCIAL INFORMATION
Note 1 - Description of the Business Combination
On January 25, 2024 (the “Closing Date”), Psyence Biomedical Ltd., a corporation organized under the laws of Ontario, Canada (“Psyence Biomedical” or the “Company”), consummated the previously announced business combination pursuant to the Amended and Restated Business Combination Agreement (as amended, the “BCA”), dated as of July 31, 2023, by and among the Company, Newcourt Acquisition Corp., a Cayman Islands exempted company (“NCAC”), Newcourt SPAC Sponsor LLC, a Delaware limited liability company (“Sponsor”), Psyence Group Inc., a corporation organized under the laws of Ontario, Canada (“Parent”), Psyence (Cayman) Merger Sub, a Cayman Islands exempted company and a direct and wholly owned subsidiary of the Company (“Merger Sub”), Psyence Biomed Corp., a corporation organized under the laws of British Columbia, Canada (“Original Target”), and Psyence Biomed II Corp., a corporation organized under the laws of Ontario, Canada (“Psyence II”).
Prior to the execution of the Amended and Restated Business Combination Agreement, Parent formed Psyence II and Psyence Biomedical as wholly owned subsidiaries, and prior to the Closing, Parent and the Original Target were amalgamated. Thereafter, Parent transferred the shares of Psyence Australia Pty Ltd. and its related business assets that were previously owned by the Original Target to Psyence II.
The following transactions occurred pursuant to the terms of the BCA (collectively, the “Business Combination”) at the effective time of the Merger (the “Effective Time”):
| · | Parent contributed Psyence II to the Company in a share for share exchange (the “Company Exchange”). |
| | |
| · | Following the Company Exchange, Merger Sub merged with and into NCAC, with NCAC being the surviving company in the merger (the “Merger”) and each outstanding ordinary share of NCAC was converted into the right to receive one common share of the Company (“Common Share”). |
| | |
| · | Each outstanding warrant to purchase NCAC Class A ordinary shares was converted at the Effective Time into a warrant to acquire one Common Share (the “Company Warrants”) on substantially the same terms as were in effect immediately prior to the Effective Time under their terms. |
On January 15, 2024 and January 23, 2024, the parties to the Business Combination Agreement entered into letter agreements (the “Closing Letter Agreements”) pursuant to which, among other things, Psyence Biomedical, Parent, the Company, Original Target and Merger Sub (collectively, the “Psyence Parties”) agreed, (X) on a conditional basis, to waive the closing conditions contained in the BCA that, at or prior to the closing of the Business Combination (the “Closing”), (i) Newcourt shall have no less than $20,000,000, net of liabilities, as of the Closing (the “Minimum Cash Condition”) and (ii) the PIPE Investment in the PIPE Investment Amount shall have occurred or shall be ready to occur substantially concurrently with the Closing (the “PIPE Investment Condition”) and (Y) to waive certain deliverables under Section 3.6 of the Business Combination Agreement (the “Closing Deliverables”). Upon the Closing, the Psyence Parties waived in full the Minimum Cash Condition, the PIPE Investment Condition and the Closing Deliverables.
On January 15, 2024, in connection with the Business Combination, the Company entered into a securities purchase agreement (the “Securities Purchase Agreement”) by and among (i) the Company, (ii) Psyence II, (iii) Sponsor and (iv) certain investors (the “Investors”) relating to up to four senior secured convertible notes (collectively, the “Notes” and the transactions pursuant to the Securities Purchase Agreement, the “Financing”), obligations under which will be guaranteed by certain assets of the Company and Psyence II, issuable to the Investors at or after the Closing, as the case may be, for the aggregate principal amount of up to $12,500,000 in exchange for up to $10,000,000 in subscription amounts.
The Note for the first tranche of the Financing (the “First Tranche Note”), for a total of $3,125,000 of principal in exchange for a total of $2,500,000 in subscription amounts and was issued to the Investors substantially concurrently with, and contingent upon, the Closing. The Financing closed immediately prior to the Business Combination.
Upon the closing of the first tranche of the Financing, the Minimum Cash Condition and PIPE Investment Condition were deemed waived by the Psyence Parties.
Merger Consideration
As consideration for all of the issued and outstanding Psyence II common shares that the Company shall receive in the Company Exchange, the Company shall issue to Parent, 5,000,000 Common Shares.
Note 2 - Basis of Presentation
The adjustments presented on the pro forma combined financial statements have been identified and presented to provide an understanding of the Company upon consummation of the Business Combination for illustrative purposes.
The following unaudited pro forma condensed combined financial information has been prepared in accordance with Article 11 of Regulation S-X as amended by the final rule, Release No. 33-10786 “Amendments to Financial Disclosures about Acquired and Disposed Businesses.” Release No. 33-10786 replaces the existing pro forma adjustment criteria with simplified requirements to depict the accounting for the transaction (“Transaction Accounting Adjustments”) and present the reasonably estimable synergies and other transaction effects that have occurred or are reasonably expected to occur (“Management’s Adjustments”). The Company has elected not to present Management’s Adjustments and will only be presenting Transaction Accounting Adjustments in the following unaudited pro forma condensed combined financial information. The historical financial information has been adjusted to reflect the pro forma adjustments that are directly attributable to the Business Combination and the Security Purchase Agreement financing as described below.
Actual Redemptions
On January 18, 2024, in connection with the extraordinary general meeting of shareholders held in connection with the proposed Business Combination, NCAC’s public shareholders holding 929,727 public shares validly elected to redeem their shares for a pro rata portion of the funds in the NCAC’s Trust Account. As a result, approximately $10.74 million (approximately $11.56 per public share redeemed in connection with the Extension Meeting) was removed from the Trust Account to pay such holders. On January 22, 2024, in connection with the NCAC’s Extension Meeting, shareholders holding 63,635 public shares exercised their right to redeem their shares for a pro rata portion of the funds in the NCAC’s Trust Account. As a result, approximately $735,000 (approximately $11.56 per public share redeemed in connection with the Extension Meeting) was removed from the Trust Account to pay such holders. The total shares redeemed was 993,362 resulting in approximately $11.49 was removed from the Trust Account to pay such holders. Following such redemptions, NCAC had 119,659 public shares outstanding and approximately $1.38 million remained in the Trust Account.
Financing Arrangements
On January 15, 2024, the Company entered into a securities purchase agreement (the “Securities Purchase Agreement”) by and among the Company, Psyence, Sponsor and a purchaser (the “Purchaser”) relating to up to four senior secured convertible notes (collectively, the “Notes”), obligations under which will be guaranteed by certain assets of the Company and Psyence, issuable to the Purchaser at or after the Closing, as the case may be, for the aggregate principal amount of up to $12,500,000 in exchange for up to $10,000,000 in subscription amounts.
The First Tranche Note will be a total of $3,125,000 of principal in exchange for a total of $2,500,000 in subscription amounts and will be issuable to the Purchaser substantially concurrently with, and contingent upon, the consummation of the Business Combination or at such other time and place as the Company and the Purchaser mutually agree upon.
The Second Tranche Note will be a total of $3,125,000 of principal in exchange for a total of $2,500,000 in subscription amounts; provided, however, that, in the event that the Market Value Traded as of the Second Tranche Closing is less than the full subscription amount of the Second Tranche Note, (A) Purchaser will invest an amount equal to the Market Value Traded as of the Second Tranche Closing and (B) on the later of (i) each subsequent 30 day anniversary of the Second Tranche Closing or (ii) the effectiveness of the registration statement registering the underlying shares for such portion of the Second Tranche Note, Purchaser will invest an amount equal to the Market Value Traded as of such date, until the Second Tranche Note is funded in full, subject to the conditions set forth in the Securities Purchase Agreement.
The Third Tranche Note, if any, will be a total of $3,125,000 of principal in exchange for a total of $2,500,000 in subscription amounts.
The Fourth Tranche Note, if any, will be a total of $3,125,000 of principal in exchange for a total of $2,500,000 in subscription amounts.
The material terms of the Notes are as follows: On the original issuance date, interest shall begin accruing at 8.0% per annum based on the outstanding principal amount of the Note, payable monthly in arrears in cash or in common shares of the Company’s (“Common Shares”) (at the Conversion Price). For purposes of the Notes, the Conversion Price, commencing on the first trading day following the closing of the Business Combination shall be $10.00; provided, however, it may be subject to adjustments according to the terms and reset dates included in the Note.
Additionally, in consideration of the willingness of the Purchaser to enter into the transactions that are the subject of the Securities Purchase Agreement and the Notes, the Company or certain of its shareholders shall deliver a structuring fee of Common Shares (the “Structuring Shares”) in connection with the Note per the terms of the attached agreement, with (i) 1,300,000 Structuring Shares delivered to the Purchaser at the First Tranche Closing and (ii) following the First Tranche Closing, 1,700,000 Structuring Shares delivered pursuant to the terms set forth in the call option agreements to be entered into between Purchaser and certain shareholders of the Company.
In connection with the foregoing, the Company and the Purchaser will enter into a registration rights agreement, pursuant to which the Company will file a Registration Statement covering the resale of registrable securities issuable pursuant to the Note.
In connection with the foregoing and as a condition to each closing under the Securities Purchase Agreement, NCAC Sponsor and Parent, shall have entered into a lock-up agreement, pursuant to which, NCAC Sponsor and Parent will agree, subject to customary exceptions, not to offer, pledge, sell, contract to sell, grant, lend, or otherwise transfer or dispose of, directly or indirectly, any Common Shares or any securities convertible into or exercisable or exchangeable for Common Shares (the “Lock-Up Securities”), whether currently owned or acquired later by NCAC Sponsor or Parent, or enter into any swap or other arrangement that transfers to another, in whole or in part, any of the economic consequences of ownership of the Lock-Up Securities until 180 days following the closing of the Business Combination, or such later date pursuant to the terms set forth therein.
The Structuring Shares are deemed to be representative of a freestanding financial instrument issued in a bundled transaction with the Note. The Structuring Shares to be issued as part of the bundled transaction are classified and accounted for as equity; therefore, the proceeds are required to be allocated based on the relative fair values of the base instrument (i.e., Note) and the Structuring Shares in accordance with the guidance in ASC 470, Debt. The accounting position is currently under review and is subject to change.
The pro forma condensed combined financial information is for illustrative purposes only. The financial results may have been different had the companies always been combined. You should not rely on the unaudited pro forma condensed combined financial information as being indicative of the historical results that would have been achieved had the companies always been combined or the future results that the Company will experience. Original Target and NCAC have not had any historical relationship prior to the Business Combination. Accordingly, no pro forma adjustments were required to eliminate activities between the companies.
The historical carve-out consolidated financial statements of Original Target. have been prepared in accordance with IFRS as issued by the IASB and in its presentation currency of the Canadian Dollar (“CDN” or “CDN$”). The historical financial statements of NCAC have been prepared in accordance with U.S. GAAP in its presentation currency of the U.S. dollar (“USD” or “$”). The condensed combined pro forma financial information reflects IFRS and in USD, the basis of accounting used by the registrant, the Company, and no material accounting policy difference is identified in converting NCAC’s historical financial statements from U.S. GAAP to IFRS or Original Target from CDN to USD. The adjustments presented in the pro forma condensed combined financial information have been identified and presented to provide relevant information necessary for an accurate understanding of the Company after giving effect to the Business Combination.
The pro forma condensed combined financial information reflects the actual redemptions as described above.
The following table sets out the share ownership of the Company following Closing on a pro forma basis:
| Pro Forma Ownership | | Shares | | | Number of Percent
Outstanding | |
| Rollover equity shares of Psyence Biomedical shareholders | | | 5,000,000 | | | | 37.34 | % |
| NCAC Public Shareholders | | | 119,659 | | | | 0.89 | % |
| Members of Sponsor | | | 3,765,071 | | | | 28.12 | % |
| Sponsor | | | 2,389,929 | | | | 17.85 | % |
| Cantor | | | 337,000 | | | | 2.52 | % |
| CCM | | | 183,000 | | | | 1.36 | % |
| Financing Investors | | | 1,300,000 | | | | 9.71 | % |
| Other Third Party Advisers | | | 296,000 | | | | 2.21 | % |
| Total shares outstanding | | | 13,390,659 | | | | 100 | % |
Included in the shares outstanding and weighted average shares outstanding as presented in the pro forma combined financial statements are an aggregate of 13.39 million the Common Shares that were issued to NCAC’s shareholders, Original Target’s shareholders, Financing Investors and to Third Party shareholders.
The pro forma adjustments do not have an income tax effect as they are either (i) incurred by legal entities that are not subject to a corporate income tax, or (ii) permanently nondeductible or nontaxable based on the laws of the relevant jurisdiction.
Note 3 - Accounting for the Business Combination
The Business Combination will be accounted for as a capital reorganization in accordance with IFRS. Under this method of accounting, NCAC will be treated as the “acquired” company for financial reporting purposes, and Original Target will be the accounting “acquirer.” This determination was primarily based on the assumption that Original Target shareholders will hold the largest minority of the voting power of the Company, Original Target’s operations will substantially comprise the ongoing operations of the Company, Original Target’s designees are expected to comprise a majority of the governing body of the Company, and Original Target’s senior management will comprise the senior management of the Company. However, NCAC does not meet the definition of a “business” pursuant to IFRS 3 Business Combinations, and thus, for accounting purposes, the Business Combination will be accounted for as a capital reorganization. The net assets of NCAC will be stated at historical cost, with no goodwill or other intangible assets recorded. The deemed costs of the shares issued by Original Target, which represents the fair value of the shares that Original Target would have had to issue for the ratio of ownership interest in the Company to be the same as if the Business Combination had taken the legal form of Original Target acquiring shares of NCAC, in excess of the net assets of NCAC will be accounted for as stock-based compensation under IFRS 2 Share-Based Payment.
Note 4 - U.S. GAAP to IFRS Conversion and Presentation Alignment
The historical financial information of NCAC has been adjusted to give effect to the differences between U.S. GAAP and IFRS as issued by the IASB for the purposes of the unaudited pro forma condensed combined financial information. One adjustment required to convert NCAC’s balance sheet from U.S. GAAP to IFRS for purposes of the unaudited pro forma condensed combined financial information was to reclassify NCAC Class A ordinary shares subject to redemption to non-current financial liabilities under IFRS 2, as shareholders have the right to require NCAC to redeem NCAC Public Shares and NCAC has an irrevocable obligation to deliver cash or another financial instrument for such redemption.
Further, as part of the preparation of the unaudited pro forma condensed combined financial information, certain reclassifications were made to align NCAC’s historical financial information in accordance with the presentation of Psyence Biomed Corp.’s historical carve-out consolidated financial information, see below for effect of conversion on the financial statements.
In addition, as part of the preparation of the unaudited pro forma condensed combined financial information since the reporting currency will be in United States dollars (“USD”), Original Target’s historical carve-out consolidated financial information was converted from Canadian dollars (“CDN”) to USD in accordance with the presentation of functional currency of Psyence Australia Pty, Ltd.’s historical financial information and the Company’s anticipated reporting currency, see below for effect of conversion on the financial statements.
NCAC’s Balance Sheet as of September 30, 2023
| NCAC’s financial statements have been prepared in accordance with U.S. GAAP and in USD currency and converted to IFRS as follows: |
| As of September 30, 2023 | | U.S. GAAP | | | IFRS
Conversion
adjustment | | | Footnote
reference | | After
conversion | |
| ASSETS | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Current assets: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Cash | | $ | 88,174 | | | | | | | | | $ | 88,174 | |
| Interest receivable | | | 53,659 | | | | | | | | | | 53,659 | |
| Prepaid expenses | | | 20,683 | | | | | | | | | | 20,683 | |
| Total current assets | | | 162,516 | | | | | | | | | | 162,516 | |
| Investments held in Trust Account | | | 12,518,199 | | | | | | | | | | 12,518,199 | |
| Total assets | | $ | 12,680,715 | | | | | | | | | $ | 12,680,715 | |
| LIABILITIES, ORDINARY SHARES SUBJECT TO POSSIBLE REDEMPTION AND SHAREHOLDERS’ DEFICIT | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Current liabilities: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Accounts payable and accrued expenses | | $ | 1,007,704 | | | | | | | | | $ | 1,007,704 | |
| Deferred underwriting commissions | | | 13,100,000 | | | | | | | | | | 13,100,000 | |
| Due to affiliate | | | 70,000 | | | | | | | | | | 70,000 | |
| Loan from sponsor | | | 1,607,770 | | | | | | | | | | 1,607,770 | |
| Derivative warrant liability | | | 392,100 | | | | | | | | | | 392,100 | |
| Class A ordinary shares subject to possible redemption, | | | — | | | | 12,571,858 | | | (a) | | | 12,571,858 | |
| Total current liabilities | | | 16,177,574 | | | | | | | | | | 28,749,432 | |
| Total liabilities | | | 16,177,574 | | | | | | | | | | 28,749,432 | |
| Commitments and contingencies | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Class A ordinary shares subject to possible redemption, | | | 12,571,585 | | | | (12,571,858 | ) | | (a) | | | — | |
| Class A ordinary shares | | | 114 | | | | | | | | | | 114 | |
| Class B ordinary shares | | | 654 | | | | | | | | | | 654 | |
| Additional paid-in capital | | | — | | | | | | | | | | — | |
| Accumulated deficit | | | (16,069,485 | ) | | | | | | | | | (16,069,485 | ) |
| Total shareholders’ deficit | | | (16,068,717 | ) | | | | | | | | | (16,068,717 | ) |
| Total liabilities, ordinary shares subject to possible redemption and shareholders’ deficit | | $ | 12,680,715 | | | | | | | | | $ | 12,680,715 | |
| | (a) | To reclassify and present redeemable NCAC Public Shares as other liabilities under IFRS, as shareholders have the right to require NCAC to redeem the NCAC Public Shares and NCAC has an irrevocable obligation to deliver cash or another financial instrument for such redemption. |
U.S. GAAP to IFRS Conversion of NCAC’s Statement of Operations for the six months ended September 30, 2023
NCAC’s financial statements have been prepared in accordance with U.S. GAAP and in USD currency and is converted to IFRS as follows:
| For the Six Months Ended September 30, 2023 | | U.S. GAAP | | | IFRS
Conversion
adjustment | | | Footnote
reference | | After
conversion | |
| General and administrative | | $ | (1,069,142 | ) | | | | | | | | $ | (1,069,142 | ) |
| Interest earned on investments held in Trust Account | | | — | | | | 358,533 | | | (b) | | | 358,533 | |
| Income (loss) from operations | | | (1,069,142 | ) | | | | | | | | | (710,609 | ) |
| Other income (expense): | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Interest earned on investments held in Trust Account | | | 358,533 | | | | (358,533 | ) | | (b) | | | — | |
| Change in fair value of warrant liabilities | | | — | | | | | | | | | | — | |
| Total other income (expense) | | | 358,533 | | | | | | | | | | — | |
| Net income (loss) | | $ | (710,609 | ) | | | | | | | | $ | (710,609 | ) |
U.S. GAAP to IFRS Conversion of NCAC’s Statement of Operations for the year ended December 31, 2022
NCAC’s financial statements have been prepared in accordance with U.S. GAAP and in USD currency and is converted to IFRS as follows:
| For the Year Ended December 31, 2022 | | U.S. GAAP | | | IFRS
Conversion
adjustment | | | Footnote
reference | | After
conversion | |
| General and administrative | | $ | (1,293,977 | ) | | | | | | | | $ | (1,293,977 | ) |
| Interest earned on investments held in Trust Account | | | — | | | | 3,551,791 | | | (b) | | | 3,551,791 | |
| Income (loss) from operations | | | (1,293,977 | ) | | | | | | | | | 2,257,814 | |
| Other income (expense): | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Interest earned on investments held in Trust Account | | | 3,551,791 | | | | (3,551,791 | ) | | (b) | | | — | |
| Change in fair value of warrant liabilities | | | 5,756,500 | | | | | | | | | | 5,756,500 | |
| Total other income (expense) | | | 9,308,291 | | | | | | | | | | 5,756,500 | |
| Net income (loss) | | $ | 8,014,314 | | | | | | | | | $ | 8,014,314 | |
| (b) | To reclassify and present interest earned on investments held in trust from non-operating income (expense) to other income from operating expenses. |
Original Target’s Carve-Out Condensed Consolidated Interim Statement of Financial Position as of September 30, 2023 and Carve-Out Condensed Consolidated Statement of Net Loss and Comprehensive Loss for the six months ended September 30, 2023
Original Targets’s carve-out consolidated financial statements have been prepared in accordance CDN currency and is converted to USD to conform with the Company expected reporting currency as follows:
| As of September 30, 2023 | | IFRS
before conversion
(in CDN) | | | USD to CDN
Exchange Rate
as of March 31,
2023 | | | IFRS
after
conversion
to (in USD) | |
| ASSETS | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Current assets: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Cash | | $ | 818,609 | | | | 1.352 | | | $ | 605,480 | |
| Restricted Cash | | | 40,000 | | | | 1.352 | | | | 29,586 | |
| Other receivables | | | 25,400 | | | | 1.352 | | | | 18,787 | |
| Prepaid expenses | | | 20,982 | | | | 1.352 | | | | 15,519 | |
| Total current assets | | | 904,991 | | | | | | | | 669,372 | |
| Total assets | | $ | 904,991 | | | | | | | $ | 669,372 | |
| LIABILITIES | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Current liabilities: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Accounts payable and accrued liabilities | | $ | 1,237,068 | | | | 1.352 | | | $ | 914,990 | |
| Loans form affiliates | | | 996,495 | | | | 1.352 | | | | 737,053 | |
| Total current liabilities | | | 2,233,563 | | | | | | | | 1,652,043 | |
| Total liabilities | | | 2,233,563 | | | | | | | | 1,652,043 | |
| EQUITY | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net Parent investment | | | (1,328,572 | ) | | | | | | | (982,671 | ) |
| Total shareholders’ deficit | | | (1,328,572 | ) | | | | | | | (982,671 | ) |
| Total liabilities and equity | | $ | 904,991 | | | | | | | $ | 669,372 | |
| For the Six Months Ended September 30, 2023 | | IFRS
before conversion
(in CDN) | | | USD to CDN
Average
Exchange Rate
for the six months
ended September 30,
2023 | | | IFRS
after
conversion
to (USD) | |
| Operating expenses | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Sales and marketing | | $ | (2,848 | ) | | | 1.3421 | | | $ | (2,122 | ) |
| Research and development | | | (1,062,212 | ) | | | 1. 3421 | | | | (791,439 | ) |
| General and administrative | | | (114,845 | ) | | | 1. 3421 | | | | (85,569 | ) |
| Professional fees and consulting fees | | | (784,375 | ) | | | 1. 3421 | | | | (582,427 | ) |
| Foreign exchange gain (loss) | | | (154,927 | ) | | | 1. 3421 | | | | (115,434 | ) |
| Interest income | | | (36,805 | ) | | | 1. 3421 | | | | (27,423 | ) |
| Net loss | | $ | (2,156,011 | ) | | | | | | $ | (1,606,414 | ) |
| For the Year Ended March 31, 2023 | | IFRS
before conversion
(in CDN) | | | USD to CDN
Average
Exchange Rate
for the year
ended March 31,
2023 | | | IFRS
after
conversion
to (USD) | |
| Operating expenses | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Sales and marketing | | $ | (9,292 | ) | | | 1.32297 | | | $ | (7,024 | ) |
| Research and development | | | (2,126,762 | ) | | | 1.32297 | | | | (1,607,565 | ) |
| General and administrative | | | (484,382 | ) | | | 1.32297 | | | | (366,132 | ) |
| Professional fees and consulting fees | | | (1,655,663 | ) | | | 1.32297 | | | | (1,251,474 | ) |
| Foreign exchange gain (loss) | | | 35,574 | | | | 1.32297 | | | | 26,890 | |
| Interest income | | | 2,054 | | | | 1.32297 | | | | 1,553 | |
| Net loss | | $ | (4,238,471 | ) | | | | | | $ | (3,203,752 | ) |
Note 5 - Adjustments to Unaudited Pro Forma Condensed Combined Balance Sheet as of September 30, 2023
The pro forma notes and adjustments, based on preliminary estimates that could change materially as additional information is obtained, are as follows:
(A) Reflects the liquidation and reclassification of $1.35 million of funds held in the Trust Account to cash and bank balances that becomes available following the Business Combination.
(B) Represents preliminary estimated transaction costs expected to be incurred by NCAC and Original Target Group of approximately $6.92 million for legal, accounting and printing fees incurred as part of the Business Combination.
For the NCAC transaction costs, $0.78 million were previously accrued and the payable has been paid at closing and reflected as of the pro forma balance sheet date. An amount of $0.54 million is reflected as an adjustment to accumulated losses as these are attributed to the listing cost. In additional 446,000 Original Target shares were issued to service provided with a transaction price value of $10 per share for a total of $4.46 million as a Transaction Fee which were allocated to additional paid-in-capital as these are attributed to Business Combination.
For the Original Target Group transaction costs, $0.29 million of these fees have been paid at closing and $0.17 million have been accrued as of the pro forma balance sheet date. An amount of $0.93 million is reflected as an adjustment to accumulated losses as these are attributed to the listing cost. The remaining amount of $0.99 million is included as an adjustment to additional paid-in capital as these are attributed to Business Combination. Due to cash limitation $1.46 million of transaction cost were included as due and payable.
(C) Represents the exchange of outstanding Original Target Group shares into 5,000,000 the Company’s Common Shares at par value of $0.0001 per share upon the Business Combination.
(D) Represents the elimination of NCAC’s historical accumulated losses after recording the transaction costs to be incurred by NCAC as described in (B) above, the waiver of the underwriting fee described in (I) below and the derecognized warrant liability as described in (O) below.
(E) Reflects the transfer of the 119,659 NCAC shares which did not redeem into permanent equity and shares of the Company.
(F) Represents the preliminary estimated expense recognized, in accordance with IFRS 2, for the excess of the deemed costs of the shares issued by Original Target Group and the fair value of SPAC’s identifiable net assets at the date of the Business Combination, resulting in a $51.37 million increase to accumulated loss. The fair value of shares issued was estimated based on a market price of $10.00 per share (based on the transaction value) and the fair value of the warrants at $0.045 (NCAC as of January 25, 2024 closing date).
| | | Actual Redemption | |
| NCAC shareholders | | Shares | | | Dollars | |
| Public warrants | | | 12,500,000 | | | | | |
| Private Placement warrants | | | 570,000 | | | | | |
| Fair value of shares to be issued to NCAC shareholders | | | | | | $ | 594,685 | |
| Public shareholders | | | 119,659 | | | | | |
| Private Placement Shares | | | 1,140,000 | | | | | |
| Founder shareholders | | | 3,535,000 | | | | | |
| Fair value of shares to be issued to NCAC shareholders | | | | | | | 64,946,590 | |
| Fair value of shares and warrants to be issued to NCAC shareholders | | | | | | | (65,541,275 | ) |
| Net assets of SPAC as of March 31, 2023 | | | | | | | (16,068,717 | ) |
| Less: January 2024 redemptions | | | | | | | (11,493,744 | ) |
| Less: SPAC warrant liabilities | | | | | | | 392,100 | |
| Add: Release of redeemable Class A shares | | | | | | | 12,571,858 | |
| Add: Release of Underwriting fee payable | | | | | | | 11,600,000 | |
| Add: Interest earned in Trust Account | | | | | | | 172,844 | |
| Less: Effect of maximum redemption of SPAC shares | | | | | | | — | |
| Adjusted net assets of SPAC as of September 30, 2023 | | | | | | | (2,825,659 | ) |
| Difference – being IFRS 2 charge for listing services | | | | | | $ | 68,366,934 | |
(G) Reflects the conversion of Class B common stock into the Company’s Common stock on a one-for-one basis.
(H) Reflect repayment of $50,000 to the NCAC Sponsor loan at the closing of the Business Combination the remaining portion will be repaid after the closing of the Business Combination. Terms of repayment to be determined.
(I) Reflects the underwriter agreeing to the settlement of deferred underwriting commissions upon the closing of the Business Combination. The underwriter has agreed to settle the fee of $13.1 million by waiving 11.60 million of the fee and the receipt of 150,000 the Company’s Common Shares at $10 per share. The waived portion of the fee reverses the original entry which was applied to the components of the unit issued at NCAC IPO. As a result, the reversal of the transaction was applied to Class A ordinary shares with the related accretion to redemption value effecting accumulated deficit. The transaction cost allocated to the warrants was applied to earnings as such the net impact of the waived fee of $11.60 million was to reverse the accumulated earning impact of both components included in the unit.
(J) Reflects the proceeds from the proposed Financing Arrangement under the Subscription Agreement where $2,500,000 in proceeds was received at closing in exchange for a Convertible Note and 1,300,000 the Company’s shares transferred from NCAC sponsor. As a result of the ASC 480 Freestanding Instrument Assessment performed at the onset of the memorandum, the Company has determined that the Subscription Agreement is deemed to be representative of TWO freestanding financial instruments, the Note and the Structured Shares. The Structures Shares are deemed to be representative of a freestanding financial instrument issued in a bundled transaction with the Note. The Structured Shares to be issued as part of the bundled transaction are classified and accounted for as equity; therefore, the proceeds are required to be allocated based on the relative fair values of the base instrument (i.e., Note) and the Structured Shares in accordance with the guidance in ASC 470, Debt. As such a debt discount of $2.64 million was recognized against the Note represented by $0.63 million of OID and $2.16 million related to the 1,300,000 Structured shares issued. The accounting for this transaction is preliminary and is subject to change.
(K) Reflects the redemption of 993,362 NCAC Public Shares for a cash payment of $11.49 million, or $11.57 per share on January 18 and 22, 2024 to approve the business combination and extend the date by which NCAC had to close on a business combination from January 22, 2024 to February 22, 2024.
(L) Reflect the borrowings from NCAC Sponsor of $100,172 in order to fund extension payments into the Trust Account.
(M) Reflects the interest earned in the NCAC’s trust subsequent to September 30, 2023 through the January 22, 2024 extension payment date.
(N) Reflects the removal of cash held by a subsidiary of Original Target that will not carry on to the Company.
(O) To derecognize warrant liability that is not being assumed by the Company, but rather re-issued as part of the consideration payable on closing of the RTO.
(P) To recognize the value of warrants re-issued by the Company on closing of the RTO transaction based valued based on the fair value of the NCAC public warrants as of January 25, 2024.
Adjustments to Unaudited Pro Forma Condensed Combined Statement of Operations for the Year Ended March 31, 2023 and for the Six Months ended September 30, 2023
The pro forma notes and adjustments, based on preliminary estimates that could change materially as additional information is obtained, are as follows:
(AA) Reflects the elimination of interest income generated from the investments held in the Trust Account.
(BB) Represents the elimination of administrative service fees that will cease to be paid upon closing of the business combination.
(CC) Represents $68.37 million of expense recognized, in accordance with IFRS 2, for the difference between the deemed costs of the shares issued by Original Target Group and the fair value of NCAC’s identifiable net assets, as described in (F) above and $1.46 million of other cost incurred as described in (B) above. This cost is a nonrecurring item and only reflected in the earlier period presented for the year ended March 31, 2023.
Note 6 - Net Earnings (Loss) per Share
Represents the earnings (loss) per share calculated using the historical weighted average shares outstanding, and the issuance of additional shares in connection with the Business Combination, assuming the shares were outstanding since April 1, 2022. As the Business Combination is being reflected as if it had occurred at the beginning of the period presented, the calculation of weighted average shares outstanding for basic and diluted earnings (loss) per share assumes that the shares issued in connection with the Business Combination have been outstanding for the entire period presented. If the number of Public Shares described under the Maximum Redemption Scenario are redeemed, this calculation is retroactively adjusted to eliminate such shares for the entire period.
The following table sets out the share ownership of the Company following Closing on a pro forma:
| | | Actual
Redemption | |
| Weighted average shares outstanding – basic and diluted | | | | |
| Rollover equity shares of Original Target Group shareholders | | | 5,000,000 | |
| NCAC Public Shareholders | | | 119,659 | |
| NCAC Sponsor Private Placement | | | 1,140,000 | |
| NCAC Sponsor and Founder shareholders(1) | | | 3,535,000 | |
| PIPE Investors | | | 2,000,000 | |
| Third Party shareholders | | | 596,000 | |
| Total | | | 13,390,659 | |
| For the Six Months Ended September 30, 2023 | | Actual
Redemptions | |
| Pro forma net loss | | $ | (2,615,556 | ) |
| Weighted average shares of common stock outstanding – basic and diluted(2) | | | 13,390,659 | |
| Net loss per share – basic and diluted | | $ | (0.20 | ) |
| Excluded securities:(3) | | | | |
| Public Warrants | | | 12,500,000 | |
| Private Placement Warrants | | | 570,000 | |
| Year Ended March 31, 2023 | | Actual
Redemptions | |
| Pro forma net loss | | $ | (68,355,218 | ) |
| Weighted average shares of common stock outstanding – basic and diluted(2) | | | 13,390,659 | |
| Net loss per share – basic and diluted | | $ | (5.10 | ) |
| Excluded securities:(3) | | | | |
| Public Warrants | | | 12,500,000 | |
| Private Placement Warrants | | | 570,000 | |
| (1) | The 1,300,000 Backstop Shares were transferred by the NCAC Sponsor and issued to financing investor. |
| (2) | Assumes all issued and outstanding shares were outstanding for the entirety of the year. |
| (3) | The potentially dilutive outstanding securities were excluded from the computation of pro forma net loss per share, basic and diluted, because their effect would have been anti-dilutive. |
BUSINESS
The following terms, as used in this section shall have the following meanings:
| | AjD | | | Adjustment Disorder |
| | PEX010 | | | Capsule containing 25mg naturally sourced psilocybin |
| | PAP | | | Psilocybin Assisted Psychotherapy |
| | API | | | Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient |
Overview
We are a life science biotechnology company that, through our operating subsidiary, Biomed II, is developing natural psilocybin products for the healing of psychological trauma and its mental health consequences in the context of palliative care. We have commenced the clinical trial process to evaluate the safety and efficacy of its product candidates.
We strive to set the global standard for excellence and consistency in drug development using nature-based psilocybin products. Psyence Therapeutics’ priority is developing pharmaceutical grade psilocybin to help heal psychological trauma and the diagnosable disorders that can result therefrom, including AjD, anxiety, depression, post-traumatic stress disorder (“PTSD”), and grief and bereavement, especially in the context of palliative care. Our focus includes therapeutic protocols for medical and scientific research including observational studies.
Our lead product candidate is PEX010, a capsule containing 25mg naturally sourced psilocybin and which is being used in our Phase IIb Study. Psyence has entered into two Filament Licensing Agreements with Filament, a Canadian company that produces natural psilocybin capsules and the proprietary owner of PEX010, for the licensing of PEX010 with respect to Psyence’s designated fields of use: anxiety and depression, including associated ailments, such as PTSD, stress, grief, and adjustment disorder within the context of palliative care. See “— Licensing and commercialization of PEX010” below.
We have contracted iNGENū, a CRO in Australia that specializes in the study of psychedelics, to conduct a Phase IIb double-blind, randomized, low-dose controlled clinical trial to assess the efficacy and safety of PEX010 in psilocybin-assisted psychotherapy for the treatment of AjD due to incurable cancer. Outsourcing the study to a CRO assists the company in operating in a more capital efficient manner without the overhead of handling in-house.
Corporate Structure
Prior to the completion of the Business Combination Psyence was the therapeutics division of Psyence Group, Inc., a life science biotechnology company listed on the Canadian Securities Exchange (CSE:PSYG), with a focus on natural psychedelics. We refer to Parent and its subsidiaries and affiliates prior to the consummation of the Business Combination as the “Psyence Group.”
The Psyence Group was created through various corporate transactions, including a prior business combination of Mindhealth Corp. with Cardinal Capital Partners Inc., a public company, in January 2021, resulting in Parent’s public listing in Canada. MindHealth Biomed Corp. (“MindHealth”) was a private corporation incorporated under the laws of British Columbia on May 21, 2020. Mind Health (Pty) Ltd (“MindHealth Lesotho”) is a private entity incorporated under the laws of the Kingdom of Lesotho, which in May 2020, was granted permission by the Minister of Health (Lesotho) to import, cultivate, produce, manufacture and export psilocybin mushrooms. The governmentally licensed commercial psilocybin cultivation and production facilities operated by MindHealth Lesotho under the name “Psyence Production” are situated in the Kingdom of Lesotho. On May 22, 2020, MindHealth Lesotho became a subsidiary of MindHealth.
Psyence Group Overview
The Psyence Group has three key divisions: Psyence Therapeutics, Psyence Function and Psyence Production. The Psyence Group has received independent local legal opinions during the latter half of the 2021 calendar year in Canada, United Kingdom and Lesotho confirming the lawfulness of the Psyence Group’s activities in such jurisdictions, as well as its compliance with material legal, regulatory and governmental developments as they pertain to and affect the Psyence Group’s operations. The Psyence Group’s operations are conducted in compliance with local laws where such activities are permissible and either (a) do not require any specific legal or regulatory approvals, or (b) the Psyence Group has obtained all necessary legal and/or regulatory approvals.
Psyence Therapeutics
Psyence Therapeutics strives to set the global standard for excellence and consistency in drug development using nature-based psilocybin products. Psyence Therapeutics’ priority is developing pharmaceutical grade psilocybin to help heal psychological trauma and the diagnosable disorders that can result therefrom, including AjD, anxiety, depression, post-traumatic stress disorder (“PTSD”) , and grief and bereavement, especially in the context of palliative care. Our focus includes therapeutic protocols for medical and scientific research including observational studies.
Psyence Therapeutics has contracted, iNGENū Pty Ltd, a contract research organization (“CRO”) in Australia that specializes in the study of psychedelics, to conduct a Phase IIb double-blind, randomized, low-dose controlled clinical trial to assess the efficacy and safety of PEX010 in psilocybin-assisted psychotherapy for the treatment of AjD due to incurable cancer. Outsourcing the study to a CRO assists the company in operating in a more capital efficient manner without the overhead of handling in-house.
Pursuant to the Business Combination, the Psyence therapeutics business was separated from the Psyence Group and became a wholly-owned subsidiary of the Company, while the other two divisions of the Psyence Group (Psyence Production and Psyence Function) remained under the Psyence Group. We intend to utilize the funds raised in the Business Combination to provide us with the capital to advance natural psilocybin into a Phase IIb clinical trial study to be conducted under an approved protocol in Australia. The Phase IIb Study, along with its associated assets, contracts and intellectual property constitute the business assets being held by Psyence following the Business Combination.
Psyence Biomedical conducts its operations through its subsidiaries based in Ontario and Australia and also owns a subsidiary in the Cayman Islands, as listed below:
| Name | | Country of Incorporation and Place of Business | | Proportion
of
Ordinary
Shares
Held by
Psyence Biomedical Ltd. | |
| Psyence Biomed II Corp | | Ontario, Canada | | | 100 | % |
| Psyence Australia Pty Ltd | | Australia | | | Indirect 100 | % |
| Newcourt Acquisition Corp | | Cayman Islands | | | Indirect 100 | % |
The diagram below depicts a simplified version of Psyence immediately following the consummation of the Business Combination.

Palliative Care Clinical Trial
On January 9, 2023, Psyence and iNGENū signed a letter of intent to further develop Psyence’s licensed natural psilocybin drug product, starting with a Phase IIb Study in order to lead a pre-IND meeting with the FDA. The product to be used in this Phase IIb Study will be the proprietary botanical drug candidate PEX010 (25mg), which Psyence sources from Filament. The planned randomized double-blind study will evaluate the use of psilocybin-assisted psychotherapy versus psychotherapy alone and will test 84 patients utilizing the HAM A scale as the primary endpoint, which is an FDA validated endpoint, and safety data will be collected throughout the study.
For safety, there are no specific endpoints as all safety findings are captured as adverse events. The primary and secondary efficacy endpoints are all established in the protocol before it is reviewed and approved by the Ethics Committee before the study can start.
The HAM-A is a rating scale developed to measure the severity of anxiety symptoms and is widely used in both clinical and research settings. The scale consists of 14 items, each defined by a series of symptoms, and measures both psychic anxiety (mental agitation and psychological distress) and somatic anxiety (physical complaints related to anxiety). During the Phase II Study, the HAM-A scale will be used to measure change in anxiety levels over time as the primary endpoint.
The 84-patient Phase IIb Study being conducted by the CRO, iNGENū, in Australia is the one that has been referred to in discussions with the FDA in the pre-IND process, which is in the late planning stage, and estimated to commence enrollment in the first half of 2024.
The estimated costs of this Phase IIb study were initially $5,575,000 made on the basis of milestones completed. Included in this original estimate were costs for 75 participants; an end of Phase II meeting preparation and attendance after the completion of the Phase IIb study with the FDA as well as psychotherapy training, psychotherapy sessions and therapist fees for participants. Subsequently, the Phase II Study was increased to 84 patients, and we anticipate the estimated cost of this study to be increased by approximately 5%.
On September 15, 2022, we received full approval of a study (the “UK Trial”) in the United Kingdom from the UK Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (“MHRA”) using natural psilocybin in the field of palliative care with oncology patients. For this study, we had partnered with Clerkenwell Clinics Limited (“Clerkenwell Health”), which would have been responsible for jointly designing and delivering the UK Trial. Following such approval, we opted to forego proceeding with the UK Trial in order to pursue the opportunity to conduct the Phase IIb Study in Australia, as Psyence could benefit from the Australian Federal Government’s Research & Development tax incentive program, which could provide up to a 43.5% rebate on Psyence’s R&D expenses in Australia, making it a more cost-effective endeavor. In addition, the Phase IIb Study adds a dose-finding arm, which allows us to accelerate our development strategy, seeking input from the FDA with our pre-IND application. If the outcome of the Phase II Study is positive, we believe we may be able to proceed directly to a Phase III trial in the United States, subject to FDA review and the opening of an IND; however, there is no guarantee that the FDA will accept data from trials conducted outside of the United States.
Licensing and commercialization of PEX010
In April 2022, Psyence entered into the Research IP Agreement with Filament for the licensing of PEX010 and its associated intellectual property, as well as for the supply of PEX010 for the specific intention of the clinical development of the product, and ultimately, for the marketing authorization for PEX010’s use in palliative care patients. Pursuant to the Research IP Agreement, Filament grants to Psyence an irrevocable, royalty free, worldwide license (with the right to sub-license, subject to certain restrictions) to use and distribute PEX010 and certain related intellectual property (such as delivery mechanism, preparation methods and know-how) solely for use in connection with pre-clinical and clinical studies and trials to be conducted in Canada, the UK and world-wide in the treatment of anxiety and depression, including associated ailments, such as PTSD, stress, grief, and adjustment disorder within the context of palliative care. This license is granted in respect of the clinical trial phase of Psyence’s activities, specifically phase II clinical trials. The license is granted on an exclusive basis solely within the territory of the UK with respect to the designated fields of use, and Psyence has a right of first refusal to extend its exclusive license beyond the territory of the UK. Psyence does not have any rights to use PEX010 for any profit-making or commercial purposes under the Research IP Agreement. Any results of testing, research, conduct of and any information derived from the clinical studies and trials using PEX010 shall be the sole property of Psyence. Under the Research IP Agreement, Filament is entitled to receive milestone payments of up to CAD$250,000 in aggregate based on four distinct phase II clinical trial milestones to be achieved by Psyence. Should Psyence pursue a second or multiple indications, such aggregate milestone payments will increase accordingly. For the six months ended September 30, 2023, Psyence incurred zero costs under the Research IP Agreement related to milestone payments, which was account for as research and development costs.
In addition to the licensing rights described above, per the terms of the Research IP Agreement, Filament has undertaken to support Psyence’s clinical trial efforts through the supply of the required quantities of PEX010 to Psyence, for no additional charge, based on Psyence’s good faith forecasts of its needs. Filament will also create and provide such information, assistance and support for the execution of the dossiers, IMBP and other documents required to conduct Psyence’s clinical trials in accordance with the trial schedules. The license term is 5 years, expiring in April 2027, however the license may be terminated early (a) by either party upon notice to the other party, where Psyence notifies Filament in writing that all of its clinical trials have been completed or abandoned; (b) by a party upon notice to the other party, if the other party becomes subject to bankruptcy proceedings; (c) by a party if the other party commits a breach of a material term of the Research IP Agreement and fails to remedy such breach; or (d) by a party upon notice to the other party, if the other party has a licence, permit or approval revoked by competent authorities which compromises its ability to grant the licenses contemplated in the Research IP Agreement or its ability to perform under the Research IP Agreement.
In December 2022, Psyence entered into a royalty-bearing, binding term sheet for the commercial licensing of intellectual property (with the right to sub-license) from Filament, which is subject to the terms of a definitive license agreement, and grants Psyence the worldwide right to commercialize PEX010 within the designated fields of use, being anxiety and depression, including associated ailments, such as PTSD, stress, grief, and adjustment disorder within the context of palliative care. The license is granted on an exclusive basis within the UK, the European Union and the United States, and Psyence has a right of first refusal to extend its exclusive license beyond such territories, including Australia. Such commercial licensing rights apply in respect of phase III clinical trials, as well as the commercialization phase of the development of PEX010. Upon the entry of a generic product for sale in a country, the parties shall, in good faith, re-negotiate (on a country-by-country basis) the royalty rate or determine a termination date for the definitive license agreement and the royalty payments.
Under the Commercial IP Term Sheet, Filament is entitled to receive milestone payments of up to CAD$3 million over the course of Psyence’s clinical development and marketing authorizations achieved by Psyence, however should Psyence pursue a second or multiple indications, such aggregate milestone payments will increase accordingly. The second of these milestone payments is based on the size of each jurisdiction in which marketing authorization is obtained and is subject to an overall cap. Filament will also receive a royalty of 10% of future net sales, as well as an annual exclusivity fee of CDN$250,000 per year (commencing on the date of Psyence’s Phase II clinical trial study report), which will be creditable against these future royalty fees.
In addition to the licensing rights described above, Filament has undertaken to support Psyence’s clinical trial efforts through the exclusive supply of the required quantities of PEX010 to Psyence based on Psyence’s good faith forecasts of its needs. Pursuant to the Commercial IP Term Sheet, Filament agrees to be the exclusive supplier to Psyence of any and all drug candidates within the designated fields of use and agrees not to supply PEX010 to any other clients pursuing a target indication within the designated fields of use in the territories in which Psyence has licensing exclusivity, subject to certain conditions. Filament will supply PEX010 to Psyence for no additional charge, subject to certain shared costs agreed upon on a case-by-case basis between the parties. Psyence agrees not to conduct research, development or analysis activities and agrees not to develop any products other than PEX010 within the designated fields of use, and Psyence and its representatives shall not solicit or engage in discussions with another supplier for the supply of drug candidates within the designated fields of use. Psyence has agreed to make clinical trial safety and efficacy data available to Filament for internal business use (among other things). Should Filament wish to use such data to pursue the commercialization of PEX010 outside of Psyence’s exclusive territories, Filament shall pay Psyence a percentage of future net sales in the low double digits, for a period no more than 8 (eight) years.
The term of Commercial IP Term Sheet expires on a country-by-country basis, based on the entry of a generic product into the affected market. The license may be terminated early (a) by a party if the other party commits a breach of a material term of or warranty in this agreement and fails to remedy such breach; (b) by a party upon notice to the other party, if the other party becomes subject to bankruptcy proceedings; or (c) by Psyence upon 60 days’ notice to Filament.
Psyence has not performed any pre-clinical or clinical trials on PEX010. PEX010 is owned and has undergone clinical trials directed by Filament. PEX010 has received regulatory approval to proceed into Phase I and II clinical trials in several jurisdictions worldwide. The FDA, Health Canada, MHRA, and the EMA have reviewed the chemistry, manufacturing, and controls and quality information of PEX010 through its associated filed DMFs/ IMPDs. The DMF for PEX010 is also on file with the Therapeutic Goods Administration (the “TGA”) in Australia. In addition to clinical trials, PEX010 is also already being administered to real-world patients via the Health Canada Special Access Program (“SAP”). Through the SAP, PEX010 is being prescribed for end of life distress as well as Major Depressive Disorder.
In addition to clinical trial exposures, PEX010 is also being administered to real-world patients via the Health Canada Special Access Program (SAP). Through the SAP, PEX010 is being prescribed for End of life Distress as well as Major Depressive Disorder. As of June 23, 2023, 79 doses of PEX010 have been administered to 67 patients. Despite the serious condition of many of these patients, no serious adverse events or unexpected adverse events have been reported in any SAP administration.
Relationships with Third Parties
Psyence’s UK-based research and development was to be conducted by way of its licensed partner, and its CRO partner, Clerkenwell Health, in the UK. Psyence’s Australian-based research and development will be conducted by its CRO partner, iNGENū, in Australia. As stated above, Filament’s PEX010 will serve as the product candidate under investigation during the Phase IIb Study.
Psyence’s R&D capabilities
Psyence’s CEO (Dr. Neil Maresky) and Medical Director (Dr. Clive Ward-Able) are both medically trained physicians with close to 60 years of experience between them within the pharmaceutical industry related to R&D and the commercialization of new products. This experience provides the foundations for an excellent understanding of the clinical development, regulatory and commercialization needs of various pharmaceutical markets to design the optimal development program.
Psyence plans on working with various CROs and consultancy agencies to prepare and operationalize their protocols for the various phases of the clinical development program.
Intellectual Property
Psyence engages a team of lawyers and advisors that helps strengthen the protection of its IP assets. As psilocybin is a naturally occurring substance, it cannot be patented. However, patents may be granted on formulations, methods of use, compositions of matter and formulation processes, provided that such items are novel, non-obvious and have significant improvements to existing inventions.
Psyence’s IP strategy is built around:
| · | Establishing and maintaining a competitive advantage on formulation, dosage and administration of psilocybin, as well as psychedelic-assisted therapy modules for palliative care indications; and |
| · | Ensuring business flexibility through directing its research in areas which maintain freedom to operate (relative to third party patent positions) and secures the most favorable commercial terms in agreements with other companies in collaborating on later research, and the commercialization of Psyence’s IP assets. |
Psyence has a specialist, experienced in-house team focused on delivery of this strategy, including internationally recognized patent professionals working directly with Psyence’s board on these issues.
Specific actions are being taken towards delivery of this strategy include:
| · | Ongoing patent landscaping on the competitor patent landscape. Psyence has completed a patent landscaping review and has ongoing patent watching searches in place on the back of this to identify any new filings made in this space; |
| · | Actively considering potential patent filings, with the intention to identify, file, prosecute and eventually maintain Psyence’s patent portfolio. This patent portfolio is intended to be built out incrementally across the proprietary formulation and treatment technologies that are under development by Psyence; |
| · | Active management of key know-how and trade secrets (in order to supplement the patent portfolio); and |
| · | Thoughtful negotiation of in-licensing arrangements of third-party IP rights that can enhance or accelerate the building of our business. |
Psyence does not currently hold any patents. PEX010 is protected by a portfolio of patents comprising five patent families. A patent family is a group of patent applications covering the same or similar technical content, or a group of patents registered in several countries to protect an invention. This occurs when a patent application is made in one country and then obtains priority. This priority is then extended to numerous countries. In other words, applications in a family are related to each other through priority claims. Filament holds a worldwide, exclusive, and sub-licensable license from its wholly-owned subsidiary, Psilo, for the intellectual property portfolio relating to PEX010, and Psilo is responsible for maintaining and defending the intellectual property currently being sub-licensed to Psyence under the Filament Licensing Agreements, and which is relevant for use in Psyence’s proposed Australian palliative care clinical trial. Below is a summary of the five patent families that are relevant to Psyence’s licenses granted by Filament.
| · | Filament patent family 1 is focused on extraction methods, and consists of eleven (11) total granted patents, of which six (6) were issued by the Canadian Intellectual Property Office (“CIPO”) and five (5) were issued by the United States Patent and Trademark Office (“USPTO”), as well as thirteen (13) pending patent applications. Issued patents in this family are scheduled to expire twenty years from the earliest nonprovisional filing date, which in this case indicates an expiry date in July of 2040. |
| · | Filament patent family 2 is focused on purification processes, and consists of one (1) granted Canadian patent as well as five (5) patent applications. Issued patents in this family are scheduled to expire twenty years from the earliest nonprovisional filing date, which in this case indicates an expiry date in October of 2040. |
| · | Filament patent family 3 is focused on the standardization processes, and consists of one (1) allowed patent application and five (5) pending patent applications. Issued patents in this family are scheduled to expire twenty years from the earliest nonprovisional filing date, which in this case indicates an expiry date in December of 2040. |
| · | Filament patent family 4 is focused on chemical processes for stabilizing psychoactive alkaloids. This family consists of two (2) granted patents, of which one was issued by the CIPO and one was issued by the USPTO, as well as eleven (11) pending applications. Issued patents in this family are scheduled to expire twenty years from the earliest nonprovisional filing date, which in this case indicates an expiry date in December of 2040. |
| · | Filament patent family 5 is focused on methods and formulations for delivering psychoactive alkaloids. This family consists of six granted patents, of which five (5) were issued by the CIPO and one (1) was issued by the USPTO, as well as four pending patent applications. Issued patents in this family are scheduled to expire twenty years from the earliest nonprovisional filing date, which in this case indicates an expiry date in March of 2041. |
A summary table of Filament’s patent portfolio relevant to Psyence’s licenses is provided below:
| · @ | | | Internal
Reference
Number | | | Family | | | Patent
Number | | | Status | | | Title | | | Jurisdiction* | | | Filing Date/
Appl. No. | | | Issue Date | |
| 1 | | | PSU001a-AUNE | | | · 1 | | | N/A | | | Pending | | | Extraction of psychoactive compounds from psychedelic fungus | | | · AU | | | 16-Dec-22; 2021291583 | | | N/A | |
| 2 | | | PSU001a-BRNE | | | · 1 | | | N/A | | | Pending | | | Extraction of psychoactive compounds from psychedelic fungus | | | · BR | | | 16-Jul-21; 112022025777 | | | N/A | |
| 3 | | | PSU001a-CADIV1 | | | · 1 | | | 3123908 | | | Issued | | | Ethanol extraction of psychoactive compounds from psilocybin fungus | | | · CA | | | 29-Jul-20
(exam requested
5-Jul-21); 3123908 | | | 22-Mar-22 | |
| 4 | | | PSU001a-CADIV2 | | | · 1 | | | 3124367 | | | Issued | | | Aqueous extraction of psychoactive compounds from psilocybin fungus | | | · CA | | | 29-Jul-20
(exam requested
9-Jul-21); 3124367 | | | 26-Apr-22 | |
| 5 | | | PSU001a-CANE | | | · 1 | | | 3161623 | | | Issued | | | Extraction of psychoactive compounds from psychedelic fungus | | | · CA | | | 16-Jun-21
(exam requested
13-May-22); 3161623 | | | 4-Apr-23 | |
| 6 | | | PSU001a-CANP | | | · 1 | | | 3088384 | | | Issued | | | Extraction of psychoactive compounds from psilocybin fungus | | | · CA | | | 29-Jul-20;
3088384 | | | 3-Aug-21 | |
| 7 | | | PSU001a-EPNE | | | · 1 | | | N/A | | | Pending | | | Extraction of psychoactive compounds from psychedelic fungus | | | · EP | | | 6-Jan-23; EP20210827107 | | | N/A | |
| 8 | | | PSU001a-ILNE | | | · 1 | | | N/A | | | Pending | | | Extraction of psychoactive compounds from psychedelic fungus | | | · IL | | | 30-Oct-22;
297791 | | | N/A | |
| 9 | | | PSU001a-JMPC | | | · 1 | | | N/A | | | Pending | | | Extraction of psychoactive compounds from psilocybin fungus | | | · JM | | | 29-Sep-21;
18/2/000123 | | | N/A | |
| 10 | | | PSU001a-MXNE | | | · 1 | | | N/A | | | Pending | | | Extraction of psychoactive compounds from psychedelic fungus | | | · MX | | | 16-Dec-22;
MX/a/2022/016531 | | | N/A | |
| 11 | | | PSU001a-USCON1 | | | · 1 | | | US11510952 | | | Issued | | | Ethanol extraction of psychoactive compounds from psilocybin fungus | | | · US | | | 28-Jan-22;
17587731 | | | 29-Nov-22; | |
| 12 | | | PSU001a-USCON2 | | | · 1 | | | US11571450 | | | Issued | | | Aqueous extraction of psychoactive compounds from psilocybin fungus | | | · US | | | 17-Mar-22;
17697798 | | | 7-Feb-23; | |
| 13 | | | PSU001a-USPC | | | · 1 | | | US11382942 | | | Issued | | | Extraction of psychoactive compounds from psilocybin fungus | | | · US | | | 17-Jun-21;
17351149 | | | 12-Jul-22; | |
| 14 | | | PSU001b-AUNE | | | · 1 | | | N/A | | | Pending | | | Methanol-based extraction of psychoactive alkaloids from fungus | | | · AU | | | 16-Dec-22; 2021291726 | | | N/A | |
| 15 | | | PSU001b-BRNE | | | · 1 | | | N/A | | | Pending | | | Methanol-based extraction of psychoactive alkaloids from fungus | | | · BR | | | 16-Dec-22; CA2021050823; BR112022025778 | | | N/A | |
| 16 | | | PSU001b-CADIV1 | | | · 1 | | | N/A | | | Pending | | | Hydro-methanol extraction of psychoactive compounds from fungus | | | · CA | | | 16-Jun-21
(exam requested
28-Apr-23); 3198238 | | | N/A | |
| 17 | | | PSU001b-CANE | | | · 1 | | | 3163795 | | | Issued | | | Methanol-based extraction of psychoactive alkaloids from fungus | | | · CA | | | 13-Jun-23
(exam requested
3-Jun-22); 3163795 | | | 13-Jun-23 | |
| 18 | | | PSU001b-CANP | | | · 1 | | | 3089455 | | | Issued | | | Methanol-based extraction of psychoactive compounds from fungus | | | · CA | | | 7-Aug-20
(exam requested
5-Jul-21); 3089455 | | | 5-Jul-22 | |
| 19 | | | PSU001b-EPNE | | | · 1 | | | N/A | | | Pending | | | Methanol-based extraction of psychoactive alkaloids from fungus | | | · EP | | | 6-Jan-23; EP20210825822 | | | N/A | |
| · @ | | | Internal
Reference
Number | | | Family | | | Patent
Number | | | Status | | | Title | | | Jurisdiction* | | | Filing Date/
Appl. No. | | | Issue Date | |
| 20 | | | PSU001b-ILNE | | | · 1 | | | N/A | | | Pending | | | Methanol-based extraction of psychoactive alkaloids from fungus | | | · IL | | | 24-Nov-22; 298561 | | | N/A | |
| 21 | | | PSU001b-MXNE | | | · 1 | | | N/A | | | Pending | | | Methanol-based extraction of psychoactive alkaloids from fungus | | | · MX | | | 16-Dec-22;
MX/a/2022/016530 | | | N/A | |
| 22 | | | PSU001b-USNE | | | · 1 | | | N/A | | | Pending | | | Methanol-based extraction of psychoactive alkaloids from fungus | | | · US | | | 15-Jun-22; 17841323 | | | N/A; | |
| 23 | | | PSU001c-USCON1 | | | · 1 | | | 11642385 | | | Issued | | | Basic extraction of psychoactive compounds from psychoactive organisms | | | · US | | | 23-Mar-22; 17702701 | | | 9-May-23; | |
| 24 | | | PSU001c-USNE | | | · 1 | | | 11331357 | | | Issued | | | Methods and compositions comprising psychoactive compounds from psychoactive organisms | | | · US | | | 15-Jun-21; 17348697 | | | 17-May-22 | |
| 25 | | | PSU002-AUNE | | | · 2 | | | N/A | | | Pending | | | Process for obtaining a purified psychoactive alkaloid solution | | | · AU | | | 5-Dec-22; 2021290454 | | | N/A | |
| 26 | | | PSU002-BRNE | | | · 2 | | | N/A | | | Pending | | | Process for obtaining a purified psychoactive alkaloid solution | | | · BR | | | 16-Dec-22; BR112022025782 | | | N/A | |
| 27 | | | PSU002-CANP | | | · 2 | | | 3097246 | | | Issued | | | Process for obtaining a purified psychoactive alkaloid solution | | | · CA | | | 23-Oct-20 | | | 28-Mar-23 | |
| 28 | | | PSU002-EPNE | | | · 2 | | | N/A | | | Pending | | | Process for obtaining a purified psychoactive alkaloid solution | | | · EP | | | 6-Jan-23; EP20210881426 | | | N/A | |
| 29 | | | PSU002-ILNE | | | · 2 | | | N/A | | | Pending | | | Process for obtaining a purified psychoactive alkaloid solution | | | · IL | | | 25-Dec-22; 299448 | | | N/A | |
| 30 | | | PSU002-MXNE | | | · 2 | | | N/A | | | Pending | | | Process for obtaining a purified psychoactive alkaloid solution | | | MX | | | 13-Apr-23;
MX/a/2023/004350 | | | N/A | |
| 31 | | | PSU003-AUNE | | | · 3 | | | N/A | | | Pending | | | Standardized psychoactive alkaloid extract composition | | | · AU | | | 19-Dec-22; 2022291410 | | | N/A | |
| 32 | | | PSU003-BRNE | | | · 3 | | | N/A | | | Pending | | | Standardized psychoactive alkaloid extract composition | | | · BR | | | 16-Dec-22; CA2021050813; BR112022025780 | | | N/A | |
| 33 | | | PSU003-CANP | | | · 3 | | | N/A | | | Pending | | | Standardized psychoactive alkaloid extract composition | | | · CA | | | 18-Dec-20; 3103707 | | | N/A | |
| 34 | | | PSU003-EPNE | | | · 3 | | | N/A | | | Pending | | | Standardized psychoactive alkaloid extract composition | | | · EP | | | 6-Jan-23; EP20210825817 | | | N/A | |
| 35 | | | PSU003-ILNE | | | · 3 | | | N/A | | | Pending | | | Standardized psychoactive alkaloid extract composition | | | · IL | | | 25-Dec-22; 299449 | | | N/A | |
| 36 | | | PSU003-MXNE | | | · 3 | | | N/A | | | Pending | | | Standardized psychoactive alkaloid extract composition | | | · MX | | | 16-Dec-22;
MX/a/2022/016533 | | | N/A | |
| · @ | | | Internal
Reference
Number | | | Family | | | Patent
Number | | | Status | | | Title | | | Jurisdiction* | | | Filing Date/
Appl. No. | | | Issue Date | |
| 37 | | | PSU004-AUDIV1 | | |
—
4 | | | N/A | | | Pending | | | Dephosphorylation-controlled extraction of phosphorylatable psychoactive alkaloids | | |
—
AU | | | 19-Dec-22; 2022291416 | | | N/A | |
| 38 | | | PSU004-AUDIV2 | | | · 4 | | | N/A | | | Pending | | | Predominantly phosphorylated psychoactive alkaloid extraction using alkali | | | · AU | | | 19-Dec-22; 2022291413 | | | N/A | |
| 39 | | | PSU004-AUDIV3 | | | · 4 | | | N/A | | | Pending | | | Psychoactive alkaloid extraction and composition with controlled dephosphorylation | | | · AU | | | 19-Dec-22; 2022291414 | | | N/A | |
| 40 | | | PSU004-AUNE | | | · 4 | | | N/A | | | Pending | | | Psychoactive alkaloid extraction and composition with inhibited dephosphorylation | | | · AU | | | 19-Dec-22; 2022291411 | | | N/A | |
| 41 | | | PSU004-CADIV1 | | | · 4 | | | N/A | | | Pending | | | Dephosphorylation-controlled extraction of phosphorylatable psychoactive alkaloids | | | · CA | | | 14-Jun-21
(exam requested
25-Jul-22); 3169140 | | | N/A | |
| 42 | | | PSU004-CADIV2 | | | · 4 | | | N/A | | | Pending | | | Predominantly phosphorylated psychoactive alkaloid extraction using alkali | | | · CA | | | 14-Jun-21
(exam requested
7-Sep-22); 3173030 | | | N/A | |
| 43 | | | PSU004-CANE | | | · 4 | | | 3137016 | | | Issued | | | Psychoactive alkaloid extraction and composition with inhibited dephosphorylation | | | · CA | | | 16-Aug-22
(exam requested
29-Oct-21); 3137016 | | | 16-Aug-22 | |
| 44 | | | PSU004-CANP | | | · 4 | | | N/A | | | Pending | | | Psychoactive alkaloid extraction and composition with controlled dephosphorylation | | | · CA | | | 4-Dec-20; 3101765 | | | N/A | |
| 45 | | | PSU004-ILDIV1 | | | · 4 | | | N/A | | | Pending | | | Dephosphorylation-controlled extraction of phosphorylatable psychoactive alkaloids | | | · IL | | | 25-Dec-22; 299450 | | | N/A | |
| 46 | | | PSU004-ILDIV2 | | | · 4 | | | N/A | | | Pending | | | Predominantly phosphorylated psychoactive alkaloid extraction using alkali | | | · IL | | | 25-Dec-22; 299451 | | | N/A | |
| 47 | | | PSU004-ILDIV3 | | | · 4 | | | N/A | | | Pending | | | Psychoactive alkaloid extraction and composition with controlled dephosphorylation | | | · IL | | | 25-Dec-22; 299452 | | | N/A | |
| 48 | | | PSU004-ILNE | | | · 4 | | | N/A | | | Pending | | | Psychoactive alkaloid extraction and composition with inhibited dephosphorylation | | | · IL | | | 25-Dec-22; 299453 | | | N/A | |
| 49 | | | PSU004-USNE | | | · 4 | | | US11298388 | | | Issued | | | Psychoactive alkaloid extraction and composition with controlled dephosphorylation | | | · US | | | 23-Sep-21; 17483601 | | | 12-Apr-22 | |
| — @ | | | Internal
Reference
Number | | | Family | | | Patent
Number | | | Status | | | Title | | | Jurisdiction* | | | Filing Date/
Appl. No. | | | Issue Date | |
| 50 | | | PSU005a-CADIV1 | | | · 5 | | | N/A | | | Pending | | | Process for transmucosal psychoactive alkaloid composition | | | · CA | | | 24-Mar-21
(exam requested
18-Apr-23); 3197443 | | | N/A | |
| 51 | | | PSU005a-CANE | | | · 5 | | | 3152326 | | | Issued | | | Preparation of transmucosal psychoactive alkaloid composition | | | · CA | | | 29-Nov-21
(exam requested
12-Mar-22); 3152326 | | | 9-May-23 | |
| 52 | | | PSU005a-CANP | | | · 5 | | | N/A | | | Pending | | | Transmucosal psychoactive alkaloid composition and preparation thereof | | | · CA | | | 24-Mar-21; 3113240 | | | N/A | |
| 53 | | | PSU005a-USNE | | | · 5 | | | N/A | | | Pending | | | Transmucosal psychoactive alkaloid composition and preparation thereof | | | · US | | | 14-Jun-22; 17840482 | | | N/A | |
| 54 | | | PSU005b-CANP | | | · 5 | | | 3123774 | | | Allowed | | | Transdermal psychoactive alkaloid composition and preparation thereof | | | · CA | | | 1-Jul-21; 3123774 | | | Forecasted
Issue Date:
8-Aug-23 | |
| 55 | | | PSU005b-USNE | | | · 5 | | | N/A | | | Pending | | | Transdermal psychoactive alkaloid composition and preparation thereof | | | · US | | | 28-Jun-23; 18259697 | | | N/A | |
| 56 | | | PSU005c-CANE | | | · 5 | | | 3161491 | | | Allowed | | | Vaporizable psychoactive alkaloid composition and preparation thereof | | | · CA | | | 22-Dec-21
(exam requested
3-Jun-22); 3161491 | | | 25-Jul-23 | |
| 57 | | | PSU005c-USNE | | | · 5 | | | N/A | | | Pending | | | Vaporizable psychoactive alkaloid composition and preparation thereof | | | · US | | | 14-Jun-22; 17840502 | | | N/A | |
| 58 | | | PSU005d-CANE | | | · 5 | | | 3157550 | | | Issued | | | Injectable psychoactive alkaloid composition and preparation thereof | | | · CA | | | 17-Dec-21
(exam requested
27-Apr-22); 3157550 | | | 3-Jan-23 | |
| 59 | | | PSU005d-USNE | | | · 5 | | | US11491138 | | | Issued | | | Injectable psychoactive alkaloid composition and preparation thereof | | | · US | | | 16-Mar-22;
17/696,584 | | | 18-Nov-22 | |
| · | Legend: CA: Canada; IL: Israel, AU: Australia; US: United States; BR: Brazil; MX: Mexico; EP: Europe; PCT: Patent Cooperation Treaty International Patent System; JM: Jamaica |
Competitive Environment
There are currently no pharmaceutical agents with regulatory approval for the treatment of AjD within palliative care or any other arena. The current treatment of AjD is empirical, with either psychotherapy or off-label pharmacological agents, such as anti-depressants or anxiolytics, or a combination of both.
We believe that the competitive landscape analysis of other commercial psychedelic-assisted treatments in clinical trials strongly suggests that Psyence’s clinical asset has a first-mover advantage in both the palliative care and cancer-related AjD market upon approval. PEX010 and its associated IP has been licensed to Psyence, giving it exclusivity for the indications of anxiety and depression within the context of palliative care in the UK and exclusive commercialization rights in the same indications and fields of use in the UK, EU and US. Psyence plans to expand their targeted indication of cancer-related AjD to address different types of AjD and other secondary indications both in a palliative and non-palliative context.
This provides the possibility that PEX010 may be eligible for a number of processes that could result in expedited marketing approval of PEX010, such as Fast Track, Accelerated Approval, Priority Review and Breakthrough Status. Breakthrough therapy designation is intended to expedite the development and review of drugs for serious or life-threatening conditions. The criteria for breakthrough therapy designation require preliminary clinical evidence that demonstrates the drug may have substantial improvement on at least one clinically significant endpoint over available therapy.
Psyence intends to submit the NDA requesting assessment via the 505(b)(2) pathway. A 505(b)(2) application is an NDA that contains full reports of investigations of safety and effectiveness, where at least some of the information required for approval comes from studies not conducted by or for the applicant, and for which the applicant has not obtained a right of reference or use, including, for example, the agency’s finding of safety and/or effectiveness for a listed drug or published literature. This could potentially allow for a shorter development program along with less data that is developed by Psyence, as compared to a regular NDA submission. Despite the usage of psilocybin for decades, there have been relatively few studies pertaining to psilocybin products due to the ban on the research into psychedelics. However, recently, academic institutions have been allowed to conduct such studies.
A breakthrough therapy designation conveys all of the fast track program features (see below for more details on fast track designation), more intensive FDA guidance on an efficient drug development program, an organizational commitment involving senior managers, and eligibility for rolling review and priority review.
In 2019, the FDA designated psilocybin therapy as “breakthrough therapy” for the treatment of severe depressive disorder. This precedent provides the possibility that PEX010 may be eligible for a number of processes that could result in expedited marketing approval of PEX010, such as Fast Track, Accelerated Approval, Priority Review and Breakthrough Status. Breakthrough therapy designation is intended to expedite the development and review of drugs for serious or life-threatening conditions. The criteria for breakthrough therapy designation require preliminary clinical evidence that demonstrates the drug may have substantial improvement on at least one clinically significant endpoint over available therapy.
A breakthrough therapy designation conveys all of the fast track program features (see below for more details on fast track designation), more intensive FDA guidance on an efficient drug development program, an organizational commitment involving senior managers, and eligibility for rolling review and priority review, however there can be no guarantees as to how the FDA may assess PEX010.
Additionally, even if we are granted an accelerated approval pathway, that may or may not lead to a faster development or regulatory review or approval process and may or may not increase the likelihood that PEX010 or any other product candidate will receive marketing approval. The European Medicines Agency (EMA) PRIME program, similar to the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) breakthrough therapy designation program, was launched in March 2016 to enhance support for the development of medicines that target an unmet medical need. PRIME and the U.S. breakthrough therapy designation share the same objective (timely patient access to innovative medicines).
Business Objectives:
Psyence intends to further expand the development of its product candidates for additional indications. While Psyence’s initial focus will be on the development of PEX010 for the treatment of AjD in patients with a recent diagnosis of cancer, indication expansion will focus on other causes of AjD potentially leading to an increased opportunity within the indication. Further indications will be considered once the AjD program is ongoing in areas such as Alcohol Use Disorder.
Psyence’s Psilocybin Asset
In order to accelerate clinical development of a palliative care, psilocybin-based asset, Psyence has initially licensed Filament Health’s proprietary botanical drug candidate, PEX010, and its associated IP. Filament has developed innovative technology to extract and standardize stable doses of natural compounds from mushrooms. PEX010 is currently covered by up to ten patents (five patents by the USPTO and five by the Canadian Intellectual Property Office). The product candidate has also previously received authorization from the FDA and Health Canada to enter into Phase 1 and Phase 2 human clinical trials. The license granted to Psyence in respect of the early trial phases grants Psyence exclusivity in the UK to use PEX010 in future clinical trials for the indications of depression and anxiety, including associated ailments, such as PTSD, stress, grief, and AjD within the context of palliative care. Pursuant to the license, Psyence will own all the data, results of testing, research, any information and any other IP derived or arising from any clinical trials, with the exclusion of IP related to the manufacture, processing or production of the Filament input material, which will vest in Filament.
PEX010 is a pharmaceutical-grade, natural psilocybin drug candidate. It is an oral capsule containing 25mg of naturally derived psilocybin. PEX010 will be used as an adjunct to psychotherapy for the treatment of AjD due to an incurable cancer diagnosis versus psychotherapy alone within a palliative care context.
Description of PEX010
PEX010 is extracted and purified from the psilocybes species of mushroom. Psilocybin is rapidly metabolized in the body to form psilocin, a psychoactive molecule. There has recently been a resurgence in the study of the use of psychedelics in a multitude of potential indications such as depression, anxiety disorders, PTSD, addictions and within palliative care, which is the focus area for Psyence’s development of PEX010.
PEX010 is being tested in patients with a recent terminal cancer diagnosis and who have developed AjD which can severely affect their quality of life as well as those closely related to them.
Natural versus synthetic psilocybin
Naturally extracting psychedelic compounds for medicinal use has the exciting opportunity of exploring the ‘entourage effect’, which refers to the synergistic interaction of two or more psychoactive molecules that are present in low concentrations in the final product after psilocybin extraction, resulting in a smoother, more tolerable onset and offset of the psychedelic experience. There are other active molecules within the mushrooms that have psychedelic effects, although less than psilocybin (see diagram below). A small amount of these additional active molecules is contained in the extracts derived from natural mushrooms, which contribute to the entourage effect. In the case of ‘magic mushrooms,’ psychedelic effects are achieved either by ingesting natural psilocybin-containing extracts or engineered formulations of psilocybin derivatives. It is important to note that the pharmacological properties of the psilocybin molecule remain unchanged whether the drug is synthetically or naturally derived. Current synthetic versions of psilocybin exist as distinct polymorphic structures and are synthesized via reactions using certain substrates and enzymes that direct the production of psilocybin. Naturally derived psilocybin is obtained by cultivating and processing psilocybin-containing mushrooms into a crude API for further use.
What distinguishes naturally derived psilocybin formulations from synthetic formulations is the potential to explore the ‘entourage effect’ by varying the amounts of different tryptamines yielded in the host mushroom during the growing process. The ‘entourage effect’ has important ramifications for the overall therapeutic effectiveness of psilocybin-assisted psychotherapy due to the potential of modulating the psychedelic effects and the neuroplastic processes, which help form connections between multiple neurons, typically induced by psilocybin. This is because the subjective effects derived from the type or intensity of ‘mystical experiences’ occasioned by psilocybin, might additionally contribute to the overall effectiveness of the treatment. Whilst this area of research is still largely unexplored, a few preclinical studies have shown that different species of magic mushrooms procure nuanced changes in psychedelic experiences due to their differing levels of psilocybin, psilocin and other tryptamine derivatives. As the psilocybin industry continues to evolve, we believe that it is likely that there will be demand for both naturally derived psilocybin formulations as well as synthetic psilocybin (and derivatives) due to both the increasing demand in psilocybin-based research and more importantly, patient accessibility of psilocybin medicines. Whole Psilocybe mushrooms contain tryptamine derivatives that may contribute to a synergistic therapeutic effect.

Figure 1 Source: ChemDraw
Psilocybin, 3-[2-(Dimethylamino)ethyl]-1 H-indol-4-yl dihydrogen phosphate is a naturally occurring tryptamine derivative found in over 100 species of mushrooms.1 Psilocybin quickly dephosphorylates into psilocin upon ingestion. Psilocin is a partial-agonist of serotonin receptors in the brain. Tryptamine derivatives and serotonin share many similarities in their chemical structure. Psilocin binds with high affinity to the serotonin 2A receptors (5-HT2A).2
Psilocybin reliably induces profound changes in sensory perception, emotion, thought, and sense of self, characterized by marked alterations in all mental functions, including perception, mood, volition, cognition and self-experience.3 These profound changes are often referred to as “mystical-type” experiences. Measures of mystical-type experience occurring during psilocybin treatment have been repeatedly observed to predict later effects on behavior and emotions, including reductions in depressive and anxious symptoms.4,5
Oral psilocybin has about a 50% bioavailability and psilocin is detectable in plasma within 15 minutes of administration of the parent compound.6,7 The half-life of psilocin in blood is 2-3 hours. Onset of noticeable psychoactive effects for a 25 mg dose typically occur within one hour, peaks at two hours after a dose and finishes at six hours after the dose.
The investigational medicinal product PEX010 is a capsule for oral administration that contains the herbal drug substance PYEX; a Psilocybe cubensis mushroom extract containing Psilocybin 9[3-[2-(dimethylamino)ethyl]-1H-indol-4-yl] dihydrogen phosphate). The drug product PEX010 is manufactured with the drug substance PYEX (12.5-14.0% psilocybin), excipients, and hydroxypropyl methylcellulose capsules.
Indication and Treatments
Adjustment Disorder
Incurable cancer is predictably associated with challenges and burdens that may lead to symptoms of depression, demoralization, and fears of suffering, dependency, and mortality.8 Up to 50% of individuals with advanced cancer report symptoms that are sufficiently severe to reach clinical levels, exacerbating physical symptoms and impairing quality of life.9,10 Multiple physical symptoms, dramatic alteration in support needs and personal relationships, difficulty navigating a complex health care system, and the threat of impending mortality all may constitute pathways to distress.11
1 Daniel J, Haberman M. Clinical potential of psilocybin as a treatment for mental health conditions. Ment Health Clin. 2017;7:24 – 28
2 PubChem. Psilocybine. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Psilocybine. Accessed 25 February 2021.
3 Studerus E, Kometer M, Hasler F, Vollenweider FX. Acute, subacute and long-term subjective effects of psilocybin in healthy humans: a pooled analysis of experimental studies. J Psychopharmacol. 2011;25:1434 – 1452.
4 MacLean KA, Johnson MW, Griffiths RR. Mystical experiences occasioned by the hallucinogen psilocybin lead to increases in the personality domain of openness. J Psychopharmacol. 2011;25:1453 – 1461.
5 Ross S, Bossis A, Guss J, Agin-Liebes G, Malone T, Cohen B, et al. Rapid and sustained symptom reduction following psilocybin treatment for anxiety and depression in patients with life-threatening cancer: a randomized controlled trial. J Psychopharmacol. 2016;30:1165 – 1180.
6 Brown RT, Nicholas CR, Cozzi NV, Gassman MC, Cooper KM, Muller D, et al. Pharmacokinetics of Escalating Doses of Oral Psilocybin in Healthy Adults. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2017;56:1543–1554.
7 Hasler F, Bourquin D, Brenneisen R, Bär T, Vollenweider FX. Determination of psilocin and 4-hydroxyindole-3-acetic acid in plasma by HPLC-ECD and pharmacokinetic profiles of oral and intravenous psilocybin in man. Pharm Acta Helv. 1997;72:175 – 184.
8 Lo C, Zimmermann C, Rydall A, Walsh A, Jones JM, Moore MJ, et al. Longitudinal study of depressive symptoms in patients with metastatic gastrointestinal and lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28:3084 – 3089.
9 Hopwood P, Stephens RJ. Depression in patients with lung cancer: prevalence and risk factors derived from quality-of-life data. J Clin Oncol. 2000;18:893 – 903.
10 Delgado-Guay M, Parsons HA, Li Z, Palmer JL, Bruera E. Symptom distress in advanced cancer patients with anxiety and depression in the palliative care setting. Support Care Cancer. 2009;17:573 – 579.
11 Rodin G, Lo C, Mikulincer M, Donner A, Gagliese L, Zimmermann C. Pathways to distress: the multiple determinants of depression, hopelessness, and the desire for hastened death in metastatic cancer patients. Soc Sci Med. 2009;68:562 – 569.
Adjustment to an incurable cancer diagnosis can be characterized as an ongoing process of trying to gain mastery or control over cancer-related and end-of-life events, and acceptance of death.12 Unsuccessful adjustment to these stressful events can be defined by disengagement, withdrawal, and helplessness to an incurable cancer diagnosis reflect an adjustment disorder, or AjD. AjD is the most common stress associated disorder observed in cancer patients, with an estimated prevalence of 19% of all diagnosed cancer patients.13
AjD is defined in International Classification of Diseases 11th Revision (ICD-11) as a maladaptive reaction, which usually emerges within one month of a significant life-stressor, such as illness, family or partnership problems, job-related issues, or financial difficulties.14 There are two core categories of symptoms that characterize AjD: a preoccupation with the stressor or its consequences, and failure to adapt. Preoccupation includes recurring distressing thoughts about the stressor, constant worry, and rumination. Failure to adapt describes a generalized stress-response (e.g., sleep disturbances or concentration problems) that results in significant impairment in social, interpersonal, occupational, educational, or other significant areas of functioning.
AjD is also defined in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM) diagnostic criteria,15 and while there is great overlap with the definition and symptomatology compared to the ICD 11 classification, the DSM definition separates AjD into 6 different subtypes, Both the ICD and DSM have had substantial impact on global psychiatric practice and research. While the DSM has been used more often in research around the world,16 a study of nearly 5,000 psychiatrists in 44 countries demonstrated that the majority of psychiatrists outside the U.S. utilize ICD classifications in their daily clinical practice.17 The DSM-5 conceptualizes AjD as a stress-related syndrome in a separate chapter of “Trauma and Stress Related Disorders”,18 representing the most significant change from DSM-IV.19 However, the current diagnostic construct is crucially dependent on an exclusion criterion, so that a diagnosis of AjD is rarely applicable when another mental disorder is present.
12 Roth AJ, Kornblith AB, Batel-Copel L, Peabody E, Scher HI, Holland JC. Rapid screening for psychologic distress in men with prostate carcinoma: a pilot study. Cancer. 1998;82:1904 – 1908.
13 Mitchell AJ, Chan M, Bhatti H, Halton M, Grassi L, Johansen C, et al. Prevalence of depression, anxiety, and AjD in oncological, haematological, and palliative-care settings: a meta-analysis of 94 interview-based studies. Lancet Oncol. 2011;12:160 – 174.
14 Maercker A, Brewin CR, Bryant RA, Cloitre M, van Ommeren M, Jones LM, et al. Diagnosis and classification of disorders specifically associated with stress: proposals for ICD-11. World Psychiatry. 2013;12:198 – 206.
15 Casey P, Doherty A. AjD: implications for ICD-11 and DSM-5. Br J Psychiatry. 2012;201:90 – 92.
16 Clark LA, Cuthbert B, Lewis-Fernández R, Narrow WE, Reed GM. Three Approaches to Understanding and Classifying Mental Disorder: ICD-11, DSM-5, and the National Institute of Mental Health’s Research Domain Criteria (RDoC). Psychol Sci Public Interest. 2017;18:72 – 145.
17 Reed GM, Mendonça Correia J, Esparza P, Saxena S, Maj M. The WPA-WHO Global Survey of psychiatrists’ attitudes towards mental disorders classification. World Psychiatry. 2011;10:118 – 131.
18 Kangas M. DSM-5 Trauma and Stress-Related Disorders: Implications for Screening for Cancer-Related Stress. Front Psychiatry. 2013;4:122.
19 Strain JJ, Friedman MJ. Considering AjDs as stress response syndromes for DSM-5. Depress Anxiety. 2011;28:818 – 823.
Treatment Plans
Traditional Treatments
Evidence suggests that addressing psychosocial, emotional, and physical symptoms early in the cancer trajectory, through such steps as palliative care or psychological interventions, may positively influence survival outcomes.20,21,22,23 Comorbid depression with cancer leads to worsened quality of life, increased sensitivity to pain, difficulties with treatment, communication difficulties, caregiver burnout, increased risk of suicide, longer periods of hospitalization, and a reduced expectation of survival.24,25,26,27,28 The National Institute for Clinical Excellence Palliative Cancer Care Guidelines29 recommend that if experiencing more severe types of psychological distress — which would include moderate to severe AjD — patients should be offered specialist psychological interventions such as psychotherapy, including cognitive behavioral therapy (“CBT”).
20 Temel JS, Greer JA, Muzikansky A, Gallagher ER, Admane S, Jackson VA, et al. Early palliative care for patients with metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2010;363:733 – 742.
21 Bakitas MA, Tosteson TD, Li Z, Lyons KD, Hull JG, Li Z, et al. Early Versus Delayed Initiation of Concurrent Palliative Oncology Care: Patient Outcomes in the ENABLE III Randomized Controlled Trial. J Clin Oncol. 2015;33:1438 – 1445.
22 Giese-Davis J, Collie K, Rancourt KMS, Neri E, Kraemer HC, Spiegel D. Decrease in depression symptoms is associated with longer survival in patients with metastatic breast cancer: a secondary analysis. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29:413 – 420.
23 Spiegel D, Giese-Davis J. Depression and cancer: mechanisms and disease progression. Biol Psychiatry. 2003;54:269 – 282.
24 Skarstein J, Aass N, Fosså SD, Skovlund E, Dahl AA. Anxiety and depression in cancer patients: relation between the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale and the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer Core Quality of Life Questionnaire. J Psychosom Res. 2000;49:27 – 34.
25 Depression as a predictor of disease progression and mortality in cancer patients: a meta-analysis. Centre for Reviews and Dissemination (UK); 2009.
26 Prieto JM, Blanch J, Atala J, Carreras E, Rovira M, Cirera E, et al. Psychiatric morbidity and impact on hospital length of stay among hematologic cancer patients receiving stem-cell transplantation. J Clin Oncol. 2002;20:1907 – 1917.
27 Misono S, Weiss NS, Fann JR, Redman M, Yueh B. Incidence of suicide in persons with cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:4731 – 4738.
28 Colleoni M, Mandala M, Peruzzotti G, Robertson C, Bredart A, Goldhirsch A. Depression and degree of acceptance of adjuvant cytotoxic drugs. Lancet. 2000;356:1326 – 1327.
29 Nice N. Improving supportive and palliative care for adults with cancer. London: NICE. 2004. 2004.
Psilocybin-assisted psychotherapy
CBT has been shown to improve anxiety in patients diagnosed with incurable cancer, but appears to be less effective at improving depressive symptoms.30 Several recently published trials have examined the efficacy of psilocybin, a classic serotonergic psychedelic drug that induces its acute subjective effects through the agonism of serotonin 2A (5-HT2A) receptors, to treat depression and anxiety in patients with life -threatening cancer, amongst other psychiatric conditions.31,32,33,34 Psilocybin-assisted psychotherapy is a course of therapy involving single or multiple sessions in which a dose of psilocybin is administered in conjunction with psychotherapy, delivered by a suitably trained therapist in a controlled setting. This intervention consists of three therapy stages: (1) preparation, (2) dosing session(s), and (3) integration, which allow for a more patient-centric approach compared to other therapy models. The pharmacological effects of psilocybin, in synergy with the psychotherapy, are considered to give rise to increased neuroplasticity, which facilitates rapid and deep psychological transformation that may accelerate and augment the effects of the psychotherapy process.34
PAP has been demonstrated in various academic studies to cause expeditious, substantial, and sustained improvements in cancer-related anxiety and depression, existential distress, quality of life, and orientation toward death.32,33 For example, in an academic study32 of 29 patients with cancer-related depression and anxiety, at the 6.5-month follow up, psilocybin was associated with enduring anxiolytic and anti-depressant effects (approximately 60-80% of participants continued with clinically significant reductions in depression or anxiety respectively), sustained benefits in existential distress and quality of life, as well as improved attitudes towards death.35 In another study of 51 patients,33 similar results were reported. At 6-month follow-up, these changes were sustained, with about 80% of participants continuing to show clinically significant decreases in depressed mood and anxiety. Participants attributed improvements in attitudes about life/self, mood, relationships, and spirituality to the “high” experience resulting from the psilocybin, with over 80% endorsing moderately or greater increased well-being/life satisfaction.36,37,38,39,40,41,42
A number of factors provide rationale for focusing on patients with AjD following a diagnosis of incurable cancer as the target population. The size of the cancer population, which generally makes up approximately 30% of target country palliative patients, provides justification for research, in regard to both the magnitude of needs and the access to participant recruitment. Additionally, previous clinical trials have demonstrated the feasibility and efficacy of PAP for people with depression and anxiety symptoms, both within and outside of the palliative care setting, highlighting the versatility and universality of this intervention. Moreover, the sustained reductions in anxiety and depression amongst palliative care patients suggest the longevity of positive outcomes mediated by PAP and the potential to dramatically improve patient quality of life, in what remains of their life.
30 Hayes SC, Luoma JB, Bond FW, Masuda A, Lillis J. Acceptance and commitment therapy: model, processes and outcomes. Behav Res Ther. 2006;44:1 – 25.
31 Carhart-Harris R, Giribaldi B, Watts R, Baker-Jones M, Murphy-Beiner A, Murphy R, et al. Trial of Psilocybin versus Escitalopram for Depression. N Engl J Med. 2021;384:1402 – 1411.
32 Grob CS, Danforth AL, Chopra GS, Hagerty M, McKay CR, Halberstadt AL, et al. Pilot study of psilocybin treatment for anxiety in patients with advanced-stage cancer. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2011;68:71 – 78.
33 Griffiths RR, Johnson MW, Carducci MA, Umbricht A, Richards WA, Richards BD, et al. Psilocybin produces substantial and sustained decreases in depression and anxiety in patients with life-threatening cancer: A randomized double-blind trial. J Psychopharmacol. 2016;30:1181 – 1197.
34 Brouwer A, Carhart-Harris RL. Pivotal mental states. J Psychopharmacol. 2021;35:319 – 352.
35 Agin-Liebes GI, Malone T, Yalch MM, Mennenga SE, Ponté KL, Guss J, et al. Long-term follow-up of PAP for psychiatric and existential distress in patients with life-threatening cancer. J Psychopharmacol. 2020;34:155 – 166.
36 Carhart-Harris RL, Bolstridge M, Rucker J, Day CMJ, Erritzoe D, Kaelen M, et al. Psilocybin with psychological support for treatment-resistant depression: an open-label feasibility study. Lancet Psychiatry. 2016;3:619 – 627.
37 Carhart-Harris RL, Bolstridge M, Day CMJ, Rucker J, Watts R, Erritzoe DE, et al. Psilocybin with psychological support for treatment-resistant depression: six-month follow-up. Psychopharmacology. 2018;235:399 – 408.
38 Davis AK, Barrett FS, May DG, Cosimano MP, Sepeda ND, Johnson MW, et al. Effects of PAP on Major Depressive Disorder: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Psychiatry. 2021;78:481 – 489.
39 Bogenschutz MP, Forcehimes AA, Pommy JA, Wilcox CE, Barbosa PCR, Strassman RJ. Psilocybin- assisted treatment for alcohol dependence: a proof-of-concept study. J Psychopharmacol. 2015;29:289 – 299.
40 Johnson MW, Garcia-Romeu A, Cosimano MP, Griffiths RR. Pilot study of the 5-HT2AR agonist psilocybin in the treatment of tobacco addiction. J Psychopharmacol. 2014;28:983 – 992.
41 Moreno FA, Wiegand CB, Taitano EK, Delgado PL. Safety, tolerability, and efficacy of psilocybin in 9 patients with obsessive-compulsive disorder. J Clin Psychiatry. 2006;67:1735 – 1740.
42 Griffiths RR, Johnson MW, Carducci MA, Umbricht A, Richards WA, Richards BD, et al. Psilocybin produces substantial and sustained decreases in depression and anxiety in patients with life-threatening cancer: A randomized double-blind trial. J Psychopharmacol. 2016;30:1181 – 1197.
Classic psychedelics, a term referring to naturally -derived psychedelics including mescaline, lysergic acid diethylamide and psilocybin, all share a common mechanism of action via the serotonergic pathways. Psilocybin is a prodrug that, when ingested, is metabolized into the psychoactive compound psilocin. Psilocin acts as a partial agonist at the serotonergic 5-HT2A receptor, and research has demonstrated that activation of the 5-HT2A receptor subtype is integral to the mechanism of action leading to subjective psychedelic experience.43,44,45,46,47
The pharmacological effects of psilocybin, in synergy with psychotherapy, are considered to give rise to increased neuroplasticity and create a ‘pivotal mental state,’ which facilitates rapid and deep psychological transformation that may accelerate and augment the effects of the psychotherapy process.34 This is thought to underlie the transdiagnostic efficacy of PAP for a wide range of difficult to treat psychiatric conditions, including treatment-resistant depression, PTSD, substance use disorders, psychological distress with a life-threatening illness and obsessive-compulsive disorder.
Clinical Studies
In recent palliative care clinical trials conducted at New York School of Medicine and Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, in which participants received PAP at doses of 22 mg/70 kg, 30 mg/70 kg, and 0.3 mg/kg, no serious adverse events (“SAEs”) were reported. Adverse effects of PAP amongst participants had all been previously described for psilocybin and were mild and transient, and included physical discomfort, psychological discomfort, increased systolic and diastolic blood pressure without criteria for medical intervention, increased heart rate with a mild sympathomimetic effect, nausea and vomiting, transient anxiety and headaches or migraines. None of the participants experienced prolonged psychosis or hallucinogen persisting perception disorder (“HPPD”).
There are currently five registered studies investigating the efficacy of PAP to treat depression, anxiety and demoralization in patients with incurable illnesses:
| Study | | | Study Design | | | Description | |
| Yvan Beaussant from the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute (NCT04950608). | | | Open-label, single-arm pilot study — Recruiting | | | Safety and efficacy of a fixed 25 mg psilocybin dose and psychotherapy in hospice care patients with demoralization and existential distress | |
| | | | | | | | |
| Maryland Oncology Hematology (NCT04593563). | | | Phase 2, open-label, single-arm study — Active, not recruiting | | | Safety and efficacy of a fixed 25 mg dose of psilocybin to treat MDD in 30 patients with malignant neoplasm | |
| | | | | | | | |
| University of Utah (NCT04522804). | | | Open-label study, single-arm — Recruiting | | | Safety and tolerability of psilocybin in cancer patients assessed by the number and severity of Adverse Events (“AEs”), and the feasibility to recruit, enroll and consent patients with a cancer diagnosis or hematologic malignancy to the study | |
43 Willins DL, Meltzer HY. Direct injection of 5-HT2A receptor agonists into the medial prefrontal cortex produces a head-twitch response in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1997;282:699 – 706.
44 Glennon RA, Teitler M, Sanders-Bush E. Hallucinogens and serotonergic mechanisms. NIDA Res Monogr. 1992;119:131 – 135.
45 Vollenweider FX, Vollenweider-Scherpenhuyzen MF, Bäbler A, Vogel H, Hell D. Psilocybin induces schizophrenia-like psychosis in humans via a serotonin-2 agonist action. Neuroreport. 1998;9:3897 – 3902.
46 Ray TS. Psychedelics and the human receptorome. PLoS One. 2010;5:e9019.
47 González-Maeso J, Weisstaub NV, Zhou M, Chan P, Ivic L, Ang R, et al. Hallucinogens Recruit Specific Cortical 5-HT2A Receptor-Mediated Signaling Pathways to Affect Behavior. Neuron. 2007;53:439 – 452.
| Study | | | Study Design | | | Description | |
| St Vincent’s Hospital in Melbourne (U1111-1237-8914). | | | Phase 2 parallel 2-part study, where part 1 is a randomized, controlled trial comparing an active placebo of 100 mg Niacin with 25 mg psilocybin, and part 2 is an open-label single-arm study of 25 mg of psilocybin — Recruiting | | | Assess the efficacy of PAP to treat depression and/or anxiety associated with an incurable illness diagnosis | |
| | | | | | | | |
| University of Nebraska. | | | Phase 1, open-label, single-arm study — Not yet recruiting | | | Exploratory pilot study of palliadelic treatment to reduce psychological distress and improve quality of life in persons with pancreatobiliary cancer, with a parallel assessment of healthcare utilization and family wellbeing | |
Known and Potential Risks of Psilocybin
Abuse Potential
To date, there have been no confirmed reports of an overdose of pharmaceutical psilocybin. Currently, psilocybin is placed in Schedule 1 in the UK Misuse of Drugs Regulations 2001, defined as having no medical use, possessing high abuse liability, and lack of accepted safety when used under medical supervision. However, in preclinical studies using non-human primates, psilocybin, mescaline and N,N-Dimethyltryptamine did not serve as positive reinforcers in 3,4-Methylenedioxy methamphetamine (MDMA) experienced rhesus monkeys. This suggests that non-human primates do not find the psychoactive effects of the 5-HT2A receptor agonists addictive.
Analysis of long-term follow-up data from eight pooled experimental trials with healthy volunteers indicated no subsequent drug abuse, no changes to overall drug consumption habits (including alcohol, nicotine, cannabis and MDMA) or functional impairment following exposure to psilocybin in the laboratory. Where changes in drug consumption habits were noted, most respondents described decreased consumption, particularly with reference to psilocybin use. Large-scale survey research indicates that hallucinogens are selected as a primary substance of abuse in only a fraction of responders.
In clinical studies with psilocybin, exposing individuals with either no history of hallucinogen use, or a history of minimal use (less than ten times in total and not within the previous five years) have not resulted in reported instances of subsequent illicit hallucinogen abuse. Additionally, studies have shown side effects that are potentially predictive of low abuse potential, such as elevations in fear and anxiety. Based on available literature, it is not expected that either psilocybin-naïve or experienced individuals will develop dependence after exposure.
Safety
Psilocybin has been found to be of very low toxicity in humans and research animals.
In recent palliative care clinical trials conducted at New York School of Medicine and Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, in which participants received PAP at a dose of 22 mg/70 kg, 30 mg/70 kg, and 0.3 mg/kg, no serious adverse events (“SAEs”) were reported. Adverse effects of PAP amongst participants had all been previously described for psilocybin and were mild and transient, and included physical discomfort, psychological discomfort, increased systolic and diastolic blood pressure without criteria for medical intervention, increased heart rate with a mild sympathomimetic effect, nausea and vomiting, transient anxiety and headaches or migraines. None of the participants experienced prolonged psychosis or hallucinogen persisting perception disorder (“HPPD”).
The clinical safety of psilocybin has been extensively studied in open-label and double-blind, controlled trials, both as a single agent and as adjunctive treatment in a number of clinical and non-clinical adult populations. Dosing regimens used in previous clinical trials with psilocybin have ranged from 0.014 mg/kg to 0.6 mg/kg, administered orally as either a single dose, or multiple doses weeks apart. Thousands of participants have received psilocybin under controlled conditions in a clinical setting for various indications, with results published in peer-reviewed journals. Knowledge gained from previous clinical trials with psilocybin and discussions with researchers leading other randomized control trials in this area has directed the design of Psyence’s planned Phase IIb Study.
Psilocybin (also known as ‘magic mushrooms’) is rated as one of the least harmful recreational drugs. Commonly cited risks include prolonged psychotic reactions, flashback phenomena/HPPD, and bad trips. Prolonged psychotic responses are extremely rare in clinical studies with psilocybin (<1%), even at very high doses, and none have been reported in modern studies or studies with patients. The risk of flashback phenomena is minimal (or even negligible), and no cases have been observed in other studies with psilocybin. Periods of psychological challenge (for example, increased anxiety) are more commonly reported, but may be predictive of positive clinical outcomes.
Psilocybin Related Adverse Events by Incidence (at 25 mg)
Common
>20% | | | Less common
<15% | | | Rare
< 2% | |
1) Increased anxiety, particularly at the onset of the drug effects 2) Mild-moderate increase in heart rate 3) Visual hallucinations 4) Transient headaches, lasting for one to two days (maximum) post-dosing | | | 1) Paranoia or suspiciousness. 2) Nausea 3) Dizziness 4) A ‘bad trip’ i.e. negative thoughts and mood during the acute drug effects | | | 1) HPPD/flashbacks 2) Worsening of mental state after the drug experience | |
It is not uncommon for people to experience some negative psychological content during a psilocybin ‘trip’, particularly if they suffer from ongoing psychological distress, as is characteristic of depression. Typically, this is managed by ensuring good preparation before, support during, and integration after the experience. While challenging episodes have been relatively commonly reported in previous trials, some of these have contributed to a psychological ‘breakthrough’ on the part of the participant. Recent evidence indicates that challenging psychological experiences can produce therapeutic benefits, improving psychological well-being in the long-term.
Negative aftereffects of challenging psychological experiences under psychedelics are thought to be a consequence of inadequate ‘set and setting’ and post-session integration work — and they may also relate to the duration of the challenging period. In the Phase IIb Study and further studies, such risks will be reduced via thorough psychological preparation and integration, good patient-staff rapport and a positive, supportive environment. Challenging experiences/periods will be managed principally through psychological support, but oral and injectable lorazepam and olanzapine, as rescue medications, will be available. These would only be used in cases of severe panic that were unresponsive to psychological intervention, and where the patient’s behavior was putting themselves and/or staff in danger. Consent for such medication will be sought from the patient ahead of study participation.
Before, during and after the dosing session, patients will receive psychological support from therapists who have been specifically trained to deliver PAP in the context of research studies, including clinical trials. An onsite psychiatrist will also be available to support where needed. Monitoring of participants’ vital signs, behavior and mood will be conducted prior to the psilocybin being administered, and prior to the participant being discharged. On the dosing day, patients will only be allowed to return home only once the study psychiatrist is confident they are fit to do so, and authorizes the patient’s release. 24-hour emergency contact numbers will be provided for a member of the study team, and localized support and crisis services will also be provided.
Due to the psychoactive nature of psilocybin, the safety of participants in clinical trials can be enhanced by testing psilocybin within a “set and setting” protocol. By addressing the set (the emotional, cognitive, behavioral states, mindset and expectations of study participants just prior to psilocybin exposure) and setting (the physical environment in which the exposure occurs) of the experience, the risk of the subject reporting an event which is distressing or injuring themselves can be reduced. This approach generally incorporates three components: (1) preparation, (2) drug session and (3) post -session meetings to integrate the classic psychedelic experience.
During the preparation phase, participants undergo pre-exposure sessions designed to build rapport with the therapist who will be present during the drug dosing session and to identify personal themes and struggles that might be especially likely to impact the session experience. The drug session itself is conducted by a trained therapist (the gender of which is selected by the participant) and an appropriately trained member of the study team, who are present throughout the session. Sessions are typically conducted in a room designed to be quiet, comfortable, and aesthetically pleasing, and participants are encouraged to wear eyeshades and listen to a program of music through headphones during the drug exposure to aid them in focusing their attention inwards. In the third phase, participants are engaged in a series of drug-free therapy sessions to discuss their dosing session experience thoroughly, with the goal of maximizing its therapeutic benefit.
Suicide
While most trials with psilocybin have demonstrated reduced suicidality following dosing, one recent large-scale study conducted by Compass Pathways with 233 participants on the efficacy of psilocybin in a treatment-resistant depression (TRD) population reported that suicidal ideation and intentional self-injury were seen in all treatment groups, as is common in TRD studies. Most cases occurred more than a week after the COMP360 psilocybin session. There was no mean worsening of suicidal ideation scores on the MADRS scale in any treatment group. Suicidal behaviors were reported at least one month after COMP360 administration for three non-responders in the 25mg arm.
It is important to note that subjects with AjD and patients with a terminal cancer diagnosis are also at increased risk of suicide. As such, in the Psyence Phase IIb Study, the risk of suicide and other AE’s will be assessed by thorough and regular screening using the Sheehan-Suicide Tracking Scale (S-STS) at every study visit. Participants with suicidal tendencies and histories of suicide attempts will be excluded from the study. The study psychiatrist and psychotherapist contact details will be provided to patients in case of emergency, in addition to providing localized information for support services and crisis management. A standard operating procedure for dealing with both AEs and any unexpected suicide attempt has been prepared. As such, we believe that the risk of suicide and other AEs will be reduced by thoroughly screening participants for any suicidal tendencies, by excluding patients with histories of suicide attempts and by regular monitoring of suicidal ideation and behavior.
Target Population and Market — Palliative Care Patients
Previous trials have demonstrated that PAP is well tolerated in samples of palliative care patients, with no SAEs. Recruitment of palliative care participants may require screening of large samples in order to achieve the intended sample size. In previous PAP trials with palliative care participants, 10%-27% of screened individuals were enrolled in the study. Recruitment for trials of psychiatric disorders is complex, as such conditions may affect motivation and adherence, relating to both the physical and mental health of participants with a cancer diagnosis. Moreover, there is an exogenous risk of participant death during the trial for clinical trials in the palliative care setting. Similarly, as cancer may metastasize further, diligence must be paid to exclude participants with metastatic cancer to the brain, considering the potential impact on cognitive function. Together, this indicates that the success of recruitment and screening relies on the selection of participants with appropriate life expectancy, extent of cancer, and post-diagnosis time for the inclusion/exclusion criteria in PAP trials with palliative care patients.
Targeted Market for First Indication (AjD in Patients with a Terminal Cancer Diagnosis)
The total Palliative Care Market is large, with an expected robust CAGR of 9.4% over the next 7 years. The figures below are drawn from commissioned market research performed by Insight Ace Analytic (insightaceanalytic.com) in September 2022.
The total market value was calculated using two approaches simultaneously; namely top-down and bottom-up approaches.
In the top-down approach, the total market revenue is calculated by conducting the parent market analysis for deducing the revenue for global palliative care market revenue. Analyst perspective and subject-matter-expert based heuristic form of market sizing also plays an integral role in this step. For forecasting the current estimates, the following key sources were considered:
| · | American Cancer Society International Association for Hospice & Palliative Care, |
| · | UK Palliative Medicine Association National Hospice and Palliative Care Organization (NHPCO), |
| · | Worldwide Hospice Palliative Care Alliance (WHPCA),International Association for Hospice & Palliative Care (IAHPC), |
| · | Investor presentation of palliative care providers, |
| · | Psychedelic drug development companies, |
| · | Hospice care providers and associations |
| · | Worldpopulationreview gco.,iarc.fr, webmed.com, acsjournals,.onlinelibrary.wiley.com, NCBI, www.cancer.org, ecancer.org, canadian-cancer-statistics-2021, www150.statcan.gc.ca cancer.ca, canceratlas.cancer.org, bmcmedicine, biomedcentral.com, www.who.int, ascopubs.org, www.jpsmjournal.com,OECD |
In the bottom-up approach, we used different mathematical models to estimate the market sizes of different economies and segments, which we then summed up to define the total market. The key data points that enabled the estimation of global palliative care market are as follows:
| · | Palliative Care Service Revenues from major service providers |
| · | Palliative care different disease and treatment penetration by region and key countries |
As a part of the market engineering, both ‘top-down’ as well as ‘bottom-up’ approaches were extensively utilized along with data triangulation models to derive & verify the market sizes & forecast through 2028. Market forecast was performed through proprietary software that analyses various qualitative and quantitative factors. Growth rate and CAGR were estimated through intensive secondary and primary research. Data triangulation across various data points provided accuracy in different market segments in the report.
A holistic approach was used to ensure that the granular and uncommon parameters were taken into consideration to ensure accurate results. The information from the paid databases were further combined to the raw data in order to standardize it.
Data validation is the most crucial stage of the research process. Primary interviews were conducted to validate the data and analysis, which provides first-hand information on the market dynamics, outlook, and growth parameters. Industry experts validate the estimates, which helps the company to cement the on-going research study and primary research includes online surveys and telephonic interviews with different distributors and manufacturers.

Figure 2 The estimated year of launch of Pallicybin (PEX010) in the treatment of Adjustment Disorder in palliative care patients is 2027. Robust growth of the total palliative care market continues through 2030.
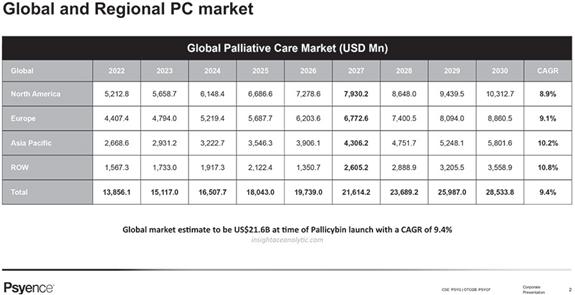
Figure 3 Robust growth in the palliative market across major regions of the world continue through 2030

Figure 4 The initial indication within the cancer segment of palliative care is about 37% of the total market which provides a large segment of other chronic illnesses to be targeted with label expansion opportunities.

Figure 5 There will be approximately 2.25 million patients in North America and Europe with distress related to cancer in 2030

Figure 6 This table gives a directional indication of what the size of the revenue could be with very conservative estimates of percentage of number of cancer patients with distress on PAP and the costs charged for PAP or just the psilocybin. Growth in percentage market obtained will be dependent on awareness and ability to provide PAP in sufficient clinics. Whichever scenario is considered, the Serviceable Obtainable Market could be three times higher when other chronic disease sources of distress are available.
Business Model
Psilocybin-assisted psychotherapy, once approved, will have to be delivered to patients in a guided manner over a period of 6 – 8 weeks, including the intention setting meetings, the psychedelic event (dosing session) and the subsequent integration meetings. This implies having trained guides who will spend a long time with patients over the course of the PAP, suitable clinic settings and psychologists’ oversight.
The final business model for the provision of PEX010 will depend on a number of aspects, including the final outcomes of the studies a, the indication(s) that will be allowed by the regulatory agencies and the state of the environment and market to provide psychedelic therapy at the time of approval. It is expected that the number of clinics available to be able to provide PAP will increase dramatically once the first psychedelic is approved for any indication.
Our possible business models will take into consideration of whether to merely supply the PEX010 product for clinics to administer, through including a premium price for the intellectual property of a proprietary PAP, to enter into partnerships with clinics to administer PAP, or even to own dedicated clinics for administration of PAP.
The target audience for the initial indication will be oncology sites, including their oncologists and other health care professionals to create awareness of the effectiveness of PAP for terminal cancer patients who have AjD. The principal marketing message will be to offer patients a better quality of life for their remaining years with a single administration of PEX010 within a PAP. It has been shown that patients in palliative care who are less anxious or depressed utilize fewer healthcare resources, which is an aspect that will help justify the costs of the PAP.
Legal and Regulatory Framework
Current Regulatory Landscape of Target Markets
Psyence will focus on the initial countries and regions to perform their clinical development and to commercialize the final product, being North America (US & Canada), EU, UK and Australia. Introductions into other regions will be contemplated at a later phase.
In the United States, foods, drugs and dietary supplements are subject to extensive regulation. The U.S. Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (the “FDCA”) and other federal and state statutes and regulations govern, among other things, the research, development, testing, manufacturing, storage, recordkeeping, approval, labelling, promotion and marketing, distribution, post-approval monitoring and reporting, sampling, and import and export of pharmaceutical products. We must ensure that all promotion and marketing, distribution, and labeling of any pharmaceutical products comply with the U.S. regulations, including the FDCA and the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (the “FDA”).
Psilocybin and psilocin are strictly controlled under the U.S. Controlled Substances Act (“CSA”) as Schedule I substances. By definition, Schedule I substances have no currently accepted medical use in the United States, a lack of accepted safety for use under medical supervision, and a high potential for abuse. Schedule I and II drugs are subject to the strictest controls under the CSA, including manufacturing and procurement quotas, security requirements and criteria for importation. Anyone wishing to conduct research on substances listed in Schedule I under the CSA must register with the DEA and obtain DEA approval of the research proposal. A majority of state laws in the United States also classify psilocybin and psilocin as Schedule I controlled substances. For any product containing psilocybin or any Schedule I substance to be available for commercial marketing in the United States, such substance must be rescheduled, or the product itself must be scheduled, by the DEA to Schedule II, III, IV or V. Scheduling determinations by the DEA are dependent on FDA approval of a substance or a specific formulation of a substance.
Prescription drugs are classified and regulated under the federal Food and Drugs Act (Canada). Labeling, marketing and selling of any prescription drug must comply with Health Canada. The regulations in the European Union are similar to those in the U.S. and Canada.
Psyence will focus the phase IIb portion of its clinical development program in Australia. The TGA is Australia’s government authority responsible for evaluating, assessing and monitoring products that are defined as therapeutic goods, and the use of therapeutic goods supplied in clinical trials in Australia under the therapeutic goods legislation. Such legislation includes The Therapeutic Goods Act 1989 (“TG Act”), Regulations and Orders which set out the requirements for inclusion of therapeutic goods in the Australian Register of Therapeutic Goods (ARTG).
For a prescription medicine to be registered in the ARTG, a sponsor of the product (usually a pharmaceutical company such as Psyence) is required to submit a dossier of evidence on the clinical efficacy, safety and manufacturing quality for evaluation by the TGA. Clinical trials of medicines and biologicals regulated under the Clinical Trial Notification (CTN) or Clinical Trial Approval (CTA) schemes are subject to the TGA’s Good Clinical Practice (GCP) Inspection Program. The TGA has issued a handbook which provides guidance on the legislative, regulatory and good clinical practice (GCP) requirements when conducting clinical trials in Australia using ‘unapproved’ therapeutic goods in order to assist trial sponsors, Human Research Ethics Committees (HRECs), investigators and approving authorities (institutions) in understanding their roles and responsibilities under the therapeutic goods legislation.
Until recently, psilocybin was included in Schedule 9 (Prohibited Substances) of the Poisons Standard which, because of interaction with state and territory regulation, largely restricted the lawful supply of goods containing psilocybin to clinical trial settings only. However, effective 1 July 2023, the TGA made the decision to down schedule psilocybin to Schedule 8 in the Poisons Standard when used in respect of certain conditions, namely for the treatment of treatment-resistant depression.
To import products that contain a controlled substance (such as psilocybin), the importer requires both an exemption, approval or authority under the TG Act and a license and/or permit to import from the Office of Drug Control under the Customs (Prohibited Imports) Regulations 1956. Licenses and permits to import psilocybin are only granted by the Office of Drug Control where the use of the substance is permitted by the relevant state or territory under their respective medicines and poisons legislation and the use of the of psilocybin is to be prescribed by an Authorised Prescriber or for an authorised clinical trial.
Psyence will monitor the evolution of Australia’s regulations as they pertain to psilocybin and the conduct of clinical trials in Australia.
Regulatory Changes on the Horizon for Therapeutic Psychedelics
With the reintroduction of the Breakthrough Therapies Act in March 2023, there appears to be momentum to develop a legal-regulatory framework for therapeutic psychedelics. Congress also announced on November 17, 2022, the bipartisan Congressional Psychedelics Advancing Clinical Treatments Caucus (the PACT Caucus). The PACT Caucus will focus on exploring psychedelic research to alleviate the U.S. mental health crisis.
Headquarters and Operational Office
Psyence’s headquarters address is 121 Richmond Street West, Penthouse Suite 1300, Toronto, Ontario, M5H 2K1, Canada. The company has an operational office in South Africa at Unit A210 The Old Biscuit Mil, 373-375 Albert Road, Woodstock, Cape Town, 7925.
MANAGEMENT
The following sets forth certain information, as of the date of this prospectus, concerning the directors and executive officers of the Company. All executive officers are appointed by the Board to serve in their roles. Each executive officer is appointed for such term as may be prescribed by the Board or until a successor has been chosen and qualified or until such officer’s death, resignation or removal.
| Name | | Age | | Position(s) |
| Jody Aufrichtig | | 50 | | Chairman of the Board and Strategic Business Development Officer |
| Dr. Neil Maresky | | 59 | | Chief Executive Officer and Director |
| Warwick Corden-Lloyd | | 44 | | Chief Financial officer |
| Marc Balkin | | 49 | | Director |
| Christopher (Chris) Bull | | 55 | | Director |
| Dr. Seth Feuerstein | | 51 | | Director |
Executive Officers
Dr. Neil Maresky has served as the Company’s Chief Executive Officer since January 25, 2024 and Director since June 29, 2023. Dr. Maresky has also served as Parent’s chief executive officer and director since July 1, 2021. Dr. Maresky has more than 20 years of enterprise leadership and biopharmaceutical expertise and currently oversees the strategy and operations of Psyence. From 2010 to 2021, Dr. Maresky, spent more than a decade at AstraZeneca Canada as Vice President of Scientific Affairs. Dr. Maresky is a South African trained doctor. In Canada, he has held various executive leadership positions in “Big Pharma”, including leading research and development and driving scientific strategy at Bayer Pharmaceuticals (1998-2002) as well as Wyeth Pharmaceuticals (2002-2008), where he was interim President and general manager in 2008. In South Africa, Dr. Maresky was trained in emergency room medicine and cardiology, and practiced as a family physician. In the mid-1990s, Dr. Maresky emigrated to Canada and began his career in the pharmaceutical industry. During the course of his career, Dr. Maresky has positively impacted the health of millions of patients across Canada. With extensive experience and relationships with academic institutions, health authorities and decision-making bodies across Canada, Dr. Maresky has contributed to many innovative medical therapies and technologies, including over 50 approvals of new medicines and new indications. One of Dr. Maresky’s most recent achievements was the approval of the AstraZeneca Covid-19 vaccine by Health Canada. Dr. Maresky holds a Medical Degree M.B.,B.Ch.. from the University of Witwatersrand (1987).
Warwick Corden-Lloyd has served as the Chief Financial Officer of the Company since January 25, 2024. Mr. Corden-Lloyd has also served as Chief Financial Officer of Parent since May 21, 2020. Mr. Corden-Lloyd is a Chartered Accountant and Certified Project Manager. He has over 19 years of experience working in public accounting, consulting and listed financial services companies in the UK, US and South Africa. Mr. Corden-Lloyd has listed company financial and regulatory reporting experience in international and emerging markets. He has served as Chief Financial Officer and Company Secretary of Psyence Group Inc. (CSE: PSYG; OTCQB: PSYGF) since listing to date. From May 2020 to January 2021, Mr. Corden-Lloyd was the Corporate Finance Advisor and Chief Financial Officer of MindHealth Biomed Corp, the predecessor company prior to Parent. Mr. Corden-Lloyd was previously the Vice President of Operations and Finance at Canopy Growth Africa, (a wholly owned subsidiary of Canopy Growth Corporation (NYSE: CGC / TSX: WEED) from May 2019 to May 2020. Whilst at Canopy Growth, he oversaw the Finance, Legal, Supply Chain, Human Resources, Quality Assurance and Regulatory, Project Management and Country Manager divisions. Prior to that he was Head of Financial Accounting at Capitec Bank, South Africa’s largest customer retail bank, from February 2015 to May 2019 where he was responsible for managing the financial and regulatory reporting, budgeting and financial accounting for the bank. Mr. Corden-Lloyd received a Bachelor of Accounting from the University of Stellenbosch, South Africa in 2002, a Bachelor of Accounting Honours from the University of Natal, South Africa in 2003 and registered with the South African Institute of Chartered Accountants in 2006. He is also registered with The Institute of Chartered Accountants in England and Wales.
Jody Aufrichtig has served as Strategic Business Development Officer and Chairman of the Board since January 25, 2024, and a Director of Parent since May 21, 2020. He has served in the same roles at Parent since May 21, 2020. Mr. Aufrichtig is a chartered accountant and experienced entrepreneur with extensive experience in emerging markets. Mr. Aufrichtig is the founder of MindHealth Biomed Corp and has built multiple award-winning businesses and created substantial shareholder value in cannabis, commercial and residential property, private equity, tourism, leisure and other industries. Prior to founding MindHealth Biomed Corp, he was the Managing Director of Canopy Growth Africa (a wholly owned subsidiary of Canopy Growth Corporation (NYSE: CGC / TSX: WEED)) from May 2018 until he led a management buyout of the African operations in April 2020. Mr. Aufrichtig founded Daddy Cann Lesotho (Pty) Limited in July 2017 and was granted a license by the Ministry of Health (Lesotho) to cultivate, manufacture, supply, hold, import, export and transport cannabis. Daddy Cann Lesotho (Pty) Limited was subsequently acquired by Canopy Growth Corporation in May 2018. In 2000, Mr. Aufrichtig co-founded Indigo Properties, a business is focused on commercial and residential property, tourism and leisure. Mr. Aufrichtig holds a Bachelor of Accounting and a Bachelor of Accounting Honours from the University of Cape Town, South Africa and is registered with the South African Institute of Chartered Accountants.
Board of Directors
Marc Balkin has served as a director of the Company since January 25, 2024. He served as the Chief Executive Officer and served as a member of the board of directors of NCAC from March 2021 until January 25, 2024. Mr. Balkin is a founder of Balkin and Co, an advisory firm that has advised private equity firms and family offices on mergers, acquisitions and investments in Africa since 2015. Clients have included HP Bet (part of the family office of Dr. Hasso Plattner, a founder and current Chairman of SAP), Omidyar Network (part of the family office of Pierre Omidyar, the founder of eBay) and Rand Merchant Bank. Prior to founding Balkin and Co, Mr. Balkin was the Managing Partner of Hasso Plattner Ventures Africa, a Venture Fund in which Dr. Plattner was the key limited partner. Mr. Balkin also held responsibility for managing the Emerging Market portfolio of private equity and venture capital assets of Dr. Plattner’s family office. Mr. Balkin is currently a partner at DiGame, a growth fund focused on Africa and the Middle East in which the key investor is Abu Dhabi Investment Counsel (“ADIC”). Mr. Balkin represents DiGame on the board of direct-to-consumer asset manager 10X Investments. Since 2004, Mr. Balkin has served on and chaired a range of venture capital and private equity fund investment committees as the representative of the limited partners or investors. These include Enablis, First National Bank Vumela Fund, Telkom Future Makers and Alithea IDF. Between 2000 and 2007, Mr. Balkin was the founding partner of O2 Capital, a private equity fund manager for the Msele Nedventures Fund. The LPs in the fund included a range of development finance institutions such as Proparco (France), DEG (Germany) and IDC (South Africa) and the fund invested primarily in technology businesses in South Africa. Mr. Balkin obtained his BA in 1995 and his LLB in 1997 from University of Witwatersrand in Johannesburg.
Chris Bull has serve as a director of the Company since January 25, 2024 and has served as a strategic advisor of Parent since December 2022. Chris is a qualified chemical engineer, attorney, patent attorney and Certified Licensing Professional®. Over his thirty year career, Mr. Bull has been an investor, director, founder and advisor to a range of successful companies in Europe and North America with novel technologies in the fields of pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, food sciences, chemical processing, and extraction technologies. Mr. Bull has served as a Chairman and director of a venture capital firm (Knife Capital). Mr. Bull has also been recognized through receipt of a number of international awards, including IAM Strategy 300, IAM Patent 1000, IAM Licensing 250; Euromoney Expert Guides: World’s Leading Patent Attorneys; Chambers and Partners’ Global Guide to the World’s Leading Lawyers Legal 500 Guide to Outstanding Lawyers, in recognition of his skills in relation to the development and execution of venture capital investment, patent and intellectual property strategies for high-technology companies.
Dr. Seth Feuerstein has served as a director of the Company since January 25, 2024. Dr. Feuerstein has expertise across multiple areas of medicine including Suicide Prevention, Technology and Suicide, Telehealth, Social Media and Mental Health, Digital Medicine, Suicide, Digital Health, Digital Therapeutics, Healthcare Innovation, Emerging Medical Technologies, forensic psychiatry, technology transfer, technology investment, intellectual property and the intersection of technology, law and medicine. He is a founding board member of the Center for Biomedical and Interventional Technology at Yale and Executive Director of the Center for Digital Health, Innovation and Excellence. He has been teaching at the Yale School of Medicine, Department of Psychiatry, since 2004 and is the faculty advisor for Innovation in Healthcare at the medical school. He works across multiple sectors in healthcare including health insurance, healthcare startups, healthcare investing, clinical care delivery innovation and early stage emerging medical technologies. He is the founder and CEO of Oui Therapeutics, Inc. SINCE 2019, which is developing a prescription digital therapeutic for suicide attempt reduction. Dr. Feuerstein has been appointed senior advisor/Highly Qualified Advisor (HQE) for the Department of Defense, advising on behavioral health innovation, since June 2019. From 2014 to August 2018, he was the chief medical and innovation officer at Magellan Healthcare. He has also co-founded and/or held leadership roles in a number of biotechnology and healthcare companies. Dr. Feuerstein received his Bachelor of Science from Cornell University, a J.D. from New York University School of Law, and an M.D. from New York University School of Medicine. We believe that Dr. Feuerstein is well-qualified to serve on the Company's Board of Directors due to his extensive experience in the fields of psychiatry and biotechnology.
Number and Terms of Office of Officers and Directors
Our officers are appointed by the board of directors. Our board of directors is authorized to appoint officers as it deems appropriate. Our Board currently consists of 5 members, and pursuant to our Articles of Incorporation, may consist of a maximum of 10 members and a minimum of 3 members.
Corporate Governance
We have structured our corporate governance in a manner we believe will closely align our interests with those of our shareholders. Notable features of this corporate governance include:
| · | we have a majority of independent directors on our Board, and our independent directors will meet regularly in executive sessions without the presence of our corporate officers or non-independent directors; |
| · | we have an audit committee that consists of three independent directors, at least one of whom qualifies as an “audit committee financial expert” as defined by the SEC; and |
| · | we have implemented a range of other corporate governance practices, including implementing a robust director education program. |
Independence of our Board of Directors
Three of our five directors are be independent directors and our Board has an independent audit committee. The Board determines which members are “independent.” The Board has determined that each of Messrs. Balkin, Bull and Feuerstein is “independent” as such term is defined under the Exchange Act and the rules of Nasdaq.
Committees of the Board of Directors
The Board directs the management of our business and affairs and conducts its business through meetings of the Board and standing committees. The Company has audit, compensation and nominating and governance committees, each of which operates under a written charter.
In addition, from time to time, special committees may be established under the direction of the Board when the Board deems it necessary or advisable to address specific issues. Current copies of the Company’s committee charters will be posted on the Company’s website, as required by applicable SEC and Nasdaq rules. The information on or available through any of such website is not deemed incorporated in this prospectus and does not form part of this prospectus.
Audit Committee
The Company’s Audit Committee consists of Marc Balkin, Chris Bull and Dr. Seth Feuerstein. Mr. Balkin is an “audit committee financial expert” within the meaning of SEC regulations. Mr. Balkin serves as the chairperson of the audit committee. Each member of the Audit Committee can read and understand fundamental financial statements in accordance with applicable requirements. In arriving at these determinations, the Board will examine each Audit Committee member’s scope of experience and the nature of their employment.
The Company has adopted an audit committee charter, which details the principal functions of the Audit Committee, including:
| · | evaluating the independence and performance of, and assesses the qualifications of, our independent auditor, and engages such independent auditor; |
| · | approving the plan and fees for the annual audit, quarterly reviews, tax and other audit-related services, and approves in advance any non-audit service to be provided by the independent auditor; |
| · | monitoring the independence of the independent auditor and the rotation of partners of the independent auditor on our engagement team as required by law; |
| · | reviewing the financial statements to be included in our Annual Report on Form 20-F and Current Reports on Form 6-K and reviews with management and the independent auditors the results of the annual audit and reviews of our quarterly financial statements; |
| · | overseeing all aspects of our systems of internal accounting control and corporate governance functions on behalf of the board; |
| · | reviewing and approving in advance any proposed related-party transactions and report to the full Board on any approved transactions; and |
| · | providing oversight assistance in connection with legal, ethical and risk management compliance programs established by management and our board of directors, including Sarbanes-Oxley Act implementation, and makes recommendations to our board of directors regarding corporate governance issues and policy decisions. |
Compensation Committee
The compensation committee consists of Marc Balkin, Chris Bull and Dr. Seth Feuerstein. The chair of the compensation committee is Chris Bull.
The Compensation Committee is governed by a written charter approved by the Board. The charter of the Compensation Committee permits the Compensation Committee to engage outside consultants and to consult with human resources consultants when appropriate to assist in carrying out its responsibilities. Compensation consultants have not been engaged by the Company to recommend or assist in determining the amount or form of compensation for any current executive officers or directors of the Company. The Compensation Committee may also obtain advice and assistance from internal or external legal, accounting, or other advisers selected by the Compensation Committee. Our Compensation Committee is responsible for overseeing and making recommendations to our board of our directors regarding the salaries and other compensation of our executive officers and general employees and providing assistance and recommendations with respect to our compensation policies and practices.
Nominating and Corporate Governance Committee
The nominating and corporate governance committee consists of Marc Balkin, Chris Bull and Dr. Seth Feuerstein. The chair of the nominating and corporate governance committee is Marc Balkin.
The Nominating and Corporate Governance Committee is governed by a written charter approved by the Board. Our Nominating and Corporate Governance Committee is responsible for identifying and proposing new potential director nominees to the Board for consideration and reviewing our corporate governance policies.
Code of Ethics
We have adopted a code of ethics that applies to all of our executive officers, directors and employees in accordance with the rules of the Nasdaq and the SEC. The code of ethics codifies the business and ethical principles that govern all aspects of our business. You will be able to review these documents by accessing our public filings at the SEC’s website at www.sec.gov.
Corporate Governance Practices and Foreign Private Issuer Status
The Company is a foreign private issuer within the meaning of the rules under the Exchange Act and, as such, the Company is permitted to follow the corporate governance practices of its home country in lieu of the corporate governance standards of Nasdaq applicable to U.S. domestic companies. For example, the Company is not required to file periodic reports and financial statements with the SEC as frequently or within the same time frames as U.S. companies with securities registered under the Exchange Act, although it may elect to file certain periodic reports and financial statements with the SEC on a voluntary basis on the forms used by U.S. domestic issuers. The Company is not required to comply with Regulation FD, which imposes restrictions on the selective disclosure of material information to shareholders. In addition, the Company’s officers, directors and principal shareholders are exempt from the reporting and short-swing profit recovery provisions of Section 16 of the Exchange Act and the rules under the Exchange Act with respect to their purchases and sales of the Company’s securities.
In addition, as a “foreign private issuer”, the Company is permitted to follow certain home-country corporate governance practices in lieu of certain Nasdaq requirements. A foreign private issuer must disclose in its annual reports filed with the SEC each Nasdaq requirement with which it does not comply followed by a description of its applicable home country practice. The Company currently intends to follow some, but not all, of the corporate governance requirements of Nasdaq. With respect to the corporate governance requirements of the Company that it does follow, the Company cannot give assurances that it will continue to follow such corporate governance requirements in the future, and may therefore in the future, rely on available Nasdaq exemptions that would allow the Company to follow its home country practice. Unlike the requirements of Nasdaq, the Company is not required, under the corporate governance practice and requirements in Ontario, to have its board consist of a majority of independent directors, nor is the Company required to have a compensation committee, a nominating or a corporate governance committee consisting entirely of independent directors, or to have regularly scheduled executive sessions with only independent directors each year. Such home country practices may afford less protection to holders of Common Shares.
The Company intends to rely on this “foreign private issuer exemption” with respect to the quorum requirement for shareholder meetings and with respect to Nasdaq shareholder approval rules. Whereas under the corporate governance rules of Nasdaq, a quorum requires the presence, in person or by proxy, of holders of at least 331∕3% of the total issued and outstanding voting power of our shares at each general meeting, pursuant to our bylaws, the quorum required for a general meeting will consist of at least two shareholders present in person or by proxy who hold or represent at least 25% of the total outstanding voting power of our shares.
Limitation on Liability and Indemnification of Officers and Directors
Section 136 of the Business Corporations Act (Ontario) (the “OBCA”) governs the indemnification of directors and officers of a corporation and provides that a corporation may indemnify a director or officer of the corporation, a former director or officer of the corporation or another individual who acts or acted at the corporation’s request as a director or officer, or an individual acting in a similar capacity, of another entity, against all costs, charges and expenses, including an amount paid to settle an action or satisfy a judgment, reasonably incurred by the individual in respect of any civil, criminal, administrative, investigative or other proceeding in which the individual is involved because of that association with the corporation or other entity. A corporation shall not indemnify an individual unless the individual acted honestly and in good faith with a view to the best interests of the corporation or, as the case may be, to the best interests of the other entity for which the individual acted as a director or officer or in a similar capacity at the corporation’s request. If the matter is a criminal or administrative action or proceeding that is enforced by a monetary penalty, a corporation shall not indemnify an individual unless the individual had reasonable grounds for believing that the individual’s conduct was lawful.
The Company has entered into indemnification agreements with each director and officer of the Company in accordance with the provisions of the OBCA cited above, which are incorporated into such agreements. Under the indemnification agreements the termination of any proceedings by any judgment, order, settlement, conviction or the entering of a nolle prosequi does not, by itself, create a presumption that the individual did not act honestly and in good faith and with a view to the best interests of the corporation or that the individual had reasonable cause to believe that his or her conduct was unlawful. To the extent permissible by law, there shall be a presumption that the individual acted honestly and in good faith and with a view to the best interests of the corporation and that the individual had no reasonable cause to believe that his or her conduct was unlawful in the absence of fraud unless a question of law is involved.
Non-Employee Director Compensation
In connection with the consummation of the Business Combination, the Board has adopted a non-employee director compensation policy designed to align compensation with the Company’s business objectives and the creation of shareholder value, while enabling the Company to attract and retain directors to contribute to the Company’s long-term success.
Cash Compensation
Each non-employee director will be entitled to compensation consisting of cash and/or stock, as to be determined by the Company’s compensation committee following the Closing. In addition, the Company’s policy is to reimburse directors for reasonable and necessary out-of-pocket expenses incurred in connection with attending board and committee meetings or performing other services in their capacities as directors.
Equity Compensation
Following the closing of the Business Combination, the compensation committee of the Company intends to review and implement a non-employee director cash and equity compensation policy, which will include initial and annual equity awards.
Except as disclosed in the section entitled “— Employment Agreements and Indemnification Agreements” below, Psyence is not party to any agreements with its executive officers and directors that provide for benefits upon termination of employment.
For information regarding share options granted to Psyence’s directors and executive officers, see the section entitled “— Equity Incentive Plans” below.
Employment Agreements and Indemnification Agreements
Each of Psyence’s executive officers is party to an employment agreement with Parent. The employment of the executive officers under these employment agreements is for an indefinite period, but may be terminated by the employer for cause at any time without advance notice or for any other reason by giving prior written notice or by paying specified amounts of compensation, and the executive officer may terminate his or her employment at any time by giving the employer prior written notice. The employment agreements with the executive officers also include confidentiality and non-disclosure restrictions and non-competition and non-solicitation restrictions that apply during employment for certain periods following termination of employment. For more information, see section entitled “Executive and Director Compensation – Employment, Consulting and Management Agreements.”
The Company has entered into indemnification agreements with each of its officers and directors. Under these agreements, the Company may agree to indemnify its directors against certain liabilities and expenses incurred by such persons in connection with claims made by reason of their being a director of the Company.
Equity Incentive Plans
The 2023 Equity Incentive Plan
The Company has adopted the Psyence Biomedical Ltd. 2023 Equity Incentive Plan, which is referred to herein as the “Incentive Plan.” The following is a summary of the material features of the Incentive Plan.
Purpose
The purpose of the Incentive Plan is to enhance the ability of the Company to attract, retain, and motivate persons who make (or are expected to make) important contributions to the Company by providing these individuals with equity ownership opportunities and/or equity-linked compensatory opportunities that are intended to motivate high levels of performance and align the interests of directors, employees, and consultants with those of the Company’s shareholders.
Eligibility
Persons eligible to participate in the Incentive Plan are employees, non-employee directors, and consultants of the Company and its subsidiaries as selected from time to time by the plan administrator in its discretion, including prospective employees, non-employee directors and consultants. Any awards granted to such a prospect before the individual’s start date may not become vested or exercisable, and no shares may be issued to such individual, before the date the individual first commences performance of services with the Company or its subsidiaries. As of the date of this prospectus, approximately 11 individuals will be eligible to participate in the Incentive Plan, which includes approximately 2 officers, 0 employees who are not officers, 4 non-employee directors, and 5 consultants.
Administration
The Incentive Plan will be administered by the Board, the Compensation Committee of the Board, or such other similar committee pursuant to the terms of the Incentive Plan. The plan administrator, which initially will be the Compensation Committee of the Board, will have full power to select, from among the individuals eligible for awards, the individuals to whom awards will be granted, to make any combination of awards to participants, and to determine the specific terms and conditions of each award, subject to the provisions of the Incentive Plan. The plan administrator may delegate to one or more officers of the Company, the authority to grant awards to individuals who are not subject to the reporting and other provisions of Section 16 of the Exchange Act.
Share Reserve
The number of the Common Shares that may be issued under the Incentive Plan is equal to 15% of the aggregate number of the Common Shares issued and outstanding immediately after the Closing (calculated on a fully-diluted basis), or 2,008,599 Common Shares. All of the shares initially available under the Incentive Plan may be issued upon the exercise of incentive stock options.
The number of shares available for issuance under the Incentive Plan also will include an automatic annual increase, or the evergreen feature, on the first day of each calendar year, beginning January 1, 2025 and ceasing as described below, equal to the lesser of:
| · | a number of the Common Shares equal to 1% of the aggregate number of the Common Shares issued and outstanding as of December 31 of the immediately preceding calendar year; or |
| · | such number of the Common Shares as the plan administrator may determine. |
Shares issuable under the Incentive Plan may be authorized, but unissued, or reacquired the Common Shares.
Shares underlying any awards under the Incentive Plan that are forfeited, cancelled, held back upon exercise of a share option or settlement of an award to cover the exercise price or tax withholding satisfied without the issuance of the Common Shares or otherwise terminated (other than by exercise) will be added back to the shares available for issuance under the Incentive Plan and, to the extent permitted under
Section 422 of the Code and the Treasury Regulations promulgated thereunder, the shares that may be issued as incentive stock options.
Types of Awards
The Incentive Plan provides for the grant of share options, share appreciation rights, restricted shares, restricted share units, and other stock-based awards (collectively, “awards”). Unless otherwise set forth in an individual award agreement, each award shall vest over a three (3) year period, with one-third (1/3) of the award vesting on the first annual anniversary of the date of grant and the remaining portion of the award vesting annually thereafter.
Share Options. The Incentive Plan permits the granting of both options intended to qualify as incentive stock options under Section 422 of the Code and share options that do not so qualify. Share options granted under the Incentive Plan will be nonqualified options if they fail to qualify as incentive stock options or exceed the annual limit on incentive stock options. Incentive stock options may only be granted to employees of the Company and its subsidiaries. Nonqualified options may be granted to any persons eligible to receive awards under the Incentive Plan.
The exercise price of each share option will be determined by the plan administrator, but such exercise price may not be less than 100% of the fair market value of one the Common Share on the date of grant (which shall be the volume weighted average trading price during the thirty (30) preceding days) or, in the case of an incentive stock option granted to a 10% or greater shareholder, 110% of such share’s fair market value. The term of each share option will be fixed by the plan administrator and may not exceed ten (10) years from the date of grant (or five (5) years for an incentive stock option granted to a 10% or greater shareholder). The plan administrator will determine at what time or times each share option may be exercised, including the ability to accelerate the vesting of such share options.
Upon exercise of a share option, the exercise price must be paid in full either in cash, check or, surrender of other the Common Shares which meet the conditions established by the plan administrator to avoid adverse accounting consequences to the Company. Subject to applicable law and approval of the plan administrator, the exercise price may also be made by means of a broker-assisted cashless exercise. In addition, the plan administrator may permit nonqualified options to be exercised using a “net exercise” arrangement that reduces the number of shares issued to the optionee by the largest whole number of shares with fair market value that does not exceed the aggregate exercise price.
Share Appreciation Rights. The plan administrator may award share appreciation rights subject to such conditions and restrictions as it may determine. Share appreciation rights entitle the recipient to the Common Shares or cash, equal to the value of the appreciation in the Company’s share price over the exercise price, as set by the plan administrator. The term of each share appreciation right will be fixed by the plan administrator and may not exceed ten years from the date of grant. The plan administrator will determine at what time or times each share appreciation right may be exercised, including the ability to accelerate the vesting of such share appreciation rights.
Restricted Shares. A restricted share award is an award of the Common Shares that vests in accordance with the terms and conditions established by the plan administrator. The plan administrator will determine the persons to whom grants of restricted share awards are made, the number of restricted shares to be awarded, the price (if any) to be paid for the restricted shares, the time or times within which restricted share awards may be subject to forfeiture, the vesting schedule and rights to acceleration thereof, and all other terms and conditions of restricted share awards. Unless otherwise provided in the applicable award agreement, a participant generally will have the rights and privileges of a shareholder as to such restricted shares, including without limitation the right to vote such restricted shares and the right to receive dividends, if applicable.
Restricted Share Units. Restricted share units are the right to receive the Common Shares at a future date in accordance with the terms of such grant upon the attainment of certain conditions specified by the plan administrator. Restrictions or conditions could include, but are not limited to, the attainment of performance goals, continuous service with the Company or its subsidiaries, the passage of time or other restrictions or conditions. The plan administrator determines the persons to whom grants of restricted share units are made, the number of restricted share units to be awarded, the time or times within which awards of restricted share units may be subject to forfeiture, the vesting schedule, and rights to acceleration thereof, and all other terms and conditions of the restricted share unit awards. The value of the restricted share units may be paid in the Common Shares, cash, other securities, other property, or a combination of the foregoing, as determined by the plan administrator.
The holders of restricted share units will have no voting rights. Prior to settlement or forfeiture, restricted share units awarded under the Incentive Plan may, at the plan administrator’s discretion, provide for a right to dividend equivalents. Such right entitles the holder to be credited with an amount equal to all dividends paid on one the Common Share while each restricted share unit is outstanding. Dividend equivalents may be converted into additional restricted share units. Settlement of dividend equivalents may be made in the form of cash, the Common Shares, other securities, other property, or a combination of the foregoing. Prior to distribution, any dividend equivalents shall be subject to the same conditions and restrictions as the restricted share units to which they are payable.
Other Share-Based Awards. Other share-based awards may be granted either alone, in addition to, or in tandem with, other awards granted under the Incentive Plan and/or cash awards made outside of the Incentive Plan. The plan administrator shall have authority to determine the persons to whom and the time or times at which other share-based awards will be made, the amount of such other share-based awards, and all other conditions, including any dividend and/or voting rights.
Prohibition on Repricing
Except for an adjustment pursuant to the terms of the Incentive Plan or a repricing approved by shareholders, in no case may the plan administrator (i) amend an outstanding share option or share appreciation right to reduce the exercise price of the award, (ii) cancel, exchange, or surrender an outstanding share option or share appreciation right in exchange for cash or other awards for the purpose of repricing the award, or (iii) cancel, exchange, or surrender an outstanding share option or share appreciation right in exchange for a share option or share appreciation right with an exercise price that is less than the exercise price of the original award.
Tax Withholding
Participants in the Incentive Plan are responsible for the payment of any federal, state, or local taxes that the Company or its subsidiaries are required by law to withhold upon the exercise of share options or share appreciation rights or vesting of other awards. The plan administrator may cause any tax withholding obligation of the Company or its subsidiaries to be satisfied, in whole or in part, by the applicable entity withholding from the Common Shares to be issued pursuant to an award a number of shares with an aggregate fair market value that would satisfy the withholding amount due. The plan administrator may also require any tax withholding obligation of the Company or its subsidiaries to be satisfied, in whole or in part, by an arrangement whereby a certain number of the Common Shares issued pursuant to any award are immediately sold and proceeds from such sale are remitted to the Company or its subsidiaries in an amount that would satisfy the withholding amount due.
Equitable Adjustments
In the event of a merger, consolidation, recapitalization, share split, reverse share split, reorganization, split-up, spin-off, combination, repurchase or other change in corporate structure affecting the Common Shares, the maximum number and kind of shares reserved for issuance or with respect to which awards
may be granted under the Incentive Plan will be adjusted to reflect such event, and the plan administrator will make such adjustments as it deems appropriate and equitable in the number, kind, and exercise price of the Common Shares covered by outstanding awards made under the Incentive Plan.
Change in Control
In the event of any proposed change in control (as defined in the Incentive Plan), the plan administrator will take any action as it deems appropriate, which action may include, without limitation, the following: (i) the continuation of any award, if the Company is the surviving corporation; (ii) the assumption of any award by the surviving corporation or its parent or subsidiary; (iii) the substitution by the surviving corporation or its parent or subsidiary of equivalent awards; (iv) accelerated vesting of the award, with all performance objectives and other vesting criteria deemed achieved at targeted levels, and a limited period during which to exercise the award prior to closing of the change in control, or (v) settlement of any award for the change in control price (less, to the extent applicable, the per share exercise price). Unless determined otherwise by the plan administrator, in the event that the successor corporation refuses to assume or substitute for the award, a participant shall fully vest in and have the right to exercise the award as to all the Common Shares covered by the award, including those that would not otherwise be vested or exercisable, all applicable restrictions will lapse, and all performance objectives and other vesting criteria will be deemed achieved at targeted levels.
Transferability of Awards
Unless determined otherwise by the plan administrator, an award may not be sold, pledged, assigned, hypothecated, transferred, or disposed of in any manner, except to a participant’s estate or legal representative, and may be exercised, during the lifetime of the participant, only by the participant. If the plan administrator makes an award transferable, such award will contain such additional terms and conditions as the plan administrator deems appropriate.
Term
The Incentive Plan became effective when adopted by the Board, and, unless terminated earlier, the Incentive Plan will continue in effect for a term of ten (10) years.
Amendment and Termination
The Board may amend or terminate the Incentive Plan at any time. Any such termination will not affect outstanding awards. No amendment or termination of the Incentive Plan will materially impair the rights of any participant, unless mutually agreed otherwise between the participant and the Company. Approval of the shareholders shall be required for any amendment, where required by applicable law, as well as (i) to increase the number of shares available for issuance under the Incentive Plan and (ii) to change the persons or class of persons eligible to receive awards under the Incentive Plan.
Form S-8
The Company intends to file with the SEC a registration statement on Form F-8 covering the Common Shares issuable under the Incentive Plan.
Material United States Federal Income Tax Considerations
The following is a general summary under current law of the material U.S. federal income tax considerations related to awards and certain transactions under the Incentive Plan, based upon the current provisions of the Code and Treasury Regulations promulgated thereunder. This summary deals with the general U.S. federal income tax principles that apply and is provided only for general information. It does not describe all U.S. federal tax consequences under the Incentive Plan, nor does it describe state, local, or foreign income tax consequences or employment tax consequences. The rules governing the tax treatment of such awards are quite technical, so the following discussion of tax consequences is necessarily general in nature and is not complete. In addition, statutory provisions are subject to change, as are their interpretations, and their application may vary in individual circumstances. This summary is not intended as tax advice to participants, who should consult their own tax advisors.
The Incentive Plan is not qualified under the provisions of Section 401(a) of the Code and is not subject to any of the provisions of the U.S. Employee Retirement Income Security Act of 1974, as amended.
The ability of the Company or its subsidiaries to realize the benefit of any tax deductions described below depends on generation of taxable income as well as the requirement of reasonableness and the satisfaction of tax reporting obligations.
Incentive Stock Options. No taxable income is generally realized by the optionee upon the grant or exercise of an incentive stock option. If the Common Shares issued to an optionee pursuant to the exercise of an incentive stock option are sold or transferred after two years from the date of grant and after one year from the date of exercise, then generally (i) upon sale of such shares, any amount realized in excess of the option exercise price (the amount paid for the shares) will be taxed to the optionee as a long- term capital gain, and any loss sustained will be a long-term capital loss, and (ii) neither the Company nor its subsidiaries will be entitled to any deduction for U.S. federal income tax purposes; provided that such incentive stock option otherwise meets all of the technical requirements of an incentive stock option. The exercise of an incentive stock option will give rise to an item of tax preference that may result in alternative minimum tax liability for the optionee.
If the Common Shares acquired upon the exercise of an incentive stock option are disposed of prior to the expiration of the two-year and one-year holding periods described above (a “disqualifying disposition”), generally (i) the optionee will realize ordinary income in the year of disposition in an amount equal to the excess (if any) of the fair market value of the Common Shares at exercise (or, if less, the amount realized on a sale of such the Common Shares) over the option exercise price thereof, and (i) the Company or its subsidiaries will be entitled to deduct such amount. Special rules will apply where all or a portion of the exercise price of the incentive stock option is paid by tendering the Common Shares.
If an incentive stock option is exercised at a time when it no longer qualifies for the tax treatment described above, the share option is treated as a nonqualified option. Generally, an incentive stock option will not be eligible for the tax treatment described above if it is exercised more than three months following termination of employment (or one year, in the case of termination of employment by reason of disability). In the case of termination of employment by reason of death, the three-month rule does not apply.
Nonqualified Options. No income is generally realized by the optionee at the time a nonqualified option is granted. Generally, (i) at exercise, ordinary income is realized by the optionee in an amount equal to the difference between the option exercise price and the fair market value of the Common Shares issued on the date of exercise, and the Company or its subsidiaries receive a tax deduction for the same amount, and (ii) at disposition, appreciation or depreciation after the date of exercise is treated as either short-term or long- term capital gain or loss depending on how long the Common Shares have been held. Special rules will apply where all or a portion of the exercise price of the nonqualified option is paid by tendering the Common Shares. Upon exercise, the optionee will also be subject to Social Security taxes on the excess of the fair market value of the Common Shares over the exercise price of the share option.
Share Appreciation Rights, Restricted Shares, Restricted Share Units, and Other Share-Based Awards. The current U.S. federal income tax consequences of other awards authorized under the Incentive Plan generally follow certain basic patterns: (i) share appreciation rights are taxed and deductible in substantially the same manner as nonqualified options; (ii) nontransferable restricted shares subject to a substantial risk of forfeiture result in income recognition equal to the excess of the fair market value of the Common Shares over the price paid, if any, only at the time the restrictions lapse (unless the recipient elects to accelerate recognition as of the date of grant through a Code Section 83(b) election); and (iii) restricted share units, dividend equivalents, and other share or cash based awards are generally subject to tax at the time of payment. the Company or its subsidiaries generally should be entitled to a U.S. federal income tax deduction in an amount equal to the ordinary income recognized by the participant at the time the participant recognizes such income.
The participant’s basis for the determination of gain or loss upon the subsequent disposition of the Common Shares acquired from a share appreciation right, restricted share award, restricted share unit, or other share-based award will be the amount paid for such shares plus any ordinary income recognized when the shares were originally delivered, and the participant’s capital gain holding period for those shares will begin on the day after they are transferred to the participant.
Parachute Payments. The vesting of any portion of an award that is accelerated due to the occurrence of a change in control (such as a sale event) may cause all or a portion of the payments with respect to such accelerated awards to be treated as “parachute payments” as defined in the Code. Any such parachute payments may be non-deductible to either the Company or its subsidiaries, in whole or in part, and may subject the recipient to a non-deductible 20% U.S. federal excise tax on all or a portion of such payment (in addition to other taxes ordinarily payable).
Section 409A. The foregoing description assumes that Section 409A of the Code does not apply to an award under the Incentive Plan. In general, share options and share appreciation rights are exempt from Section 409A if the exercise price per share is at least equal to the fair market value per share of the underlying share at the time the share option or share appreciation right was granted. Restricted share awards are not generally subject to Section 409A. Restricted share units are subject to Section 409A unless they are settled within two and one-half months after the end of the later of (1) the end of the Company’s fiscal year in which vesting occurs or (2) the end of the calendar year in which vesting occurs. If an award is subject to Section 409A and the provisions for the exercise or settlement of that award do not comply with Section 409A, then the participant would be required to recognize ordinary income whenever a portion of the award vested (regardless of whether it had been exercised or settled). This amount would also be subject to a 20% U.S. federal tax and premium interest in addition to the U.S. federal income tax at the participant’s usual marginal rate for ordinary income.
New Plan Benefits
No awards have been previously granted under the Incentive Plan. The awards that are to be granted to any participant or group of participants are indeterminable at the date of this prospectus because participation and the types of awards that may be granted under the Incentive Plan are subject to the discretion of the plan administrator. Consequently, no new plan benefits table is included in this prospectus.
EXECUTIVE AND DIRECTOR COMPENSATION
Unless the context otherwise requires, any reference in this section of this prospectus to the “Company,” “we,” “us,” “our,” or “Psyence” refers to Psyence Biomed Corp. and its consolidated subsidiaries prior to the consummation of the Business Combination and to Psyence Biomedical Ltd. and its consolidated subsidiaries following the Business Combination.
The following tables and discussions relate to the compensation paid to or earned by our executive officers and directors who were serving during the financial year ended March 31, 2023.
Dr. Neil Maresky currently serves as chief executive officer of Parent and the Company. Warwick Corden-Lloyd currently serves as chief financial officer of Parent and the Company. Jody Aufrichtig currently serves as Director and Executive Chairman of Psyence Biomed Corp. and the Company’s Director and Strategic Business Development Officer. Dr. Maresky, Mr. Corden-Lloyd and Mr. Aufrichtig are referred to collectively in this information statement as our “named executive officers.”
Prior to the Business Combination, Psyence was part of the Psyence Group and not an independent company and, as such, the historical compensation shown below was determined by Parent and the Parent Compensation Committee. Following the Business Combination, compensation arrangements for the Company’s executive officers will be determined based on the compensation policies, programs and procedures to be established by the compensation committee Accordingly, the amounts and forms of compensation reported below are not necessarily indicative of the compensation that our named executive officers will receive following the Business Combination, which could be higher or lower than the amounts shown below.
Summary Compensation Table
The following table summarizes the compensation awarded to, earned by, or paid to our named executive officers for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2023:
| Name and principal position(1) | | Year | | Salary
(US$) | | Bonus
(US$) | | Option
awards
(US$)(2) | | Stock
Awards
(US$)(3) | | Nonequity
incentive plan
compensation
(US$) | | All other
compensation
(US$) | | Total
(US$) | |
Neil Maresky
(Chief Executive Officer) | | 2023 | | 256,997 | | — | | 39,218 | | 126,231 | | — | | — | | 442,446 | |
Jody Aufrichtig
(Executive Chairman) | | 2023 | | 113,381 | | — | | 39,218 | | 126,231 | | — | | — | | 278,830 | |
Warwick Corden Lloyd
(Chief Financial Officer) | | 2023 | | 113,381 | | — | | 14,661 | | 58,845 | | — | | — | | 186,887 | |
| (1) | The average exchange rate used to convert amounts in this table from, Canadian dollars to USD are reported above based on a rate of 1.3230. |
| (2) | The amounts reported in the “Option awards” column represent the aggregate grant date fair value of the stock options granted to the named executive officers during 2023 computed in accordance with IFRS. The option awards value was calculated using the Black-Scholes valuation model. The options vest as follows: 50% on March 31, 2023 and 50% on September 30, 2023. Note that the amounts reported in these columns reflect the accounting cost for these stock options and do not correspond to the actual economic value that may be received by the named executive officers from the stock options. |
| (3) | The amounts reported in the “Stock awards” column represent the aggregate grant date fair value of the restricted stock units (RSUs) granted to the named executive officers during 2023 computed in accordance with IFRS. The stock awards value was based on the share price on the date of grant of RSUs. The RSUs vest as follows: 33.33% on March 31, 2024, 33.33% on March 31, 2025 and 33.34% on March 31, 2026. Note that the amounts reported in these columns reflect the accounting cost for these RSUs and do not correspond to the actual economic value that may be received by the named executive officers from the stock RSUs. |
Other than as set forth in the foregoing table, the named executive officers and directors have not received, during the most recently completed financial year, compensation pursuant to any standard arrangement for the compensation of directors for their services in their capacity as directors, including any additional amounts payable for committee participation or special assignments, any other arrangement, in addition to, or in lieu of, any standard arrangement, for the compensation of directors in their capacity as directors, or any arrangement for the compensation of directors for services as consultants or experts.
Share Ownership
Outstanding Equity Awards at Fiscal Year-End
The following table sets forth information regarding equity awards held by our named executive officers as of March 31, 2023.
| Name | | Number of
Securities
Underlying
Unexercised
Options ((#)
Exercisable) | | | Number of
Securities
Underlying
Unexercised
Options (#)
Unexercisable | | | Option
Exercise
Price
($)/share | | | Option
Expiration
Date | | | Number of
Shares or
Units of
Stock That
Have Not
Vested
(#) | | | Market
Value of
Shares or
Units of
Stock That
Have Not
Vested
($) | |
| Neil Maresky | | | 267,500 | | | 267,500 | | | 0.10 | | | 3/31/2028 | | | — | | | — | |
| | | | 612,000 | | | 1,188,000 | | | 0.22 | | | 6/30/2026 | | | — | | | — | |
| | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 1,000,000 | | | 96,061 | |
| | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 247,900 | | | 23,814 | |
| | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 647,141 | | | 62,165 | |
| Jody Aufrichtig | | | 267,500 | | | 267,500 | | | 0.10 | | | 3/31/2028 | | | — | | | — | |
| | | | 643,333 | | | 321,667 | | | 0.22 | | | 12/31/2025 | | | — | | | — | |
| | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 1,000,000 | | | 96,061 | |
| | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 247,900 | | | 23,814 | |
| Warwick Corden-Lloyd | | | 100,000 | | | 100,000 | | | 0.10 | | | 3/31/2028 | | | — | | | — | |
| | | | 300,000 | | | 150,000 | | | 0.22 | | | 12/31/2025 | | | — | | | — | |
| | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 445,000 | | | 42,747 | |
| | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 134,000 | | | 12,872 | |
The exchange rate used to convert the option exercise price from Canadian $ to USD is 1.3533. The market value of the restricted stock unit award is based on the closing price of Canadian $0.13 per share for Parent’s common stock on March 31, 2023.
2021 Stock Option Plan
Parent’s stock option plan (the “Stock Option Plan”) was adopted on November 9, 2021 and was confirmed by the Parent ’s shareholders on December 9, 2021.
The purpose of the Stock Option Plan is to provide Parent with a share-related mechanism to enable Parent to attract, retain and motivate qualified directors, officers, employees and other service providers, to reward directors, officers, employees and other service providers for their contribution toward the long-term goals of Parent, and to enable and encourage such individuals to acquire shares of Parent as long-term investments.
The Stock Option Plan is a “rolling” plan that limits the number of stock options that may be granted pursuant to the plan to a number equal to 10% of Parent’s issued and outstanding common shares, calculated at the date of the stock option grant. Share incentives granted under any share incentive plans of Parent will not have a bearing on the number of shares that may be subject to option under the Stock Option Plan.
Eligible Persons. Only executives (including directors and officers) employees, and consultants of Parent or its subsidiaries are eligible to receive stock options under the Stock Option Plan.
Limitations. The Stock Option Plan contains the following limitations:
(a) the maximum number of shares which may be reserved for issuance to any one person under the Stock Option Plan must not exceed five percent (5%) of the issued shares (determined at the date the option was granted) in a twelve (12) month period, unless Parent first obtains any required disinterested shareholder approval of this plan;
(b) the number of shares granted to any one Consultant (as defined in the Stock Option Plan) under the Stock Option Plan together with all other security based compensation arrangements in a twelve (12) month period must not exceed two percent (2%) of the issued shares of Parent;
(c) the aggregate number of options granted to an option holder providing services that include investor relations activities under the Stock Option Plan must not exceed two percent (2%) of the issued shares of Parent in any twelve (12) month period, calculated at the date the option was granted; and
(d) the aggregate number of shares (i) issued to insiders under the Stock Option Plan within a twelve-month period, and (ii) issuable to insiders of the Company at any time under the plan, together with all of Parent’s other security based compensation arrangements, shall not exceed ten percent (10%) of the total number of shares then outstanding, unless Parent has first obtained disinterested shareholder approval of the plan, pursuant to applicable law or stock exchange rules (but only if the law or stock exchange rules require such approval).
Term of the Options. The expiry date of an option must be no later than the tenth anniversary of the grant date. Any shares subject to an option which for any reason is cancelled or terminated without having been exercised shall again be available for grants under the Stock Option Plan.
Exercise Price. The exercise price at which an option holder may purchase a share upon exercising their option shall be determined by the price determined by Parent and shall be set out in the option agreement.
Additional provisions included in the Stock Option Plan are as follows:
| | · | A provision permitting the personal representative of an option holder who has become disabled to exercise the option on or before the date which is the earlier of one year following the termination of employment, engagement or appointment as a director or officer and the applicable expiry date; |
| | · | A provision permitting the personal representative of an option holder who ceased to be employed by Parent by reason of a disability and who dies within six months after their termination to exercise the option on or before the date which is the earlier of one year following the death of such option holder and the applicable expiry date; |
| | · | A broad ability for Parent to cause stock options to terminate on an accelerated basis without the consent of option holders, in order to facilitate certain transactions that might be beneficial to PGI; and |
| | · | An ability to grant stock options to investor relations consultants. |
Black-out Period. The Stock Option Plan provides that any options expiring during a disclosure “black-out period” will benefit from a 10-day extension beyond the end of the black-out period.
Transferability. Options are generally non-assignable and non-transferable.
Powers of the Board. The Stock Option Plan permits Parent’s board of directors to appoint a committee (the “Committee”) whose purpose is to administer the plan. The Committee (or the Board if no Committee is in place) may also:
| · | determine all questions arising in connection with the administration, interpretation and application of the plan; |
| · | correct any defect, supply any information or reconcile any inconsistency in the plan in such manner and to such extent as shall be deemed necessary or advisable to carry out the purposes of the plan; |
| · | prescribe, amend, and rescind rules and regulations relating to the administration of the plan; |
do the following with respect to the granting of options:
| · | determine the executives, employees or consultants to whom options shall be granted, based on the eligibility criteria set out in this plan; |
| · | determine the terms of the option to be granted to an option holder including, without limitation, the grant date, expiry dates, exercise price and vesting schedule (which need not be identical with the terms of any other option); |
| · | determine when options shall be granted; |
| · | determine the number of shares subject to each option; and |
| · | accelerate the vesting schedule of any option previously granted, subject to certain limitations. |
Restricted Share Unit Plan
Parent’s restricted share unit plan (the “RSU Plan”) was originally adopted on August 13, 2021 and underwent certain amendments on December 9, 2021. Parent’s board of directors subsequently amended the plan on February 16, 2022, with effect from March 1, 2022. The RSU Plan is designed to provide certain directors, officers, consultants and other key employees (collectively, an “Eligible Person”) of Parent and its related entities with the opportunity to acquire restricted share units (“RSUs”) of PGI. The acquisition of RSUs allows an Eligible Person to participate in the long-term success of the Company thus promoting the alignment of an Eligible Persons. The RSU Plan provides that the aggregate number of shares reserved for issuance pursuant to awards granted, at any time, shall not exceed 7.5% of the issued and outstanding shares in the capital of Parent.
Eligible Persons. All employees, officers, directors, management company employees or consultants (as defined in the RSU Plan) of Parent and its related entities are eligible to participate in the RSU Plan (as “Participants”), and the Company reserves the right to restrict eligibility or otherwise limit the number of persons eligible for participation as Participants in the RSU Plan. Eligibility to participate as a Participant in the RSU Plan does not confer upon any person a right to receive an award of RSUs.
Subject to certain restrictions, the board of directors or its appointed Committee (as defined in the RSU Plan) can, from time to time, award RSUs to Eligible Persons. RSUs will be credited to an account maintained for each Participant on the books of Parent as of the award date. The number of RSUs to be credited to each Participant’s account shall be determined at the discretion of the board of directors and pursuant to the terms of the RSU Plan.
Rolling Plan. The aggregate number of shares that may be reserved for issuance under the RSU Plan at any time shall not exceed 7.5% of Parent’s outstanding shares. This 7.5% limit shall not include the number of shares reserved for issuance under any other incentive plans of Parent.
Vesting. The Board or the Committee may, in its sole discretion, determine the time during which RSUs shall vest (except that no RSU, or portion thereof, may vest after the expiry date) and whether there shall be any other conditions or performance criteria to vesting. In the absence of any determination by the Board or the Committee to the contrary, RSUs will vest and be payable as to one third (1/3) of the total number of RSUs granted on each of the first, second and third anniversaries of the date or dates on which an award of RSUs is made to a Participant (computed in each case to the nearest whole RSU), provided that in all cases payment in satisfaction of a RSU shall occur prior to the Outside Payment Date (which, in respect of a RSU, means December 31 of the calendar year in which the expiry date of the RSUs occurs). Notwithstanding the foregoing, the Committee may, in its sole discretion at any time or in the RSU agreement in respect of any RSUs granted, accelerate, or provide for the acceleration of vesting (in whole or in part) of RSUs previously granted. The award value of any RSU shall be determined as of the applicable vesting date.
Transferability. RSUs and all other rights, benefits or interests in the plan are non-transferable and may not be pledged or assigned or encumbered in any way and are not subject to attachment or garnishment, except that if a Participant dies the legal representatives of the Participant will be entitled to receive the amount of any payment otherwise payable to the Participant hereunder in accordance with the provisions of the RSU Plan.
Limitations. Unless Parent has first obtained disinterested shareholder approval of the plan, the RSU Plan limits the total number of shares issuable at any time to insiders of PGI, when combined with all other shares issuable to insiders under any security based compensation arrangement, to 10% of the total number of issued and outstanding equity securities of Parent. Unless Parent has first obtained disinterested shareholder approval of the plan, it further limits the total number of shares issuable to insiders during any one year period under the plan, when combined with all other shares issuable to insiders under any security based compensation arrangement, to 10% of the total number of issued and outstanding equity securities of Parent.
No RSU may be issued to anyone engaged to perform investor relations activities for Parent. In no event can the issuance of RSUs, when combined with any grant made pursuant to any other security based compensation arrangement, result in: (i) any one person being granted share-based compensation awards equaling or exceeding 5% of the issued shares, within a 12 month period; and (ii) any one consultant in a 12 month period being granted share-based compensation equaling or exceeding 2% of the issued shares.
Resignation, Termination, Engagement, Death or Disability. Upon the voluntary resignation or the termination for cause of a Participant, all of the Participant’s RSUs which remain vested, but unexercised or unvested in the Participant’s Account shall be forfeited without any entitlement to such Participant.
Generally, if a Participant dies, or their employment or engagement terminates with the Company due to total disability, while employed or retained by the Company, or while an officer or director, the expiry date of any vested or unvested RSUs held by the Participant at the date of death or date of termination due to total disability, which have not yet been subject to an exercise notice and subsequent award payout, shall be amended to the earlier of (i) one (1) year after the date of death or date of termination due to total disability, and (ii) the expiry date of such award, except that in the event the expiration of the award is earlier than one (1) year after the date of death or date of termination due to total disability, the expiry date shall be up to one (1) year after the date of death or date of termination due to total disability as determined by the Board.
Change of Control. Subject to any provision to the contrary contained in an RSU agreement or other written agreement (such as an agreement of employment) between the Company and a Participant, if a change of control takes place, all issued and outstanding RSUs shall vest (whether or not then vested) and the vesting date shall be the date which is immediately prior to the time such change of control takes place, or at such earlier time as may be established by the Board or the Committee, in its absolute discretion, prior to the time such change of control takes place.
Credit For Dividends. Within ten (10) days following the declaration and payment of dividends on PGI’s common shares, the Board may determine to make a cash payment to a Participant in respect of outstanding RSUs credited to the Participant’s Account, which shall be calculated in accordance with the RSU Plan.
Terms of RSUs. Subject to an earlier expiry date as may be determined by the Board and set out in the RSU agreement, RSUs will expire either at the earlier of the tenth anniversary of the date of the RSU grant and such earlier expiry date as may be determined by the Board, in its sole discretion, and set out in the applicable RSU Agreement.
Adjustments and Reorganizations. In the event of any dividend paid in shares, share subdivision, combination or exchange of shares, merger, consolidation, spin-off, or other distribution of PGI assets to shareholders, or any other change in the capital of PGI affecting shares, the Board, in its sole and absolute discretion, will make, with respect to the number of RSUs outstanding under this Plan, any proportionate adjustments as it considers appropriate to reflect that change.
2023 Equity Incentive Plan
For a description of the material terms of the 2023 Equity Incentive Plan, see “Management – Equity Incentive Plans.”
Employment, Consulting and Management Agreements
During the year ended March 31, 2023, Parent had the following agreements in place with its named executive officers:
Jody Aufrichtig
Parent and Jody Aufrichtig entered into a consulting agreement dated January 1, 2021 (“First CEO Agreement”), pursuant to which he shall perform the services of Chief Executive Officer of Parent in consideration for a base fee of approximately $9,448.42 per month ($113,381 per annum); rendering a significant number of hours a day or days a week to such services. This First CEO Agreement has been assigned to an entity controlled by Mr. Aufrichtig.
Either of Mr. Aufrichtig or Parent may terminate this First CEO Agreement at any time upon no less than sixty (60) days’ written notice to the other party, save that Parent may terminate the First CEO Agreement at any time without prior notice, for cause, provided that if the act, omission, event or breach giving rise to the cause is capable of being remedied, Mr. Aufrichtig shall be entitled to remedy same within 10 (ten) business days of written notice requiring such remediation.
Parent may terminate the First CEO Agreement without cause or Mr. Aufrichtig may terminate the First CEO Agreement for good reason (as defined in the First CEO Agreement) at any time, in which case Parent shall pay Mr. Aufrichtig an amount equal to one month’s base fee for every completed month worked, up to a maximum of 12 months (“Termination Pay”). If notice of such termination is served within 12 months of effective date of the agreement (i.e. January 1, 2021), 50% of the stock options granted to Mr. Aufrichtig (whether vested or not) to Mr. Aufrichtig shall immediately vest. If notice of termination is served on or after 12 months of the effective date of the agreement, 100% of the stock options granted (whether vested or not) to Mr. Aufrichtig shall immediately vest. In the event of termination by Parent for any reason whatsoever (other than for cause) or by Mr. Aufrichtig for any reason whatsoever within sixty (60) days of a change of control event (as defined in the First CEO Agreement), Parent shall pay Mr. Aufrichtig Termination Pay and 100% of his stock options granted (whether vested or not) shall immediately vest. Parent may terminate the First CEO Agreement for cause or Mr. Aufrichtig may terminate the First CEO Agreement for convenience, in which case Mr. Aufrichtig shall not be entitled to Termination Pay (or any other severance payment) and all unvested stock options granted to him shall be forfeited.
On July 1, 2021 Mr. Aufrichtig resigned as Chief Executive Officer of Parent to take up the role of Executive Chairman of the Board of Directors. Other than an amendment to Mr. Aufrichtig’s title and scope of service, the terms of the First CEO Agreement remain unchanged.
Warwick Corden-Lloyd
Parent and Warwick Corden-Lloyd entered into a consulting agreement dated February 1, 2021 (“CFO Agreement”), pursuant to which he shall perform the services of Chief Financial Officer and Secretary to Parent in consideration for a base fee of approximately $9,448.42 per month ($113,381 per annum). The CFO Agreement has been assigned to an entity controlled by Mr. Corden-Lloyd.
The termination provisions, severance payments and entitlements and accelerated stock option vesting terms contained within the CFO Agreement are identical to those contained within the First CEO Agreement as set out in more detail above (mutatis mutandis).
Dr. Neil Maresky
Parent and Dr. Neil Maresky entered into an employment agreement dated July 1, 2021 (“Second CEO Agreement”), pursuant to which he shall perform the services of Chief Executive Officer of Parent in consideration for a base fee of approximately $21,416.42 per month ($256,997 per annum). Dr. Maresky’s compensation package included share-based incentives.
Either Dr. Maresky or Parent may terminate this Second CEO Agreement at any time upon no less than sixty (60) days’ written notice to the other party.
Parent may terminate the Second CEO Agreement without cause or Dr. Maresky may terminate the Second CEO Agreement for good reason (as defined in the Second CEO Agreement) at any time, in which case Parent shall (subject to and inclusive of the minimum requirements of the Ontario Employment Standards Act, 2000 (“ESA”)) pay Dr. Maresky the following severance:
| | (a) | if termination occurs prior to the first anniversary of employment, one (1) week of notice, pay in lieu of notice or a combination thereof (with pay in lieu based on base fee) for every completed month worked; |
| | (b) | if termination occurs after the first anniversary of employment but prior to the second anniversary of employment, notice, pay in lieu of notice or a combination thereof (with pay in lieu based on the base fee) equal to twelve (12) weeks plus two (2) additional weeks for each completed month of employment after the first anniversary of employment but prior to the second anniversary of employment, capped at a maximum of twenty-four (24) weeks; or |
| | (c) | if termination occurs after the second anniversary of employment, an immediate lump sum payment of twenty-four (24) months of the base fee. In addition, Dr. Maresky shall be entitled to a prorated payment on account of the employee’s annual non-discretionary performance-based bonus for all active service rendered up to the date of termination (calculated at target). |
In the event that Parent terminates the Second CEO Agreement without cause or Dr. Maresky terminates the Second CEO Agreement for good reason (as defined in the Second CEO Agreement) after Parent has secured a successful capital raise of not less than $6 million, Dr. Maresky’s severance terms will be more favorable than set out above.
Should Parent terminate the Second CEO Agreement for cause, Dr. Maresky will shall not be entitled to any pay in lieu of notice or any other payments except as required to comply with the minimum requirements of the ESA in respect of the termination of employment.
Pension
Parent does not have any pension, defined benefit, defined contribution or deferred compensation plans in place.
Director Compensation
Members of the Board did not receive any compensation as directors during financial years ended March 31, 2023 and 2022. Following the completion of the Business Combination, our compensation committee and Board adopted a non-employee director compensation program, which includes payment of $30,000 per year to such directors, as well as annual equity grants in the form of RSUs with a value of $180,000 vesting over 3 years.
New Employment Agreements Between our Named Executive Officers and the Company
Following the Business Combination, the Company expects to enter into new employment agreements with each of its named executive officers, which will govern the terms of their continuing employment with the Company. The Company is still in the process of negotiating, approving and implementing these agreements, but our compensation committee and Board have approved the following terms:
Dr. Neil Maresky (CEO)
The compensation committee and Board approved an annual salary of $360,000, along with a bonus with a value of 50% - 100% of the annual salary, depending on various metrics. Additionally, if finalized, Dr. Maresky would be entitled to RSUs with a value of $1.44 million, vesting over three years. Finally, Dr. Maresky would be entitled to a signing bonus in the form of 200,000 RSUs, which would be surrendered if Dr. Maresky terminates his employment within the first 12 months of signing.
Jody Aufrichtig
The compensation committee and Board approved an annual salary of $200,000, along with a bonus with a value of 50% - 100% of the annual salary, depending on various metrics. Additionally, if finalized, Mr. Aufrichtig would be entitled to RSUs with a value of $800,000, vesting over three years. Finally, Mr. Aufrichtig would be entitled to a signing bonus in the form of 200,000 RSUs, which would be surrendered if Mr. Aufrichtig terminates his employment within the first 12 months of signing.
Warwick Corden-Lloyd
The compensation committee and Board approved an annual salary of $180,000, along with a bonus with a value of 30% - 80% of the annual salary, depending on various metrics. Additionally, if finalized, Mr. Corden-Lloyd would be entitled to RSUs with a value of $450,000, vesting over three years. Finally, Mr. Corden-Lloyd would be entitled to a signing bonus in the form of 80,000 RSUs, which would be surrendered if Mr. Corden-Lloyd terminates his employment within the first 12 months of signing.
CERTAIN RELATIONSHIPS AND RELATED PERSON TRANSACTIONS
Related Party Transactions
On January 25, 2024, the Company issued an unsecured convertible promissory note to Parent (the “PGI Note”), in the principal amount of $1,610,657, which is equal to the total amount owed to Parent in connection with loans the Parent had previously made to the Company. The PGI Note bears no interest, and (i) $150,000 of the principal balance of the PGI Note was payable on the date of the Closing and (ii) $1,460,657 of the principal balance of the PGI Note will be payable on the date that is the one-year anniversary after the Business Combination, or January 25, 2025. On or prior to the maturity date, at the option of PGI, any amounts outstanding under the PGI Note may be converted into securities of the Company or securities of its affiliate, at a conversion price and with terms to be mutually agreed; provided however, such conversion price and terms shall not be less favorable to the conversion price and terms agreed by the parties to the NCAC Replacement Note (as described below).
On January 25, 2024, NCAC issued an unsecured convertible promissory note to the Sponsor (the “NCAC Replacement Note”), in the principal amount of $1,615,501, which is equal to the total amount owed to Sponsor under certain existing promissory notes previously issued by NCAC to the Sponsor (the “Existing Notes”). The NCAC Replacement Note bears no interest, and (i) $100,000 of the principal balance of the NCAC Replacement Note was payable on the date of the Closing and (ii) $1,515,501 of the principal balance of the NCAC Replacement Note will be payable on the date that is the one-year anniversary after the Business Combination, or January 25, 2025 . On or prior to the maturity date, at the option of Sponsor, any amounts outstanding under the NCAC Replacement Note may be converted into securities of the Company or securities of its affiliate, at a conversion price and with terms to be mutually agreed; provided however, such conversion price and terms shall not be less favorable to the conversion price and terms agreed by the parties to the PGI Note. Upon receipt by Sponsor of the NCAC Replacement Note, any and all obligations owing by NCAC under the Existing Notes was satisfied and discharged in full and the respective Existing Notes immediately and automatically terminated and will be of no further effect.
Equity Incentive Plans
See “Management — Equity Incentive Plans.”
Employment Agreements and Indemnification Agreements
See “Executive Compensation — Employment, Consulting and Management Agreements” and “Management – Limitation on Liability and Indemnification of Officers and Directors.”
Related Party Transaction Policy
The Board of directors has adopted a written related party transaction policy, which sets forth the policies and procedures for the review and approval or ratification or related person transactions.
A “Related Person Transaction” is a transaction, arrangement or relationship in which the Company or any of its subsidiaries was, is or will be a participant, the amount of which involved exceeds $120,000, and in which any related person had, has or will have a direct or indirect material interest.
A “Related Person” means:
| | ● | any person who is, or at any time during the applicable period was, one of the Company’s officers or one of the Company’s directors; |
| | ● | any person who is known by the Company to be the beneficial owner of more than five percent (5%) of its voting stock; |
| | ● | any immediate family member of any of the foregoing persons, which means any child, stepchild, parent, stepparent, spouse, sibling, mother-in-law, father-in-law, daughter-in-law, brother-in-law or sister-in-law of a director, officer or a beneficial owner of more than five percent (5%) of its voting stock, and any person (other than a tenant or employee) sharing the household of such director, officer or beneficial owner of more than five percent (5%) of its voting stock; and |
| | ● | any firm, corporation or other entity in which any of the foregoing persons is a partner or principal or in a similar position or in which such person has a ten percent (10%) or greater beneficial ownership interest. |
The Company has policies and procedures designed to minimize potential conflicts of interest arising from any dealings it may have with its affiliates and to provide appropriate procedures for the disclosure of any real or potential conflicts of interest that may exist from time to time. Specifically, pursuant to its charter, the audit committee will have the responsibility to review related party transactions.
BENEFICIAL OWNERSHIP OF SECURITIES
The following table sets forth information regarding the beneficial ownership of Common Shares on the date of this prospectus, based on information obtained from the persons named below, by:
| · | each person known by Psyence to be the beneficial owner of more than 5% of the outstanding Common Shares; |
| | · | each of Psyence’s officers and directors; and |
| · | all of Psyence’s executive officers and directors as a group. |
Unless otherwise indicated, Psyence believes that all persons named in the tables below have sole voting and investment power with respect to all shares beneficially owned by them. Except as otherwise noted herein, the number and percentage of Common Shares beneficially owned is determined in accordance with Rule 13d-3 of the Exchange Act, and the information is not necessarily indicative of beneficial ownership for any other purpose. Under such rule, beneficial ownership includes any Common Shares as to which the holder has sole or shared voting power or investment power and also any Common Shares which the holder has the right to acquire within 60 days of the date of this prospectus through the exercise of any option, warrant, convertible security or other right. As of the date of this prospectus, there were 13,390,659 Common Shares issued and outstanding.
| Name of Beneficial Owner(1) | | Number of
Company
Common
Shares | | | % of Company
Common
Shares | |
| 5% Holders | | | | | | | | |
| Tabula Rasa Limited(2) | | | 4,149,929 | | | | 31.0 | % |
| Harraden Circle Investors, LP / Harraden Circle Special Opportunities, LP(3) | | | 1,300,000 | | | | 9.7 | % |
| Newcourt SPAC Sponsor LLC | | | 2,515,429 | (4) | | | 18.6 | % |
| Psyence Group Inc | | | 5,000,000 | | | | 37.3 | % |
| Directors and Executive Officers | | | | | | | | |
| Dr. Neil Maresky | | | - | | | | - | |
| Warwick Corden-Lloyd | | | - | | | | - | |
| Jody Aufrichtig | | | - | | | | - | |
| Marc Balkin | | | - | | | | - | |
| Christopher (Chris) Bull | | | - | | | | - | |
| Dr. Seth Feuerstein | | | - | | | | - | |
| All Directors and Executive Officers as a group (six individuals) | | | - | | | | - | |
* Less than 1%.
Notes:
(1) Unless otherwise noted, the business address of each of those listed in the table above is 121 Richmond Street West, Penthouse Suite 1300, Toronto, Ontario M5H 2K1.
(2) Consists of (i) 1,300,000 Common Shares held by Tabula Rasa Limited and (ii) 2,389,929 Common Shares and 460,000 private placement warrants exercisable into Common Shares held by the Sponsor, of which Tabula Rasa Limited is the sole manager.
(3) Includes (i) 650,000 Common Shares held by Harraden Circle Investors, LP, and (ii) 650,000 Company Common Shares held by Harraden Circle Special Opportunities, LP. The principal business office of Harraden Circle Investors, LP and Harraden Circle Special Opportunities, LP is located at 299 Park Avenue, 21st Floor, New York, NY 10171. The Common Shares reported herein are directly beneficially owned by Harraden Circle Investors, LP (“Harraden Fund”). Harraden Circle Investors GP, LP (“Harraden GP”) is the general partner to Harraden Fund, and Harraden Circle Investors GP, LLC (“Harraden LLC”) is the general partner of Harraden GP. Harraden Circle Investments, LLC (“Harraden Adviser”) is investment manager to Harraden Fund and other high net worth individuals. Frederick V. Fortmiller, Jr. is the managing member of each of Harraden LLC and Harraden Adviser. In such capacities, each of Harraden GP, Harraden LLC, Harraden Adviser and Mr. Fortmiller may be deemed to indirectly beneficially own the Common Shares reported herein directly beneficially owned by Harraden Fund.
(4) Consists of 2,389,929 Common Shares and 125,500 private placement warrants exercisable into Common Shares held by the Sponsor. Tabula Rasa Limited, a British Virgin Islands company with limited liability, is the sole manager of Sponsor. Carl Linde is the director of Fiducia Trustees Limited, the sole corporate director of Tabula Rasa Limited. Consequently, Mr. Linde is deemed to be the beneficial owner of the shares held by our sponsor and to have voting and dispositive control over such securities. Mr. Linde disclaims beneficial ownership of any shares other than to the extent he may have a pecuniary interest therein, directly or indirectly.
Rule 144
Pursuant to Rule 144, a person who has beneficially owned restricted Common Shares of Psyence for at least six months would be entitled to sell their securities provided that (i) such person is not deemed to have been one of Psyence’s affiliates at the time of, or at any time during the three months preceding, a sale and (ii) Psyence is subject to the Exchange Act periodic reporting requirements for at least three months before the sale and have filed all required reports under Section 13 or 15(d) of the Exchange Act during the 12 months (or such shorter period as we were required to file reports) preceding the sale.
Persons who have beneficially owned restricted Common Shares or warrants for at least six months but who are Psyence’s affiliates at the time of, or at any time during the three months preceding, a sale, would be subject to additional restrictions, by which such person would be entitled to sell within any three-month period only a number of securities that does not exceed the greater of:
| · | 1% of the total number of Common Shares then outstanding); or |
| · | the average weekly reported trading volume of the Common Shares during the four calendar weeks preceding the filing of a notice on Form 144 with respect to the sale. |
Sales by Psyence’s affiliates under Rule 144 are also limited by manner of sale provisions and notice requirements and to the availability of current public information about us.
Substantially all of the present Psyence shareholders will be able to sell shares either pursuant to the registration statement of which this prospectus is a part or, commencing three months after Psyence becomes a reporting company, which will be prior to the Closing date, pursuant to Rule 144, although Psyence’s executive officer and directors and other affiliate will be subject to the limitation described above with respect to sales pursuant to Rule 144. These restrictions do not affect sales pursuant to this prospectus.
DESCRIPTION OF SECURITIES
The following description of the material terms of the securities of the Company includes a summary of specified provisions of the Articles of Incorporation and amended and restated by-laws (“bylaws”) of the Company. This description is qualified by reference to the Articles of Incorporation and by-laws, copies of which are attached as exhibits to the registration statement of which this prospectus forms a part and incorporated in this prospectus by reference. In this section, the terms “we,” “our” or “us” refer to the Company, and all capitalized terms used in this section are as defined in the Articles of Incorporation and bylaws, unless elsewhere defined herein.
General
The following is a summary of the rights of our Common Shares as set forth in our Articles of Incorporation and bylaws and certain related sections of the OBCA. This summary does not purport t be complete and is qualified in its entirety by the full text of the Articles of Incorporation.
Our authorized share capital consists of an unlimited number of Common Shares, each without par value. We currently have 13,390,659 issued and outstanding Common Shares.
The following description of our share capital and provisions of our Articles of Incorporation and bylaws are summaries of material terms and provisions and are qualified by reference to our Articles of Incorporation and bylaws, copies of which have been filed with the SEC as exhibits to the registration statement of which this prospectus is a part. The description of our Common Shares reflects amendments to our Articles of Incorporation and bylaws.
Common Shares
The holders of our Common Shares are entitled to one vote for each share held at any meeting of shareholders. The holders of our Common Shares are entitled to receive dividends as and when declared by our board of directors. In the event of our liquidation, dissolution or winding-up or other distribution of our assets among our shareholders, the holders of our Common Shares are entitled to share pro rata in the distribution of the balance of our assets. There are no preemptive, redemption, purchase or conversion rights attaching to our Common Shares. There are no sinking fund provisions applicable to our Common Shares. Our Common Shares are issued in fully registered form.
Warrants
Each warrant is exercisable to purchase one Common Share. The warrants will expire on the date that is the fifth anniversary of the closing of the Business Combination, or January 25, 2029, at 5:00 p.m., New York City time.
Public Warrants
Each the Public Warrant shall entitle the registered holder thereof to purchase one whole Common Share at a price of $11.50 per share, subject to adjustment as discussed below, at any time commencing on the 30th day following the closing of the Business Combination, or February 24, 2024.
The Company will not be obligated to deliver any Common Shares pursuant to the exercise of a warrant and will have no obligation to settle such warrant exercise unless a registration statement under the Securities Act with respect to the Common Shares underlying the warrants is then effective and a prospectus relating thereto is current, subject to the Company satisfying its obligations described below with respect to registration. No warrant will be exercisable and the Company will not be obligated to issue Common Shares upon exercise of a warrant unless Common Shares issuable upon such warrant exercise has been registered, qualified or deemed to be exempt under the securities laws of the state of residence of the registered holder of the warrants. In the event that the conditions in the two immediately preceding sentences are not satisfied with respect to a warrant, the holder of such warrant will not be entitled to exercise such warrant and such warrant may have no value and expire worthless.
The Public Warrants and the Common Shares issuable upon exercise of the Public Warrants have been registered on the Form F-4 filed in connection with the Business Combination. The Company will use its best efforts to maintain the effectiveness of such registration statement, and a current prospectus relating thereto, until the expiration of the warrants in accordance with the provisions of the warrant agreement. Notwithstanding the above, if the Common Shares are at the time of any exercise of a warrant not listed on a national securities exchange such that it satisfies the definition of a “covered security” under Section 18(b)(1) of the Securities Act, the Company may, at its option, require holders of Public Warrants who exercise their warrants to do so on a “cashless basis” in accordance with Section 3(a)(9) of the Securities Act and, in the event the Company so elects, it will not be required to file or maintain in effect a registration statement, but the Company will be required to use its best efforts to register or qualify the shares under applicable blue sky laws to the extent an exemption is not available.
Once the warrants become exercisable, we may call the warrants for redemption:
| · | in whole and not in part; |
| · | at a price of US$0.01 per warrant; |
| · | upon not less than 30 days’ prior written notice of redemption (the “30-day redemption period”) to each warrant holder; and |
| · | if, and only if, the reported last sale price of Common Shares equals or exceeds US$18.00 per share for any 20 trading days within a 30-trading day period ending three business days before we send the notice of redemption to the warrant holders. |
If and when the warrants become redeemable by us, we may exercise our redemption right even if we are unable to register or qualify the underlying securities for sale under all applicable state securities laws.
We have established the last of the redemption criterion discussed above to prevent a redemption call unless there is at the time of the call a significant premium to the warrant exercise price. If the foregoing conditions are satisfied and we issue a notice of redemption of the warrants, each warrant holder will be entitled to exercise its warrant prior to the scheduled redemption date. However, the price of Common Shares may fall below the US$18.00 redemption trigger price as well as the US$11.50 warrant exercise price after the redemption notice is issued.
If we call the warrants for redemption as described above, our management will have the option to require any holder that wishes to exercise its warrant to do so on a “cashless basis.” This redemption feature may differ from the warrant redemption features used by other blank check companies. In determining whether to require all holders to exercise their warrants on a “cashless basis,” our management will consider, among other factors, our cash position, the number of warrants that are outstanding and the dilutive effect on our shareholders of issuing the maximum number of Common Shares issuable upon the exercise of our warrants. If our management takes advantage of this option, all holders of warrants would pay the exercise price by surrendering their warrants for that number of Common Shares equal to the quotient obtained by dividing (x) the product of the number of Common Shares underlying the warrants, multiplied by the difference between the exercise price of the warrants and the “fair market value” (defined below) by (y) the fair market value. The “fair market value” shall mean the average reported last sale price of the Common Shares for the 10 trading days ending on the third trading day prior to the date on which the notice of redemption is sent to the holders of warrants. As an example, if we elect to call the warrants for redemption on a “cashless basis” in accordance with the redemption criteria described above and the “fair market value” is determined to be US$18.00 per share, then a holder of warrants for the purchase of 100 shares of our Common Shares would receive 36 shares of our Common Shares upon such exercise. The “fair market value” for these purposes may be higher or lower than the US$18.00 redemption trigger price and will only be determinable when we elect to send a notice of redemption to holders of the warrants. If a holder does not exercise his or her warrants within the redemption period, then he or she will be forced to accept the nominal redemption price of US$0.01 per warrant which, at the time the outstanding warrants are called for redemption, is likely to be substantially less than the market value of such warrants. If we call our warrants for redemption and our Private Warrants and their permitted transferees would still be entitled to exercise their Private Warrants for cash or on a cashless basis using the same formula described above that other warrant holders would have been required to use had all warrant holders been required to exercise their warrants on a cashless basis, as described in more detail below.
A holder of a warrant may notify us in writing in the event it elects to be subject to a requirement that such holder will not have the right to exercise such warrant, to the extent that after giving effect to such exercise, such person (together with such person’s affiliates), to the warrant agent’s actual knowledge, would beneficially own in excess of 9.8% (or such other amount as a holder may specify) of the Common Shares outstanding immediately after giving effect to such exercise.
If the number of outstanding Common Shares is increased by a share dividend payable in Common Shares, or by a split-up of Common Shares or other similar event, then, on the effective date of such share dividend, sub-division or similar event, the number of Common Shares issuable on exercise of each warrant will be increased in proportion to such increase in the outstanding Common Shares. A rights offering to holders of Common Shares entitling holders to purchase Common Shares at a price less than the fair market value will be deemed a share dividend of a number of Common Shares equal to the product of (i) the number of Common Shares actually sold in such rights offering (or issuable under any other equity securities sold in such rights offering that are convertible into or exercisable for Common Shares) multiplied by (ii) one (1) minus the quotient of (x) the price per share of Common Shares paid in such rights offering divided by (y) the fair market value. For these purposes (i) if the rights offering is for securities convertible into or exercisable for Common Shares, in determining the price payable for Common Shares, there will be taken into account any consideration received for such rights, as well as any additional amount payable upon exercise or conversion and (ii) fair market value means the volume weighted average price of Common Shares as reported during the ten (10) trading day period ending on the trading day prior to the first date on which the Common Shares trade on the applicable exchange or in the applicable market, regular way, without the right to receive such rights.
In addition, if the Company, at any time while the warrants are outstanding and unexpired, pays a dividend or make a distribution in cash, securities or other assets to the holders of Common Shares on account of such Common Shares (or other shares of the Company’s capital stock into which the warrants are convertible), other than (a) as described above, (b) certain ordinary cash dividends, or (c) to satisfy the redemption rights of the holders of Common Shares in connection with a proposed initial business combination, then the warrant exercise price will be decreased, effective immediately after the effective date of such event, by the amount of cash and/or the fair market value of any securities or other assets paid on each share of Common Shares in respect of such event.
If the number of outstanding Common Shares is decreased by a consolidation, combination, reverse stock split or reclassification of Common Shares or other similar event, then, on the effective date of such consolidation, combination, reverse stock split, reclassification or similar event, the number of Common Shares issuable on exercise of each warrant will be decreased in proportion to such decrease in outstanding Common Shares.
Whenever the number of Common Shares purchasable upon the exercise of the warrants is adjusted, as described above, the warrant exercise price will be adjusted by multiplying the warrant exercise price immediately prior to such adjustment by a fraction (x) the numerator of which will be the number of Common Shares purchasable upon the exercise of the warrants immediately prior to such adjustment, and (y) the denominator of which will be the number of Common Shares so purchasable immediately thereafter.
In case of any reclassification or reorganization of the outstanding Common Shares (other than those described above or that solely affects the par value of such Common Shares), or in the case of any merger or consolidation of the Company with or into another corporation (other than a consolidation or merger in which the Company is the continuing corporation and that does not result in any reclassification or reorganization of outstanding Common Shares), or in the case of any sale or conveyance to another corporation or entity of the assets or other property of the Company as an entirety or substantially as an entirety in connection with which the Company is dissolved, the holders of the warrants will thereafter have the right to purchase and receive, upon the basis and upon the terms and conditions specified in the warrants and in lieu of the shares of its Common Shares immediately theretofore purchasable and receivable upon the exercise of the rights represented thereby, the kind and amount of shares of stock or other securities or property (including cash) receivable upon such reclassification, reorganization, merger or consolidation, or upon a dissolution following any such sale or transfer, that the holder of the warrants would have received if such holder had exercised their warrants immediately prior to such event. If less than 70% of the consideration receivable by the holders of Common Shares in such a transaction is payable in the form of Common Shares in the successor entity that is listed for trading on a national securities exchange or is quoted in an established over-the-counter market, or is to be so listed for trading or quoted immediately following such event, and if the registered holder of the warrant properly exercises the warrant within thirty days following public disclosure of such transaction, the warrant exercise price will be reduced as specified in the warrant agreement based on the Black-Scholes value (as defined in the warrant agreement) of the warrant.
The warrants will be issued in registered form under a warrant agreement between Continental Stock Transfer & Trust Company, as warrant agent, and the Company. You should review a copy of the warrant agreement, which will be filed as an exhibit to the registration statement of which this prospectus is a part, for a complete description of the terms and conditions applicable to the warrants. The warrant agreement provides that the terms of the warrants may be amended without the consent of any holder to cure any ambiguity or correct any defective provision, but requires the approval by the holders of at least 50% of the then outstanding NCAC Public Warrants to make any change that adversely affects the interests of the registered holders of NCAC Public Warrants.
The warrants may be exercised upon surrender of the warrant certificate on or prior to the expiration date at the offices of the warrant agent, with the exercise form on the reverse side of the warrant certificate completed and executed as indicated, accompanied by full payment of the exercise price (or on a cashless basis, if applicable), by certified or official bank check payable to the Company, for the number of warrants being exercised. The warrant holders do not have the rights or privileges of holders of Common Shares and any voting rights until they exercise their warrants and receive Common Shares. After the issuance of Common Shares upon exercise of the warrants, each holder will be entitled to one vote for each share held of record on all matters to be voted on by shareholders.
No fractional shares will be issued upon exercise of the warrants. If, upon exercise of the warrants, a holder would be entitled to receive a fractional interest in a share, the Company will, upon exercise, round down to the nearest whole number of Common Shares to be issued to the warrant holder.
Private Warrants
The Private Warrants were assumed by the Company upon the consummation of the Business Combination, and after the Business Combination, each warrant is exercisable for Common Shares. The Private Warrants may be exercised on a cashless basis and will not be redeemable by the Company so long as they are held by the initial holders thereof or their permitted transferees. Otherwise, the Private Warrants have terms and provisions that are identical to those of the Public Warrants. If the Private Warrants are held by holders other than the initial holders thereof or their permitted transferees, the Private Warrants will be redeemable by the Company and exercisable by the holders on the same basis as the Public Warrants. If holders of the Private Warrants elect to exercise them on a cashless basis, they would pay the exercise price by surrendering their warrants for that number of Common Shares equal to the quotient obtained by dividing (x) the product of the number of Common Shares underlying the warrants, multiplied by the difference between the exercise price of the warrants and the “fair market value” (defined below) by (y) the fair market value. The “fair market value” shall mean the average reported last sale price of the Common Shares for the 10 trading days ending on the third trading day prior to the date on which the notice of warrant exercise is sent to the warrant agent.
CERTAIN MATERIAL U.S. FEDERAL INCOME TAX CONSIDERATIONS
The following is a discussion of certain material United States federal income tax considerations relating to the acquisition, ownership, and disposition of our Common Shares by a U.S. Holder, as defined below, that acquires our Common Shares in this offering and holds our Common Shares as “capital assets” (generally, property held for investment) under the Code. This discussion is based on existing United States federal income tax law, which is subject to differing interpretations or change, possibly with retroactive effect. No ruling has been sought from the Internal Revenue Service (the “IRS”) with respect to any United States federal income tax consequences described below, and there can be no assurance that the IRS or a court will not take a contrary position. This discussion does not address all aspects of United States federal income taxation that may be important to particular investors in light of their individual circumstances, including investors subject to special tax rules (such as, for example, certain financial institutions, insurance companies, regulated investment companies, real estate investment trusts, broker-dealers, traders in securities that elect mark-to-market treatment, partnerships (or other entities treated as partnerships for United States federal income tax purposes) and their partners, tax-exempt organizations (including private foundations)), investors who are not U.S. Holders, investors that own (directly, indirectly, or constructively) 5% or more of our voting shares, investors that hold their Common Shares as part of a straddle, hedge, conversion, constructive sale or other integrated transaction), investors that are subject to the applicable financial statement accounting rules under Section 451 of the Code, or investors that have a functional currency other than the U.S. dollar, all of whom may be subject to tax rules that differ significantly from those summarized below. In addition, this discussion does not address any tax laws other than the United States federal income tax laws, including any state, local, alternative minimum tax or non-United States tax considerations, or the Medicare tax on unearned income. Each potential investor is urged to consult its tax advisor regarding the United States federal, state, local and non-United States income and other tax considerations of an investment in our Common Shares.
General
For purposes of this discussion, a “U.S. Holder” is a beneficial owner of our Common Shares that is, for United States federal income tax purposes, (i) an individual who is a citizen or resident of the United States, (ii) a corporation (or other entity treated as a corporation for United States federal income tax purposes) created in, or organized under the laws of, the United States or any state thereof or the District of Columbia, (iii) an estate the income of which is includible in gross income for United States federal income tax purposes regardless of its source, or (iv) a trust (A) the administration of which is subject to the primary supervision of a United States court and which has one or more United States persons who have the authority to control all substantial decisions of the trust or (B) that has otherwise elected to be treated as a United States person under the Code.
If a partnership (or other entity treated as a partnership for United States federal income tax purposes) is a beneficial owner of our Common Shares, the tax treatment of a partner in the partnership will depend upon the status of the partner and the activities of the partnership. Partnerships and partners of a partnership holding our Common Shares are urged to consult their tax advisors regarding an investment in our Common Shares.
The discussion set forth below is addressed only to U.S. Holders that purchase Common Shares in this offering. Prospective purchasers are urged to consult their own tax advisors about the application of U.S. federal income tax law to their particular circumstances as well as the state, local, foreign and other tax consequences to them of the purchase, ownership and disposition of our Common Shares.
Taxation of Dividends and Other Distributions on our Common Shares
Subject to the passive foreign investment company rules discussed below, distributions of cash or other property made by us to you with respect to the Common Shares (including the amount of any taxes withheld therefrom) will generally be includable in your gross income as dividend income on the date of receipt by you, but only to the extent that the distribution is paid out of our current or accumulated earnings and profits (as determined under U.S. federal income tax principles). With respect to corporate U.S. Holders, the dividends will not be eligible for the dividends-received deduction allowed to corporations in respect of dividends received from other U.S. corporations.
With respect to non-corporate U.S. Holders, including individual U.S. Holders, dividends will be taxed at the lower capital gains rate applicable to qualified dividend income, provided that (1) the Common Shares are readily tradable on an established securities market in the United States, or we are eligible for the benefits of an approved qualifying income tax treaty with the United States that includes an exchange of information program, (2) we are not a passive foreign investment company (as discussed below) for either our taxable year in which the dividend is paid or the preceding taxable year, and (3) certain holding period requirements are met. You are urged to consult your tax advisors regarding the availability of the lower rate for dividends paid with respect to our Common Shares, including the effects of any change in law after the date of this prospectus.
To the extent that the amount of the distribution exceeds our current and accumulated earnings and profits (as determined under U.S. federal income tax principles), it will be treated first as a tax-free return of your tax basis in your Common Shares, and to the extent the amount of the distribution exceeds your tax basis, the excess will be taxed as capital gain. We do not intend to calculate our earnings and profits under U.S. federal income tax principles. Therefore, a U.S. Holder should expect that a distribution will be treated as a dividend even if that distribution would otherwise be treated as a non-taxable return of capital or as capital gain under the rules described above.
Taxation of Dispositions of Common Shares
Subject to the passive foreign investment company rules discussed below, you will recognize taxable gain or loss on any sale, exchange or other taxable disposition of a share equal to the difference between the amount realized (in U.S. dollars) for the share and your tax basis (in U.S. dollars) in the Common Shares. The gain or loss will be capital gain or loss. If you are a non-corporate U.S. Holder, including an individual U.S. Holder, who has held the Common Shares for more than one year, you may be eligible for reduced tax rates on any such capital gains. The deductibility of capital losses is subject to limitations.
Passive Foreign Investment Company
A non-U.S. corporation is considered a PFIC for any taxable year if either:
| | ● | at least 75% of its gross income for such taxable year is passive income; or |
| | ● | at least 50% of the value of its assets (based on an average of the quarterly values of the assets during a taxable year) is attributable to assets that produce or are held for the production of passive income (the “asset test”). |
Passive income generally includes dividends, interest, rents and royalties (other than rents or royalties derived from the active conduct of a trade or business) and gains from the disposition of passive assets. We will be treated as owning our proportionate share of the assets and earning our proportionate share of the income of any other corporation in which we own, directly or indirectly, at least 25% (by value) of the shares. In determining the value and composition of our assets for purposes of the PFIC asset test, the value of our assets must be determined based on the market value of our Common Shares from time to time, which could cause the value of our non-passive assets to be less than 50% of the value of all of our assets on any particular quarterly testing date for purposes of the asset test.
We must make a separate determination each year as to whether we are a PFIC. Depending on the amount of our cash and other assets held for the production of passive income, it is possible that, for our current taxable year or for any subsequent taxable year, more than 50% of our assets may be assets held for the production of passive income. We will make this determination following the end of any particular tax year. Although the law in this regard is unclear, we treat our consolidated affiliated entities as being owned by us for United States federal income tax purposes, not only because we exercise effective control over the operation of such entities but also because we are entitled to substantially all of their economic benefits, and, as a result, we consolidate their operating results in our consolidated financial statements. In particular, because the value of our assets for purposes of the asset test will generally be determined based on the market price of our Common Shares and because cash is generally considered to be an asset held for the production of passive income, our PFIC status will depend in large part on the market price of our Common Shares and the amount of our cash and other assets held for the production of passive income. Accordingly, fluctuations in the market price of the Common Shares may cause us to become a PFIC. In addition, the application of the PFIC rules is subject to uncertainty in several respects. We are under no obligation to take steps to reduce the risk of our being classified as a PFIC. As stated above, the determination of the value of our assets will depend upon material facts (including the market price of our Common Shares from time to time) that may not be within our control, and no opinion of counsel has or will be provided regarding our classification as a PFIC. If we are a PFIC for any year during which you hold Common Shares, we will continue to be treated as a PFIC for all succeeding years during which you hold Common Shares. However, if we cease to be a PFIC and you did not previously make a timely “mark-to-market” election as described below, you may avoid some of the adverse effects of the PFIC regime by making a “purging election” (as described below) with respect to the Common Shares.
If we are a PFIC for your taxable year(s) during which you hold Common Shares, you will be subject to special tax rules with respect to any “excess distribution” that you receive and any gain you realize from a sale or other disposition (including a pledge) of the Common Shares, unless you make a “mark-to-market” election as discussed below. Distributions you receive in a taxable year that are greater than 125% of the average annual distributions you received during the shorter of the three preceding taxable years or your holding period for the Common Shares will be treated as an excess distribution. Under these special tax rules:
| | ● | the excess distribution or gain will be allocated ratably over your holding period for the Common Shares; |
| | ● | the amount allocated to your current taxable year, and any amount allocated to any of your taxable year(s) prior to the first taxable year in which we were a PFIC, will be treated as ordinary income, and |
| | ● | the amount allocated to each of your other taxable year(s) will be subject to the highest tax rate in effect for that year and the interest charge generally applicable to underpayments of tax will be imposed on the resulting tax attributable to each such year. |
The tax liability for amounts allocated to years prior to the year of disposition or “excess distribution” cannot be offset by any net operating losses for such years, and gains (but not losses) realized on the sale of the Common Shares cannot be treated as capital, even if you hold the Common Shares as capital assets.
A U.S. Holder of “marketable stock” (as defined below) in a PFIC may make a mark-to-market election for such stock to elect out of the tax treatment discussed above. If you make a mark-to-market election for the first taxable year during which you hold (or are deemed to hold) Common Shares and for which we are determined to be a PFIC, you will include in your income each year an amount equal to the excess, if any, of the fair market value of the Common Shares as of the close of such taxable year over your adjusted basis in such Common Shares, which excess will be treated as ordinary income and not capital gain. You are allowed an ordinary loss for the excess, if any, of the adjusted basis of the Common Shares over their fair market value as of the close of the taxable year. However, such ordinary loss is allowable only to the extent of any net mark-to-market gains on the Common Shares included in your income for prior taxable years. Amounts included in your income under a mark-to-market election, as well as gain on the actual sale or other disposition of the Common Shares, are treated as ordinary income. Ordinary loss treatment also applies to any loss realized on the actual sale or disposition of the Common Shares, to the extent that the amount of such loss does not exceed the net mark-to-market gains previously included for such Common Shares. Your basis in the Common Shares will be adjusted to reflect any such income or loss amounts. If you make a valid mark-to-market election, the tax rules that apply to distributions by corporations which are not PFICs would apply to distributions by us, except that the lower applicable capital gains rate for qualified dividend income discussed above under “— Taxation of Dividends and Other Distributions on our Common Shares” generally would not apply.
The mark-to-market election is available only for “marketable stock”, which is stock that is traded in other than de minimis quantities on at least 15 days during each calendar quarter (“regularly traded”) on a qualified exchange or other market (as defined in applicable U.S. Treasury regulations), including Nasdaq. U.S. holders should consult their own tax advisors regarding the availability and tax consequences of a mark-to-market election in respect to our Common Shares under their particular circumstances.
Alternatively, a U.S. Holder of stock in a PFIC may make a “qualified electing fund” election with respect to such PFIC to elect out of the tax treatment discussed above. A U.S. Holder who makes a valid qualified electing fund election with respect to a PFIC will generally include in gross income for a taxable year such holder’s pro rata share of the corporation’s earnings and profits for the taxable year. However, the qualified electing fund election is available only if such PFIC provides such U.S. Holder with certain information regarding its earnings and profits as required under applicable U.S. Treasury regulations. We do not currently intend to prepare or provide the information that would enable you to make a qualified electing fund election. If you hold Common Shares in any taxable year in which we are a PFIC, you will be required to file IRS Form 8621 in each such year and provide certain annual information regarding such Common Shares, including regarding distributions received on the Common Shares and any gain realized on the disposition of the Common Shares.
If you do not make a timely “mark-to-market” election (as described above), and if we were a PFIC at any time during the period you hold our Common Shares, then such Common Shares will continue to be treated as stock of a PFIC with respect to you even if we cease to be a PFIC in a future year, unless you make a “purging election” for the year we cease to be a PFIC. A “purging election” creates a deemed sale of such Common Shares at their fair market value on the last day of the last year in which we are treated as a PFIC. The gain recognized by the purging election will be subject to the special tax and interest charge rules treating the gain as an excess distribution, as described above. As a result of the purging election, you will have a new basis (equal to the fair market value of the Common Shares on the last day of the last year in which we are treated as a PFIC) and holding period (which new holding period will begin the day after such last day) in your Common Shares for tax purposes.
You are urged to consult your tax advisors regarding the application of the PFIC rules to your investment in our Common Shares and the elections discussed above.
Information Reporting and Backup Withholding
Dividend payments with respect to our Common Shares and proceeds from the sale, exchange or redemption of our Common Shares may be subject to information reporting to the IRS and possible U.S. backup withholding. Backup withholding will not apply, however, to a U.S. Holder who furnishes a correct taxpayer identification number and makes any other required certification on IRS Form W-9 or who is otherwise exempt from backup withholding. U.S. Holders who are required to establish their exempt status generally must provide such certification on IRS Form W-9. U.S. Holders are urged to consult their tax advisors regarding the application of the U.S. information reporting and backup withholding rules.
Backup withholding is not an additional tax. Amounts withheld as backup withholding may be credited against your U.S. federal income tax liability, and you may obtain a refund of any excess amounts withheld under the backup withholding rules by filing the appropriate claim for refund with the IRS and furnishing any required information. We do not intend to withhold taxes for individual shareholders. However, transactions effected through certain brokers or other intermediaries may be subject to withholding taxes (including backup withholding), and such brokers or intermediaries may be required by law to withhold such taxes.
Under the Hiring Incentives to Restore Employment Act of 2010, certain U.S. Holders are required to report information relating to our Common Shares, subject to certain exceptions (including an exception for Common Shares held in accounts maintained by certain financial institutions), by attaching a complete IRS Form 8938, Statement of Specified Foreign Financial Assets, with their tax return for each year in which they hold Common Shares.
MATERIAL CANADIAN TAX CONSIDERATIONS
The following summary describes the principal Canadian federal income tax considerations under the Income Tax Act (Canada) and the regulations thereunder (collectively, the “Tax Act”), as of the date hereof, that are generally applicable to an investor who acquires, as beneficial owner, Common Shares from a Selling Shareholder pursuant to this statement and who, at all relevant times, for the purposes of the Tax Act and any applicable tax treaty or convention: (i) is not, and is not deemed to be, resident in Canada; (ii) deals at arm’s length with each of the Company and the Selling Shareholder; (iii) is not affiliated with either of the Company or the Selling Shareholder; (iv) has not entered into, with respect to the Common Shares, a “derivative forward agreement” or “dividend rental arrangement” each as defined in the Tax Act; (v) does not have a “permanent establishment” or “fixed base” in Canada; and (vi) does not use or hold, and is not deemed to use or hold, the Common Shares in connection with, or in the course of carrying on, a business in Canada (each a “Non-Canadian Holder”).
Special rules, which are not discussed in this summary, may apply to a Non-Canadian Holder that is an insurer carrying on business in Canada and elsewhere. Such Non-Canadian Holders should consult their own tax advisors.
This summary does not address any income tax considerations relevant to the acquisition, holding, disposition or conversion of First Tranche Notes into Common Shares or the payment of any amount of principal or interest on First Tranche Notes. This summary also does not address any income tax considerations that may arise as a result of a Non-Canadian Holder being an employee of the Company or its affiliates. All such persons should consult their own tax advisors with respect to the Canadian federal income tax consequences to them, which may differ materially from the discussion provided in this summary.
This summary is based upon the current provisions of the Tax Act and the Canada-United States Tax Convention (1980) in force as of the date hereof and an understanding of the current administrative policies and assessing practices published in writing by the Canada Revenue Agency (“CRA”) prior to the date hereof. This summary also takes into account all specific proposals to amend the Tax Act and the Canada-United States Tax Convention (1980) publicly announced by or on behalf of the Minister of Finance (Canada) prior to the date hereof (the “Proposed Amendments”) and assumes that all Proposed Amendments will be enacted in the form proposed. However, no assurances can be given that the Proposed Amendments will be enacted as proposed, or at all. Except for the Proposed Amendments, this summary does not take into account or anticipate any changes in law or administrative policies, whether by legislative, regulatory, administrative or judicial action or decision, nor does it take into account other federal or any provincial, territorial or foreign tax legislation or considerations, which may be different from those discussed in this summary.
This summary is of a general nature only, is not exhaustive of all possible Canadian federal income tax considerations and is not intended to be, nor should it be construed to be, legal or tax advice to any particular Non-Canadian Holder. Accordingly, Non-Canadian Holders should consult their own tax advisors with respect to their particular circumstances.
Currency
Generally, for purposes of the Tax Act, all amounts relating to the acquisition, holding or disposition of Common Shares must be expressed in Canadian dollars. Amounts denominated in another currency must be converted into Canadian dollars using the exchange rate quoted by the Bank of Canada on the date such amounts first arose, or such other rate of exchange as is acceptable to the CRA.
Adjusted cost base of Common Shares
The adjusted cost base of a Common Share to a Non-Canadian Holder will generally include all amounts paid by the Non-Canadian Holder for the Common Share. When Common Shares are acquired by a Non-Canadian Holder who already owns Common Shares, the cost of newly acquired Common Shares will generally be averaged with the adjusted cost base of all Common Shares held by the Non-Canadian Holder as capital property immediately prior to the acquisition for the purpose of determining the Non-Canadian Holder’s adjusted cost base of each Common Share held by such Non-Canadian Holder.
Dividends
Dividends paid or credited, or deemed to be paid or credited, on Common Shares to a Non-Canadian Holder generally will be subject to Canadian withholding tax. Under the Tax Act, the rate of withholding tax is 25% of the gross amount of such dividends, which rate may be subject to reduction under the provisions of an applicable income tax treaty. For example, a Non-Canadian Holder who is resident in the United States for the purposes of the Canada-United States Tax Convention (1980), fully entitled to the benefits of such convention and the beneficial owner of the dividends, will generally be subject to Canadian withholding tax at a rate of 15% of the amount of such dividends.
Disposition of Common Shares
A Non-Canadian Holder who disposes or is deemed to dispose of a Common Share in a taxation year will not be subject to tax in Canada, unless the Common Share is, or is deemed to be, “taxable Canadian property” to the Non-Canadian Holder at the time of disposition and the Non-Canadian Holder is not entitled to relief under an applicable income tax treaty between Canada and the country in which the Non-Canadian Holder is resident.
Provided the Common Shares are listed on a “designated stock exchange”, as defined in the Tax Act (which currently includes the Nasdaq), at the time of disposition, the Common Shares generally will not constitute taxable Canadian property of a Non-Canadian Holder at that time, unless at any time during the 60-month period immediately preceding the disposition the following two conditions are met concurrently: (i) one or any combination of (a) the Non-Canadian Holder, (b) persons with whom the Non-Canadian Holder did not deal at arm’s length, and (c) partnerships in which the Non-Canadian Holder or a person described in (b) holds a membership interest directly or indirectly through one or more partnerships owned 25% or more of the issued shares of any class or series of shares of the Company; and (ii) more than 50% of the fair market value of the Common Shares was derived directly or indirectly from one or any combination of (a) real or immovable property situated in Canada, (b) “Canadian resource property”(as defined in the Tax Act), (c) “timber resource property”(as defined in the Tax Act), or (d) an option in respect of, an interest in, or for civil law rights in, property described in any of (a) through (c), whether or not such property exists.
Non-Resident Holders who dispose of Common Shares that are taxable Canadian property should consult their own tax advisors with respect to the requirement to file a Canadian income tax return in respect of the disposition in their particular circumstances.
EXPENSES RELATING TO THIS OFFERING
Set forth below is an itemization of the total expenses, excluding underwriting discounts and commissions, that we expect to incur in connection with this offering. With the exception of the SEC registration fee, all amounts are estimates.
| SEC registration fee | | $ | 4,781.21 | |
| Legal fees and expenses | | | * | |
| Accounting fees and expenses | | | * | |
| Printing fees | | | * | |
| Miscellaneous expenses | | | * | |
| Total | | | 4,781.21 | |
*These fees are calculated based on the securities offered and the number of issuances and accordingly cannot be determined at this time.
LEGAL MATTERS
The validity of the Common Shares offered by this prospectus and certain other Canadian legal matters will be passed upon by WeirFoulds LLP, and the material U.S. federal income tax considerations will be passed upon by Ellenoff Grossman & Schole LLP. We are contractually bound to issue to Ellenoff Grossman & Schole LLP 150,000 Common Shares, which such shares are being registered for resale pursuant to this prospectus.
EXPERTS
The carve-out consolidated financial statements of Psyence Biomed Corp. as of March 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021 and for each of the years in the two-year period ended March 31, 2023 included in this prospectus have been audited by MNP LLP, independent registered public accounting firm, as set forth in their report thereon, appearing elsewhere herein, and are included in reliance upon such report given on the authority of such firm as experts in accounting and auditing.
WHERE YOU CAN FIND ADDITIONAL INFORMATION
Psyence has filed with the SEC a registration statement on Form F-1 under the Securities Act with respect to the securities being sold by the Selling Shareholders. This prospectus does not contain all of the information included in the registration statement. For further information about us and our securities, you should refer to the registration statement and the exhibits and schedules filed with the registration statement. Whenever we make reference in this prospectus to any of our contracts, agreements or other documents, the references are materially complete but may not include a description of all aspects of such contracts, agreements or other documents, and you should refer to the exhibits attached to the registration statement for copies of the actual contract, agreement or other document.
Upon the effectiveness of the Merger, Psyence will be subject to the information requirements of the Exchange Act and will file annual and other periodic and current event reports, proxy statements and other information with the SEC. You can read Psyence’s SEC filings, including the registration statement, over the Internet at the SEC’s website at www.sec.gov.
INDEX TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Carve-Out Consolidated Financial Statements for Psyence Biomed Corp. as of and for the Years Ended March 31, 2023 and 202
| | | Page(s) |
| Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm | | F-4 |
| Carved-Out Consolidated Statements of Financial Position as at March 31, 2023, March 31, 2022 and March 31, 2021 | | F-6 |
| Carved-Out Consolidated Statements of Net Loss and Comprehensive Loss for the years ended March 31, 2023 and March 31, 2022 | | F-7 |
| Carved-Out Consolidated Statements of Changes in Net Parent Investment for the years ended March 31, 2023 and March 31, 2022 | | F-8 |
| Carved-Out Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows for the years ended March 31, 2023 and March 31, 2022 | | F-9 |
| Notes to Financial Statements | | F-10 - F-20 |
Carve-Out Unaudited Condensed Consolidated Interim Financial Statements for Psyence Biomed Corp. for the Three and Six Months Ended September 30, 2023:

Psyence Biomed Corp.
Carve-Out Consolidated Financial Statements
For the Years ended March 31, 2023
and 2022
Expressed in Canadian Dollars
(CAD $)
Management’s Responsibility for Financial Reporting
The accompanying carve-out consolidated financial statements of the Company have been prepared by management in accordance with International Financial Reporting Standards. These carve-out financial statements contain estimates based on management’s judgment. Management maintains an appropriate system of internal controls to provide reasonable assurance that transactions are authorized, assets safeguarded, and proper records maintained.
The Audit Committee of the Board of Directors reviews the results of the audit and the carve-out consolidated financial statements prior to submitting the carve-out consolidated financial statements to the Board for approval.
The Company’s auditors, MNP LLP, are appointed by the shareholders to conduct an audit and their report follows.
Chief Executive Officer
Toronto, Canada
July 28, 2023

Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
To the Shareholder and Board of Directors of Psyence Biomed Corp.:
Opinion on the Carve-Out Consolidated Financial Statements
We have audited the accompanying carve-out consolidated statements of financial position of Psyence Biomed Corp. (the Company) as of March 31, 2023, March 31, 2022 and March 31, 2021, and the related carve-out consolidated statements of net loss and comprehensive loss, changes in net parent investment, and cash flows for each of the years in the two-year period ended March 31, 2023, and the related notes (collectively referred to as the carve-out consolidated financial statements).
In our opinion, the carve-out consolidated financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the carve-out consolidated financial position of the Company as of March 31, 2023, March 31, 2022 and March 31, 2021, and the results of its consolidated operations and its consolidated cash flows for each of the years in the two-year period ended March 31, 2023, in conformity with International Financial Reporting Standards as issued by the International Accounting Standards Board.
Material Uncertainty Related to Going Concern
The accompanying carve-out consolidated financial statements have been prepared assuming that the Company will continue as a going concern. As discussed in Note 1 to the carve-out consolidated financial statements, the Company has not yet achieved profitable operations and has accumulated losses that raise substantial doubt about its ability to continue as a going concern. Management’s plans in regard to these matters are also described in Note 1. The carve-out consolidated financial statements do not include any adjustments that might result from the outcome of this uncertainty.
Basis for Opinion
These carve-out consolidated financial statements are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s carve-out consolidated financial statements based on our audits. We are a public accounting firm registered with the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB) and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the carve-out consolidated financial statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud. The Company is not required to have, nor were we engaged to perform, an audit of its internal control over financial reporting. As part of our audits, we are required to obtain an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, but not for the purpose of expressing an opinion on the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting. Accordingly, we express no such opinion.
Our audits included performing procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the carve- out consolidated financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures that respond to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the carve-out consolidated financial statements. Our audits also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the carve-out consolidated financial statements. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
We have served as the Company’s auditor since 2021.
| 
|
| Toronto,Canada | Chartered Professional Accountants |
| July 28, 2023 | Licensed Public Accountants |
MNP LLP
1 Adelaide Street East, Suite 1900, Toronto ON, M5C 2V9 | 1.877.251.2922 T: 416.596.1711 F: 416.596.7894 |
CARVE-OUT CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF FINANCIAL POSITION
As at March 31, 2023, March 31, 2022 and March 31, 2021
| | | | | | As at | | | As at | | | As at | |
| CAD $ | | Note | | | March 31, 2023 | | | March 31, 2022 | | | March 31, 2021 | |
| ASSETS | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Current assets | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | | 5 | | | | 1,805,766 | | | | 2,191,095 | | | | 6,006,436 | |
| Restricted cash | | 5 | | | | 40,000 | | | | 40,000 | | | | — | |
| Other receivables | | | | | | 202,150 | | | | 49,372 | | | | 174,283 | |
| Prepaids | | | | | | 104,276 | | | | 6,729 | | | | 6,889 | |
| Total current assets | | | | | | 2,152,192 | | | | 2,287,196 | | | | 6,187,608 | |
| TOTAL ASSETS | | | | | | 2,152,192 | | | | 2,287,196 | | | | 6,187,608 | |
| LIABILITIES | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Current liabilities | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Accounts payable and accrued liabilities | | 6 | | | | 2,423,467 | | | | 164,500 | | | | 127,590 | |
| Total current liabilities | | | | | | 2,423,467 | | | | 164,500 | | | | 127,590 | |
| TOTAL LIABILITIES | | | | | | 2,423,467 | | | | 164,500 | | | | 127,590 | |
| EQUITY | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net parent investment | | | | | | (271,275 | ) | | | 2,122,696 | | | | 6,060,018 | |
| NET PARENT INVESTMENT | | | | | | (271,275 | ) | | | 2,122,696 | | | | 6,060,018 | |
TOTAL LIABILITIES AND NET PARENT INVESTMENT | | | | | | 2,152,192 | | | | 2,287,196 | | | | 6,187,608 | |
Nature of operations and going concern (note 1)
Approved on behalf of Board of Directors
| “Dr. Neil Maresky” | | “Jody Aufrichtig” |
| Chief Executive Officer and Director | | Executive Chairman and Director |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of the Carve-Out Consolidated Financial Statements
CARVE-OUT CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF NET LOSS AND COMPREHENSIVE LOSS
For the years ended March 31, 2023 and March 31, 2022
| | | Year ended | | | Year ended | |
| CAD $ | | March 31, 2023 | | | March 31, 2022 | |
| Expenses | | | | | | | | |
| Sales and marketing | | | 9,292 | | | | 21,862 | |
| Research and development | | | 2,126,762 | | | | 171,335 | |
| General and administrative | | | 484,382 | | | | 482,305 | |
| Professional fees and consulting fees | | | 1,655,664 | | | | 1,641,574 | |
| Foreign exchange (gain)/loss | | | (35,574 | ) | | | 2,856 | |
| Interest Income | | | (2,054 | ) | | | — | |
| NET LOSS | | | 4,238,471 | | | | 2,319,932 | |
| TOTAL COMPREHENSIVE LOSS | | | 4,238,471 | | | | 2,319,932 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of the Carve-Out Consolidated Financial Statements
CARVE-OUT CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CHANGES IN NET PARENT INVESTMENT
For the years ended March 31, 2023 and March 31, 2022
| | | Net parent
investment | |
| Opening balance as at April 1, 2021 | | | 6,060,018 | |
| Net investment returned to parent in the year | | | (1,617,390 | ) |
| Net loss | | | (2,319,932 | ) |
| Balance, March 31, 2022 | | | 2,122,696 | |
| Opening balance as at April 1, 2022 | | | 2,122,696 | |
| Net investment by parent in the year | | | 1,844,500 | |
| Net loss | | | (4,238,471 | ) |
| Balance, March 31, 2023 | | | (271,275 | ) |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of the Carve-Out Consolidated Financial Statements
CARVE-OUT CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
For the years ended March 31, 2023 and March 31, 2022
| | | | | | Year ended | | | Year ended | |
| | | Note | | | March 31, 2023 | | | March 31, 2022 | |
| Net loss | | | | | | | (4,238,471 | ) | | | (2,319,932 | ) |
| Non-cash adjustment: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Share based compensation | | | 10 | | | | 292,756 | | | | 414,574 | |
| Changes in working capital: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Other receivables | | | | | | | (152,778 | ) | | | 124,911 | |
| Prepaids | | | | | | | (97,547 | ) | | | 160 | |
| Accounts payable and accrued liabilities | | | 6 | | | | 2,258,967 | | | | 36,910 | |
| Cash used in operating activities | | | | | | | (1,937,073 | ) | | | (1,743,377 | ) |
| Increase in restricted cash | | | 5 | | | | — | | | | (40,000 | ) |
| Cash used in investing activities | | | | | | | — | | | | (40,000 | ) |
| Amounts advanced from/(to) parent | | | | | | | 1,551,744 | | | | (2,031,964 | ) |
| Cash provided from/(used in) financing activities | | | | | | | 1,551,744 | | | | (2,031,964 | ) |
| Change in cash and cash equivalents | | | | | | | (385,329 | ) | | | (3,815,341 | ) |
| Cash and cash equivalents, beginning of year | | | | | | | 2,191,095 | | | | 6,006,436 | |
| Cash and cash equivalents, end of year | | | | | | | 1,805,766 | | | | 2,191,095 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of the Carve-Out Consolidated Financial Statements
NOTES TO THE CARVE-OUT CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
| 1. | Nature of operations and going concern |
Psyence Biomed Corp. (the “Company” or “PBC”) is a life science biotechnology company owned by Psyence Group Inc. (“Psyence Group”). It is pioneering the use of natural psychedelics in the treatment of psychological trauma and mental health disorders. It was incorporated under the laws of the province of British Columbia, Canada on May 21, 2020. The Company’s registered office is at 121 Richmond Street West, PH Suite 1300, Toronto, Ontario M5H 2K1.
The Company is currently conducting clinical trials to evaluate the safety and effectiveness of natural psilocybin in treating adjustment disorder in patients with an incurable cancer diagnosis in a palliative care context (the “Clinical Trials”).
The UK Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA) granted full approval for the Company’s Stage I clinical study, including ethics review board approval, on September 15, 2022.
In January 2023, the Company signed a letter of intent with iNGENū Pty Ltd to conduct a Phase IIb study in Australia to further develop the Company’s licensed natural psilocybin drug product. The study will evaluate the safety and efficacy of psilocybin-assisted psychotherapy versus psychotherapy alone for the treatment of adjustment disorder due to an incurable cancer diagnosis in a palliative care context.
84 patients will participate in the study, which will use FDA-recommended primary endpoints. The investigational product will be the proprietary botanical drug candidate PEX010 sourced from Filament Health Corp. Upon successful completion of the study, Psyence intends to conduct a multinational Phase III registrational study.
On February 15, 2023, the Company incorporated a wholly-owned subsidiary by the name of Psyence Australia Pty Ltd., registered in Victoria, Australia.
On January 9, 2023 Psyence Group announced that it had entered into a definitive business combination agreement (the “Business Combination Agreement”) with Newcourt Acquisition Corp (NASDAQ: NCAC), a special purpose acquisition company (“SPAC”) formed for the purpose of acquiring or merging with one or more businesses (“Newcourt”). Newcourt has entered into the Business Combination Agreement with the Company, in order to create a public company leveraging natural psilocybin in the treatment of palliative care (the “Pubco”).
The Business Combination is anticipated to conclude in the second half of 2023, with the Pubco to go public. The Business Combination is expected to be completed by the Company acquiring the SPAC through the merger of the SPAC with a to-be-incorporated subsidiary of PBC. As a consequence of the Business Combination, the SPAC will become a wholly-owned subsidiary of PBC, the SPAC shareholders will become shareholders of PBC, and PBC would complete filings to become a public company in the United States in which Psyence Group would retain a significant ownership stake. The actual level of Psyence Group ownership of PBC upon conclusion of the Business Combination will depend on the ultimate size of the PIPE financing the SPAC intends to complete in conjunction with the Business Combination, the extent of redemptions by SPAC shareholders and the impact of such redemptions on the SPAC shareholder base.
The purpose of these carve-out consolidated financial statements (the “Financial Statements”) is to provide historical financial information of PBC, to reflect PBC as if it had been operating separately from Psyence Group and its subsidiaries that do not partake in the Clinical Trials. Pursuant to the Business Combination Agreement, Newcourt is acquiring only the Clinical Trial related assets and liabilities of PBC, which are considered to be less than substantially all of PBC’s key operating assets. Therefore, the Financial Statements have been prepared on a “carve-out basis” from the consolidated financial statements of Psyence Group for the purposes of presenting the financial position, results of operations and cash flows of the Company and investments and operations relevant to the Clinical Trials on a stand-alone basis, excluding the continuing operations retained by PBC that are not being acquired by Newcourt. Accordingly, the Financial Statements reflect all the costs of business associated with the Clinical Trials, including both direct and indirect expenses allocable to the business. The carve-out consolidated Financial Statements represents the assets and liabilities of the Clinical Trials business that are specifically identifiable, and a reasonable basis exists to allocate items that are not specifically identifiable to the acquired business. Assets and liabilities excluded from the Financial Statements that are not considered to be relevant, both directly and indirectly, to the Clinical Trials include investments in subsidiaries, joint ventures, inter-company loans and website costs previously held by PBC that are not being acquired as part of the Business Combination Agreement. No assets or liabilities exist outside of PBC that are being acquired by Newcourt.
These Financial Statements are prepared on a going concern basis, which contemplates that the Company will continue in operation for the foreseeable future and will be able to realize its assets and discharge its liabilities in the normal course of business. During the year ended March 31, 2023, the Company incurred a net loss and comprehensive loss of $4,238,471 (Year ended March 31, 2022: $2,319,932) and the Company has no sources of revenue. The ability of the Company to continue operations is dependent on the Company’s ability to raise additional financing. There is no certainty that additional financing at terms that are acceptable will be available, and an inability to obtain financing would have a direct impact on the Company’s ability to continue as a going concern. These conditions indicate a material uncertainty that cast substantial doubt on the Company’s ability to continue as a going concern.
These Financial Statements do not reflect the adjustments to the carrying values and classifications of assets and liabilities that would be necessary if the Company were unable to realize its assets and settle its liabilities as a going concern in the normal course of operations. Such adjustments could be material.
2. Basis of presentation
Statement of compliance
The Financial Statements of the Company have been prepared using accounting policies in compliance with International Financial Reporting Standards (“IFRS”) issued by the International Accounting Standards Board (“IASB”).
The Financial Statements were authorized for issue on July 28, 2023 by the directors of the Company.
Carve-Out Consolidated Statements of Financial Position
The carve-out consolidated statements of financial position include the assets and liabilities that are the Clinical Trial related assets and liabilities, which have been determined in the following manner:
| · | Cash is comprised of cash and cash equivalents which the Company utilizes for working capital purposes. |
| · | Restricted cash is held in a guaranteed investment certificate with a bank as collateral for a credit facility agreement. |
| · | Other receivables are comprised of sales tax receivable from the Canadian Revenue Agency and the Australian Taxation Office. |
| · | Prepaids consists of a research report retainer and accounting fees prepaid. |
| · | Accounts payable and accrued liabilities consists of audit, consulting fees and legal fees related to the Company and its Clinical Trials. |
| · | Investments in subsidiaries and joint ventures of the Company that do not contain Clinical Trial related assets and liabilities have been excluded. |
Carve-Out Consolidated Statements of Net Loss and Comprehensive Loss
| · | The carve-out statements of net loss and comprehensive loss include operating expenses that are related to the Company and its Clinical Trials. |
| · | Psyence Group issued share-based compensation which has been included in the Company’s carve- out consolidated statements of loss and comprehensive loss based on the proportionate share of services received by the Company from the holder. |
Basis of consolidation
These Financial Statement incorporate the accounts of PBC and its subsidiaries relevant to the Clinical Trials. A subsidiary is an entity controlled by PBC and its results are consolidated into the financial results of the Company from the effective date of control up to the effective date of loss of control.
Control exists when an investor is exposed, or has the rights, to variable returns from the involvement with the investee and has liability to affect those returns through its power over the investee.
The subsidiaries of PBC relevant to the Clinical Trials that have been consolidated for the purpose of these Financial Statements are as follows:
| Name of entity | | Place of incorporation | | | % ownership | | | Accounting method |
| Psyence Australia Pty Ltd. | | | Australia | | | | 100% | | | Consolidated |
Inter-company balances and transactions are eliminated upon consolidation.
Basis of measurement
These Financial Statements have been prepared on an accrual basis, are based on historical costs and are presented in Canadian dollars, unless otherwise noted.
Functional and presentation currency
These Financial Statements are presented in Canadian Dollars (“CAD $”), which is also PBC’s functional currency. The functional currency of Psyence Australia Pty Ltd. is determined to be United States Dollars (“USD”).
3. Significant accounting policies
IFRS 9 Financial instruments
The Company recognizes a financial asset or a financial liability when, and only when, it becomes a party to the contractual provisions of the instrument. Such financial assets or financial liabilities are initially recognized at fair value plus or minus transaction costs that are directly attributable to the acquisition or issue of financial instruments that are not classified as fair value through profit or loss.
The classification and measurement approach for financial assets reflect the business model in which assets are managed and their cash flow characteristics. Financial assets are classified and measured based on these categories: amortized cost, fair value through other comprehensive income (“FVOCI”) and fair value through profit and loss (“FVTPL”). Financial assets are not reclassified subsequent to their initial recognition unless the Company identifies changes in its business model in managing financial assets.
A financial asset is measured at amortized cost if it meets both of the following conditions and is not designated as FVTPL:
| · | The financial asset is held within a business model whose objective is to hold assets in order to collect contractual cash flows; and |
| · | The contractual terms of the financial asset give rise on specified dates to cash flows that are solely payments of principal and interest on the principal amount outstanding. |
On initial recognition of an equity investment that is not held for trading, the Company may irrevocably elect to measure the investment at FVOCI whereby changes in the investment’s fair value (realized and unrealized) will be recognized permanently in OCI with no reclassification to profit or loss. The election is made on an investment-by-investment basis.
A financial asset shall be measured at FVTPL unless it is measured at amortized cost or at FVOCI.
Financial liabilities are classified and measured based on two categories — amortized cost or FVTPL:
Amortized cost
Financial liabilities are classified as measured at amortized cost unless they fall into one of the following categories: financial liabilities at FVTPL, financial liabilities that arise when a transfer of a financial asset does not qualify for derecognition, financial guarantee contracts, commitments to provide a loan at a below-market interest rate, or contingent consideration recognized by an acquirer in a business combination.
FVTPL
Financial liabilities are classified as FVTPL if they fall into one of the five exemptions detailed above. Classification and measurement of the financial instruments is as follows:
| Financial instrument | | Classification |
| Cash and cash equivalents | | Amortized cost |
| Restricted cash | | Amortized cost |
| Accounts payable and accrued liabilities | | Amortized cost |
Under IFRS 9, the Company applies a forward-looking expected credit loss (“ECL”) model, at each balance sheet date, to financial assets measured at amortized cost or those measured at FVOCI, except for investments in equity instruments.
The three-stage approach to recognizing ECL under IFRS 9 is intended to reflect the increase in credit risk of a financial instrument and are:
| · | Stage 1 is comprised of all financial instruments that have not had a significant increase in credit risk since initial recognition or that have low credit risk at the reporting date. The Company recognizes an impairment loss for those financial instruments at an amount equal to the twelve-month expected credit loss following the balance sheet date. |
| · | Stage 2 is comprised of all financial instruments that have had a significant increase in credit risk since initial recognition but that do not have objective evidence of a credit loss event. The Company recognizes an impairment loss for those financial instruments at an amount equal to the lifetime expected credit losses. |
| · | Stage 3 is comprised of all financial instruments that have objective evidence of impairment at the reporting date. The Company recognizes an impairment loss for those financial instruments at an amount equal to the lifetime expected credit losses. |
Impairment losses are recorded in the carve-out statements of net loss and comprehensive loss with the carrying amount of the financial assets reduced through the use of impairment allowance accounts.
The Company reverses impairment losses on financial assets carried at amortized cost when the decrease in impairment can be objectively related to an event occurring after the impairment loss was initially recognized.
Cash and cash equivalents
Cash and cash equivalents include cash on hand and, when applicable, short-term, highly liquid deposits which are either cashable or with original maturities of less than three months at the date of their acquisition.
Related party transactions
Parties are considered to be related if one party has the ability, directly or indirectly, to control the other party in making financial and operating decisions. Parties are also considered to be related if they are subject to common control. Related parties may be individuals or entities. A transaction is considered to be a related party transaction when there is transfer of resources or obligations between related parties.
Provisions
Provisions are recognized when the Company has a present obligation, legal or constructive as a result of a previous event, if it is probable that the Company will be required to settle the obligation and a reliable estimate can be made of the obligation. The amount recognized is the best estimate of the expenditure required to settle the present obligation at the end of the reporting period, taking into account the risks and uncertainties surrounding the obligations. Provisions are reviewed at the end of each reporting period and adjusted to reflect the current best estimate of the expected future cash flows.
Share based compensation
The proportionate share of the fair value of the options and warrants granted by Psyence Group shall be recognized as an expense in the Carve-Out Financial Statements of the Company. The expense shall be recognized over the vesting period of the options. The fair value of the options shall be determined using the Black-Scholes model.
The expense associated with the options and warrants shall be allocated to the Company based on the proportion of services received by the Company from the employees and consultants who have been granted the options.
Net parent investment
The net parent investment represents the net financings that the Company received from Psyence Group to fund its operations through contributions to the Clinical Trials, cash extended to the Company’s subsidiaries and joint ventures that were not related to the Clinical Trials, and the net effect of cost allocations from transactions with Psyence Group, all of which did not require repayments.
Research and development
Expenditures on research activities, undertaken with the prospect of gaining new scientific or technical knowledge and understanding, are recognized in the carve-out statements of net loss and comprehensive loss as incurred.
Development expenditures are capitalized only if development costs can be measured reliably, the product or process is technically and commercially feasible, future economic benefits are probable, and the Company intends to complete development and has sufficient resources to complete development and to use or sell the asset. Other development expenditures are expensed as incurred. Research and development expenses include all direct and indirect operating expenses supporting the products in development. The costs incurred in establishing and maintaining patents are expensed as incurred.
Foreign currency translation
The Financial Statements are presented in CAD $ which is PBC’s functional currency. The functional currency of its subsidiary consolidated within these Financial Statements is USD.
In each individual entity, a foreign currency transaction is initially recorded in the functional currency of the entity, by applying the exchange rate between the functional currency and the foreign currency at the date of the transaction.
At the end of the reporting period, monetary assets and liabilities of the Company which are denominated in foreign currencies are translated at the period-end exchange rate. Non-monetary assets and liabilities are translated at rates in effect at the date the assets were acquired, and liabilities incurred.
The resulting exchange gains or losses arising on the settlement of monetary items or on translating monetary items at rates different from those at which they were translated on initial recognition, are included in profit or loss in the period in which they arise.
For the purpose of presenting these Financial Statements, the assets and liabilities of the subsidiary are translated into CAD $ at the exchange rates prevailing at the end of the reporting period. Income and expenses are translated at the average rates for the period. Exchange differences arising are recognized in net parent investment.
| 4. | Critical accounting estimates and judgements |
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with IFRS requires management to make certain estimates, judgments and assumptions concerning the future. Actual results may differ from these estimates. The Company’s management reviews these estimates, judgments, and assumptions on an ongoing basis, based on experience and other factors, including expectations of future events that are believed to be reasonable under the circumstances. Revisions to estimates are adjusted prospectively in the period in which the estimates are revised. The following are deemed to be critical accounting policies by as these require a high level of subjectivity and judgement and could have a material impact on PBC’s financial statements.
Going concern
These Financial Statements have been prepared on the assumption that the Company will continue as a going concern, meaning it will continue in operation for the foreseeable future and will be able to realize assets and discharge liabilities in the ordinary course of operations.
Management routinely plans future activities including forecasting future cash flows and forming judgements collectively with directors of the Company.
Judgement is required in determining if the Company’s has sufficient cash reserves, together with all other available information, to continue as a going concern for a period of at least twelve months.
As at March 31, 2023 the Company has concluded that a material uncertainty exists that casts significant doubt about the Company’s ability to continue as a going concern.
Contingencies
From time to time, the Company is named as a party to claims or involved in proceedings, including legal, regulatory and tax related, in the ordinary course of its business. While the outcome of these matters may not be estimable at the reporting date, the Company makes provisions, where possible, for the estimated outcome of such claims or proceedings. Should a loss result from the resolution of any claims or proceedings that differs from these estimates, the difference will be accounted for as a charge to profit or loss in that period. The actual results may vary and may cause significant adjustments.
Share based compensation
The allocation of the expenses associated with the options and warrants granted by Psyence Group to the Company is based on the proportion of services received from the employees and consultants who have been granted the options. However, determining the proportion of services received by the Company involves judgment. Additionally, estimating the fair value for share-based payment transactions requires judgement in determining the most appropriate valuation model, which is dependent on the terms and conditions of the grant. This also requires estimation of the most appropriate inputs to the valuation model including the expected life of the share option or warrant, volatility, dividend yield and share price.
5. Cash, restricted cash and cash equivalents
Cash and cash equivalents include the following amounts:
| | | | |
| | | March 31,
2023 | | | March 31,
2022 | | | March 31,
2021 | |
| Unrestricted cash held with chartered banks | | | 1,800,539 | | | | 2,185,868 | | | | 6,001,436 | |
| Held in trust for brokerage account | | | 5,227 | | | | 5,227 | | | | 5,000 | |
| Restricted Cash | | | 40,000 | | | | 40,000 | | | | — | |
| Total | | | 1,845,776 | | | | 2,231,095 | | | | 6,006,436 | |
| · | an amount held in trust by a brokerage firm as security for foreign currency exchanges; |
| · | unrestricted cash held with chartered banks and |
| · | the Company entered into a cash collateral agreement with a major chartered bank in Canada with regards to a credit facility against which the Company deposited $40,000 in a guaranteed investment certificate with the bank. Amounts are held in restricted cash on the carve-out statements of financial position. |
6. Accounts payable and accrued liabilities
Accounts payable and accrued liabilities include the following amounts:
| | | March 31,
2023 | | | March 31,
2022 | | | March 31,
2021 | |
| Trade payables | | | 2,203,468 | | | | 46,054 | | | | 16,976 | |
| Accrued liabilities | | | 219,999 | | | | 118,446 | | | | 110,614 | |
| Total | | | 2,423,467 | | | | 164,500 | | | | 127,590 | |
7. Income taxes
The reconciliation of the combined Canadian federal and provincial statutory income tax rate of 26.5% (March 31, 2022 – 26.5%) to the effective tax rate is as follows:
| | | March 31,
2023 | | | March 31,
2022 | |
| Net Loss before recovery of income taxes | | | (4,238,471 | ) | | | (2,319,932 | ) |
| Expected income tax (recovery)/expense | | | (1,123,195 | ) | | | (614,782 | ) |
| Stock based compensation | | | 77,580 | | | | 109,862 | |
| Difference in tax rates | | | (60,111 | ) | | | — | |
| Change in tax benefits not recognized | | | 1,105,726 | | | | 504,920 | |
| Income tax (recovery)/expense | | | — | | | | — | |
Deferred tax
Unrecognized deferred tax asset
Deferred taxes are provided as a result of temporary differences that arise due to the differences between the income tax values and the carrying amounts of assets and liabilities. Deferred tax assets have not been recognized in respect of the following deductible temporary differences:
| | March 31, | | March 31, | |
| Unrecognized deferred tax | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| Non-capital losses carried forward – Canada | | | 5,137,001 | | | | 2,883,658 | |
| Non-capital losses carried forward – Australia | | | 1,717,450 | | | | — | |
| Intangible assets | | | 148,955 | | | | 2,749 | |
| Share issuance costs – 20(1)(e) | | | 380,888 | | | | 547,172 | |
| | | | 7,384,294 | | | | 3,433,580 | |
The Company’s Canadian non-capital income tax losses expire as follows:
| Expiry | | | Amount $ | |
| 2041 | | | | 827,846 | |
| 2042 | | | | 2,055,812 | |
| 2043 | | | | 2,253,343 | |
| Total | | | | 5,137,001 | |
The Company’s Australian non-capital income tax losses can be carried forward indefinitely.
The Company manages its cash and net parent investment as capital. The Company’s objectives when managing capital are to safeguard the Company’s ability to continue as a going concern in order to pursue the development of natural health business, to maintain a flexible capital structure which optimizes the cost of capital at an acceptable risk level.
The Company manages its capital structure and makes adjustments to it in light of changes in economic conditions and the risk characteristics of the underlying assets. To maintain or adjust its capital structure, the Company may obtain additional funding from its parent, issue new debt, acquire or dispose of assets or adjust the amount of cash and cash equivalents on hand.
In order to facilitate the management of its capital requirements, the Company prepares annual budgets that are updated as necessary depending on various factors, including successful capital deployment and general industry conditions. The annual and updated budgets are approved by the Board of Directors.
Management considers its approach to capital management to be appropriate given the relative size of the Company. There were no changes in the Company’s approach to capital management during the year.
| 9. | Transactions with related parties |
All related party transactions are measured at the exchange amount, which is the amount of consideration established and agreed to by the related parties. All amounts either due from or due to related parties other than specifically disclosed are non-interest bearing, unsecured and have no fixed terms of repayments. The Company incurred the following transactions with related parties during the years ended March 31, 2023 and March 31, 2022:
Compensation to key management personnel
Key management personnel are those persons having authority and responsibility for planning, directing and controlling the activities of the Company, directly or indirectly. Key management personnel include the Company’s executive officers and Board of Directors.
| | March 31, | | March 31, | |
| Key Management Personnel | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| Short term benefits | | | 785,487 | | | | 764,965 | |
| Share based compensation | | | 231,231 | | | | 370,037 | |
| Total | | | 1,016,718 | | | | 1,135,002 | |
Short term benefits consist of consulting fees, payroll and other benefits paid to key management personnel. Share based compensation is options granted to key management personnel. Accounts payable included balances for related parties of $100,355 ($22,005 – March 31, 2022 & $28,125 – March 31, 2021).
| 10. | Share based compensation |
During the year ended March 31, 2023 $292,756 (Year ended March 31, 2022 – $414,574) was recognized for options and restricted stock units (“RSU’s”) granted by Psyence Group under professional fees and consulting expenses and general and administrative expenses on the carve-out consolidated statements of net loss and comprehensive loss.
The allocation of share based compensation expense to the Company was comprised of a total of 2,558,401 (year ended March 31, 2022 – 1,350,000) options granted by Psyence Group during the year ended March 31, 2023 with a weighted average fair value of $0.09 (year ended March 31, 2022 – $0.19) and a total of 3,528,750 (year ended March 31, 2022 – 735,387) RSUs granted by Psyence Group during the year ended March 31, 2023 with a weighted average fair value of $0.12 (year ended March 31, 2022 – $0.16).
Options and RSUs granted were subject to various time-based vesting terms. This allocation was based on services received from consultants and employees who were granted options in Psyence Group.
The fair value of the RSU’s was based on the Company’s share price at the date of grant.
The fair value of the options was determined at the grant date based on the Black Scholes pricing model, using the following weighted average assumptions:
| | | Options granted during year
ended March 31, 2023 | | | Options granted during year
ended March 31, 2022 | |
| Numbers issued | | | 2,558,401 | | | | 1,350,000 | |
| Share price | | | $0.09 – $0.14 | | | | $0.26 | |
| Expected dividend yield | | | Nil | | | | Nil | |
| Exercise price | | | $0.14 – $0.20 | | | | $0.30 | |
| Risk-free interest rate | | | 2.78% – 3.49% | | | | 0.96% | |
| Expected life | | | 3.00 – 5.00 | | | | 5.00 | |
| Expected volatility | | | 100% | | | | 100% | |
| 11. | Advances from Psyence Group |
During the year ended March 31, 2023, the Company received cash advances from Psyence Group in the amount of $1,551,744 (March 31, 2022 - $2,031,964), that have been utilized by the Company to conduct its Clinical Trial operations to date. As the advances made by Psyence Group are not expected to be repaid in future periods, the advances have been classified as part of the Company’s net parent investment from Psyence Group in the Clinical Trials.
| Advances from (repayments to) Psyence Group | | March 31, 2023 | | | March 31, 2022 | |
| Opening balance | | | 5,060,331 | | | | 7,092,295 | |
| Amounts advanced (repaid) | | | 1,551,744 | | | | (2,031,964 | ) |
| Ending Balance | | | 6,612,075 | | | | 5,060,331 | |
| 12. | Financial instruments and financial risk management |
In the normal course of business, the Company is exposed to a variety of financial risks: credit risk, liquidity risk, foreign exchange risk and interest rate risk. These financial risks are subject to normal credit standards, financial controls, risk management as well as monitoring. The Company’s Board of Directors has overall responsibility for the establishment and oversight of the Company’s risk management framework.
Credit risk
Credit risk arises from cash and cash equivalents held with banks. The maximum exposure to credit risk is equal to the carrying value of the financial assets. The objective of managing counterparty credit risk is to prevent losses on financial assets. The Company minimizes the credit risk of cash and cash equivalents by depositing with only reputable financial institutions.
Liquidity risk
Liquidity risk is the risk that the Company will not be able to meet its financial obligations as they fall due.
The Company manages liquidity risk through an ongoing review of future commitments and cash balances available. Historically, the Company’s main source of funding has been through investments from its parent. The Company’s access to financing is always uncertain. There can be no assurance of continued access to significant equity or debt funding.
Interest rate risk
Interest rate risk is the risk that the fair value of future cash flows of a financial instrument will fluctuate because of changes in market interest rates. The Company has no significant interest-bearing assets or liabilities and therefore its income and operating cash flows are substantially independent of changes in market interest rates.
Foreign exchange risk
Foreign currency risk is the risk that the fair values of future cash flows of a financial instrument will fluctuate because they are denominated in currencies that differ from the respective functional currency.
As at March 31, 2023, a 10% fluctuation in foreign exchange rates would result in a $5,482 impact to profit or loss.

Psyence Biomed Corp.
Carve-Out Unaudited Condensed Consolidated Interim Financial Statements
For the three and six months ended September 30, 2023
Expressed in Canadian Dollars
(CAD $)
PSYENCE BIOMED CORP.
Carve-Out Condensed Consolidated Interim Financial Statements (unaudited)
Management's Responsibility for Financial Reporting
The accompanying carve-out unaudited condensed consolidated interim financial statements of the Company have been prepared by management in accordance with International Financial Reporting Standards. These carve-out financial statements contain estimates based on management’s judgment. Management maintains an appropriate system of internal controls to provide reasonable assurance that transactions are authorized, assets safeguarded, and proper records maintained.
The Audit Committee of the Board of Directors reviews the results of the audit and the carve-out condensed consolidated interim financial statements prior to submitting the carve-out condensed consolidated interim financial statements to the Board for approval.
“Dr. Neil Maresky”
___________________
Chief Executive Officer
Toronto, Canada
January 31, 2024
 | F-21 |
| | |
PSYENCE BIOMED CORP.
Carve-Out Condensed Consolidated Interim Financial Statements (unaudited)
Carve-Out Condensed Consolidated Interim Statements of Financial Position
As at September 30, 2023 and March 31, 2023
| CAD $ | | Note | | | As at
September 30, 2023 | | | As at
March 31, 2023 | |
| ASSETS | | | | | | | | | |
| Current assets | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | | 5 | | | | 818,609 | | | | 1,805,766 | |
| Restricted cash | | 5 | | | | 40,000 | | | | 40,000 | |
| Other receivables | | | | | | 25,400 | | | | 202,150 | |
| Prepaids | | | | | | 20,982 | | | | 104,276 | |
| Total current assets | | | | | | 904,991 | | | | 2,152,192 | |
| TOTAL ASSETS | | | | | | 904,991 | | | | 2,152,192 | |
| LIABILITIES | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Current liabilities | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Accounts payable and accrued liabilities | | 6 | | | | 1,237,068 | | | | 2,423,467 | |
| Loan payable | | 10 | | | | 996,495 | | | | - | |
| Total current liabilities | | | | | | 2,233,563 | | | | 2,423,467 | |
| TOTAL LIABILITIES | | | | | | 2,233,563 | | | | 2,423,467 | |
| EQUITY | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net parent investment | | | | | | (1,328,572 | ) | | | (271,275 | ) |
| NET PARENT INVESTMENT | | | | | | (1,328,572 | ) | | | (271,275 | ) |
TOTAL LIABILITIES AND NET PARENT INVESTMENT | | | | | | 904,991 | | | | 2,152,192 | |
Nature of operations and going concern (note 1)
Approved on behalf of Board of Directors
| “Dr. Neil Maresky” | | “Jody Aufrichtig” |
| Chief Executive Officer and Director | | Executive Chairman and Director |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of the Carve-Out Condensed Consolidated Interim Financial Statements
 | F-22 |
| | |
PSYENCE BIOMED CORP.
Carve-Out Condensed Consolidated Interim Financial Statements (unaudited)
Carve-Out Condensed Consolidated Interim Statements of Net Loss and Comprehensive Loss
For the three and six months ended September 30, 2023 and September 30, 2022
| CAD $ | | Note | | Three months
ending
September 30, 2023 | | | Three months
ending
September 30, 2022 | | | Six months
ending
September 30, 2023 | | | Six months
ending
September 30, 2022 | |
| Expenses | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Sales and marketing | | | | 1,471 | | | - | | | 2,848 | | | - | |
| Research and development | | | | (11,454 | ) | | 2,533 | | | 1,062,212 | | | 207,446 | |
| General and administrative | | | | (21,627 | ) | | 102,912 | | | 114,845 | | | 222,825 | |
| Professional fees and consulting fees | | | | 267,918 | | | 228,242 | | | 784,375 | | | 441,219 | |
| Foreign exchange loss | | | | 141,626 | | | 2,005 | | | 154,927 | | | 3,731 | |
| Interest Expense/(Income) | | | | 37,474 | | | (1,090 | ) | | 36,805 | | | (1,298 | ) |
| NET LOSS | | 10 | | 426,862 | | | 334,602 | | | 2,156,012 | | | 873,923 | |
| TOTAL COMPREHENSIVE LOSS | | | | 426,862 | | | 334,602 | | | 2,156,012 | | | 873,923 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of the Carve-Out Condensed Consolidated Interim Financial Statements
 | F-23 |
| | |
PSYENCE BIOMED CORP.
Carve-Out Condensed Consolidated Interim Financial Statements (unaudited)
Carve-Out Condensed Consolidated Statements of Changes in Net Parent Investment
For the periods ended September 30, 2023 and September 30, 2022
| | Note | | Net parent investment | |
| Opening balance as at April 1, 2022 | | | | 2,122,696 | |
| Net investment returned to parent in the year | | | | (1,237,340 | ) |
| Net loss | | | | (873,923 | ) |
| Balance, September 30, 2022 | | | | 11,433 | |
| | | | | | |
| Opening balance as at April 1, 2023 | | | | (271,275 | ) |
| Net investment by parent in the year | | | | 1,098,715 | |
| Net loss | | | | (2,156,012 | ) |
| Balance, September 30, 2023 | | | | (1,328,572 | ) |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of the Carve-Out Condensed Consolidated Interim Financial Statements
 | F-24 |
| | |
PSYENCE BIOMED CORP.
Carve-Out Condensed Consolidated Interim Financial Statements (unaudited)
Carve-Out Condensed Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows
For the six months period ended September 30, 2023 and September 30, 2022
| | | Note | | | Six months
ended
September 30, 2023 | | | Six months
ended
September 30, 2022 | |
| Net loss | | | | | | (2,156,012 | ) | | | (873,923 | ) |
| Non-cash adjustment: | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Share based compensation | | 11 | | | | (54,625 | ) | | | 78,964 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Changes in working capital: | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Other receivables | | | | | | 176,750 | | | | (76,209 | ) |
| Prepaids | | | | | | 83,294 | | | | 6,730 | |
| Accounts payable and accrued liabilities | | 6 | | | | (189,904 | ) | | | 122,690 | |
| Cash used in operating activities | | | | | | (2,140,497 | ) | | | (741,748 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Increase in restricted cash | | 5 | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Cash used in investing activities | | | | | | - | | | | - | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Amounts advanced from/(to) parent | | | | | | 193,810 | | | | (1,339,171 | ) |
| Proceeds received from loan | | | | | | 959,530 | | | | - | |
| Cash provided from/(used in) financing activities | | | | | | 1,153,340 | | | | (1,339,171 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Change in cash and cash equivalents | | | | | | (987,157 | ) | | | (2,080,919 | ) |
| Cash and cash equivalents, beginning of period | | | | | | 1,805,766 | | | | 2,191,095 | |
| Cash and cash equivalents, end of period | | | | | | 818,609 | | | | 110,176 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of the Carve-Out Condensed Consolidated Interim Financial Statements
 | F-25 |
| | |
PSYENCE BIOMED CORP.
Carve-Out Condensed Consolidated Interim Financial Statements (unaudited)
Notes to the Carve-Out Condensed Consolidated Interim Financial Statements
1. Nature of operations and going concern
Psyence Biomed Corp. (the “Company” or “PBC”) is a life science biotechnology company owned by Psyence Group Inc. (“Psyence Group”). It is pioneering the use of natural psychedelics in the treatment of psychological trauma and mental health disorders. It was incorporated under the laws of the province of British Columbia, Canada on May 21, 2020. The Company’s registered office is at 121 Richmond Street West, PH Suite 1300, Toronto, Ontario M5H 2K1.
The Company is currently conducting clinical trials to evaluate the safety and effectiveness of natural psilocybin in treating adjustment disorder in patients with an incurable cancer diagnosis in a palliative care context (the “Clinical Trials”).
The UK Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA) granted full approval for the Company’s Stage I clinical study, including ethics review board approval, on September 15, 2022.
In January 2023, the Company signed a letter of intent with iNGENū Pty Ltd to conduct a Phase IIb study in Australia to further develop the Company’s licensed natural psilocybin drug product. The study will evaluate the safety and efficacy of psilocybin-assisted psychotherapy versus psychotherapy alone for the treatment of adjustment disorder due to an incurable cancer diagnosis in a palliative care context.
Over 75 patients will participate in the study, which will use FDA-recommended primary endpoints. The investigational product will be the proprietary botanical drug candidate PEX010 sourced from Filament Health Corp. Upon successful completion of the study, Psyence intends to conduct a multinational Phase III registrational study.
On February 15, 2023, the Company incorporated a wholly-owned subsidiary by the name of Psyence Australia Pty Ltd., registered in Victoria, Australia.
On January 9, 2023 Psyence Group announced that it had entered into a definitive business combination agreement (the “Business Combination Agreement”) with Newcourt Acquisition Corp (NASDAQ: NCAC), a special purpose acquisition company (“SPAC”) formed for the purpose of acquiring or merging with one or more businesses (“Newcourt”). Newcourt has entered into the Business Combination Agreement with the Company, in order to create a public company leveraging natural psilocybin in the treatment of palliative care (the “Pubco”).
The transaction is anticipated to conclude early in 2024, with the Pubco to go public. The transaction is expected to be completed by the Company acquiring the SPAC through the merger of the SPAC with a subsidiary of PBC. As a consequence of the transaction, the SPAC will become a wholly-owned subsidiary of PBC, the SPAC shareholders will become shareholders of PBC, and PBC would complete filings to become a public company in the United States in which Psyence Group would retain a significant ownership stake. The actual level of Psyence Group ownership of PBC upon conclusion of the Business Combination will depend on the ultimate size of the PIPE financing the SPAC intends to complete in conjunction with the Business Combination, the extent of redemptions by SPAC shareholders and the impact of such redemptions on the SPAC shareholder base.
The purpose of these carve-out condensed consolidated interim financial statements (the “Financial Statements”) is to provide historical financial information of PBC, to reflect PBC as if it had been operating separately from Psyence Group and its subsidiaries that do not partake in the Clinical Trials. The Financial Statements have been prepared on a “carve-out basis” from the consolidated financial statements of Psyence Group Inc. for the purposes of presenting the financial position, results of operations and cash flows of the Company and investments and operations relevant to the Clinical Trials on a stand-alone basis.
These Financial Statements are prepared on a going concern basis, which contemplates that the Company will continue in operation for the foreseeable future and will be able to realize its assets and discharge its liabilities in the normal course of business. During the period ended September 30, 2023, the Company incurred a net loss and comprehensive loss of $2,156,012 (Period ended September 30, 2022: $873,923) and the Company has no sources of revenue. The ability of the Company to continue operations is dependent on the Company’s ability to raise additional financing. There is no certainty that additional financing at terms that are acceptable will be available, and an inability to obtain financing would have a direct impact on the Company’s ability to continue as a going concern. These conditions indicate a material uncertainty that cast substantial doubt on the Company’s ability to continue as a going concern.
These Financial Statements do not reflect the adjustments to the carrying values and classifications of assets and liabilities that would be necessary if the Company were unable to realize its assets and settle its liabilities as a going concern in the normal course of operations. Such adjustments could be material.
 | F-26 |
| | |
PSYENCE BIOMED CORP.
Carve-Out Condensed Consolidated Interim Financial Statements (unaudited)
2. Basis of presentation
Statement of compliance
The Financial Statements of the Company have been prepared using accounting policies in compliance with International Financial Reporting Standards (“IFRS”) issued by the International Accounting Standards Board (“IASB”).
The Financial Statements were authorized for issue on January 31, 2024 by the directors of the Company.
Carve-Out Condensed Consolidated Interim Statements of Financial Position
The carve-out condensed consolidated interim statements of financial position include the assets and liabilities that are the Clinical Trial related assets and liabilities, which have been determined in the following manner:
| · | Cash is comprised of cash and cash equivalents which the Company utilizes for working capital purposes. |
| · | Restricted cash is held in a guaranteed investment certificate with a bank as collateral for a credit facility agreement. |
| · | Other receivables are comprised of sales tax receivable from the Canadian Revenue Agency and the Australian Taxation Office. |
| · | Prepaids consists of a research report retainer and accounting fees prepaid. |
| · | Accounts payable and accrued liabilities consists of audit, consulting fees and legal fees related to the Company and its Clinical Trials. |
| · | Investments in subsidiaries and joint ventures of the Company that do not contain Clinical Trial related assets and liabilities have been excluded. |
Carve-Out Condensed Consolidated Interim Statements of Net Loss and Comprehensive Loss
| · | The carve-out condensed consolidated interim statements of net loss and comprehensive loss include operating expenses that are related to the Company and its Clinical Trials. |
| | · | Psyence Group issued share-based compensation which has been included in the Company’s carve-out condensed consolidated statements of net loss and comprehensive loss based on the proportionate share of services received by the Company from the holder. |
Basis of consolidation
These Financial Statement incorporate the accounts of PBC and its subsidiaries relevant to the Clinical Trials. A subsidiary is an entity controlled by PBC and its results are consolidated into the financial results of the Company from the effective date of control up to the effective date of loss of control.
Control exists when an investor is exposed, or has the rights, to variable returns from the involvement with the investee and has liability to affect those returns through its power over the investee.
 | F-27 |
| | |
PSYENCE BIOMED CORP.
Carve-Out Condensed Consolidated Interim Financial Statements (unaudited)
The subsidiaries of PBC relevant to the Clinical Trials that have been consolidated for the purpose of these Financial Statements are as follows:
| Name of entity | | Place of incorporation | | | % ownership | | | Accounting method |
| Psyence Australia Pty Ltd. | | | Australia | | | | 100 | % | | Consolidated |
Inter-company balances and transactions are eliminated upon consolidation.
Basis of measurement
These Financial Statements have been prepared on an accrual basis, are based on historical costs and are presented in Canadian dollars, unless otherwise noted.
Functional and presentation currency
These Financial Statements are presented in Canadian Dollars (“CAD $”), which is also PBC’s functional currency. The functional currency of Psyence Australia Pty Ltd. is determined to be United States Dollars (“USD”).
3. Significant accounting policies
IFRS 9 Financial instruments
The Company recognizes a financial asset or a financial liability when, and only when, it becomes a party to the contractual provisions of the instrument. Such financial assets or financial liabilities are initially recognized at fair value plus or minus transaction costs that are directly attributable to the acquisition or issue of financial instruments that are not classified as fair value through profit or loss.
The classification and measurement approach for financial assets reflect the business model in which assets are managed and their cash flow characteristics. Financial assets are classified and measured based on these categories: amortized cost, fair value through other comprehensive income (“FVOCI”) and fair value through profit and loss (“FVTPL”). Financial assets are not reclassified subsequent to their initial recognition unless the Company identifies changes in its business model in managing financial assets.
A financial asset is measured at amortized cost if it meets both of the following conditions and is not designated as FVTPL:
| · | The financial asset is held within a business model whose objective is to hold assets in order to collect contractual cash flows; and |
| · | The contractual terms of the financial asset give rise on specified dates to cash flows that are solely payments of principal and interest on the principal amount outstanding. |
On initial recognition of an equity investment that is not held for trading, the Company may irrevocably elect to measure the investment at FVOCI whereby changes in the investment’s fair value (realized and unrealized) will be recognized permanently in OCI with no reclassification to profit or loss. The election is made on an investment-by-investment basis.
A financial asset shall be measured at FVTPL unless it is measured at amortized cost or at FVOCI.
Financial liabilities are classified and measured based on two categories – amortized cost or FVTPL:
Amortized cost
Financial liabilities are classified as measured at amortized cost unless they fall into one of the following categories: financial liabilities at FVTPL, financial liabilities that arise when a transfer of a financial asset does not qualify for derecognition, financial guarantee contracts, commitments to provide a loan at a below-market interest rate, or contingent consideration recognized by an acquirer in a business combination.
 | F-28 |
| | |
PSYENCE BIOMED CORP.
Carve-Out Condensed Consolidated Interim Financial Statements (unaudited)
FVTPL
Financial liabilities are classified as FVTPL if they fall into one of the five exemptions detailed above.
Classification and measurement of the financial instruments is as follows:
| Financial instrument | | Classification |
| | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | | Amortized cost |
| Restricted cash | | Amortized cost |
| Accounts payable and accrued liabilities | | Amortized cost |
| Loan payable | | Amortized cost |
Under IFRS 9, the Company applies a forward-looking expected credit loss (“ECL”) model, at each balance sheet date, to financial assets measured at amortized cost or those measured at FVOCI, except for investments in equity instruments.
The three-stage approach to recognizing ECL under IFRS 9 is intended to reflect the increase in credit risk of a financial instrument and are:
| · | Stage 1 is comprised of all financial instruments that have not had a significant increase in credit risk since initial recognition or that have low credit risk at the reporting date. The Company recognizes an impairment loss for those financial instruments at an amount equal to the twelve-month expected credit loss following the balance sheet date. |
| | | |
| · | Stage 2 is comprised of all financial instruments that have had a significant increase in credit risk since initial recognition but that do not have objective evidence of a credit loss event. The Company recognizes an impairment loss for those financial instruments at an amount equal to the lifetime expected credit losses. |
| | | |
| · | Stage 3 is comprised of all financial instruments that have objective evidence of impairment at the reporting date. The Company recognizes an impairment loss for those financial instruments at an amount equal to the lifetime expected credit losses. |
Impairment losses are recorded in the carve-out statements of net loss and comprehensive loss with the carrying amount of the financial assets reduced through the use of impairment allowance accounts.
The Company reverses impairment losses on financial assets carried at amortized cost when the decrease in impairment can be objectively related to an event occurring after the impairment loss was initially recognized.
Cash and cash equivalents
Cash and cash equivalents include cash on hand and, when applicable, short-term, highly liquid deposits which are either cashable or with original maturities of less than three months at the date of their acquisition.
Related party transactions
Parties are considered to be related if one party has the ability, directly or indirectly, to control the other party in making financial and operating decisions. Parties are also considered to be related if they are subject to common control. Related parties may be individuals or entities. A transaction is considered to be a related party transaction when there is transfer of resources or obligations between related parties.
Provisions
Provisions are recognized when the Company has a present obligation, legal or constructive as a result of a previous event, if it is probable that the Company will be required to settle the obligation and a reliable estimate can be made of the obligation. The amount recognized is the best estimate of the expenditure required to settle the present obligation at the end of the reporting period, taking into account the risks and uncertainties surrounding the obligations. Provisions are reviewed at the end of each reporting period and adjusted to reflect the current best estimate of the expected future cash flows.
Net parent investment
The net parent investment represents the net financings that the Company received from Psyence Group to fund its operations through contributions to the Clinical Trials, cash extended to the Company's subsidiaries and joint ventures that were not related to the Clinical Trials, and the net effect of cost allocations from transactions with Psyence Group, all of which did not require repayments.
 | F-29 |
| | |
PSYENCE BIOMED CORP.
Carve-Out Condensed Consolidated Interim Financial Statements (unaudited)
Research and development
Expenditures on research activities, undertaken with the prospect of gaining new scientific or technical knowledge and understanding, are recognized in the carve-out statements of net loss and comprehensive loss as incurred.
Development expenditures are capitalized only if development costs can be measured reliably, the product or process is technically and commercially feasible, future economic benefits are probable, and the Company intends to complete development and has sufficient resources to complete development and to use or sell the asset. Other development expenditures are expensed as incurred. Research and development expenses include all direct and indirect operating expenses supporting the products in development. The costs incurred in establishing and maintaining patents are expensed as incurred.
Foreign currency translation
The Financial Statements are presented in CAD $ which is PBC’s functional currency. The functional currency of its subsidiary consolidated within these Financial Statements is USD.
In each individual entity, a foreign currency transaction is initially recorded in the functional currency of the entity, by applying the exchange rate between the functional currency and the foreign currency at the date of the transaction.
At the end of the reporting period, monetary assets and liabilities of the Company which are denominated in foreign currencies are translated at the period-end exchange rate. Non-monetary assets and liabilities are translated at rates in effect at the date the assets were acquired, and liabilities incurred.
The resulting exchange gains or losses arising on the settlement of monetary items or on translating monetary items at rates different from those at which they were translated on initial recognition, are included in profit or loss in the period in which they arise.
For the purpose of presenting these Financial Statements, the assets and liabilities of the subsidiary are translated into CAD $ at the exchange rates prevailing at the end of the reporting period. Income and expenses are translated at the average rates for the period. Exchange differences arising are recognized in net parent investment.
4. Critical accounting estimates and judgements
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with IFRS requires management to make certain estimates, judgments and assumptions concerning the future. Actual results may differ from these estimates. The Company’s management reviews these estimates, judgments, and assumptions on an ongoing basis, based on experience and other factors, including expectations of future events that are believed to be reasonable under the circumstances. Revisions to estimates are adjusted prospectively in the period in which the estimates are revised. The following are deemed to be critical accounting policies by as these require a high level of subjectivity and judgement and could have a material impact on PBC’s financial statements.
Going concern
These Financial Statements have been prepared on the assumption that the Company will continue as a going concern, meaning it will continue in operation for the foreseeable future and will be able to realize assets and discharge liabilities in the ordinary course of operations.
Management routinely plans future activities including forecasting future cash flows and forming judgements collectively with directors of the Company.
Judgement is required in determining if the Company's has sufficient cash reserves, together with all other available information, to continue as a going concern for a period of at least twelve months.
As at September 30, 2023 the Company has concluded that a material uncertainty exists that casts significant doubt about the Company’s ability to continue as a going concern.
 | F-30 |
| | |
PSYENCE BIOMED CORP.
Carve-Out Condensed Consolidated Interim Financial Statements (unaudited)
Contingencies
From time to time, the Company is named as a party to claims or involved in proceedings, including legal, regulatory and tax related, in the ordinary course of its business. While the outcome of these matters may not be estimable at the reporting date, the Company makes provisions, where possible, for the estimated outcome of such claims or proceedings. Should a loss result from the resolution of any claims or proceedings that differs from these estimates, the difference will be accounted for as a charge to profit or loss in that period. The actual results may vary and may cause significant adjustments.
Share based compensation
The allocation of the expenses associated with the options and warrants granted by Psyence Group to the Company is based on the proportion of services received from the employees and consultants who have been granted the options. However, determining the proportion of services received by the Company involves judgment. Additionally, estimating the fair value for share-based payment transactions requires judgement in determining the most appropriate valuation model, which is dependent on the terms and conditions of the grant. This also requires estimation of the most appropriate inputs to the valuation model including the expected life of the share option or warrant, volatility, dividend yield and share price.
5. Cash, restricted cash and cash equivalents
Cash and cash equivalents include the following amounts:
| | | September 30,
2023 | | March 31,
2023 |
| Unrestricted cash held with chartered banks | | | 813,382 | | | 1,800,539 |
| Held in trust for brokerage account | | | 5,227 | | | 5,227 |
| Restricted Cash | | | 40,000 | | | 40,000 |
| Total | | | 858,609 | | | 1,845,766 |
| · | an amount held in trust by a brokerage firm as security for foreign currency exchanges; |
| · | unrestricted cash held with chartered banks and |
| · | the Company entered into a cash collateral agreement with a major chartered bank in Canada with regards to a credit facility against which the Company deposited $40,000 in a guaranteed investment certificate with the bank. Amounts are held in restricted cash on the carve-out statements of financial position. |
6. Accounts payable and accrued liabilities
Accounts payable and accrued liabilities include the following amounts:
| | | September 30,
2023 | | March 31,
2023 |
| Trade payables | | | 1,994,702 | | | 2,203,468 |
| Accrued liabilities | | | 238,861 | | | 219,999 |
| Total | | | 2,233,563 | | | 2,423,467 |
7. Capital management
The Company manages its cash and net parent investment as capital. The Company’s objectives when managing capital are to safeguard the Company’s ability to continue as a going concern in order to pursue the development of natural health business, to maintain a flexible capital structure which optimizes the cost of capital at an acceptable risk level.
 | F-31 |
| | |
PSYENCE BIOMED CORP.
Carve-Out Condensed Consolidated Interim Financial Statements (unaudited)
The Company manages its capital structure and makes adjustments to it in light of changes in economic conditions and the risk characteristics of the underlying assets. To maintain or adjust its capital structure, the Company may obtain additional funding from its parent, issue new debt, acquire or dispose of assets or adjust the amount of cash and cash equivalents on hand.
In order to facilitate the management of its capital requirements, the Company prepares annual budgets that are updated as necessary depending on various factors, including successful capital deployment and general industry conditions. The annual and updated budgets are approved by the Board of Directors.
Management considers its approach to capital management to be appropriate given the relative size of the Company. There were no changes in the Company’s approach to capital management during the year.
8. Transactions with related parties
All related party transactions are measured at the exchange amount, which is the amount of consideration established and agreed to by the related parties. All amounts either due from or due to related parties other than specifically disclosed are non-interest bearing, unsecured and have no fixed terms of repayments. The Company incurred the following transactions with related parties during the periods ended September 30, 2023 and September 30, 2022:
Compensation to key management personnel
Key management personnel are those persons having authority and responsibility for planning, directing and controlling the activities of the Company, directly or indirectly. Key management personnel include the Company’s executive officers and Board of Directors.
| Key Management Personnel | | September 30,
2023 | | September 30,
2022 |
| Short term benefits | | | 251,514 | | | 327,439 |
| Total | | | 251,514 | | | 327,439 |
Short term benefits consist of consulting fees, payroll and other benefits paid to key management personnel.
9. Net Parent Investment
As at September 30, 2023 the Company had inter-company loans of $6,805,885 (March 31, 2023 - $6,612,075) to Psyence Group, which it received in order to fund its operations. The loans are non-interest bearing and repayable on demand.
10. Loan payable
On August 21, 2023 the Company entered into a loan agreement (the “Loan Agreement”) via its Australian subsidiary Psyence Australia (Pty) Ltd (the “Borrower”), to borrow up to AUD$1,100,000 by way of a secured loan (the “Loan”) from RH Capital Finance Co., LLC. The Loan is secured by way of a General Security Agreement and parent company guarantee against the assets of the Borrower and the Company. The loan was granted to the Borrower after it successfully registered its research and development activities with the Australian Federal Government. The Borrower benefits from the Australian Federal Government’s Research & Development tax incentive program, which provides up to a 43.5% rebate on research and development expenses in Australia. The Loan bears interest at 16% per annum subject to a minimum interest chargeable period of 91 days, and is repayable at the earlier of: (a) 21 business days after the notice of assessment (in respect of R&D refunds) is issued by the Australian Taxation Office to the Borrower for the financial year ended June 30, 2023 (b) an event of default and (c) 30 November 2023.
$37,615 in interest expense was incurred during the six months ended September 30, 2023. The loan and all outstanding interest was repaid after quarter end after the Australian Taxation Office refunded 43.5% of expenditure incurred on research and development in Australia.
 | F-32 |
| | |
PSYENCE BIOMED CORP.
Carve-Out Condensed Consolidated Interim Financial Statements (unaudited)
11. Share based compensation
During the period ended September 30, 2023, $54,625 was reversed due to voluntary cancelled options (Period ended September 30, 2022 - $0 was recognized) for options and restricted stock units (“RSU’s”) granted by Psyence Group under professional fees and consulting expenses and general and administrative expenses on the carve-out condensed consolidated interim statements of net loss and comprehensive loss.
Options and RSUs granted were subject to various time-based vesting terms. This allocation was based on services received from consultants and employees who were granted options in Psyence Group.
12. Financial instruments and financial risk management
In the normal course of business, the Company is exposed to a variety of financial risks: credit risk, liquidity risk, foreign exchange risk and interest rate risk. These financial risks are subject to normal credit standards, financial controls, risk management as well as monitoring. The Company’s Board of Directors has overall responsibility for the establishment and oversight of the Company’s risk management framework.
Credit risk
Credit risk arises from cash and cash equivalents held with banks. The maximum exposure to credit risk is equal to the carrying value of the financial assets. The objective of managing counterparty credit risk is to prevent losses on financial assets. The Company minimizes the credit risk of cash and cash equivalents by depositing with only reputable financial institutions.
Liquidity risk
Liquidity risk is the risk that the Company will not be able to meet its financial obligations as they fall due.
The Company manages liquidity risk through an ongoing review of future commitments and cash balances available. Historically, the Company’s main source of funding has been through investments from its parent. The Company’s access to financing is always uncertain. There can be no assurance of continued access to significant equity or debt funding.
Interest rate risk
Interest rate risk is the risk that the fair value of future cash flows of a financial instrument will fluctuate because of changes in market interest rates. The Company has no significant interest-bearing assets or liabilities and therefore its income and operating cash flows are substantially independent of changes in market interest rates.
Foreign exchange risk
Foreign currency risk is the risk that the fair values of future cash flows of a financial instrument will fluctuate because they are denominated in currencies that differ from the respective functional currency.
As at September 30, 2023, a 10% fluctuation in foreign exchange rates would result in a $110,468 impact to profit or loss.
13. Subsequent Events
The loan agreement with RH Capital Finance Co., LLC was repaid in full on October 5, 2023 when the Company received the research and development rebate of AUD $1,336,622 ($1,165,935) from the Australian Taxation office which was utilised to settle the loan payable.
On January 25, 2024 (the “Closing Date”), Psyence Biomedical Ltd., a corporation organized under the laws of Ontario, Canada (“Psyence Biomedical”), consummated the previously announced business combination pursuant to the Amended and Restated Business Combination Agreement (as amended, the “BCA”), dated as of July 31, 2023, by and among Psyence Biomedical, Newcourt, Newcourt SPAC Sponsor LLC, a Delaware limited liability company (“Sponsor”), Psyence Group, a corporation organized under the laws of Ontario, Canada, Psyence (Cayman) Merger Sub, a Cayman Islands exempted company and a direct and wholly owned subsidiary of Pubco (“Merger Sub”), the Company, and Psyence Biomed II Corp., a corporation organized under the laws of Ontario, Canada (“Psyence II”).
Prior to the execution of the BCA, Psyence Group formed Psyence II and Psyence Biomedical as wholly owned subsidiaries, and prior to the Closing, Psyence Group and the Company were amalgamated. Thereafter, Psyence Group transferred the shares of Psyence Australia Pty Ltd. and its related business assets that were previously owned by the Company to Psyence II.
The following transactions occurred pursuant to the terms of the BCA (collectively, the “Business Combination”) at the effective time of the Merger (the “Effective Time”):
| | · | Psyence Group contributed Psyence II to the Psyence Biomedical in a share for share exchange (the “Company Exchange”). |
| | · | Following the Company Exchange, Merger Sub merged with and into NCAC, with NCAC being the surviving company in the merger (the “Merger”) and each outstanding ordinary share of NCAC was converted into the right to receive one common share of the Psyence Biomedical (“Common Share”). |
| | · | Each outstanding warrant to purchase NCAC Class A ordinary shares was converted at the Effective Time into a warrant to acquire one Company Psyence Biomedical Common Share (the “Company Psyence Biomedical Warrants”) on substantially the same terms as were in effect immediately prior to the Effective Time under their terms. |
On January 15, 2024 and January 23, 2024, the parties to the Business Combination Agreement entered into letter agreements (the “Closing Letter Agreements”) pursuant to which, among other things, Psyence Biomedical, Psyence Group, the Company and Merger Sub (collectively, the “Psyence Parties”) agreed, (X) on a conditional basis, to waive the closing conditions contained in the BCA that, at or prior to the closing of the Business Combination (the “Closing”), (i) Newcourt shall have no less than $20,000,000, net of liabilities, as of the Closing (the “Minimum Cash Condition”) and (ii) the PIPE Investment in the PIPE Investment Amount shall have occurred or shall be ready to occur substantially concurrently with the Closing (the “PIPE Investment Condition”) and (Y) to waive certain deliverables under Section 3.6 of the Business Combination Agreement (the “Closing Deliverables”). Upon the Closing, the Psyence Parties waived in full the Minimum Cash Condition, the PIPE Investment Condition and the Closing Deliverables.
On January 15, 2024, in connection with the Business Combination, Psyence Biomedical entered into a securities purchase agreement (the “Securities Purchase Agreement”) by and among (i) Psyence Biomedical, (ii) Psyence II, (iii) Sponsor and (iv) certain investors (the “Investors”) relating to up to four senior secured convertible notes (collectively, the “Notes” and the transactions pursuant to the Securities Purchase Agreement, the “Financing”), obligations under which will be guaranteed by certain assets of Psyence Biomedical and Psyence II, issuable to the Investors at or after the Closing, as the case may be, for the aggregate principal amount of up to $12,500,000 in exchange for up to $10,000,000 in subscription amounts.
The Note for the first tranche of the Financing (the “First Tranche Note”), for a total of $3,125,000 of principal in exchange for a total of $2,500,000 in subscription amounts and was issued to the Investors substantially concurrently with, and contingent upon, the Closing. The Financing closed immediately prior to the Business Combination.
Upon the closing of the first tranche of the Financing, the Minimum Cash Condition and PIPE Investment Condition were deemed waived by the Psyence Parties.
The transaction concluded on January 25, 2024, with the closing of the BCA, and with the Pubco went public on January 26, 2024. The transaction was completed by Psyence Biomedical acquiring the SPAC through the merger of the SPAC with the Company. Psyence Group relinquished full control of the Company and in return received 5,000,000 shares in Psyence Biomedical, a newly listed NASDAQ entity.
 | F-33 |
| | |
PART II
INFORMATION NOT REQUIRED IN PROSPECTUS
Item 6. Indemnification of Directors and Officers
Under the Ontario Business Corporations Act (“OBCA”), we may indemnify our current or former directors or officers or another individual who acts or acted at our request as a director or officer, or an individual acting in a similar capacity, of another entity, against all costs, charges and expenses, including an amount paid to settle an action or satisfy a judgment, reasonably incurred by the individual in respect of any civil, criminal, administrative, investigative or other proceeding in which the individual is involved because of his or her association with us or another entity. The OBCA also provides that we may also advance moneys to a director, officer or other individual for costs, charges and expenses incurred in connection with such a proceeding.
However, indemnification is prohibited under the OBCA unless the individual:
| · | acted honestly and in good faith with a view to our best interests, or the best interests of the other entity for which the individual acted as director or officer or in a similar capacity at our request; and |
| · | in the case of a criminal or administrative action or proceeding that is enforced by a monetary penalty, the individual had reasonable grounds for believing that his or her conduct was lawful. |
Our bylaws require us to indemnify each of our current or former directors or officers and each individual who acts or acted at our request as a director or officer, or an individual acting in a similar capacity, of another entity, against all costs, charges and expenses, including an amount paid to settle an action or satisfy a judgment, reasonably incurred by the individual in respect of any civil, criminal, administrative, investigative or other proceeding in which the individual is involved because of his or her association with us or another entity.
Under the OBCA, we are permitted to purchase and maintain insurance for the benefit of each of our current or former directors or officers and each person who acts or acted at our request as a director or officer, or an individual acting in a similar capacity, of another entity.
Prior to the completion of the transaction we intend to enter into indemnity agreements with our directors and certain officers which provide, among other things, that we will indemnify, including but not limited to the indemnity permitted under the OBCA, him or her for losses reasonably incurred by reason of being or having been a director or officer; provided that, we shall not indemnify such individual if, among other things, he or she did not act honestly and in good faith with a view to our best interests and, in the case
of a criminal or administrative action or proceeding that is enforced by a monetary penalty, the individual did not have reasonable grounds for believing that his or her conduct was lawful, and in so acting was in breach of the obligations under the indemnity agreement.
At present, we are not aware of any pending or threatened litigation or proceeding involving any of our directors, officers, employees or agents in which indemnification would be required or permitted.
Item 7. Recent Sales of Unregistered Securities
Prior to and in connection with consummating the Business Combination, the registrant issued securities to, among other parties, to the Sponsor, to certain vendors in respect of transaction expenses, as consideration for services or pursuant to advisory agreements, and as otherwise described above in relevant sections of this prospectus (such securities, collectively, the “Closing Issuances”). The securities issued in such Closing Issuances were not registered under the Securities Act in reliance on the exemption from registration provided by Section 4(a)(2) of the Securities Act and/or Regulation D promulgated thereunder as a transaction by an issuer not involving a public offering without any form of general solicitation or general advertising.
Item 8. Exhibits and Financial Statement Schedules
| Exhibit No. | | Description |
| 2.1* | | Amended and Restated Business Combination Agreement, dated as of July 31, 2023, by and among Newcourt Acquisition Corp, Newcourt SPAC Sponsor LLC, Psyence Group Inc., Psyence Biomedical Ltd., Psyence (Cayman) Merger Sub, Psyence Biomed Corp. and Psyence Biomed II Corp. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 2.2 to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form F-4 (File No. 333-273553) filed with the SEC on November 13, 2023). |
| 2.2 | | First Amendment to the Amended and Restated Business Combination Agreement, dated as of November 9, 2023, by and among Newcourt Acquisition Corp, Newcourt SPAC Sponsor LLC, Psyence Group Inc., Psyence Biomedical Ltd., Psyence (Cayman) Merger Sub, Psyence Biomed Corp. and Psyence Biomed II Corp. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 2.3 to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form F-4 (File No. 333-273553) filed with the SEC on November 13, 2023). |
| 2.3 | | Securities Purchase Agreement, dated as of January 15, 2024, by and among Psyence Biomedical Ltd., Psyence Biomed II Corp. and the investors party thereto (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to Newcourt Acquisition Corp’s Form 8-K (File No. 001-40929) filed with the SEC on January 16, 2024). |
| 3.1 | | Certificate of Incorporation of Psyence Biomedical Ltd. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.2 to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form F-4 (File No. 333-273553) filed with the SEC on November 13, 2023). |
| 3.2 | | Amended and Restated Bylaws of Psyence Biomedical Ltd. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.3 to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form F-4 (File No. 333-273553) filed with the SEC on November 13, 2023). |
| 4.1 | | Specimen Share Certificate of Psyence Biomedical Ltd. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.4 to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form F-4 (File No. 333-268525) (File No. 333-273553) filed with the SEC on November 13, 2023). |
| 4.2 | | Specimen Warrant Certificate of Psyence Biomedical Ltd. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.1 to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form F-4 (File No. 333-268525) (File No. 333-273553) filed with the SEC on November 13, 2023). |
| 5.1 | | Opinion of WeirFoulds LLP(1) |
| 10.1 | | Form of Guaranty (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.4 to the Company’s Annual Report on Form 20-F (File No. 001-41937) filed with the SEC on January 31, 2024). |
| 10.2 | | Form of Lock-Up Agreement (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form F-4 (File No. 333-273553) filed with the SEC on November 13, 2023). |
| 10.3 | | Sponsor Support Agreement (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.3 to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form F-4 (File No. 333-273553) filed with the SEC on November 13, 2023). |
| 10.4 | | Parent Support Agreement (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.4 to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form F-4 (File No. 333-273553) filed with the SEC on November 13, 2023). |
| 10.5† | | Psyence Biomedical Ltd. 2023 Equity Incentive Plan (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.8 to the Company’s Annual Report on Form 20-F (File No. 001-41937) filed with the SEC on January 31, 2024). |
| 10.6† | | Form of Director and Officer Indemnification Agreement (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.9 to the Company’s Annual Report on Form 20-F (File No. 001-41937) filed with the SEC on January 31, 2024). |
| 10.7 | | Research IP Agreement, by and between Psyence and Filament (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.5 to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form F-4 (File No. 333-273553) filed with the SEC on November 13, 2023). |
| 10.8 | | Commercial IP Term Sheet, by and between Psyence and Filament (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.6 to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form F-4 (File No. 333-273553) filed with the SEC on November 13, 2023). |
| 10.9 | | Amendment to Engagement Letter, dated as of January 25, 2024, by and between J.V.B. Financial Group, LLC, acting through its Cohen & Company Capital Markets division and Newcourt Acquisition Corp. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.12 to the Company’s Annual Report on Form 20-F (File No. 001-41937) filed with the SEC on January 31, 2024). |
| 10.10 | | Fee Modification Agreement, dated as of January 25, 2024, by and between Cantor Fitzgerald & Co. and Newcourt Acquisition Corp. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.13 to the Company’s Annual Report on Form 20-F (File No. 001-41937) filed with the SEC on January 31, 2024). |
| 10.11 | | Amendment to Engagement Letter, dated as of January 25, 2024, by and between Maxim Group LLC and Psyence Group Inc. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.14 to the Company’s Annual Report on Form 20-F (File No. 001-41937) filed with the SEC on January 31, 2024). |
| 10.12 | | Form of Registration Rights Agreement, dated as of January 25, 2024, by and among Psyence Biomedical Ltd. and the investors party thereto (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.15 to the Company’s Annual Report on Form 20-F (File No. 001-41937) filed with the SEC on January 31, 2024). |
| 10.13 | | Form of General Security Agreement, executed by Psyence Biomedical Ltd. and Psyence Biomed II Corp. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.16 to the Company’s Annual Report on Form 20-F (File No. 001-41937) filed with the SEC on January 31, 2024). |
| 10.14 | | Form of Lock-Up Agreement, dated as of January 25, 2024, by and among Psyence Biomedical, Newcourt Acquisition Corp. and the other parties thereto (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.17 to the Company’s Annual Report on Form 20-F (File No. 001-41937) filed with the SEC on January 31, 2024). |
| 10.15 | | Form of Senior Secured Convertible Note, dated as of January 25, 2024, issued by Psyence Biomedical Ltd. to the Investors (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.18 to the Company’s Annual Report on Form 20-F (File No. 001-41937) filed with the SEC on January 31, 2024). |
| 10.16 | | Promissory Note, dated January 25, 2024, issued by Newcourt Acquisition Corp to Newcourt SPAC Sponsor LLC (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.3 to Newcourt Acquisition Corp’s Form 8-K (File No. 001-40929) filed with the SEC on January 31, 2024). |
| 21.1 | | List of Subsidiaries of Psyence(1) |
| 23.1 | | Consent of MNP LLP(1) |
| 24.1 | | Power of Attorney(2) |
| 107 | | Filing Fee Table(1) |
____________
* The exhibits and schedules to this Exhibit have been omitted in accordance with Item 601(b)(2) of Regulation S-K. The Registrant agrees to furnish supplementally to the SEC a copy of all omitted exhibits and schedules upon its request.
† Indicates a management contract or compensation plan.
(1) Filed herewith.
(2) Included on the signature page.
Item 9. Undertakings
(a) The undersigned registrant hereby undertakes:
(1) To file, during any period in which offers or sales are being made, a post-effective amendment to this registration statement:
(i) To include any prospectus required by section 10(a)(3) of the Securities Act of 1933;
(ii) To reflect in the prospectus any facts or events arising after the effective date of the registration statement (or the most recent post-effective amendment thereof) which, individually or in the aggregate, represent a fundamental change in the information set forth in the registration statement. Notwithstanding the foregoing, any increase or decrease in volume of securities offered (if the total dollar value of securities offered would not exceed that which was registered) and any deviation from the low or high end of the estimated maximum offering range may be reflected in the form of prospectus filed with the Commission pursuant to Rule 424(b) if, in the aggregate, the changes in volume and price represent no more than a 20% change in the maximum aggregate offering price set forth in the “Calculation of Registration Fee” table in the effective registration statement; and
(iii) To include any material information with respect to the plan of distribution not previously disclosed in the registration statement or any material change to such information in the registration statement.
(2) That, for the purpose of determining any liability under the Securities Act of 1933, each such post-effective amendment shall be deemed to be a new registration statement relating to the securities offered therein, and the offering of such securities at that time shall be deemed to be the initial bona fide offering thereof.
(3) To remove from registration by means of a post-effective amendment any of the securities being registered which remain unsold at the termination of the offering.
(4) To file a post-effective amendment to the registration statement to include any financial statements required by Item 8.A of Form 20-F at the start of any delayed offering or throughout a continuous offering.
(5) That, for the purpose of determining liability of the Registrant under the Securities Act of 1933 to any purchaser in the initial distribution of the securities, in a primary offering of securities of the undersigned registrant pursuant to this registration statement, regardless of the underwriting method used to sell the securities to the purchaser, if the securities are offered or sold to such purchaser by means of any of the following communications, the undersigned registrant will be a seller to the purchaser and will be considered to offer or sell such securities to such purchaser:
(i) Any preliminary prospectus or prospectus of the undersigned registrant relating to the offering required to be filed pursuant to Rule 424;
(ii) Any free writing prospectus relating to the offering prepared by or on behalf of the undersigned registrant or used or referred to by the undersigned registrant;
(iii) The portion of any other free writing prospectus relating to the offering containing material information about the undersigned registrant or its securities provided by or on behalf of the undersigned registrant; and
(iv) Any other communication that is an offer in the offering made by the undersigned registrant to the purchaser.
(6) That, for the purpose of determining any liability under the Securities Act of 1933 to any purchaser, each filing of the registrant’s annual report pursuant to section 13(a) or section 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 (and, where applicable, each filing of an employee benefit plan’s annual report pursuant to section 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934) that is incorporated by reference in the registration statement shall be deemed to be a new registration statement relating to the securities offered therein, and the offering of such securities at that time shall be deemed to be the initial bona fide offering thereof.
(b) The undersigned registrant hereby undertakes as follows:
(1) That prior to any public reoffering of the securities registered hereunder through use of a prospectus which is a part of this registration statement, by any person or party who is deemed to be an underwriter within the meaning of Rule 145(c), the issuer undertakes that such reoffering prospectus will contain the information called for by the applicable registration form with respect to reofferings by persons who may be deemed underwriters, in addition to the information called for by the other items of the applicable form.
(2) That every prospectus (i) that is filed pursuant to paragraph (g)(i) immediately preceding, or (ii) that purports to meet the requirements of section 10(a)(3) of the Securities Act and is used in connection with an offering of securities subject to Rule 415, will be filed as a part of an amendment to the registration statement and will not be used until such amendment is effective, and that, for purposes of determining any liability under the Securities Act of 1933, each such post-effective amendment shall be deemed to be a new registration statement relating to the securities offered therein, and the offering of such securities at that time shall be deemed to be the initial bona fide offering thereof.
(c) Insofar as indemnification for liabilities arising under the Securities Act of 1933 may be permitted to directors, officers and controlling persons of the registrant pursuant to the foregoing provisions, or otherwise, the registrant has been advised that in the opinion of the Securities and Exchange Commission such indemnification is against public policy as expressed in the Act and is, therefore, unenforceable. In the event that a claim for indemnification against such liabilities (other than the payment by the registrant of expenses incurred or paid by a director, officer or controlling person of the registrant in the successful defense of any action, suit or proceeding) is asserted by such director, officer or controlling person in connection with the securities being registered, the registrant will, unless in the opinion of its counsel the matter has been settled by controlling precedent, submit to a court of appropriate jurisdiction the question whether such indemnification by it is against public policy as expressed in the Act and will be governed by the final adjudication of such issue.
(d) The undersigned registrant hereby undertakes to respond to requests for information that is incorporated by reference into the prospectus pursuant to Items 4, 10(b), 11 or 13 of this Form, within one business day of receipt of such request, and to send the incorporated documents by first class mail or other equally prompt means. This includes information contained in documents filed subsequent to the effective date of the registration statement through the date of responding to the request.
(e) The undersigned registrant hereby undertakes to supply by means of a post-effective amendment all information concerning a transaction, and the company being acquired involved therein, that was not the subject of and included in the registration statement when it became effective.
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Act, the registrant has duly caused this registration statement to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized, in the city of Toronto, Ontario, Canada on the 9th day of February, 2024.
| | Psyence Biomedical Ltd. |
| | |
| | By: | /s/ Neil Maresky |
| | | Neil Maresky |
| | | Chief Executive Officer |
KNOW ALL PERSONS BY THESE PRESENTS, that each person whose signature appears below does hereby constitute and appoint Neil Maresky and Warwick Corden-Lloyd, each acting alone, as his true and lawful attorneys-in-fact and agents, each with full power of substitution and re-substitution, for him and in his name, place and stead, in any and all capacities, to sign any and all amendments (including post-effective amendments) to this Registration Statement and to file the same, with all exhibits thereto, and other documents in connection therewith, with the Securities and Exchange Commission, granting unto said attorneys-in-fact and agents, and each of them, full power and authority to do and perform each and every act and thing requisite and necessary to be done in connection therewith and about the premises, as fully to all intents and purposes as he might or could do in person, hereby ratifying and confirming all that said attorneys-in-fact and agents, or any of them, or their or his substitutes or substitutes, may lawfully do or cause to be done by virtue hereof.
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Act of 1933, this registration statement has been signed by the following persons in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
| Name | | Title | | Date |
| | | | | |
| /s/ Neil Maresky | | Chief Executive Officer and Director | | February 9, 2024 |
| Neil Maresky | | (Principal Executive Officer) | | |
| | | | | |
| /s/ Warwick Corden-Lloyd | | Chief Financial Officer | | February 9, 2024 |
| Warwick Corden-Lloyd | | (Principal Financial and Accounting Officer) | | |
| | | | | |
| /s/ Jody Aufrichtig | | Chairman of the Board and Strategic Business Development Officer | | February 9, 2024 |
| Jody Aufrichtig | | | | |
| | | | | |
| /s/ Marc Balkin | | Director | | February 9, 2024 |
| Marc Balkin | | | | |
| | | | | |
| /s/ Christopher (Chris) Bull | | Director | | February 9, 2024 |
| Christopher (Chris) Bull | | | | |
| | | | | |
| /s/ Seth Feuerstein | | Director | | February 9, 2024 |
| Seth Feuerstein | | | | |
AUTHORIZED U.S. REPRESENTATIVE
Pursuant to the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, the undersigned, the duly authorized representative in the United States of Psyence Biomedical Ltd. has signed this registration statement in the city of Newark, Delaware on the 9th day of February, 2024.
| | Puglisi & Associates |
| | |
| | By: | /s/ Donald J. Puglisi |
| | Name: | Donald J. Puglisi |
| | Title: | Authorized Representative |











